鲤肠道寄生岳阳碘泡虫新种的形态特征及系统发育分析
2017-11-29习丙文
李 鹏 习丙文, 陈 凯 谢 骏
(1. 南京农业大学无锡渔业学院, 无锡 214081; 2. 中国水产科学研究院淡水渔业研究中心, 农业部淡水渔业和种质资源利用重点实验室, 无锡 214081; 3. 淡水水产健康养殖湖北省协同创新中心, 武汉 430070)
鲤肠道寄生岳阳碘泡虫新种的形态特征及系统发育分析
李 鹏1,2习丙文2,3陈 凯2谢 骏1
(1. 南京农业大学无锡渔业学院, 无锡 214081; 2. 中国水产科学研究院淡水渔业研究中心, 农业部淡水渔业和种质资源利用重点实验室, 无锡 214081; 3. 淡水水产健康养殖湖北省协同创新中心, 武汉 430070)
在洞庭湖岳阳地区开展鱼类寄生虫调查中,发现一种寄生于鲤Cyprinus carpioL.肠道的黏孢子虫。该黏孢子虫的孢囊呈白色,椭圆形,大小为(1.0±0.2) mm (0.8—1.2 mm)。成熟孢子具有壳瓣,壳面观近似圆形,后端有4—6个“V”形褶皱;缝面观呈纺锤形,缝脊直而粗;孢质均匀,含有一个嗜碘泡;孢子长(9.8±0.6) μm (9.6—10.0 μm),孢子宽(8.2±0.3) μm (8.0—8.5μm),孢子厚(7.3±0.1) μm (7.0—7.5 μm);2个极囊梨形,位于孢子顶端,大小相等,呈“八”字形;极囊长(4.4±0.4) μm (3.8—5.1 μm),宽(2.7±0.2) μm (2.2—3.2 μm),极丝4—5圈。该黏孢子虫与肠膜碘泡虫、丑陋圆形碘泡形态特征非常相似,但其极囊/孢子小于1/2;与文献已报道的鲤肠道寄生北京碘泡虫和鲤肠碘泡虫相比较,其在孢子形态、孢子和极囊大小方面分别存在明显差异。基于该黏孢子虫18S rDNA基因序列(GenBank登录号KY203795)比对分析,该黏孢子虫与山东碘泡虫相似率最高,仅为96%。系统发育分析发现,该黏孢子虫与山东碘泡虫、倪李碘泡虫、住心碘泡虫、Myxobolus encephalicus、Sphaerospora molnari、多涅茨尾孢虫和Henneguya zikaweiensis聚为独立分支,和其他已报道的黏孢子虫亲缘关系较远。综合形态学和18S rDNA基因序列数据,文章报道的鲤肠道寄生黏孢子虫为碘泡虫属一新物种,将其命名为岳阳碘泡虫。
鲤; 碘泡虫; 分类; 系统发育
黏体动物(Myxozoa)是一种形态结构非常简单、个体非常微小、高度适应寄生生活的后生动物, 在进化上与刺胞动物亲缘关系较近[1—3], 可寄生在鱼类、两栖类、爬行类、鸟类及哺乳类动物各个组织器官[4,5], 是水生动物养殖中非常重要的寄生虫病原。目前全世界报道的黏孢子虫隶属于60个属, 约2600多种[4,6]。在黏孢子虫传统分类学研究中主要依据成熟孢子的形态特征进行种类鉴定、分类阶元划分[7]。然而, 黏孢子虫种类繁多, 结构简单, 单从形态上很难区分一些相似的物种, 所以在种类鉴定中普遍存在一些同物异名或者异物同名的问题[7,10]。随着对黏孢子虫的研究不断深入, 宿主和寄生部位特异性特征被逐渐发现并广泛应用到新的分类鉴定中[8—11]。近年来, 分子生物学技术在黏孢子虫分类学研究中的得到广泛的运用,在种类准确鉴定和阐明类群间系统亲缘关系的研究中发挥重要作用[12]。当前, 基于黏孢子虫形态特征和基因标记系统分析(如18S rRNA)相结合的方法进行新种的厘定成为主流[13], 对深入揭示我国鱼类黏孢子虫多样性有重要意义。
鲤Cyprinus carpioL.是东亚地区重要的养殖品种, 在中国已经有4000多年的养殖历史[14]。截至目前已经报道的寄生于鲤不同组织器官的黏孢子虫种类约75种[6]。其中一些种类可造成养殖鱼苗和成鱼的大量死亡[15,16], 如引起鲤鱼养殖中肠道“巨囊病”的吉陶单极虫(Thelohanellus kitauei), 大量寄生于鲤鳃丝造成宿主死亡的野鲤碘泡虫(Myxobolus koi)。我国鱼类物种多样性高、分布广泛, 随着鱼类寄生虫调查的深入开展, 一些新的寄生黏孢子虫种类不断被发现和报道。作者在进行黏孢子虫调查和分类研究过程中, 从洞庭湖鲤肠道中发现一种黏孢子虫新种, 本文详细描述和分析了该黏孢子虫的形态特征和系统发育关系。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样品采集
2015年9月在湖南岳阳洞庭湖区鱼码头购买野生鲤进行寄生虫调查, 按照《鱼病诊断与防治手册》[17]检查每一条鱼的体表、鳃丝、口腔、肠道,将取得的孢囊保存于装有100%酒精的1.5 mL离心管中, 标注时间、地点、寄生部位, 带回实验室。
1.2 形态学检查
