硬膜外镇痛分娩中发生持续性枕后位的临床分析
2020-06-11李利平

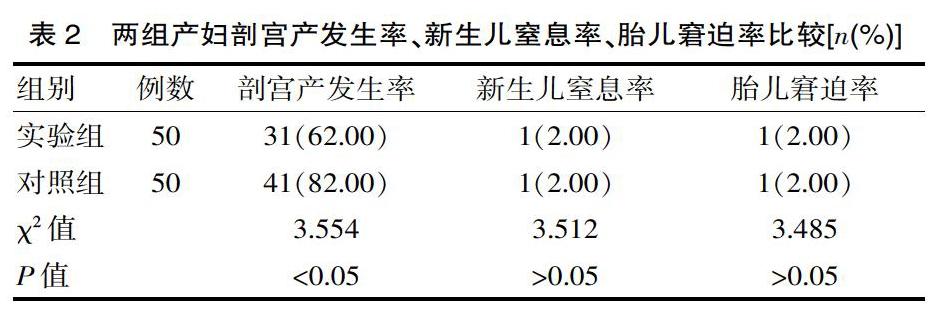
[摘要] 目的 观察分析硬膜外镇痛分娩中发生持续性枕后位临床情况(枕后位发生率、母婴解决以及临床分娩方式)。方法 方便选取该院在2017年1月—2019年2月收治的100例产妇,按照有无接受硬膜外镇痛分娩分为实验组(50例,接受硬膜外镇痛分娩)和对照组(50例,未接受硬膜外镇痛分娩)。采用统计学分析两组产妇的持续性枕后位发生率、母婴结局。 结果 实验组产妇的持续性枕后位发生率、第一产程催产素使用率、第二产程催产素使用率、产后平均出血量分别为12.00%、60.00%、32.00%、(200.02±100.15)mL,對照组分别为10.00%、30.00%、30.00%、(290.36±110.38)mL,两组产妇的持续性枕后位发生率、第二产程催产素比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=10.455、10.212,P>0.05),实验组产妇第一产程催产素使用率高于对照组(χ2=5.993,P<0.05),实验组产妇产后平均出血量显著少于对照组(t=18.326,P<0.05);实验组新生儿窒息率、胎儿窘迫率、新生儿出生体重分别为2.00%、2.00%、(3.26±0.21)kg,对照组分别为2.00%、2.00%、(3.30±0.14)kg,两组新生儿窒息率、胎儿窘迫率、新生儿出生体重比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=3.512、3.485、3.522,P>0.05);实验组产妇剖宫产发生率为62.00%,对照组为82.00%,实验组产妇剖宫产发生率显著低于对照组(χ2=3.554,P<0.05)。结论 硬膜外镇痛分娩可有效改善母婴结局。
[关键词] 硬膜外镇痛;分娩;持续性枕后位;母婴结局
[中图分类号] R5 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2020)02(b)-0048-03
Clinical Analysis of Persistent Occipital Posterior Position in Epidural Analgesia during Delivery
LI Li-ping
Department of Anesthesiology, Changsha Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Changsha, Hunan Province, 410007 China
[Abstract] Objective To observe and analyze the clinical situation of persistent occipital posterior position in epidural analgesia delivery (incidence of occipital posterior position, maternal and infant solutions and clinical delivery mode). Methods A total of 100 parturients admitted to our hospital (from January 2017 to February 2019) were convenienty selected and divided into an experimental group (50 parturients who received epidural analgesia) and a control group (50 parturients who did not receive epidural analgesia). Statistics were used to analyze the incidence of persistent posterior occipital position and maternal and infant outcomes in the two groups. Results Experimental group the incidence of persistent pillow after a maternal, the first stages of oxytocin utilization, the second labor oxytocin average utilization rate, postpartum blood loss were 12.00%, 60.00%, 32.00%, (200.02±100.15)mL, the control group were 10.00%, 30.00%, 30.00%, (290.36±110.38)mL, two groups of maternal persistent pillow after the incidence, the second labor oxytocin is no statistical significance (x2=10.455, 10.212, P>0.05). The utilization rate of oxytocin in the first stage of labor in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group(χ2=5.993, P<0.05), and the average postpartum blood loss in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group(t=18.326, P<0.05). The rates of neonatal asphyxia, fetal distress and neonatal birth weight in the experimental group were 2.00%, 2.00% and (3.26±0.21) kg, respectively, while those in the control group were 2.00%, 2.00% and (3.30±0.14) kg, respectively. There were no statistically significant differences in the rates of neonatal asphyxia, fetal distress and neonatal birth weight in the two groups(χ2=3.512, 3.485,3.522, P>0.05). The incidence of cesarean section was 62.00% in the experimental group and 82.00% in the control group. The incidence of cesarean section in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group(χ2=3.554, P<0.05). Conclusion Epidural analgesia can improve maternal and infant outcomes.
