食品中展青霉素检测方法及脱除技术研究进展
2015-06-05徐明悦李洪军贺稚非
徐明悦,李洪军,王 珊,项 怡,员 璐,贺稚非
(西南大学食品科学学院,重庆 400716)
食品中展青霉素检测方法及脱除技术研究进展
徐明悦,李洪军,王 珊,项 怡,员 璐,贺稚非*
(西南大学食品科学学院,重庆 400716)
展青霉素是由多种真菌产生的一种有毒代谢产物,广泛存在于自然界中,易在水果及其制品中残留,并可通过食物链进行富集,严重威胁人类健康。本文对展青霉素的来源、性质、检测、脱除、存在问题及研究趋势进行概述,为后续研究提供理论依据。
展青霉素,检测方法,脱除
近年来,真菌毒素污染食品事件时有发生。其中,展青霉素具有“三致”毒性,主要污染水果及其制品,并能通过食物链传递在生物体中蓄积。据报道,该毒素在世界范围内广泛分布。Funes等[1]研究表明在阿根廷的苹果和梨制品中,展青霉素的检出率为21.6%(平均61.7μg/kg),苹果酱中检出率高达50%(平均123μg/kg);葡萄牙的婴儿食品原料中展青霉素的检出率高达7%,苹果制品中检出率高达23%[2];在中国东北市售的苹果制品中仅12.6%的样品中检测不到展青霉素[3];Marín等[4]研究显示西班牙市场中梨和苹果浓缩汁中展青霉素的检出量高达126μg/kg,远高于欧盟限量;突尼斯的果汁样品和婴儿食品样品中展青霉素的检出率分别为18%、28%[5]。目前,有关于展青霉素在食物中的检测及脱除技术的研究较其他真菌毒素有所欠缺,且国内对展青霉素的研究、存在问题和发展趋势的系统性分析和总结的文章较少。本文通过对展青霉素相关的研究进行综述,为后续深入研究提供一定的理论基础和实践依据。
1 展青霉素概述
1.1 结构、性质及来源
展青霉素,化学名称为4-羟基-4-氢-呋喃-[3,2c]-吡喃-2(6)-酮,是由多种霉菌产生的一种非挥发性的水溶性多聚乙酰内酯类真菌毒素[6-7],产生菌有青霉青霉、曲霉、丝衣霉等[8-9],其中扩展青霉是主要产生菌[10],产毒菌株易在采摘、加工、贮运过程中污染苹果、梨、山楂、草莓、桃、葡萄等及其制品[11-12]。
1.2 生物合成
展青霉素跟黄曲霉毒素、伏马菌素等毒素一样都是真菌通过聚酮代谢途径产生的[13](如图1),其编码基因是在染色体上成簇存在的(PatA、PatB、PatC、PatD、PatE、PatF、PatG、PatH、PatI、PatJ、PatK、PatL、PatM、PatN、PatO)[14]。目前,PatK、PatH、PatI、PatN、PatE基因已被证实分别合成参与展青霉素产生过程中的限速酶 6-甲基水杨酸合酶、间甲酚甲基羟化酶、间羟基苯甲醇羟化酶、异环氧菌素脱氢酶和GMC氧化还原酶[15-17],其中m-cresol methyl hydroxylase、m-hydroxybenzyl alcohol hydroxylase是两种细胞色素氧化酶P450类蛋白[17]。现阶段,对于展青霉素产生基因的研究较少,对于两条产生途径是否同时存在存在争论,需要更多深入的研究。
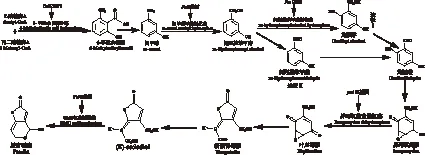
图1 展青霉素生物合成途径Fig.1 Biosynthetic pathway of Patulin
1.3 毒理作用
展青霉素具有广泛的急性和慢性毒作用,主要表现在生殖毒性、遗传毒性、免疫毒性、细胞毒性、致癌性等方面[18-27]。展青霉素能促进谷胱甘肽与丁硫氨酸亚砜胺结合,诱导p53蛋白在细胞中累积,同时可能造成DNA分子交联形成核质桥,形成微核,造成细胞复制延迟,激活有丝分裂蛋白酶原,导致纺锤体加倍,进而产生强烈的遗传毒性[18-21]。Flávia等[22]证实小鼠经腹腔注射2.5、3.75mg/kg的展青霉素,肝脏、脑、肾脏出现明显的DNA损伤,并能显著提高细胞的氧化活性。Dickens等[23]发现大白鼠皮下注射展青霉素后,注射部位诱发肿瘤,并相继发现了致畸性和致突变性。Smith等[24]研究发现当老鼠胚胎置于47~55μmol/L的展青霉素环境下,蛋白质和DNA浓度等均有不同程度的下降;当展青霉素浓度达62μmol/L时,胚胎40h内死亡。此外,展青霉素能够抑制白细胞的吞噬作用[25],改变结肠上皮细胞的膜电位和通透性[26],显著提高睾丸酮和甲状腺激素的含量[27]。