用灭菌的解剖针刺破孢囊, 滴少量蒸馏水, 并且用移液枪吸取5 μL黏孢子虫白色浆液均匀涂抹于载玻片上, 用Olympus CX-31显微镜100倍油镜检查。黏孢子虫形态采用图森(TAC-9.0C)图像软件进行拍摄。参考《中国动物志(黏体门: 黏孢子纲)》[6]形态数据测量标准, 随机选取25个黏孢子虫孢子个体, 采用软件自带测量工具进行形态特征数据测量。
1.3 18S rDNA基因序列扩增
从100%酒精中取出保存的孢囊, 置于2 mL离心管中加入200 μL蒸馏水复水, 共换水3次。基因组DNA提取采用Mag-MK磁珠法(磁珠法深加工产品基因组DNA抽提试剂盒, 上海生工)。18S rDNA基因序列片段扩增采用引物ERI-B1 (ACCTGGT TGATCCTGCCAG)和ERI-B10 (CCTCCGCAG GTTCACCTACGG)[9]。PCR反应体系(50 μL)组成为10×ExTaqBuffer 5 μL, dNTP Mix 4 μL, 正反向引物(10 μmol/L) 2 μL, 模板3 μL, TaKaRa ExTaq(5 U/μL) 0.3 μL, 用RNase-free Water将体系补加到50 μL。反应程序设置为94℃预变性5min; 94℃变性30s, 56℃退火45s, 72℃延伸60s, 30个循环; 72℃末端延伸7min。PCR阳性产物送到生工(上海)生物工程股份有限公司测序。
1.4 序列分析
样品测序数据采用SeqMan (Lasergen package,DNAStar Inc.)生物软件检查和拼接。采用Blastn(http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)在GenBank数据库中检索同源序列。序列多重比对采用CLUSTAL 1.8(默认设置)。序列一致性和DNA碱基替换最佳模型分析采用MEGA7.0软件包Modeltest。序列系统进化分析分别采用最大似然法(Maximum likelihood, ML)和贝叶斯法(Bayesian Inferences, BI)。最大似然法模型参数设置为(T93+G+I), 分支节点的支持率采用Bootstrop 1000次检验; 核苷酸频率为(A=0.2651、C=0.2349、G=0.2350、T=0.2650); 6种核苷酸替换率分别为[AC]=0.081, [AG]=0.338,[AT]=0.086, [CG]=0.076, [CT]=0.338, [GT]=0.081;不变位点的比例为0.3872, 伽马分布值为0.3825。贝叶斯法分析在MrBayes (Ronquist and Huelaenbeck 2003)软件进行(参数设置为nruns=4, nst=6,rates=invagamma, ngen=5000000), 每100代对系统树进行抽样, 以后验概率来表示分支的可信性。
2 结果
2.1 岳阳碘泡虫, 新种Myxobolus yueyangensis sp. nov. (图1)
孢囊特征: 孢囊呈白色, 椭圆形, 寄生鲤鱼肠道肌层组织(图2), 直径约为1.0 ± 0.2 (0.8—1.2) mm(n=10)。
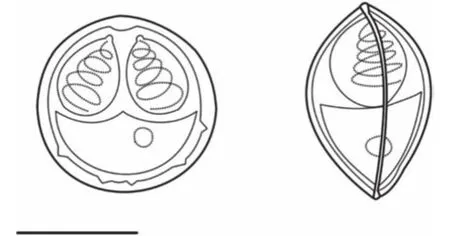
图1 岳阳碘泡虫(壳面、缝面, 比例尺=5 μm)Fig. 1 The schematic drawing of Myxobolus yueyangensis sp.nov., scale bar=5 μm
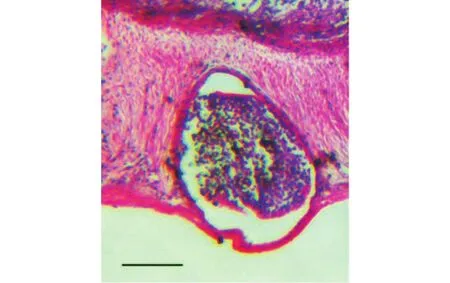
图2 岳阳碘泡虫寄生于肠道组织切片(比例尺=500 μm)Fig. 2 Histopathological section of intestine of common carp infected by Myxobolus yueyangensis, scale bar=500 μm
孢子特征: 成熟孢子具有碘泡虫属典型特征,壳面观近似圆形, 前端稍尖(图1), 壳片表面光滑,后端有4—6个“V”形褶皱(图3a), 囊间突小而明显,孢质均匀, 含有一个嗜碘泡; 缝面观呈纺锤形(图1、 图3b), 缝脊直而粗(图3c); 孢子长9.8±0.6 (9.6—10.0) μm, 孢子宽8.2±0.3 (8.0—8.5) μm; 孢子厚7.3±0.1 (7.0—7.5) μm; 2个极囊梨形, 大小相同, 稍微呈“八”字形叉开并列于孢子前段, 在其顶端存在一个半圆形凸起(图3d); 极囊长4.4±0.4 (3.8—5.1) μm,极囊宽2.7±0.2 (2.2—3.2) μm, 极丝圈数4—5圈。
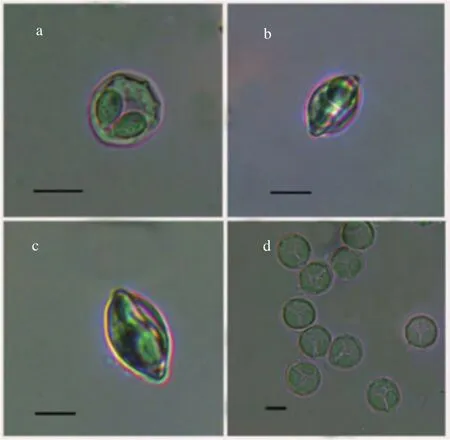