该文研究结果显示,实验组产妇产后平均出血量显著少于对照组(P<0.05)。子宫收缩可有益于胎头内旋转,如果子宫收缩力道不足,会难以旋转胎头。虽然硬膜外镇痛分娩方式所面临的持续性枕后位概率较高,但是只要在硬膜外镇痛过程中注意合理给药,密切监测宫缩进展情况以及产程发展,及时处理枕后位能够帮助胎头旋转,最终显著提高自然分娩率,减少术后出血量。该文研究结果显示实验组新生儿窒息率、胎儿窘迫率、新生儿出生体重分别为2.00%、2.00%、(3.26±0.21)kg,对照组分别为2.00%、2.00%、(3.30±0.14)kg,两组新生儿窒息率、胎儿窘迫率、新生儿出生体重比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。翟利平[8]在相关研究中显示,治疗结束后新生儿窒息率为1.00%,胎儿窘迫率为2.00%,新生儿出生体重为(3.33±0.15)kg,与该文研究结果保持高度一致。在产妇分娩过程中,不管有无接受硬膜外镇痛分娩方式,助产士或者医师均需要帮助产妇及时纠正宫缩乏力情况,积极指导产妇正确用力,可显著降低新生儿窒息率、胎儿窘迫率。
综上所述,硬膜外镇痛分娩可显著提高第一产程催产素使用率、第二产程催产素使用率,减少产后平均出血量,提高母婴生活质量。
[参考文献]
[1] 杨同文,熊巍,任自刚,等.系统评价硬膜外分娩镇痛时机对初产妇分娩过程的影响:Meta分析[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2018,17(11):1206-1212.
[2] Vincenzo Zanardo,Francesca Volpe,Matteo Parotto,et al.Nitrous oxide labor analgesia and pain relief memory in breast feeding women[J].The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine,2018,31(24):3243-3248.
[3] 李瑞,罗志锴,杨丽珍,等.不同浓度罗哌卡因复合舒芬太尼在硬膜外镇痛分娩中的效果评价[J].实用临床医药杂志,2018,22(23):82-84,87.
[4] 王芳,姜文,邢梅,等.腰硬联合麻醉复合术后硬膜外镇痛对足月妊娠初产妇无痛分娩产程时间及术后血清PRL、tPA水平的影响[J].中国医学前沿杂志:电子版,2018,10(8):60-64.
[5] 杨会义,安丽,许萍,等.右美托咪定用于妊娠期高血压产妇硬膜外分娩镇痛的疗效及护理方式[J].河北医药,2017,39(11):1746-1748.
[6] 李冰,陈绪军,郭艳,等.不同浓度罗哌卡因复合舒芬太尼在硬膜外阶梯式分娩镇痛中的应用[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2016, 32(4):361-365.
[7] 宗银东,聂颖,姜义铁,等.罗哌卡因硬膜外患者自控镇痛的无痛分娩效果及应激反应的临床研究[J].重庆医学,2016, 45(17):2407-2409.
[8] 翟利平,徐公元,鄧爱华,等.不同时机实施硬膜外镇痛分娩对母婴结局的影响[J].中国妇幼保健,2017,32(15):3688-3690.
(收稿日期:2019-11-10)
[作者简介] 李利平(1986-),女,湖南长沙人,硕士,主治医师,研究方向:镇痛分娩,单肺通气。
