Therapeutic effects of hyperbaric oxygen:integrated review
2021-03-03SumanSenSheuliSen
Suman Sen ,Sheuli Sen
1 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology,Haldia Institute of Dental Sciences and Research,Haldia,West Bengal,India
2 Department of Pediatric Nursing,Sumandeep Nursing College,Sumandeep University,Vadodara,Gujarat,India
Abstract Hyperbaric oxygen therapy refers to inhalation of pure oxygen in a closed chamber.Hyperbaric oxygen has a therapeutic effect in numerous pathological conditions,such as decompression sickness,arterial gas embolism,carbon monoxide poisoning and smoke inhalation,osteomylitis,osteoradionecrosis and wound healing.Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used for treating underlying hypoxia.This review indicates the action of hyperbaric oxygen on biochemical and various physiological changes in cellular level.Narrative review covers the current indications and contraindications of hyperbaric oxygen therapy.The review also focuses on the therapeutic effects of hyperbaric oxygen pretreatment and precondition in different pathological conditions.The complications and side effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy are discussed.
Key words:carbon monoxide poisoning; decompression sickness; hyperbaric oxygen therapy; osteomylitis; osteoradionecrosis; wound healing
INTRODUCTION
The prefix “hyper” means increased while “baric” refers to pressure.During hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) a patient inhales 100% pure oxygen greater than normal atmospheric pressure inside a highly pressured chamber.Inside this chamber,the oxygen pressure is usually 1.5-3 times than that at sea level.In 1620,Drebbel developed a one-atmosphere diving bell.1Use of hyperbaric therapy was first documented in 1662.Nathaniel Henshaw,a British clergy and physician,used a system of organ bellows with unidirectional valves to change the atmospheric pressure in a sealed air tight chamber called domicilium in which oxygen is compressed and decompressed.In 1937,Behnke and Shaw for the first time used hyperbaric chamber in treating patients with decompression sickness.Since 1955,HBOT has been used for the management of various medical conditions.2
Oxygen (O2) transportation in blood is mainly by hemoglobin that has an oxygen saturation of about 97% while plasma contains 0.32% of dissolved oxygen under normal atmospheric pressure.3The blood circulation helps to delivery of oxygen and other nutrients to the tissues and to remove the products of metabolism including carbon dioxide.4Oxygen delivery is dependent on oxygen availability,the ability of arterial blood to transport oxygen and tissue perfusion.5Normal concentration of oxygen in blood at sea level is 3 mL/L.Tissues of a healthy individual during rest need around 60 mL of oxygen per 1 L of blood flow that helps in metabolism of cells.At atmospheric pressure of 304 kPa dissolved oxygen approaches 60 mL/L plasma,that is the total oxygen needed by tissues at rest.6During the HBOT procedure,the oxygen pressure in arterial blood can increase to 2000 mmHg (~266.6 kPa),and the high blood-to-tissue oxygen pressure gradient increases the tissue oxygen pressure to 500 mmHg (~66.7 kPa).7This has a positive effect on the healing of inflammatory and microcirculatory disorders under ischemic conditions.
In the HBOT the individual is placed in a closed chamber and breathes pure oxygen.The oxygen pressure inside the chamber and the duration are increased depending on individual pathological conditions.The HBOT duration varies from 3 minutes to 2 hours till the pressure inside the chamber becomes normal.There may be little discomfort and ear pain during the alteration of oxygen pressure inside the chamber.6
MECHANISMS UNDERLYING THE THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS
At cellular level around 80% of oxygen is utilized by mitochondria which is a power house of cells while remaining 20%is used by other organelles.Mitochondria require oxygen to receive the electrons at the end of the electron transport chain to utilize that energy to make adenosine triphosphate.Hypoxia leads to increase the oxidative stress that results in generation of reactive free radicals of oxygen and nitrogen.8Free radicals of oxygen and nitrogen are extremely toxic to cells and result in damage which induces cellular death and apoptosis.9The HBOT helps to correct hypoxic condition by increasing oxygen delivery leading antimicrobial activity and the attenuation of the hypoxia-inducible factor mediated effects.Its effects also reduce the formation of reduce oxidative stress,increasing the body’s ability to heal,vasoconstriction,and angiogenesis resulting in reduced inflammation.10Hyperbaric oxygen dissociates carbon monoxide from cytochrome C oxidase,improving electron transport and cellular energy state.6The therapeutic pressures used in HBOT are described in terms of atmospheres absolute pressure ranging from 1.5 to 3.0 atm (1 atm = 101.325 kPa).Biochemical changes in cellular level of HBOT are indicated in Table1.

