Regulation and mechanism of miR-2904 on bovine viral diarrhea virus replication
2021-11-02GAOYataoRENZhijunLIYanGUANYifanCHENYingbinCHANGLiyunWANGXiaangQINJianhuaZHAOYuelan070007000
GAO Yatao,REN Zhijun,LI Yan,GUAN Yifan,CHEN Yingbin,CHANG Liyun,WANG Xiaang,QIN Jianhua*,ZHAO Yuelan* (. , ,, 0700,;. ,, 07000,)
Abstract:Bovine viral diarrhoea/mucosal disease (BVD/MD) is caused by bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV),which is widespread throughout the world and causes serious harm to livestock.MicroRNAs,an endogenous non-coding RNA and a key factor regulating genes at the transcriptional level in organisms,plays an important regulatory role in animals and plants,but its mechanism remains unclear.To investigate the regulation mechanism of the key microRNAs on BVDV infections and inflammatory response in MDBK cells,key microRNAs involved with viral infection and inflammatory responses were screened and identified using MDBK cells infected with BVDV by microRNAs microarray.Results showed that miR-2904 was one of the candidates of key microRNA,and TNFAIP8L2 was identified as its potential target gene by luciferase reporter system.The miR-2904 expression level was validated by qRT-PCR and Western blot.Inflammatory response indicated that expression of miR-2904 was induced by the BVDV infection and correspondingly downregulated the expression level of TNFAIP8L2.Additionally miR-2904 could increase the expression level of inflammatory cytokines COX-2,IL-8 and GRO-α mRNA and decrease the level of BVDV replication in MDBK cells.In conclusion,interaction of miR-2904 and TNFAIP8L2 may play an important role in the antivirus activity during the infection process.Overall,we identified the key microRNA involved in the regulation of BVDV infection in MDBK cells,which provides the scientific data for prevention and control of BVDV.
Keywords:BVDV;microRNA;miR-2904;TNFAIP8L2;inflammatory cytokine;viral replication
MicroRNAs (miRNAs),a small,noncoding RNA molecules that regulate post-transcriptional gene expression by base pairing with partially complementary sequences within target messenger RNAs (mRNAs)[1].There are three main perspectives about the regulation mechanisms of miRNAs:inhibition of target protein translation,degradation of target mRNA and adjustment of target gene transcription.In recent years,many studies have reported that host miRNAs are involved in regulating the viral replication,infection and pathogenesis,etc.,and the miRNAs encoded by the virus itself can regulate the genes of the host or the virus itself to help the virus avoid from being killed by the immune system,and stay latent in the host or inhibit host cell apoptosis[2].With the advancement of the miRNAs functional research,the interaction between miRNAs and virus has become a new research field.
The tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein8-like (TIPE/TNFAIP8) family is a recently identified family that is closely associated with the regulation of immunity and tumorigenesis.This family is comprised of four members which have the existence of a significant sequence homology,named respectively,tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein 8 (TIPE/TNFAIP8),tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein 8-like 1 (TIPE1/TNFAIP8L1),tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein 8-like 2 (TIPE2/TNFAIP8L2),and tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein 8-like 3 (TIPE3 /TNFAIP-8L3)[3].Current studies have showed that the absence of TNFAIP8L2 in germlines leads to lethal inflammation and hypersensitivity to toll-like receptor stimulation.The expression of the TNFAIP8L2 gene drastically decreased in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages.TNFAI-P8L2 serves as a “brake” for immunometabolism,inhibits leukocyte activation,lipid biosynthesis pathways and mitochondrial activity.Consequently,it becomes an immune checkpoint regulator of inflammation and metabolism in bone marrow cells,and the unique anti-inflammatory and metabolic-modulatory function of TNFAIP8L2 renders it a novel therapeutic target for inflammatory and metabolic diseases[4].
Bovine viral diarrhea/mucosal disease (BVD/MD) is an infectious disease of cattle with a worldwide distribution,remains a major economic problem for both beef and dairy industries.This disease is caused by bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV),which is belonged to the genus Pestivirus within the family Flaviviridae.BVDV can infect a wide range of mammalian hosts,including cattle,sheep,goat,deer,camel and other ruminants[5].Broad range of clinical manifestations in susceptible animals can be attributed to BVDV infection,including depression,inappetence,oral erosions and ulcerations,diarrhea,respiratory disorders,nervous system affections,abortion and premature birth as well as immunosuppression,especially in young stocks[6].Therefore,the control of the BVDV infection is economically important to the cattle industry.In this study,we employed MDBK cells infected with BVDV to identify the underlying mechanism of microRNAs involved in regulating BVDV replication.The research results provide a basis for revealing the molecular process and molecular regulation mechanism of BVDV from the RNA level.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Cells and viral strainsBVDV strain NADL was purchased from China Institute of Veterinary Drug Control.MDBK cells were maintained in Health and quarantine laboratory,college of veterinary medicine,agricultural university of Hebei.