图3 岳阳碘泡虫在显微镜下的孢子形态, 比例尺=5 μmFig. 3 Spores of Myxobolus yueyangensis under light microscope,scale bar=5 μm
宿主: 鲤Cyprinus carpioL. (Cyprinidae)
寄生部位: 肠道
采样地点: 湖南岳阳洞庭湖区 (29°37′N,113°09′E)
感染率: 20% (2/10)
模式标本分子序列: GenBank序列收录号KY203795。
样本保存: 100%酒精固定标本保存于中国水产科学研究院淡水渔业研究中心鱼病研究室, 标本号MYY201509111, MYY201509112。
种名词源: 该黏孢子虫发现于岳阳(Yueyang),故命名为岳阳碘泡虫(Myxobolus yueyangensis)。
2.2 18S rDNA基因序列分析
采用黏孢子虫通用引物成功扩增出18S rDNA基因序列片段2051 bp。该序列在NCBI中BLAST分析, 与以下几个种类相似性最高: 山东碘泡虫(Myxobolus shantungensis, KJ725079) 96% 、倪李碘泡虫(Myxobolus nielii, JQ690358) 95%、住心碘泡虫(Myxobolus hearti, GU574808) 95%、Myxobolus encephalicus(JQ801549) 95%。
系统发育分析表明该黏孢子虫与山东碘泡虫、倪李碘泡虫、住心碘泡虫、Myxobolus encephalicus、Sphaerospora molnari(AF378345)、多涅茨尾孢虫(Henneguya doneci, LC011456)和Henneguya zikaweiensis(KR020026)亲缘关系较近, 聚为稳定的独立分支。该分支类群中的种类分别寄生在鲫、鲤不同器官, 没有呈现出一致的寄生器官特异性。
3 讨论
碘泡虫属物种非常丰富, 目前已报道的种类多达856[18,19]种, 随着研究范围的扩大和调查强度的提高, 一些新的种类不断被报道。近年来国内学者在鲫(Carassius auratus)中陆续发现和命名多个碘泡虫新种类, 如: 丑陋圆形碘泡虫(Myxobolus turpisrotundus)、洪湖碘泡虫(Myxobolus honghuensis)、射阳碘泡虫(Myxobolus sheyangensis)、Myxobolus pronini等[20—23]。本文描述了1种寄生在鲤鱼肠道的碘泡虫属新种, 岳阳碘泡虫。该碘泡虫与文献记录的鲤科鱼类肠道寄生碘泡虫或者其他碘泡虫种类都有明显的形态特征差异(表1)。岳阳碘泡虫与寄生于雅罗鱼肠黏膜层的Myxobolus gayeae、草鱼肠道的饼形碘泡虫(Myxobolus artus)、鲤鱼肠道的北京碘泡虫(Myxobolus pekingensis)和鲤肠碘泡虫(Myxobolus cyprinicola)的孢子形态较为近似。然而,M. gayeae、北京碘泡虫在孢子和极囊大小方面明显大于岳阳碘泡虫, 饼形碘泡虫的则明显小于岳阳碘泡虫。此外, 岳阳碘泡虫的极丝盘绕圈数明显少于M. gayeae、北京碘泡虫和鲤肠碘泡虫。18S rDNA基因序列分析进一步表明岳阳碘泡虫与Gen-Bank已登录黏孢子虫都不一致, 其中与山东碘泡虫的序列相似率较高(96%), 但远低于种内相似水平。因此综合形态学和DNA18S rDNA基因序列分析, 本文所报道的鲤肠道寄生黏孢子虫应为碘泡虫属一新物种。
基于18S rDNA基因序列的系统发育分析表明本文报道的岳阳碘泡虫与山东碘泡虫、M. encephalicus、倪李碘泡虫、住心碘泡虫亲缘关系较近(图4), 然而, 它们在孢子、极囊大小和形态及极丝圈数方面明显不同[25,27—29]。岳阳碘泡虫所处的分支谱系中(图4), 倪李碘泡虫(M. nielii)、多涅茨尾孢虫(H. doneci)、住心碘泡虫(M. hearti)、莫氏球孢虫(S. molnari)和Henneguya zikaweiensis分别寄生于鲫鳃和心脏组织,M. encephalicus和M. shantungensis分别寄生于鲤脑和鳃组织。在该分支谱系中来自鲫、鲤的黏孢子虫分别具有较近的亲缘关系,并且呈现一定的宿主特异性。
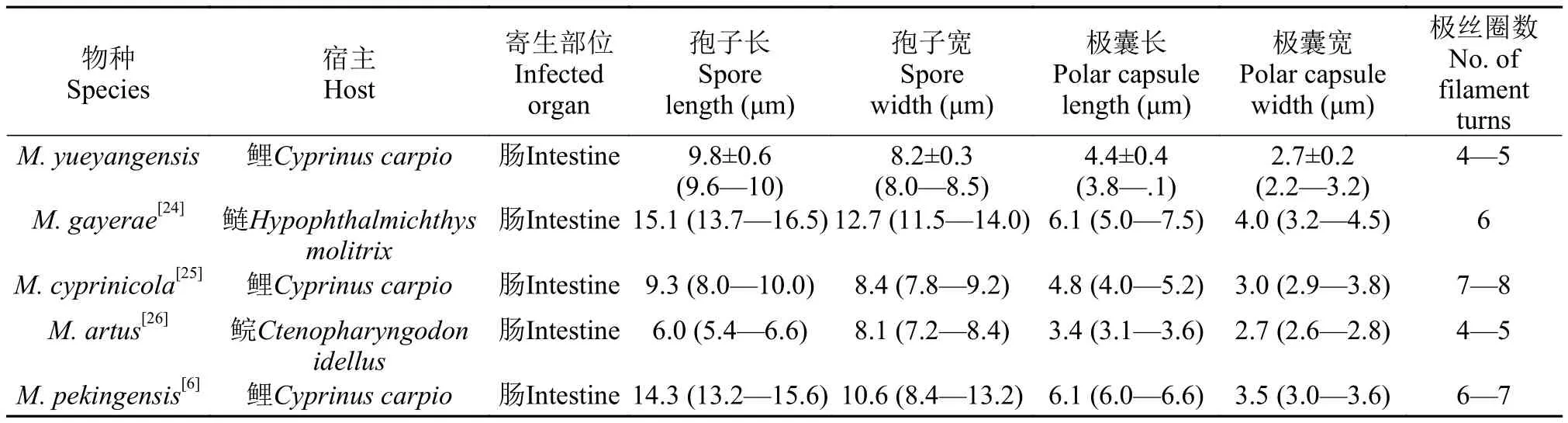
表1 岳阳碘泡虫与相似种类形态特征比较Tab. 1 The measurement comparison of spore of Myxobolus yueyangensis sp. nov. with other morphologically similar species from fish intestine
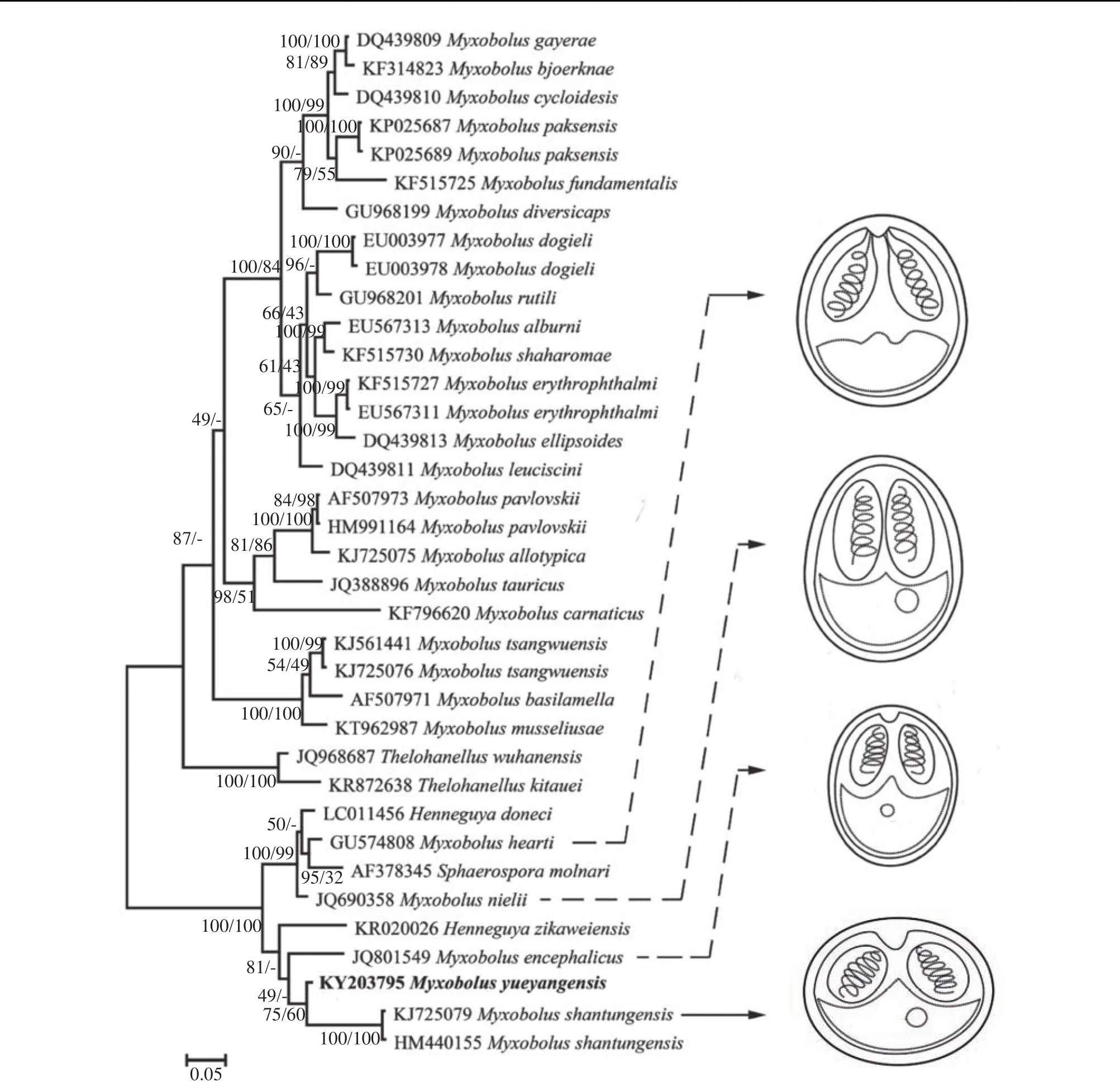