2 展青霉素残留的检测方法
2.1 预处理方法
预处理,是指从污染的食品中将待检物质提取、分离、纯化的过程。由于展青霉素是非挥发性水溶性内酯,酸性条件下稳定,实验室中通常采用乙酸乙酯、乙腈、水提取[3,28-29],使用液-液萃取、固相萃取、免疫亲和柱等方法进行纯化[29-31]。
研究表明,液-液萃取技术[31]、双溶剂微萃取(BS-DLLME)[44]、MycoSep 228 AflaPat多功能净化柱[29]、将亲水亲油平衡柱(HLB)[8]、Oasis HLB固相萃取(SPE)小柱[30]、免疫亲和柱[28]测得苹果汁中展青霉素的回收率分别为94%~97%、91.3%~95.2%、86%~92%、90%、80.6%~91.8%、80.0%~101.1%。因此,虽然不同方法的原理不同,但是对于展青霉素纯化的效果都是较理想的。
2.2 检测技术
展青霉素的检测技术大致可分为生物学方法、免疫学方法、物理化学方法3大类,如表1所示。
目前,检测食品中展青霉素的常用方法有HPLC、GC-MS、LC-MS等,但是由于其前处理繁琐,仪器设备昂贵,需要建立专一性高、特异性强、价格低廉、快速检测的技术。
2.2.1 联用技术 HPLC检测展青霉素的技术已经非常成熟,其前处理较其他色谱联用技术简单,准确性较高,是目前最常用的检测技术。随着对检测结果要求的提高,色谱联用技术将得到广泛的应用。目前,常用的检测展青霉素的联用技术有气质联用和液质联用,其中LC-MS被认为是检测霉菌毒素的最先进的技术之一[43]。
据报道,Zhou等[44]研究使用PVPP-F和MycoSep 228净化柱净化苹果汁后,用HPLC测定,效果较好,回收率分别为81.9%~100.9%和86.4%~103.9%,检出限分别为3.99μg/kg和3.56μg/kg;采用BS-DLLME纯化提取苹果汁中的展青霉素,效果稳定,回收率为91.3%~95.2%,HPLC测得展青霉素的检出限低,为2.0μg/L[45],同时使用HPLC-DAD检测展青霉素,回收率整体较BS-DLLME高,为94%~97%,检出限较高为4.0μg/L[46];Beltrán等[47]使用UHPLC-MS联用技术,对比大气压化学电离源(APCI)和生物质谱离子源(ESI)的检测效果,得出此方法的回收率波动范围较大,为71%~108%,此方法的检出限受原料的影响较大,在水果、果脯、果酱、苹果汁中的检出限分别为2、3、2μg/L、0.015mg/kg;Marsol-Vall等[48]采用QuEChERS方法分离提取苹果制品中的展青霉素,回收率为78.4%~94.7%,用UHPLC-PDA检测出四个样品中的最高含量为25.4ng/g,相对于其他方法而言此方法回收率波动较大,检出限很高。
与液相色谱相比,气相色谱检测展青霉素前需将其衍生化,操作繁琐,Llovera等[38]探索出不用衍生化而直接将展青霉素射到分析柱上,用MS检测的方法,检出限为4μg/L;Niloofar等[10]研究固相萃取后,使用N,O-双(三甲基硅烷基)三氟乙酰胺衍生展青霉素,再用GC-MS测得回收率79.9%~87.9%,检出限为0.4μg/L;Llovera等[40]创立了气相色谱-质谱-选择性离子监测(GC-MS-SIM)检测方法,该方法的检出限为1μg/L。

表1 展青霉素常用检测技术Table 1 Commonly used detection techniques for Patulin
综上所述,研究者可以根据实验要求和条件合理选择物理化学检测方法,同时探索和改进检测技术来满足检测的要求。
2.2.2 免疫技术 免疫技术以其专一性高、特异性强、检测灵敏、快速、操作简单等优点,在检测方面发展迅速,并被广泛应用,具有非常广阔的发展前景。酶联免疫吸附技术(ELISA)已经逐渐发展成为检测真菌毒素常用的方法。