1.2 BVDV infectionMDBK cells were used for BVDV infection.The infection group was inoculated with 1 mL BVDV NADL strain consists of 10 TCID50,while the control group was inoculated with 1 mL serum-free DMEM.Both groups were placed in incubators with 5% CO2and adsorbed at 37℃,the adsorption solution was discarded after 2 h and replaced with cell maintenance solution (DMEM containing 2% fetal bovine serum),then both groups were cultured at 37℃ for 12 h.MDBK cells were collected from each group after 12 h incubation and then sent to Sangon Biotech (Shanghai,China) Co.,Ltd for sequencing.Total RNA was extracted from collected cells using total RNA extraction kit (TaKaRa Corporation) according to the manufacturer's instructions.The RNA concentration and quality were assessed using a Nano Drop ND-2000 (Thermo Scientific),and the RNA integrity was assessed using an Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent Technologies) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
1.3 μParaflo microRNA microarray assayμParaflo microRNA microarray assay was performed following manufacturer's instructions.The assay was performed with 2 to 5 μg total RNA sample.The isolated small RNAs were 3′-extended with a poly (A) tail using poly (A) polymerase.An oligonucleotide tag was then ligated to the poly (A) tail for subsequent fluorescent dye staining.Hybridization was performed overnight on a μParaflo microfluidic chip (LC Sciences,USA) using a microcirculation pump (Atactic Technologies)[7].On the microfluidic chip,each detection probe consisted of a chemically modified nucleotide coding segment that is complementary to target miRNA (derived from miRBase,http://www.mirbase.org/) and a spacer segment of polyethylene glycol to extend the coding segment away from the substrate.The detection probes were made by in situ synthesis using photogenerated reagent (PGR) chemistry.The hybridization melting temperatures were equilibrated by chemical modification of detection probe.The hybridization of RNA and probe was carried out in 100 μL 6×SSPE buffer containing 25% formamide (0.90 mol/L NaCl,60 mmol/L Na2HPO4,6 mmol/L EDTA,pH=6.8),and the hybridization temperature was 34℃.After the hybridization,tag-conjugating Cy3 dye was circulated through the microfluidic chip for dye staining.Hybridization images were collected by a laser scanner (GenePix 4000B,Molecular Devices,USA) and Array-Pro image analysis software (Media Cybernetics,USA) was used for image digital conversion,followed by data analysis.
1.4 Screen and target predict of microRNAAfter comparing the miRNA chip detection results with the miRNA database,the miRNAs with low expression levels were removed,and differential miRNAs with the order of | log2(Foldchange) |> 1 (twice the difference) andP≤0.05 were screened out.Combined with online target gene analysis tool Miranda and Targetscan 6.2 software,the target gene of miRNA was predicted,and a functional miRNA was selected as the research target.
1.5 The regulatory effects of miR-2904 on BVDVTo explore the effect of miR-2904 on BVDV replication,six groups were set.Group one was untreated MDBK cells,as the control group.Group two was MDBK cells inoculated by 10 TCID50BVDV).Group three was MDBK cells transfected with 5 μL/well miR-2904 mimic,using lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen Corporation) according to the protocol of the manufacturer.Group four was MDBK cells transfected with 2.5 μL/well miR-2904 inhibitant,using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen Corporation).Group five was MDBK cells transfected with miR-2904 mimic (5 μL/well) after 6 h infected with BVDV.Group six was MDBK cells transfected with miR-2904 inhibitant (2.5 μL/well) after 6 h infection with BVDV.Untreated and treated cells were cultured at 37℃ with 5% CO2.After 48 h,the MDBK cells were collected and kept at -70℃.