图4 基于18S rDNA基因序列构建的鲤科鱼类寄生黏孢子虫贝叶斯法(BI)系统发育树Fig. 4 Phylogenetic tree of Myxozoans based on 18S rDNA sequences based on the Bayesian Inferences (BI) method
在黏孢子虫传统形态分类系统中, 孢子后端的尾突是碘泡科尾孢虫属和碘泡虫属的重要区分特征[25]。近年来, 分子系统发育分析发现尾孢虫属和碘泡虫属的种类经常交织在不同的分支类群中, 传统形态分类类群没有准确的反映出它们真实进化亲缘关系[30—32]。在本文构建的系统进化树中, 多涅茨尾孢虫、H. zikaweiensis与山东碘泡虫、M. encephalicus、倪李碘泡虫和住心碘泡虫稳定的聚为独立分支(图4)。在Bahri[33]和El-Mansy[34]发现M.bizerti与M. heteromorphs孢子基部存在与尾孢虫相似的尾突, 从而对尾突作为区分碘泡虫属和尾孢虫属分类特征的有效性提出质疑。Liu等[20]在种丑陋圆形碘泡虫(Myxobolus turpisrotundus)同一个孢囊中发现存在少数的碘泡虫孢子基部具有细小的尾突, 并对两种形态的碘泡虫分别测序, 序列相似性达到99.9%, 证明了这2种不同形态的孢子属于同一物种的不同发育阶段。截止目前已经报道的发现具有尾突的碘泡虫数量较少, 而引入物种的数量对系统发育树的进化树分析结果有着较大的影响, 尾突能否作为区分碘泡虫属和尾孢虫属的重要依据还需发现和引入更多的物种加以验证。
[1]Siddall M E, Cone D K. The demise of a phylum of protists: phylogeny of Myxozoa and other parasitic cnidarian[J].Journal of Parasitology, 1995, 81(6): 961—967
[2]Chang E S, Neuhof M, Rubinstein N D,et al. Genomic insights into the evolutionary origin of Myxozoa within Cnidaria [J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 2015, 112(48): 14912—14917
[3]Foox J, Siddal M E. The road to cnidaria: history of phylogeny of the Myxozoa [J].Journal of Parasitology,2015, 101(3): 269—274
[4]Lom J, Dyková I. Myxozoan genera: definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle terminology and pathogenic species [J].Folia Parasitologica, 2006, 53(1): 1—36
[5]Fiala I, Bartošová-Sojková P, Whipps C M. Classification and Phylogenetics of Myxozoa [M]. Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development. 2015, 85—110
[6]Chen Q L, Ma C L. Myxosporea [M]. Beijing: Science Press. 1998, 34—162 [陈启鎏, 马成伦. 动物志, 黏体动物门, 黏孢子纲. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998, 34—162]
[7]Zhang J Y, Wang J G, Li A H. Infection ofMyxobolus turpisrotundussp. n. in allogynogenetic gibel carp,Carassius auratus gibelio(Bloch), with revision ofMyxobolus rotundus(s. l.) Nemeczek reported fromC. auratus(L.) [J].Journal of Fish Diseases, 2010, 33(8): 625—638
[8]Eszterbauer E. Genetic relationship among gill-infectingMyxobolus species(Myxosporea) of cyprinids: Molecular evidence of importance of tissue-specificity [J].Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2004, 58(1): 35—40
