冠心病合并抑郁症患者血清脂联素水平及其与炎性因子相关性的临床研究
2016-06-12江莉丁建东赵剑锋李浩崔青扬敖明强东南大学医学院江苏南京0009东南大学附属中大医院心内科江苏南京0009
江莉,丁建东,赵剑锋,李浩,崔青扬,敖明强.东南大学医学院,江苏南京 0009;.东南大学附属中大医院心内科,江苏南京 0009
冠心病合并抑郁症患者血清脂联素水平及其与炎性因子相关性的临床研究
江莉1,丁建东2,赵剑锋2,李浩2,崔青扬2,敖明强2
1.东南大学医学院,江苏南京210009;2.东南大学附属中大医院心内科,江苏南京210009
[摘要]目的分析冠心病合并抑郁症患者血清脂联素水平及其与炎性因子的相关性。方法选用110例冠状动脉造影检查确诊的冠心病患者,根据汉密尔顿抑郁评分,分为冠心病合并抑郁症组52例和冠心病非抑郁组各58例,另外选取60例正常对照组,测定其血清脂联素(APN)、IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP水平。结果冠心病组患者血清IL-6(136± 18.6)ng/L、TNF-a(15.6±9.5)ng/L、hs-CRP(4.6±3.1)mg/L,均显著高于对照组(P<0.01),血清APN(12.12±3.76)mg/L显著低于对照组(P<0.01);冠心病合并抑郁症患者血清IL-6(166.2±21.6)ng/L、TNF-a(18.2±12.0)ng/L、hs-CRP(10.2±3.4)mg/L显著高于冠心病非抑郁症组(P<0.01),血清脂联素显著低于对照组(P<0.01),且冠心病合并抑郁症组血清脂联素水平与炎性因子IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP呈显著的负相关性(r值分别为-0.560,-0.462,-0.268,P<0.01)。结论冠心病合并抑郁症组血清脂联素水平明显减低,而炎性因子IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP均显著增高,这些炎性因子对脂联素具有一定的抑制作用,从而增加冠心病的发病率及冠心病患者并发抑郁症的可能。
[关键词]冠心病;抑郁症;血清脂联素;炎性因子
脂联素,又称脂连蛋白(adiponectin,APN),是一种主要由脂肪细胞分泌的蛋白质激素,大量存在于血液循环中,其水平与脂肪储量呈负相关,具有抗炎、抗动脉粥样硬化形成和血管损伤后抗内膜增生的作用。研究显示[1],脂联素与肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)分泌、脂肪和糖类的代谢、动脉平滑肌增殖和迁移以及血管内皮分泌功能都有密切关系。目前,血清脂联素与冠心病合并抑郁症患者炎性因子水平的相关研究尚不充分,该研究对2013年9月—2014年4月整群选取的110例在中大医院心内科就诊的冠心病患者进行临床检测,分析了冠心病合并抑郁患者血清脂联素水平及其与炎性因子的相关性,报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
该研究整群选取就诊于东南大学附属中大医院心内科疗区,行冠状动脉造影检查确诊的冠心病患者110例为研究对象,根据汉密尔顿抑郁量表(HAMD)评分评分测试[2],选取分数>7分者(轻度及中重度抑郁患者)52例作为冠心病合并抑郁组,其中男性患者293例,女性患者23例,平均年龄(68.71±15.81)岁;选取冠心病非抑郁患者58例作为冠心病非抑郁症组,其中男性患者30例,女性患者28例,年龄(67.31±15.49)岁;另选经知情同意参加临床研究者60例作为正常对照组,其中男30例,女30例,平均年龄(66.34±15.01)岁,经体检确定身体健康无重大疾病。
1.2研究方法
所有研究对象于清晨空腹进行静脉采血5 mL,于无菌离心管中分离血清后集中,采用酶联免疫吸附试验(EllSA)检测血清IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP的含量,测试仪器。
1.3统计方法
采用SPSS 19.0统计学软件对数据进行处理,计量资料均以均数±标准差(±s)表示,比较采用t检验,计数资料以百分数表示,应用x2检验。单因素相关分析应用Pearson相关分析,多元逐步回归分析APN的相关因素。P<0.05表示差异无统计学意义。
2 结果