展青霉素的免疫学检测方法在快速分离和检测上具有很高的研究价值。1993年,McElroy 等[41]首次制备出抗PAT-HG-BSA 的多克隆抗体(PcAb),建立了间接竞争ELISA 方法,并检测了此PcAb的滴度及特异性;2006年邓舜洲等[49]采用戊二酸酐法合成PAT-HG偶联到BSA,成功制备出展青霉素免疫抗原(PAT-HG-BSA),免疫3只BALB/c小鼠,测得1号小鼠血清抗PAT 抗体效价达1∶1600,另外两只为1∶200;2007年De Champdoré等[42]成功制备出一种高效价的抗展青霉素的多克隆抗体,并进行荧光标记,创建了竞争性荧光偏振免疫检测方法,该方法检测展青霉素的下限为10μg/L;2012年田园[50]按照McElroy提出的方法成功合成了特异性抗体,建立了直接ELISA方法,初步探索了展青霉素的免疫层析柱的制备。
Wang等[51]指出,免疫技术在对小分子真菌毒素的免疫分析中存在诸多缺点,如抗体制备繁琐,假阳性检出率较高等。由于展青霉素分子量小,是天然的半抗原,不能直接作为抗原使用,使得抗体制备繁琐,且不稳定,也为免疫检测增加了难度。
3 脱除技术
3.1 原料污染控制及机理
由于展青霉素产生菌多侵染水果及其制品,所以从源头控制展青霉素的产生尤为重要。近年来,对于展青霉素的拮抗菌的研究增多,据报道,黏红酵母、罗伦隐球酵母、清酒假丝酵母、白隐球酵母、枯草芽孢杆菌均对展青霉素产生菌有拮抗作用[52-57]。拮抗菌的作用机理大致可以分为两种:a.与展青霉素产生菌竞争养分和生存空间;b.分泌抗菌物质,合成抗菌蛋白[58-59]。此外,0.2%的植酸可增强胶红酵母的抑菌作用[60],香菇培养液可增强罗伦隐球酵母抑制扩展青霉生长的作用[52]。
3.2 产品中展青霉素的脱除
产品中展青霉素的常用的脱除技术主要分为物理法、化学法、生物法三大类,其原理及优缺点如表2所示。

表2 展青霉素常用脱除技术Table 2 Commonly used removal techniques for Patulin
近年来,脱除技术的研究已经从单一的物质吸附向两种或两种以上物质联用的方向发展,如活性炭、酵母菌体分别与海藻酸钠、明胶、磁性粒子等联用制备固定化颗粒,既可脱除展青霉素又可保证食品的品质。
目前,这种方法主要应用于苹果汁、猕猴桃汁中展青霉素的脱除。Yue等[68]研究发现活性炭含量为1%的海藻酸钠-活性炭固定化颗粒可以脱除苹果汁中69.46%的展青霉素;Guo等[69]用碱处理废弃啤酒酵母菌体,最高可吸附苹果汁中58.29%的展青霉素,苹果汁营养成分未受到较大的破坏,郭彩霞等[70]通过傅里叶近红外光谱初步判断,灭活酵母中起吸附作用的化学基团主要是存在于细胞壁蛋白质和糖类上的氨基、羧基和羟基;董媛等[71]比较了固定化失活酵母、磁性固定化失活酵母和失活酵母粉对苹果汁中展青霉素的脱除效果,发现固定化失活酵母的吸附率高达70.4%,同时对苹果汁品质影响小。
4 展望
随着研究的深入,已对展青霉素的毒性作用有了明确的认识,但是对其产生、代谢机理和途径有待于进一步研究。因此,须依托于其他学科,深入研究其调控、产生机理,代谢速度及方式,降解方式及产物性质,为水果及其制品生产加工过程中的安全控制提供有力的理论依据。
展青霉素的检测技术除运用理化方法外,还需要加强对免疫检测方法的研究,开发免疫检测与其他技术的联用和混用的快速检测技术,建立更加快速、稳定、准确的检测方法,以达到对大量样品快速检测的目的。
近年来,生物脱除技术因其成本低、安全性高、绿色环保、可行性强受到广泛关注。已有微生物及菌体脱除展青霉素的报道,但是还处于实验阶段,且大多只是研究如何脱除,并未研究脱除后展青霉素是否变成其他有毒物质,造成二次污染的安全问题。未来应重点研究:1)探索有效脱除展青霉素而又保持食品原有品质的高效脱除技术,加快新技术应用于工业生产的进程;2)通过基因工程改良拮抗菌种,应用于工业生产中,实现真正意义上的绿色生物防治;3)研究展青霉素降解后产物的种类、检测方法、安全性,为工业应用提供理论依据。