[9]Barta J R, Martin D S, Liberator P A,et al. Phylogenetic relationships among eightEimeriaspecies infecting domestic fowl inferred using complete small ribosomal DNA sequences [J].Journal of Parasitology, 1997, 83:262—271
[10]Molnár K. Site preference of fish myxosporeans in the gill [J].Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2002, 48(3):197—207
[11]Liu X H, Zhang J Y, Batueva M D,et al. Supplemental description and molecular characterization ofMyxobolus miyariiKudo, 1919 (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) infecting intestine of Amur catfish (Silurus asotus) [J].Parasitology Research, 2016, 115(4): 1—10
[12]Liu Y, Gu Z M, Luo Y L. Some additional data to the occurrence, morphology and validity ofMyxobolus turpisrotundusZhang, 2009 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) [J].Parasitology Research, 2010, 107(1): 67—73
[13]Atkinson S D, Bartošová-Sojková P, Whipps C M,et al.Approach for Characterizing Myxozoan Species [M].Springer International Publishing. 2015, 111—123
[14]Fishery bureau in ministry of Agricultural, China Fishery Statistics Yearbook. Beijing: China Agriculture Press.2014 [农业部渔业渔政管理局, 中国渔业统计年鉴. 北京: 中国农业出版社. 2014]
[15]Zhai Y H, Gu Z M, Guo Q X. New type of pathogenicity ofThelohanellus kitaueiEgusa amp; Nakajima, 1981 infecting the skin of common carpCyprinus carpioL. [J].Parasitology International, 2016, 65(1): 78—82
[16]Liu Y, Whipps C M, Liu W S,et al. Supplemental diagnosis of a myxozoan parasite from common carpCyprinus carpio: synonymy ofThelohanellus xinyangensiswithThelohanellus kitauei[J].Veterinary Parasitology,2011, 178(3—4): 355—359
[17]Pan J B. Handbook of Fish Disease Diagnosis and Prevention [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific amp; Technical Publishers. 1988, 5—8 [潘金培. 鱼病诊断与防治手册.上海: 上海科技出版社. 1988, 5—8]