1.6 Detection of miR-2904 expression by qRT-PCRThe miRNAs were extracted from each group of MDBK cells using miRcute miRNA extraction and isolation kit (TIANGEN Biotech Co.,Ltd,Beijing,China) according to the manufacturer's instructions.The cDNA synthesis performed using miRcute miRNA cDNA first-strand synthesis kit (Tailing Reaction) based on the manufacturer's procedure.The expression levels of miR-2904 were validated by qRT-PCR using the miRcute miRNA fluorescence quantitative detection kit (TIANGEN Biotech Co.,Ltd,Beijing,China) and a LightCycler®96 real-time PCR system (Roche Diagnostics,Shanghai).A upstream primer of miRNA-2904 (5′-ATGGGAGCCTCGGTTGGC-3′) was designed according to the published miRNA-2904 sequences (MIMAT0013862 ) in miRBase 19.0,and the universal downstream primer was supplied by the miRcute miRNA cDNA first-strand synthesis kit(TIANGEN Biotech Co.,Ltd,Beijing,China).The upstream primer sequence of the internal reference U6 was 5′-AGCACATGCCTGTTCGG-3′,and the downstream primer sequence was 5′-GTCTACCATGTCAGTGCAT-3′[8].The other primers sequences used in this study were designed based on the sequences registered in NCBI and synthesized by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co.,Ltd (table 1).Reaction system and reaction program were listed in table 2 and table 3.U6 snRNA was served as an endogenous control gene.Each sample was duplicated with 3 repeats.The relative expression levels of the target gene was quantified by the comparativeCt method,normalized by the housekeeping gene U6 snRNA,and relative expression values were calculated by 2-ΔΔCtmethod.* indicated significant difference from the control group (P<0.05),** indicated extremely significant difference from the control group (P<0.01),and no superscript indicated no significant difference (P>0.05) (similarly hereinafter).
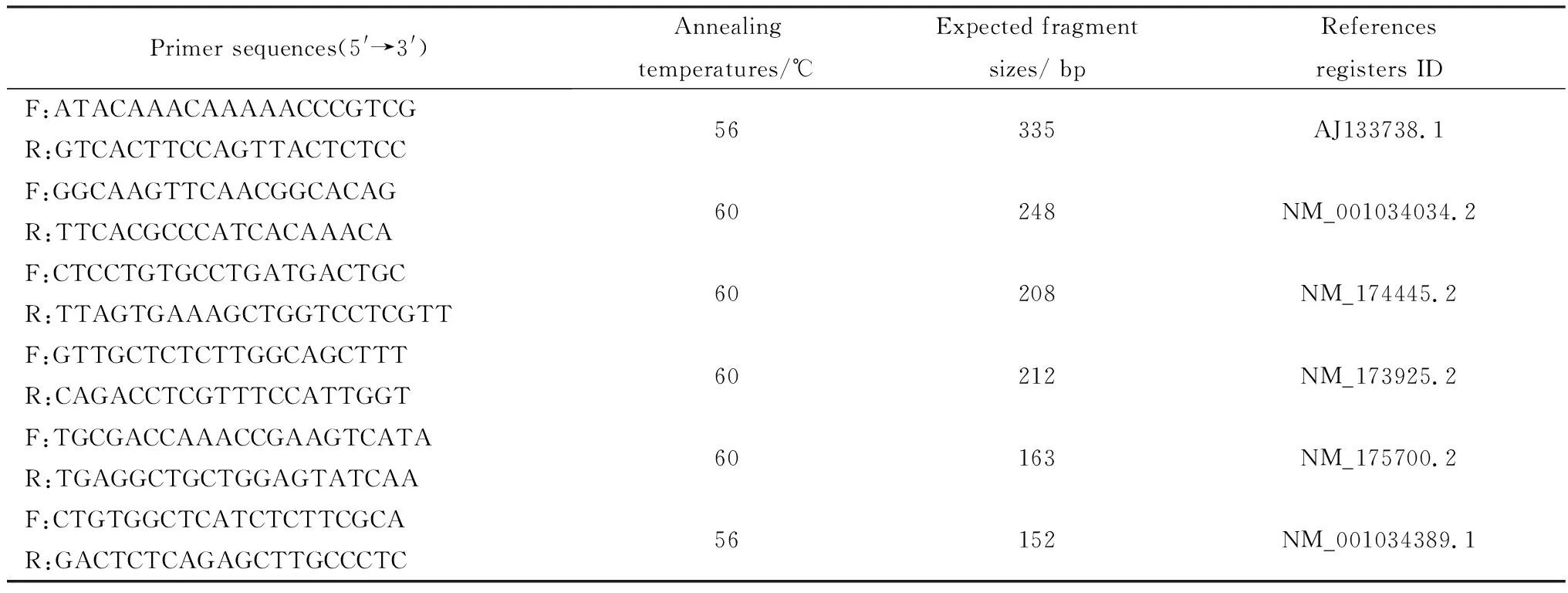
Table 1 Primers sequences used in the study
1.7 Verification of target gene TNFAIP8L2 by luciferase reporterThe total RNA was extracted from each group of MDBK cells using the total RNA extraction kit according to the manufacturer's instructions.The resultant RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA according to manufacturer's protocol of the reverse transcription kit (TaKaRa Corporation).The transcription level of the target gene TNFAIP8L2 mRNA was validated by qRT-PCR using the SYBR Green Ⅰ real-time quantitative PCR detection kit (TIANGEN Biotech Co.,Ltd,Beijing,China) according to the manufacturer's instructions.The other primer sequences were listed in table 1.Reaction system and program were listed in table 2 and table 3.The GAPDH gene served as the internal control.Each sample was duplicated for 3 times.The relative value of transcriptional level was quantified by the comparativeCt method,and calculated by 2-ΔΔCtmethod.