[1]Funes G J,Resnik S L. Determination of Patulin in solid and semisolid apple and pear products marketed in Argentina[J]. Food Control,2009,20(3):277-280.
[2]Barreira M J,Alvito P C,Almeida C M M. Occurrence of Patulin in apple-based-foods in Portugal[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,121(3):653-658.
[3]Yuan Y,Zhuang H,Zhang T,etal. Patulin content in apple products marketed in Northeast China[J]. Food Control,2010,21(11):1488-1491.
[4]Marín S,Mateo E M,Sanchis V,etal. Patulin contamination in fruit derivatives,including baby food,from the Spanish market[J].Food Chemistry,2011,124(2):563-568.
[5]Zaied C,Abid S,Hlel W,etal. Occurrence of Patulin in apple-based-foods largely consumed in Tunisia[J]. Food Control,2013,31(2):263-267.
[6]杨晓强,李家奎,郭定宗,等.展青霉素检测方法的研究进展[J].中国食品卫生杂志,2007,19(2):165-167.
[7]王娅芳,刘利亚,黄培林.展青霉素检测方法及污染情况的研究进展[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(19):5116-5118.
[9]Harrison M A. Presence and stability of Patulin in apple products:a review[J]. Journal of Food Safety,1988,9(3):147-153.
[10]Kharandi N,Babri M,Azad J. A novel method for determination of Patulin in apple juices by GC-MS[J]. Food chemistry,2013,141(3):1619-1623.
[11]Drusch S,Kopka S,Kaeding J. Stability of Patulin in a juice-like aqueous model system in the presence of ascorbic acid[J]. Food chemistry,2007,100(1):192-197.
[12]Bonerba E,Ceci E,Conte R,etal. Survey of the presence of Patulin in fruit juices[J]. Food Additives and Contaminants,2010,3(2):114-119.
[13]Moake M M,Padilla-Zakour O I,Worobo R W. Comprehensive review of patulin control methods in foods[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2005,4(1):8-21.