Table1:Biochemical changes in cellular level of hyperbaric oxygen
INDICATIONS AND CONTRADICTIONS TO HYPERBARIC OXYGEN THERAPY
The therapeutic uses of HBOT in various pathologic conditions are included in Table2.6,11-13Table3 includes contraindication and limitations for the HBOT.6,11
During prolonged duration of HBOT oxygen poisoning can be prevented by giving short breaks and breathing normal air.This will lead to lessen the excessive oxygen taken by the tissues.During HBOT each individual will be given specific dose depending on their age,pathologic condition and the site of the disease to minimize the chance of toxicity and complications.The most common symptoms during HBOT include light headache and fatigue which are reversible as the individual are taken out of the hyperbaric oxygen chamber.The side effects of the HBOT are relatively less when the individual is placed less than 2 hours inside the chamber and when the pressure does not exceed 300 kPa compared to normal atmospheric pressure.Though the side effect is mild but can be life-threatening if not managed immediately.The common side effects that may be encountered are nausea,vomiting,myopia,feeling of claustrophobia,fatigue and headache.Table4 includes the complications and side effects that can be associated with HBOT.
CLINICAL APPLICATION AS THERAPEUTIC USES OF HYPERBARIC OXYGEN
Necrotizing infections
Soft infections caused by clostridial α toxin production leads to myonecrosis and gas gangrene.Experimental evidence and clinical experience suggest that treatment with hyperbaric oxygen improves systemic illness and decreases tissue loss by demarcating the border between devitalized and healthy tissue.This reduces the extent of surgical amputation or debridement.14In necrotizing fasciitis studies suggest that hyperbaric oxygen plays an adjuvant role with surgical debridement.It enhances blood perfusion and improves innate immunity at the site of injury.15
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is an infection of bone.Bacteria present in the bloodstream from infectious diseases spreads to the bone.HBOT also has a beneficial role in refectory osteomylitis.16Osteomyelitis treatments mainly include extensive irrigation and debridement,intravenous antibiotics,and reconstruction.HBOT helps osteogenesis,neovascularization,and collagen production.17-19HBOT increases the oxygen tension in ischemic wounds under conditions of adequate arterial inflow.This effect of HBOT on tissue oxygenation is obtained through formation of new vessels by neovascularization and increase in vascular endothelial growth factor.20,21Therapeutic effects of HBOT on infections can be made by direct suppression the growth of anaerobic bacteria such as clostridia and hyperoxygenation in tissues causes increase the fibroblasts and collagen proliferation,neovascularization of ischemic tissues and stimulation of bacterial lysis by leukocytes.22,23After surgical debridement of the osteolytic region,HBO at 2.4 to 2.5 atmospheres absolute pressure (ATA; 1 ATA = 101.325 kPa) for 5 to 7 times per week provides clinical efficacy by removing swelling and pain.A total of 30 to 40 treatments are required to get the clinical results.

Table2:Therapeutic indications and uses of hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide has 200 times more binding capacity to hemoglobin in blood than oxygen thus reducing the oxygen content in blood.Hemoglobin sites that are free from binding have an increased affinity towards oxygen,and this reduces the availability of oxygen to the tissues leading to hypoxia.Hyperbaric oxygen gives an alternative source of tissue oxygenation through oxygen dissolved in the plasma.24HBOT acts by dissociation of carbon monoxide from the hemoglobin andmyoglobin.25The symptoms associated with carbon monoxide poising are loss of consciousness,neurological abnormalities,myocardial ischemia,pulmonary edema,metabolic acidosis,headache and delayed neurological features that may became permanent if not treated at an early stage.At 2-3 ATA for 60-90 minutes breathing 100% oxygen helps to treat this condition.26

Table3:Contraindications of hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Decompression sickness and arterial gas embolism
Decompression sickness caused due to sudden alteration in atmospheric pressure is commonly noted in scuba divers,aviators and deep tunnel workers as there is a change in atmospheric pressure when they leave that environment.Delay in treating decompression sickness with hydration and HBOT can result in permanent symptoms and even death.27After deep water diving when the divers surface rapidly at sea level attitude the partial pressure of nitrogen dissolved in the tissues exceed the ambient atmospheric pressure to form air bubbles in the blood and tissues.28Even at an altitude of over 5500 m decompression sickness can occur.In air embolism the air can enter the blood circulation during the placement of catheters in arteries and veins,cardiothoracic surgery,hemodialysis.Decompression sickness can cause skin rashes,joint pain,paralysis,confusion,convulsions,difficulty in speech,visual disturbances,and balance disturbance; sensory loss bladder dysfunction,sphincter dysfunction; loss of coordination in the limbs; shortness of breath,which may lead to death secondary to blockage of vital blood vessels by air emboli.Hyperbaric oxygen recompression given at a pressure of 250-300 kPa for 2-5 hours relives the symptoms.