Table 2 Reaction system of PCR

Table 3 The reaction conditions of PCR
The MDBK cells collected from each group were lysed by the cell lysate.The total proteins wereextracted and quantified using the BCA protein quantitative assay kit (TIANGEN Biotech Co.,Ltd,Beijing,China).The TNFAIP8L2 protein expression levels were determined by Western blot using anti-TNFAIP8L2 Poly clonal antibody (Bioss Bio-Technology Co.,Ltd,Beijing,China) as the first antibody β-actin as an internal reference (Bioss Bio-Technology Co.,Ltd,Beijing,China) and HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Bioss Bio-Technology Co.,Ltd,Beijing,China) as secondary antibody.Immunoreactive proteins blots were visualized using DAB Horseradish Peroxidase Color Development Kit ComWin Biotech Co.,Ltd,Beijing,China).The grayscale values of Western blot were analyzed by Image J software.
Thetarget gene TNFAIP8L2 was confirmed by luciferase reporter.The 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of target gene TNFAIP8L2 was synthesized by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai,China) and cloned into a pmirGLO (Invitrogen Corporation) vector with double luciferase reporter gene to build recombined plasmid pmirGLO-TNFAIP8L2 double luciferase vector.The MDBK cell were divided into three groups,pmirGLO-TNFAIP8L2 vector negative control (NC) group,pmirGLO-TNFAIP8L2 and miR-2904 mimic (5 μL/well) group,pmirGLO-TNFAIP8L2 and miR-2904 inhibit (2.5 μL/well) group.The relevant plasmid and miR-2904 mimic/miR-2904 inhibit were co-transfected into MDBK cells by Lipofectamine 2000.The relative luciferase activities (RLU) were detected after 48 hours by dual luciferase reporter gene system.
1.8 Detection of inflammatory cytokines by qRT-PCRTo test the effect of miR-2904 on inflammatory response,the cDNA described in Section 2.8 were used as templates,the transcription levels of inflammatory cytokines COX-2,IL-8 and GRO-α mRNA were detected by qRT-PCR using the SYBR Green Ⅰ real-time quantitative PCR detection kit and specific primers shown in table 1.Reaction system and program were shown in table 2 and table 3.The GAPDH gene served as the internal control.The calculation method of transcriptional level same as 2.7.
To test the effect of miR-2904 on BVDV replication,the cDNA described in Section 2.8 was used as templates.The transcription levels of BVDV 5′UTR were detected by the SYBR Green Ⅰ real-time quantitative PCR detection kit,using BVDV 5′UTR specific primers shown in table 1.Reaction system and program were listed in table 2 and table 3.The GAPDH gene served as the internal control.The method for calculating the relative value of BVDV 5′UTR transcription level is the same as 2.7.
2 Results
2.1 Screen and identificaton of key microRNA and its targetThe miRNAs expression profile of BVDV infected MDBK cells was established by miRNA microfluidic chip (fig 1).Overall distribution of differentially expressed miRNA with log base two (fold change) as the abscissa and negative log base ten (Pvalue) as the ordinate was depicted.A scatter plot of all miRNAs in the differential expression analysis was generated (fig 1A),in which the abscissa represents the fold change in the differential expression of miRNA in different samples and the ordinate represents the statistical significance of changes in microRNA expression.A Venn diagram was generated to display the differential miRNA expression (fig 1B).The expression of 45 miRNAs in MDBK cells infected with BVDV was significantly up-regulated,and the expression of 63 miRNAs was significantly down-regulated,compared with normal MDBK cells.