[14]Artigot M P,Loiseau N,Laffitte J,etal. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of two CYP619 cytochrome P450s involved in biosynthesis of Patulin in Aspergillus clavatus[J].Microbiology,2009,155(5):1738-1747.
[15]Beck J,Ripka S,Siegner A,etal. The multifunctional 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase gene of Penicillium patulum[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry,1990,192(2):487-498.
[16]Fedeshko R W. Polyketide enzymes and genes[D]. Canada:University of Calgary,Doctor Thesis,1992.
[17]Murphy G,Lynen F. Patulin Biosynthesis:The Metabolism of m-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol and m-Hydroxybenzaldehyde by Particulate Preparations from Penicillium patulum[J]. European journal of biochemistry,1975,58(2):467-475.
[18]Glaser N,Stopper H. Patulin:Mechanism of genotoxicity[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(5):1796-1801.
[19]Zhou S,Jiang L,Geng C,etal. Patulin-induced genotoxicity and modulation of glutathione in HepG2 cells[J]. Toxicon,2009,53(5):584-586.
[20]Zhou S,Jiang L,Geng C,etal. Patulin-induced oxidative DNA damage and p53 modulation in HepG2 cells[J]. Toxicon,2010,55(2):390-395.
[21]Saxena N,Ansari K M,Kumar R,etal. Role of mitogen activated protein kinases in skin tumorigenicity of Patulin[J]. Toxicology and applied pharmacology,2011,257(2):264-271.
[22]De Melo F T,de Oliveira I M,Greggio S,etal. DNA damage in organs of mice treated acutely with Patulin,a known mycotoxin[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(10):3548-3555.
[23]Dickens F,Jones H E H. Carcinogenic activity of a series of reactive lactones and related substances[J]. British journal of cancer,1961,15(1):85.
[24]Smith E E,Duffus E A,Small M H. Effects of Patulin on postimplantation rat embryos[J]. Archives of environmental contamination and toxicology,1993,25(2):267-270.
[25]Guo X,Dong Y,Yin S,etal. Patulin induces pro-survival functions via autophagy inhibition and p62 accumulation[J]. Cell death & disease,2013,4(10):e822.
[26]Mohan H M,Collins D,Maher S,etal. The mycotoxin Patulin increases colonic epithelial permeability in vitro[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(11):4097-4102.
[27]Selmanoglu G,Koçkaya E A. Investigation of the effects of Patulin on thyroid and testis,and hormone levels in growing male rats[J]. Food and chemical toxicology,2004,42(5):721-727.
[28]王少敏,郑荣,俞灵,等. HPLC-MS/MS 法测定中药材枳壳中展青霉素[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2011,21(7):1593-1594.
[29]赵珊,李凤琴,陈丽娟,等. 功能柱净化——高效液相色谱法测定果汁中展青霉素[J]. 卫生研究,2007,36(5):634-636.
[30]牛华,冯雷,牛之瑞,等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定果汁中的展青霉素[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2012,30(9):957-961.
[31]Farhadi K,Maleki R. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by HPLC-DAD as an Efficient and Sensitive Technique for the Determination of Patulin from Apple Juice and Concentrate Samples[J]. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society,2011,58(3):340-345.
[32]Tarter E J,Hanchay J P,Scott P M. Improved liquid chromatographic method for determination of aflatoxins in peanut butter and other commodities[J]. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists,1984,67(3):597-600.
[33]Kubacki S J. The analysis and occurrence of Patulin in apple juice[M]//P S Steyn and R. Vleffaar. Mycotoxins and phycotoxins a collection of invited papers presented at the sixth international IUPAC symposium on mycotoxins and phycotoxins,Pretoria,South Africa,1985,293-304.
[34]Abramson D,Thorsteinson T,Forest D. Chromatography of mycotoxins on precoated reverse-phase thin-layer plates[J]. Archives of environmental contamination and toxicology,1989,18(3):327-330.