Osteoradionecrosis
Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is noted when the bone exposed to radiation undergoes necrosis and becomes exposed under soft-tissue.ORN occur commonly after radiotherapy in head and neck carcinoma.29It commonly affects the mandible in orofacial region.ORN results in irreversible tissue death,which is seen as exposed bone for more than 3 months duration.30ORN can occur between an interval of 4 months to 2 years after radiotherapy.31In ORN through ulcerated mucosa exposed bone seen that causes severe pain,dysesthesia,halitosis,dysgeusia and food lodgment.In ORN initially there is suppression of osteoclast related bone turnover.32,33Radiotherapy causes hypoxia in tissues and hypocellularity resulting in tissue breakdown and chronic non-healing wounds.HBOT increases the oxygen concentration by correcting the hypoxia and cell regeneration.Around 30 preoperative and 10 post-operative HBO sessions for 90 minutes are recommended to prevent mandibular osteonecrosis after surgery on irradiated facial and neck tissue.6
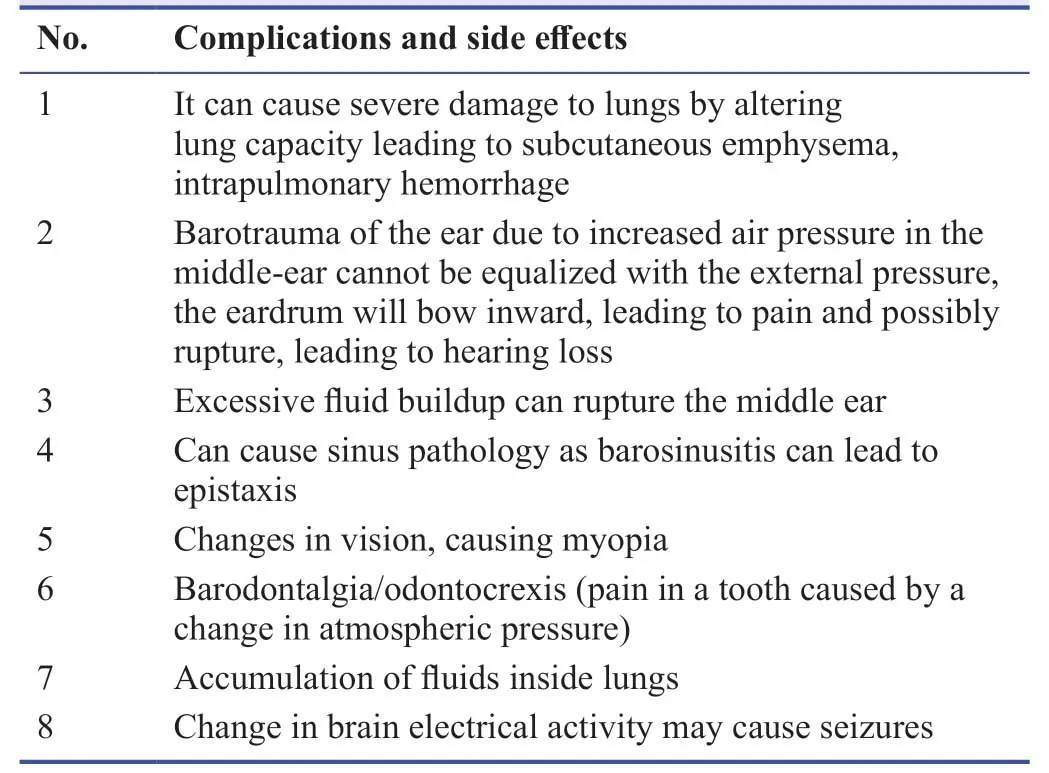
Table4:Complications associated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Skin grafts,flaps,and wound healing
HBOT is beneficial and useful in wound healing process.It can also have therapeutic importance in wounds from burns and diabetic ulcers.34-36It has a positive role in compromised flaps and can increase the effective size of composite graft survival,and improve prognosis of flap survival.Generally the skin grafts contain different tissue types with varying sizes that lack proper blood supply and are depended on the host for nutrient.HBOT acts by increasing oxygenation in the blood vessels and tissues by improving fibroblast function,collagen synthesis and neovascularization that helps in wound healing.HBO,given at a pressures of 2.0-2.5 ATA for duration of 90-120 minutes twice daily,helps in complete saturation of hemoglobin with oxygen in the circulation,along with a 10-fold increase in the dissolved oxygen plasma level.37
Brain stroke
HBOT also helps in treatment of brain trauma and acute cerebral edema mostly associated with chronic stages of strokes causing memory and speech loss.38HBOT induces angiogenesis and the recruitment of progenitor cells to the damaged regions.39Cell death is the focus of HBOT treatment,as it reduces the inflammatory cytokine level that is associated with limiting peri-infarct tissue loss.40Hyperbaric oxygen suppresses the increased circulating macrophages in the acute phase and accelerated macrophage invasion into the contused muscle.This helps to increase the number of proliferating and differentiating satellite cells and the amount of regenerated muscle fibers.
HYPERBARIC OXYGEN PRE-CONDITIONING