[18]Eiras J C, Zhang J, Molnár K. Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Butschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea,Myxobolidae) described between 2005 and 2013 [J].Systematic Parasitology, 2014, 61(1): 1—46
[19]Eiras J C. Synopsis of the species of the genus Henneguya Thélohan, 1892 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) [J].Systematic Parasitology, 2002, 52(1):43—54
[20]Liu Y, Whipps C M, Gu Z M,et al.Myxobolus turpisrotundus(Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) spores with caudal appendages: investigating the validity of the genusHenneguyawith morphological and molecular evidence [J].Parasitology Research, 2010, 107(3): 699—706
[21]Liu Y, Whipps C M, Gu Z M,et al.Myxobolus honghuensisn. sp. (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) parasitizing the pharynx of allogynogenetic gibel carpCarassius auratus gibelio(Bloch) from Honghu Lake, China [J].Parasitology Research, 2012, 110(4): 1331—1336
[22]Liu X H, Yuan S, Zhao Y L,et al. Morphological and molecular characterization ofMyxobolus sheyangensisn.sp. (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) with intralamellar sporulation in allogynogenetic gibel carp, carassius auratus gibelio(Bloch) in China [J].Parasitology Research, 2016,115: 3567—3574
[23]Liu X H, Marina-D Batueva, Zhao Y L,et al. Morphological and molecular characterization ofMyxobolus proninin. sp. (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) from the abdominal cavity and visceral serous membranes of the gibel carpcarassius auratus gibelio(Bloch) in Russia and China [J].Parasites amp; Vectors, 2016, 9: 562
[24]Molnár K, Marton S, Eszterbauer E,et al. Description ofMyxobolus gayeraen. sp. and re-description ofMyxobolus leucisciniinfecting European chub from the Hungarian stretch of the river Danube [J].Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2008, 78(2): 147—153
[25]Liu Y. Revision on genusMyxobolus(Myxozoa:Myxosporea) and taxonomy of someMyxobolusspecies in China [D]. Huazhong Agricultural University. 2014 [柳阳. 碘泡虫属的修订及中国部分碘泡虫物种的分类学研究. 华中农业大学. 2014]