[35]Vero S,Vazquez A,Cerdeiras M P,etal. A rapid TLC-scanning method for the determination of Patulin in apple products[J]. Journal of planar chromatography,modern TLC,1999,12(3):172-174.
[36]Fujimoto Y,Suzuki T,Hoshino Y. Determination of penicillic acid and Patulin by gas-liquid chromatography with an electron-capture detector[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,1975,105(1):99-106.
[37]Tarter E J,Scott P M. Determination of Patulin by capillary gas chromatography of the heptafluorobutyrate derivative[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,1991,538(2):441-446.
[38]Llovera M,Viladrich R,Torres M,etal. Analysis of underivatizated Patulin by a GC-MS technique[J]. Journal of Food Protection®,1999,62(2):202-205.
[39]Tabata S,Iida K,Suzuki J,etal. A quantification and confirmation method of Patulin in apple juice by GC/MS[J]. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi,2004,45(5):245-249.
[40]Llovera M,Balcells M,Torres M,etal. Parallel synthesis:A new approach for developing analytical internal standards. Application to the analysis of Patulin by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2005,53(17):6643-6648.
[41]McElroy L J,Weiss C M. The production of polyclonal antibodies against the mycotoxin derivative Patulin hemiglutarate[J]. Canadian journal of microbiology,1993,39(9):861-863.
[42]De Champdore M,Bazzicalupo P,De Napoli L,etal. A new competitive fluorescence assay for the detection of Patulin toxin[J]. Analytical chemistry,2007,79(2):751-757.
[43]Molinelli A,Grossalber K,Führer M,etal. Development of qualitative and semiquantitative immunoassay-based rapid strip tests for the detection of T-2 toxin in wheat and oat[J]. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry,2008,56(8):2589-2594.
[44]Zhou Y,Kong W,Li Y,etal. A new solid-phase extraction and HPLC method for determination of Patulin in apple products and hawthorn juice in China[J]. Journal of separation science,2012,35(5-6):641-649.
[45]Maham M,Karami-Osboo R,Kiarostami V,etal. Novel Binary Solvents-Dispersive Liquid—Liquid Microextraction(BS-DLLME)method for determination of Patulin in apple juice using high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2013,6(3):761-766.
[46]Farhadi K,Maleki R. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by HPLC-DAD as an Efficient and Sensitive Technique for the Determination of Patulin from Apple Juice and Concentrate Samples[J]. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society,2011,58(3):340-345.
[47]Beltrán E,Ibáez M,Sancho J V,etal. Determination of Patulin in apple and derived products by UHPLC-MS/MS. Study of matrix effects with atmospheric pressure ionisation sources[J]. Food chemistry,2014,142(1):400-407.
[48]Marsol-Vall A,Delpino-Rius A,Eras J,etal. A Fast and Reliable UHPLC-PDA Method for Determination of Patulin in Apple Food Products Using QuEChERS Extraction[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2014,7(2):465-471.
[49]邓舜洲,许杨. 展青霉素人工抗原及多克隆抗体的研制[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2007,25(6):13-17.
[50]田园. 展青霉素特异性抗体的制备及其免疫学检测方法的研究[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2012.
[51]Wang Y,Liu N,Ning B A,etal. Simultaneous and rapid detection of six different mycotoxins using an immunochip[J]. Biosens Bioelectron,2012,34(1):44-50.
[52]Tolaini V,Zjalic S,Reverberi M,etal. Lentinula edodes enhances the biocontrol activity of Cryptococcus laurentii against Penicillium expansum contamination and Patulin production in apple fruits[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2010,138(3):243-249.
[53]Fravel D R. Commercialization and implementation of biocontrol[J].Annual Review of Plant Biology,2005,43(7):337-359.
[54]Janisiewicz W J,Korsten L. Biological control of postharvest diseases of fruits[J]. Annual review of phytopathology,2002,40(1):411-441.
[55]Castoria R,Morena V,Caputol L,etal.Effect of the biocontrol yeast Rhodotorula glutinis Strain LS11 on Patulin accumulation in stored apples[J]. Phytopathology,2005,95(11):1271-1278.