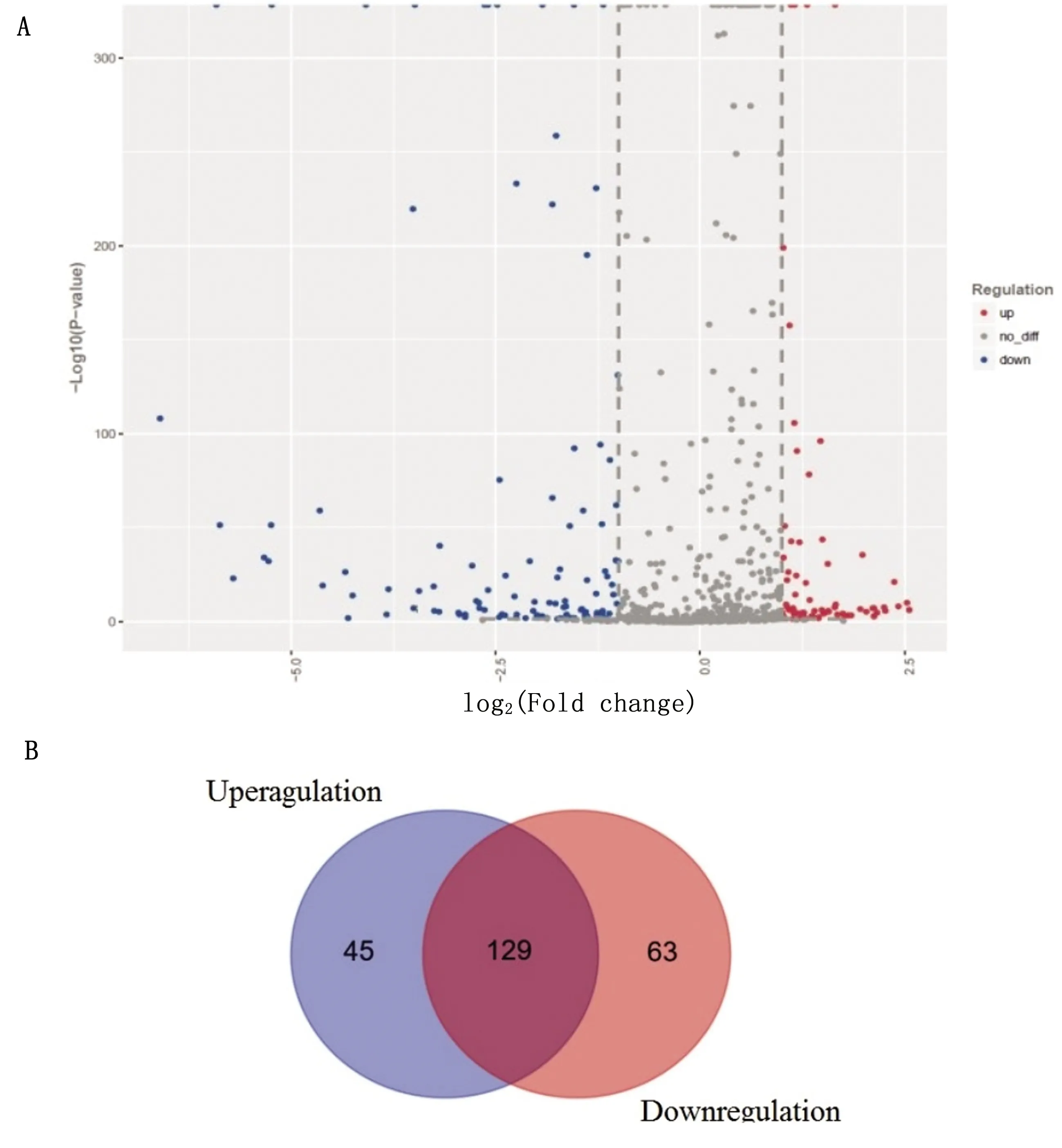
A.Scatter plot of differentially expressed miRNAs.Red represents upregulated.Blue represents down.Grey represents no difference;B.Venn diagram showing the number of differentially expressed miRNAs.All differentially expressed miRNAs showed a>2.0-fold-change threshold and P<0.05Fig 1 Differential miRNA expression profiles in BVDV-infected cells
The target proteins of differentially expressed miRNAs were predicted by bioinformatics software.Based on the analysis of target protein functions,the functions of miRNAs were speculated.The miR-2904 closely related to inflammatory response was determined and chosen as candidate microRNA for further study.Information of miR-2904 targets prediction were analyzed using miRanda and TargetScan 6.2 software (table 4).The base AGGCUCC at position 63-69 of the TNFAIP8L2-3′UTR gene bonded to complementary base UCCGAGG in the miR-2904 sequence.The Site type was 7mer-m8,which means that the nucleotide of target gene that matched the miRNA was 7-8 nt,indicating that TNFAIP8L2 may be a target of miR-2904.Context score percentile was an evaluation index of the target gene function.When context score percentile>90,it indicates that the target gene might be used as a functional target.The context score percentile in predicted TNFAIP8L2-3′UTR was 95.The above results indicated that the TNFAIP8L2 was probably the functional target of miR-2904.