[26]Yokoyama H, Danjo T, Ogawa K,et al. Hemorrhagic anemia of carp associated with spore discharge ofMyxobolus artus(Myxozoa: Myxosporea) [J].Fish Pathology,1996, 31(1): 19—23
[27]Liu Y, Gu Z, Zhang Y,et al. Redescription and molecular analysis ofMyxobolus shantungensis, Hu, 1965(Myxozoa: Myxosporea) infecting common carpCyprinus carpio haematopterus[J].Parasitology Research,2011, 109(6): 1619—1623
[28]Antychowicz J, Reichert M. Occurrence ofMyxobolus encephalicus(Muslow 1911) in Poland: Possible relationship between the parasite infection and clinical symptoms in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) [J].Bulletin of the Veterinary Institute in Pulawy, 2005, 49(1): 35—39
[29]Ye L T, Li W X, Wang W W,et al. Updated morphology,histopathology and molecular phylogeny ofMyxobolus hearti, cardiac myxosporea in gibel carp,Carassius gibelio(Bloch) [J].Journal of Fish Diseases, 2014, 37(1):11—20
[30]Kent M L, Al E. Recent advances in our knowledge of the Myxozoa [J].Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 2001,48(4): 395—413
[31]Carriero M M, Adriano E A, Silva M R M,et al. Molecular phylogeny of theMyxobolusandHenneguyagenera with several new south American species [J].PloS One,2013, 8(9): e73713
[32]Smothers J F, Spall R D. Molecular evidence that the myxozoan protists are metazoans [J].Science, 1994,265(5179): 1719—1721
[33]Bahri S. Abnormal forms ofMyxobolus bizertiandMyxobolus mülleri(Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) spores with caudal appendages [J].Bulletin-European Association of Fish Pathologists, 2008, 28(6): 252—255
[34]Elmansy A. Revision ofMyxobolus heterosporusBaker,1963 (syn.Myxosoma heterospora) (Myxozoa:Myxosporea) in African records [J].Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2005, 63(2-3): 205—214
MORPHOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR CHARACTERISTIC OF MYXOBOLUS YUEYANGENSIS SP. NOV. (MYXOZOA: MYXOBOLIDAE) FROM THE INTESTINE OF COMMON CARP (CYPRINUS CARPIO) IN CHINA
LI Peng1,2, XI Bing-Wen2,3, CHEN Kai2and XIE Jun1