血清APN、IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP测定结果显示,冠心病组患者血清IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP水平均显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),血清APN显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);冠心病合并抑郁症患者血清IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP水平显著高于冠心病组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),血清APN显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),见表1。
表1 血清APN、IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP测定结果(±s)

表1 血清APN、IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP测定结果(±s)
注:冠心病组与对照组,P<0.01;冠心病合并抑郁症组与冠心病组,P<0.01。
冠心病合并抑郁症组(n=52)冠心病非抑郁症组(n=58)对照组(n=60)t值P值组别9.44±2.98 12.12±3.76 15.98±4.66 3.012 0.004 APN (mg/L)166.2±21.6 136±18.6 109.5±15.5 3.345 0.007 APN (mg/L)18.2±12.0 15.6±9.5 7.2±10.3 3.113 0.003 10.2±3.4 4.6±3.1 1.3±1.5 3.598 0.008 TNF-a (ng/L)TNF-a (ng/L)
以血清APN水平为因变量,各指标为自变量进行Pearson相关分析显示IL-6、TNF-a、hsC-RP与APN呈负相关。冠心病合并抑郁症组血清脂联素水平与炎性因子的相关性分析见表2。
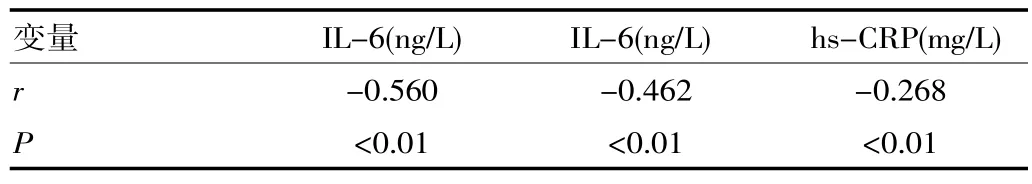
表2 冠心病合并抑郁症组血清脂联素水平与炎性因子的相关性分析
3 讨论
冠心病发病机制与机体的免疫反应及炎症反应密切相关[3]。血清脂联素可以抑制TNF-a、IL-6等炎性因子的表达,参与心肌抗炎,具有保护心肌细胞缺血再灌注损伤,在动脉硬化斑块的发展过程中发挥作用[4-7]。
在冠心病患者由于症状、心理等方面因素的影响导致临床上合并抑郁症患者逐渐增多,特别在患者症状急性发作时[8-11]。国外有研究报道单纯抑郁症患者血清IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP等炎性因子是升高的。
但目前国内外尚未有针对冠心病合并抑郁症患者的血清脂联素水平及其相关炎性因子的研究。该研究中,冠心病合并抑郁症组血清APN显著低于对照组及冠心病组(P<0.01),血清IL-6、TNF-a、hs-CRP水平显著高于冠心病组(P<0.01),其血清脂联素水平与炎性因子呈显著的负相关性,提示在冠心病形成的过程中炎性因子对脂联素具有一定的抑制作用,从而增加冠心病的发病率及其并发抑郁症的可能。
综上所述,通过检测血清脂联素及相关炎性因子,可以预测冠心病合并抑郁症的发生,对其治疗,预后及疗效评判均具有重要意义。
[参考文献]
[1]MariaDalamaga,KalliopeN.Diakopoulos,TheRoleof Adiponectin in Cancer:A Review of Current Evidence[J]. Endocrine Reviews,2012,33(4):547-594.
[2]Jing Liu,Ming Guo,Di Zhang,et al.Adiponectin is critical in determining susceptibility to depressive behaviors and has antidepressant-like activity[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012,24,109(30):12248-12253.
[3]王娟,崔景晶.冠心病相关炎性因子与冠心病患者TIPE2 mRNA水平的关系[J].实用医学杂志,2015,12(2).6.
[4]Shahzad K,Cao L,Ain QT,et a1.Postpartum spontaneous dissection of the first obtuse marginal branch of the left circumflex coronary artery causing acute coronary syndrome:a case report and literature review[J].J Med Case Rep,2013,7 (1):82.