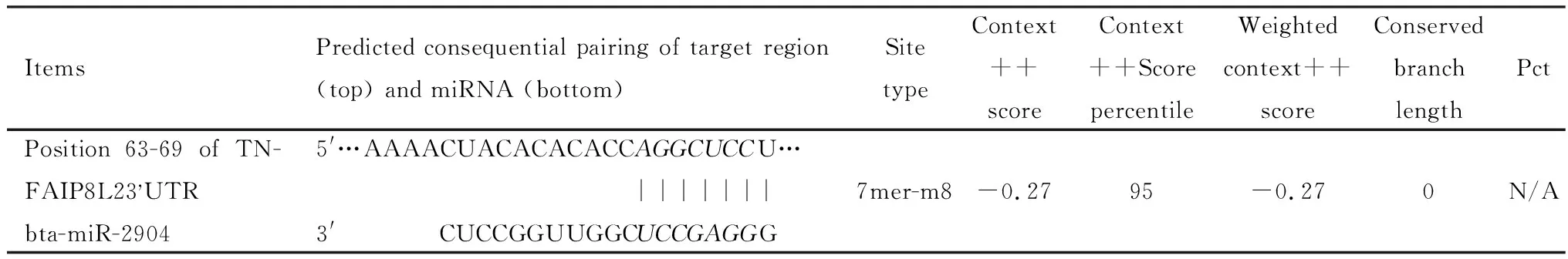
Table 4 Predicted target of miR-2904
2.2 Increase of expression of miR-2904 by BVDV infectionThe expression levels of miR-2904 in each group were validated by qRT-PCR (fig 2).The expression levels of miR-2904 in group 2,group 3 and group 5 were significantly higher than that in group one (P<0.01).However,there was no significant difference in the expression level of miR-2904 between the miR-2904 inhibit group (group four and group six) and group1 (P>0.05).The results indicated that the BVDV infection and the addition of miR-2904 mimic could induce the expression of miR-2904.

1.MDBK;2.MDBK+BVDV;3.MDBK+miR-2904 mimic;4.MDBK+miR-2904 inhibit;5.MDBK+BVDV+miR-2904 mimic;6.MDBK+BVDV+miR-2904 inhibit. ** represents P<0.01Fig 2 Expression level of miR-2904 detected by qRT-PCR
2.3 miR-2904 could inhibit the expression levels of TNFAIP8L2The expression levels of TNFAIP8L2 mRNA in all group were detected by qRT-PCR (fig 3A).There was no significant difference in expression level of TNFAIP8L2 mRNA in each group (P>0.05).The result indicated that the infection of BVDV and the addition of miR-2904 mimic or inhibit could not specifically inhibit or downregulate TNFAIP8L2 mRNA expression.
The expression levels of TNFAIP8L2 proteins in all group were identifiedwith β-actin as an internal reference by Western blot (fig 3B).The expression level of TNFAIP8L2 protein in group three was significantly lower than that in group one (P<0.05).The expression level of TNFAIP8L2 protein in group five was significantly lower than that in group one (P<0.01).There was no significant difference in the expression level of TNFAIP8L2 protein between the miR-2904 inhibition group (group four and group six) and group one (P>0.05).The results showed that miR-1249 could downregulate expression of TNFAIP8L2 protein,which means that miR-1249 could inhibit the translation of TNFAIP8L2 protein.
The relative luciferase activity (RLU) in miR-2904 mimics group was significantly lower than that in NC group (P<0.05) and there was no significant difference between NC group and miR-2904 inhibitant group (P>0.05).Luciferase reporter verification results showed that miR-2904 could directly target TNFAIP8L2 gene (fig 3C).

A.Identification of TNFAIP8L2 mRNA expression by qRT-PCR;B.Detection of TNFAIP8L2 protein expression by Western blot(1.MDBK,2.MDBK+BVDV,3.MDBK+miR-2904 mimic,4.MDBK+miR-2904 inhibit,5.MDBK+BVDV+miR-2904 mimic,6.MDBK+BVDV+miR-2904 inhibit);C.The target gene TNFAIP8L2 verified by Luciferase reporter verification. * represents P<0.05;** represents P<0.01Fig 3 miR-2904 target verification
2.4 miR-2904 promotes inflammatory cytokines expression and attenuates virus replicationThe expressions of COX-2,IL-8 and GRO-α mRNA in group 2,group 3 and group 5 were significant higher than that in group 1 (P<0.01 orP<0.05).However,the expressions of COX-2,IL-8 and GRO-α mRNA in group 4 and group 6 were not significant lower than that in group 1 (P>0.05)(fig 4A,4B,4C).The results indicated that BVDV infection and miR-2904 could promote the expression of inflammatory cytokines COX-2,IL-8 and GRO-α mRNA,which played a positive role in inducing inflammatory response.