(1. Wuxi Fisheries College, Nanjing Agricultural University, Wuxi 214081, China; 2. Key Laboratory of Freshwater Fisheries and Germplasm Resources Utilization, Ministry of Agriculture, Freshwater Fisheries Research Center, Chinese Academy of Fishery Science, Wuxi 214081, China; 3. Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for Freshwater Aquaculture, Wuhan 430070, China)
Myxobolus yueyangensissp. nov. parasitic in the intestine muscularis of common carpCyprinus carpiowith the form of round or ellipsoidal plasmodia, was found during a survey on fish myxozan diversity in Yueyang(29°37′N, 113°09′E). Mature spores were suborbicular in frontal view, and fusiform in back view, measuring 9.8±0.6(9.6—10) μm long, 8.2±0.3 (8.0—8.5) μm wide, and 7.3±0.1 (7.0—7.5) μm thick. The surface of spores was smooth,and a round iodinophilous vacuole was found in its uniform protoplasm. Two Polar capsules were pyriform with an apophysis at its top and end closed to apex of spore, measuring 4.4±0.4 (3.8—5.1) μm in length, 2.7±0.2 (2.2—3.2) μm in width. Polar filaments coiled 4 to 5 turns.M. yueyangensisis morphologically distinct from all otherMyxobolusspecies. The BLAST search indicated that the newly obtained small subunit ribosomal RNA (ssrRNA) gene sequence did not match any available sequences in GenBank, and showed the high similarity withMyxobolus yueyangensisof 96%.In the phylogenetical tree,M. yueyangensiswas closely clustered withMyxobolus yueyangensis. Based on the comparison and analysis of spore morphology, host specificity, tissue or organ parasitized specificity, and 18S rDNA sequence, the myxosporean from the intestine ofC. carpiodescribed in the study should be a new species of genusMyxobolus.
Common carp;Myxobolus; Intestine; 18S rDNA
S941.5
A
1000-3207(2017)06-1251-06
2016-12-13;
2017-05-10
国家自然科学基金(31302222); 现代农业产业技术体系建设专项资金(CARS-45)资助 [Supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (31302222); the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-45)]
李鹏(1992—), 男, 江苏南通人; 硕士研究生; 研究方向为鱼类寄生虫。E-mail: 1574944091@qq.com
习丙文, E-mail: xibw@ffrc.cn
10.7541/2017.155