Hyperbaric oxygen exposure before few procedures that create a preventive therapeutic situation is called as “preconditioning.” Hyperbaric oxygen pre-conditioning has a beneficial effect in diving,ischemic and inflammatory conditions.Oxygenpre-breathing causes reduced post-diving bubble leading to reduced decompression requirements and more rapid return to normal platelet function after a decompression.During the reperfusion of ischemic tissue,oxygenated blood increases numbers and activities of oxidants generated in tissues.Hyperbaric oxygen pre-conditioning causes the activation of antioxidative enzymes in the central nervous system,including catalase,superoxide dismutase and heme oxygenase-1.41Hyperbaric oxygen pre-conditioning also protects against focal cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury.Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning has cerebral-protective and cardiacprotective effects.42Hyperbaric oxygen pre-conditioning attenuates brain edema,microglia activation,and inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage.
CONCLUSION
Hyperbaric therapy utilizes high pressure oxygen response.It elevates the concentration of oxygen in hemoglobin and plasma.Based on its solubility under pressure increases the diffusion gradient for its delivery deeper into tissues,which is the main mechanism of HBOT.Ultimately the increases in dissolved oxygen generated by hyperbaric therapy have several physiologic effects that can change tissue responses to numerous physiological changes.Long term studies should be conducted to see its outcome in different therapeutic treatment regimens along with its complications and side effects that required obtaining the clinical and cost effective results.
Author contributions
Both authors contributed in selecting the topic,extensive searching,reviewing the current management and writing the article.
Conflicts of interest
None declared.
Financial support
None.
Copyright license agreement
The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by both authors before publication.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement
This is an open access journal,and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License,which allows others to remix,tweak,and build upon the work non-commercially,as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
杂志排行
Medical Gas Research的其它文章
- High-flow hydrogen inhalation might suppresses the immune function of middle-aged participants:a selfcontrolled study
- The effect of dexmedetomidine on decrease of cough,hemodynamic parameters and Ramsay score versus lidocaine during general anesthesia:a randomized clinical trial
- Evaluation of audible leak versus pressure volume loop closure for polyvinyl chloride cuff and polyurethane microcuff in endotracheal tube inflated with air:a prospective randomized study
- The role of nitric oxide in peptic ulcer:a narrative review
- A new mechanistic approach for the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain with nitrous oxide integrated from a systems biology narrative review
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy decreases mortality due to Fournier’s gangrene:a retrospective comparative study