In comparison with group 2,the expression of BVDV5′-UTR mRNA in group five was significantly decreased (P<0.05).There was no difference in expression of BVDV- 5′UTR mRNA between group two and group six (fig 4D).The results showed that miR-2904 inhibited the replication level of BVDV,which might play an important regulating role in antivirus infection process.
3 Discussion
miRNAs are the major effector in the complex host-pathogen relationship network[9].It plays an important role in the regulation of the pathogenetic processes of disease and the innate and adaptive immunity of the host[10].However,their roles in the regulation of the responses to BVDV infection in host and cell were unclear.In this study,analysis of miRNA variation in MDBK cell during BVDV infection were performed.After BVDV infection of MDBK cells,the expression levels of 45 miRNAs were significantly upregulated,and the expression levels of 63 miRNAs were significantly downregulated.Compared with normal cells,miR-2904 in MDBK cells infected with BVDV was significantly upregulated.
Key miRNAs are important cellular regulatory factors that regulated post-transcriptional gene expression by degrading target mRNAs or blocking their translation in plants and animals[11].miRNAs regulate the expression of target genes by binding to the 3′UTR complementary sequence of multiple target mRNAs[12].The main function of miRNAs is to regulate translation,and mainly play a negative regulation role.However,miRNAs inhibit translation not by simple complementary binding with mRNA,but by binding with proteins to form RISC (silencing complex).The main mechanisms by
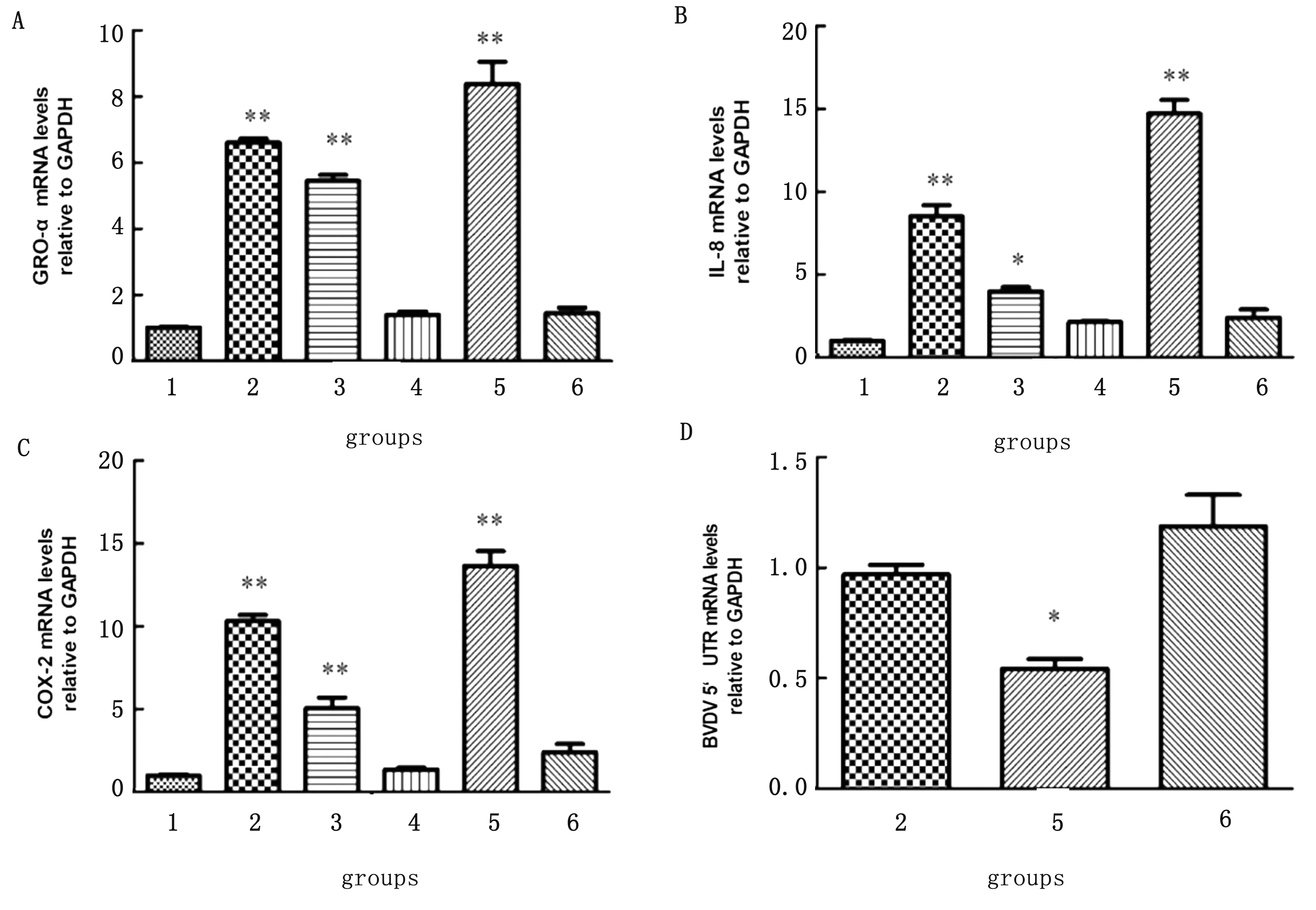
A-C.Expressions of COX-2,IL-8 and GRO-α mRNAs by qRT-PCR;D.Detection of BVDV 5′UTR mRNA expression by qRT-PCR;1.MDBK;2.MDBK+BVDV;3.MDBK+miR-2904 mimic;4.MDBK+miR-2904 inhibit;5.MDBK+BVDV+miR-2904 mimic;6.MDBK+BVDV+miR-2904 inhibit;** represents P<0.01.* represents P<0.05Fig 4 Regulatory effect of miR-2904 on virus infection
which RISC inhibit mRNA translation are as follows:one is to directly inhibit the translation of mRNA,and the other is to introduce mRNA into P-body (a multifunctional cytoplastic complex of proteins and RNAs) to prevent translation[13].In this study,double luciferase reporter transfection test was performed to verify that miR-2904 could directly target base at position 63-69 of the 3′UTR- of TNFAIP8L2 gene.And through the transfection test of miR-2904 into MDBK cells,it was found that overexpression of miR-2904 did not downregulate the expression of TNFAIP8L2 mRNA,but decreased the expression of TNFAIP8L2 protein,suggesting that miR-2904 could block the translation of TNFAIP8L2 protein by forming RISC and introducing TNFAIP8L2 mRNA into P body.