[56]Morales H,Sanchis V,Usall J,etal. Effect of biocontrol agents Candida sake and Pantoea agglomerans on Penicillium expansum growth and Patulin accumulation in apples[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2008,122(1-2):61-67.
[57]孙卉,师俊玲,杨保伟. 枯草芽孢杆菌CCTCC M 207209对苹果采后致腐真菌的抑制作用[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2009,37(12):168-174.
[58]孙卉,师俊玲.枯草芽孢杆菌CCTCCM207209抗扩展青霉特性研究——活性物质的提取、稳定性与应用[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2010,38(1):201-208.
[59]杨其亚,张红印,庞水秀,等.拮抗酵母菌控制水果及其制品中展青霉素研究进展[J].食品科学,2012,33(7):350-353.
[60]杨其亚.植酸增强胶红酵母对草莓、苹果及桃果采后病害的控制效应[D].镇江:江苏大学,2011.
[61]盛文军,韩舜愈,蒋玉梅,等.棒曲霉素脱除树脂对苹果清汁质量指标的影响[J].食品科技,2011,36(4):63-66.
[62]Raiola A,Meca G,García-Llatas G,etal. Study of thermal resistance and in vitro bioaccessibility of Patulin from artificially contaminated apple products[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(9):3068-3072.
[63]Moreau M,Lescure G,Agoulon A,etal. Application of the pulsed light technology to mycotoxin degradation and inactivation[J]. Journal of Applied Toxicology,2013,33(5):357-363.
[64]Funes G J,Gómez P L,Resnik S L,etal. Application of pulsed light to Patulin reduction in McIlvaine buffer and apple products[J]. Food Control,2013,30(2):405-410.
[65]Dong Q F,Manns D C,Feng G,etal. Reduction of Patulin in Apple Cider by UV Radiation[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2010,73(1):69-74.
[66]高振鹏,岳田利,袁亚宏,等.苹果汁中展青霉素的超声波降解[J].农业机械学报,2009,40(9):138-142.
[67]李艳玲,惠伟,赵政阳,等.臭氧对苹果汁中棒曲霉素的降解效果研究[J].食品工业科技,2012,33(10):120-123.
[68]Yue T,Guo C,Yuan Y,etal. Adsorptive Removal of Patulin from Apple Juice Using Ca-Alginate-Activated Carbon Beads[J].Journal of food science,2013,78(10):1629-1635.
[69]Guo C,Yue T,Yuan Y,etal. Biosorption of Patulin from apple juice by caustic treated waste cider yeast biomass[J]. Food Control,2013,32(1):99-104.
[70]郭彩霞,岳田利,袁亚宏,等.基于傅里叶变换红外光谱的灭活酿酒酵母菌对展青霉素的吸附机理分析[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2013,33(3):672-676.
[71]董媛,岳田利,袁亚宏,等.三种失活酵母对苹果汁中展青霉素去除研究[J].食品工业,2013,34(1):116-118.
Research advances in detection and removal of Patulin in foods
XU Ming-yue,LI Hong-jun,WANG Shan,XIANG Yi,YUAN Lu,HE Zhi-fei*
(College of Food Science,Southwest University,Chongqing 400716,China)
Patulin is a kind of mycotoxins produced by a variety of fungi. It is widespread in nature and it can be easily found in fruit and fruit products. Moreover,it results in serious threats to human health,by the enrichment in the organism and food chain. This paper summarized the origin,characteristics,detection,removal,current problems and future trends of patulin,which will provide a theoretical basis for follow-up study.
Patulin;detection;removal
2014-04-21
徐明悦(1989-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:食品微生物与发酵工程。
*通讯作者:贺稚非(1960-),女,博士,教授,研究方向:食品微生物学与食品安全。
三峡库区优质肉牛安全生产关键技术集成与示范项目(2011BAD36B01)。
TS201.2
A
1002-0306(2015)01-0375-06
10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2015.01.071