[5]AI-Daghri NM,AI-Attas OS,Alokail MS,et al.Adiponectin gene variants and the risk of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Mol Biol Rep,2011,38(6):3703-3708.
[6]Crispim F,Vendramini MF,Moises RS.Adiponeetin complexes composition in Japanese-Brazilians regarding their glucose tolerance status[J].Diabetol Metab Syndr,2013,5 (1):20.
[7]Ikeda U,Ito T,Shimada K,et a1.Interleukin-6 and acute coronarysyndrome[J].Clin Cardiol,2001,24:701-704.
[8]王大强.西酞普兰治疗冠心病合并抑郁症的临床观察[J]中国现代药物应用,2014(8):115-116.
[9]Ren Yanping,Yang Hui,Colette Browning,et al.Prevalence of depression in coronary heart disease in China:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Chinese medical journal,2014, 127(16):2991-2998.
[10]Doyle TA,de Groot M,Harris T,et al.Diabetes,Depressive Symptoms,and Inflammation in Older Adults:Results from the Health,Aging,and Body Composition Study[J] Psychosom Res,2013,75(5):10.
[11]Kiropoulos LA,Meredith I,Tonkin A,et al.Psychometric properties of the cardiac depression scale in patients with coronary heart disease[J].BMC Psychiatry,2013,12(1):216.
Clinical Research of Serum Adiponectin Levels of Patients with Coronary Heart Disease Combined with Depression and Its Correlation with Inflammatory Factors
JIANG Li1,DING Jian-dong2,ZHAO Jian-feng2,LI Hao2,CUI Qing-yang2,AO Ming-qiang2
1.Southeastern University Medical College,Nanjing,Jiangsu Province,210009 China
2.Department of cardiology,Zhongda Hospital Affiliated to Southeast University,Nanjing,Jiangsu Province,210009 China
[Abstract]Objective To analyze the serum adiponectin levels of patients with coronary heart disease combined with depression and its correlation with inflammatory factors.Methods 110 cases of patients with coronary heart disease confirmed by coronary angiography examination were selected and divided into the coronary heart disease combined with depression group with 52 cases and the coronary heart disease without depression group with 58 cases according to the Hamilton depression score,in addition,60 cases of normal people were selected as the control group,the levels of serum adiponectin (APN),IL-6,TNF-a and hs-CRP were measured.Results The serum IL-6(136±18.6)ng/L,TNF-a(15.6±9.5)ng/L and hs-CRP(4.6±3.1)mg/L in the coronary heart disease group were obviously higher than those in the control group(P<0.01), the serum APN(12.12±3.76)mg/L in the coronary heart disease group was obviously lower than that in the control group(P<0.01),the serum IL-6(166.2±21.6)ng/L,TNF-a(18.2±12.0)ng/L and hs-CRP(10.2±3.4)mg/L in the coronary heart disease combined with depression group were obviously higher than that in the coronary heart disease without depression group(P<0.01),the serum adiponectin in the coronary heart disease combined with depression group were obviously lower than that in the control group(P<0.01)and it also had an obvious negative correlation with the inflammatory factors IL-6,TNF-a and hs-CRP,(R values were respectively-0.560,-0.462 and-0.268,P<0.01).Conclusion The serum adiponectin level obviously decreases and the inflammatory factors IL-6,TNF-a and hs-CRP obviously increase in the coronary heart disease combined with depression group,these inflammatory factors have a certain inhabitation effect on adiponectin and then enhance the incidence of coronary heart disease and chances of coronary heart disease patients complicated by depression.
[Key words]Coronary heart disease;Depression;Serum adiponectin;Inflammatory factor
[中图分类号]R541.4
[文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1674-0742(2016)01(c)-0050-03
DOI:10.16662/j.cnki.1674-0742.2016.03.050
[作者简介]江莉(1983.12-),女,江苏丹阳人,本科,初级住院医师,研究方向:血清脂联素与冠心病合并抑郁的相关性研究。
收稿日期:(2015-10-25)