TNF-α-induced protein 8-like 2 is a novel death effector domain protein and a negative regulator of the innate and adaptive immune response,which could play an important role in inhibiting inflammatory response and maintaining immune homeostasis[14],by selectively expressed in the immune organs and inflammatory tissues.Although it had been demonstrated that caspase-8 contributed to the negative regulation of TNFAIP8L2,the negative regulatory mechanism was not entirely understood.In this study,expression level of the TNFAIP8L2 protein in MDBK cells infected with BVDV transfected with miR-2904 mimic was detected by Western blot.The result indicated TNFAIP8L2 was an important target of mir-2904,and miR-2904 as a key miRNA of differential expression down-regulated TNFAIP8L2 translation.Several miRNAs have been reported to play roles in the regulation of host immune responses by targeting interferon regulatory factor 2 (IRF2) or TNF-α and IL-24 or Jak2-STAT3 pathway[15].In this study,the miR-2904 could promote the expression of inflammatory cytokines COX-2,IL-8 and GRO-α mRNA,which plays a positive role in inducing inflammatory response.
A complex relationship between viral pathogenesis and host antiviral defense could define the immune ecosystem of virus-infected host tissues.During the co-evolution of the viruses and their hosts,various strategies were used to regulate the biological process of infected cells.Viruses frequently hijack host factors and efficiently utilize the host system to quickly produce large quantities of viral proteins for their replication.Some viruses block cell apoptosis.With this strategy,the viruses are able to replicate,spread and sustain infection.However,other viruses induce the cell apoptosis for virus proliferation or suppression of inflammation and other immune responses[16].For examples,miR-29c overexpression significantly inhibits hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA replication by targeting tumor necrosis factor alpha induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3),down-regulates its expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells,inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis[17].BVDV infection is a dynamic and complex process that leads to significant economic losses in the dairy and cattle industries.However,understanding of the protective and pathological mechanism underlying BVDV infection is limited.In this study,the miR-2904 was shown as a key microRNA in BVDV infection MDBK cells,directly targeted TNFAIP8L2 and inhibited the translation of TNFAIP8L2 protein.The miR-2904 was also demonstrated to induce inflammatory reaction by targeting inflammatory cytokines COX-2,IL-8,GRO-α,and reduce the level of BVDV replication.However,it remains to be proved whether miR-2904 enhances inflammation directly by inhibiting the translation pathway of TNFAIP8L2 or by inhibiting BVDV replication.
