塔河胡杨林核心区退耕地初始年土壤及植被养分特征数值分析
2024-04-28张优刘茂秀史军辉王新英艾吉尔·阿不拉张炎
张优 刘茂秀 史军辉 王新英 艾吉尔·阿不拉 张炎

doi:10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.03.020
摘 要:【目的】研究塔河中下游胡杨林核心区退耕地初始年土壤和植被的养分特征,为胡杨林公益林核心区退耕地生态恢复提供基础支撑数据。
【方法】以塔河中下游胡杨林核心区退耕地初始年的土壤和植被为研究对象,运用“S”形布点法、野外标准木全株收割法、多点混合方法分别采集植被和土壤样品,结合室内测定植被和土壤养分特征数值进行分析。
【结果】(1)土壤养分含量和植被营养成分积累量均集中分布在Ⅳ区和Ⅴ区。(2)土壤垂直深度上,养分集中在表层土壤,且随着土层深度增加,土壤养分含量依次递减,但是在60~100 cm土层处,呈现小幅增加。不同样地与不同土层深度之间土壤养分含量差异显著(P<0.05)。(3)不同样地中残存棉花(棉秆、根系)及草本植物中全N、全P、全K、有机碳含量均有显著差异(P<0.05)。
【结论】胡杨林自然保护區核心区退耕地初始年土壤养分含量较高,有利于荒漠植被群落的生长和发育,提高群落演替速率,有利于塔河胡杨林退耕地植被恢复与环境变化及其相互作用、生态过渡带植被恢复与区域生态稳定。
关键词:胡杨林;退耕地;初始年;养分特征
中图分类号:S714 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1001-4330(2024)03-0699-09
收稿日期(Received):
2023-08-09
基金项目:
新疆维吾尔自治区财政林业发展补助项目(XJLYKJ-2022-1);新疆维吾尔自治区财政林业发展补助项目(XJLYKJ-2023-27)
作者简介:
张优(1997-),女,贵州人,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物营养,(E-mail)463867715@qq.com
通讯作者:
刘茂秀(1976-),女,四川人,副研究员,硕士生导师,研究方向为荒漠化治理及植被恢复,(E-mail)402622019@qq.com
张炎(1965-),女,天津人,研究员,研究方向为土壤、植物营养与施肥技术,(E-mail)yanzhangxj@163.com
0 引 言
【研究意义】塔里木河胡杨林是新疆暖温带干旱荒漠区最主要的森林生态系统,2018年是退耕还林还草工程的第一轮初始年。因此,分析退耕地初始年的土壤及植被状况等基本特征,是研究退耕还林地植被自然演化规律、土壤变化特征的起点,是胡杨恢复生态学研究的基础。分析胡杨林退耕地初始年土壤和植被的养分特征,对研究塔河胡杨林退耕地植被恢复与环境变化及其相互作用、生态过渡带植被恢复与区域生态稳定的关系具有重要意义[1]。【前人研究进展】生态恢复是一个长期的过程,需对地表水、地下水、植被响应、生境条件、生物多样性等开展长期监测,掌握其动态情况,为采取科学有效的调控措施奠定基础[2-6];土壤是植被生长发育的载体,对植被恢复具有重要作用[7]。不仅影响植物群落的发生、发育和演替的速度[8],而且也对生态系统过程、生产力和结构等具有重要影响,是植被演替中的主要环境因子[9,10]。土壤条件的变化可以影响植物的萌发、生根,进而影响森林生态系统植被的更新和演替[11]。因此,土壤因子与植物之间关系研究是生态恢复关注的热点之一[12]。【本研究切入点】目前塔河流域退耕还林地的研究文献集中在生态、社会、经济效益等方面[13-15],目前针对胡杨林不同发育演替阶段土壤和植被养分研究多采用空间代替时间的方法[16-18],初始演替阶段的土壤和植被的营养状况影响着群落演替的过程和方向[19-20]。尤其是关于塔里木河退耕还林初始年土壤养分的研究还未见文献报道。需研究退耕地初始年土壤和植被养分特征,分析垂直塔河不同距离退耕地土壤环境条件的差异性,探讨退耕地植被演替、群落结构的改变对生态恢复的响应及相互关系。【拟解决的关键问题】以塔河中下游胡杨林核心区退耕还林地为研究对象,分析垂直塔河不同距离胡杨林退耕地初始年土壤和植被的养分特征,为胡杨林退耕地自然生态恢复提供基础数据支撑。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
研究区位于新疆巴音郭楞蒙古自治州轮台县和尉犁县。轮台县(83°38′E~85°25′E,41°05′N~42°32′E),属于暖温带大陆性干旱气候,年平均气温为10.9℃,无霜期为180~224 d。
尉犁县(84°02′E~89°58′E,40°10′N~41°39′N),属暖温带大陆性荒漠气候,冷热差异悬殊,温度的年月变化大,全年热量丰富但不稳定,空气干燥,蒸发强劲,降水稀少,且年际变化大,光照充足,全年平均日照2 975 h。土壤以胡杨林土、荒漠土、盐碱土和风沙土为主。植被类型主要以荒漠河岸林、盐生草甸为主,主要有胡杨(Populus euphratica)、柽柳(Tamarix ramosissima)、骆驼刺(Alhagi sparsifo-lia Shap)、铃铛刺(Halimodendron halodendron)、胀果甘草(Glycyrrhiza inflata Batalin)、芦苇(Phragmites australis)等,胡杨为该地区乔木层主要建群种[21]。
1.2 方 法
1.2.1 试验设计
2018年6月,在新疆轮台县与尉犁县胡杨1.07×104 hm2(16万亩)的退耕还林地中,垂直塔河1、2、3、3.5和4 km的退耕还林区域,选择大量集中连片的退耕地作为监测区,在每个监测区内按照“S”形布点法布设7个30×30(m)的标准样地,共设置35个标准样地。在每个标准样地中设置5个5 m×5 m的草本小样方,共175个小样方。标准样地的四角用PVC管定点固定。表1,图1
1.2.2 样品采集
在设置的标准样地中按“S”型连续取样多点混合采集土壤样品。在标准样地内布设7个采样点,分5层采集0~100 cm土壤样品,层次分别为0~10 cm、10~20 cm、20~40 cm、40~60 cm和60~100 cm。将每个样方中同层土样混合为一个样,每份混合样约1.0 kg左右,共计175个份土样。土壤样品采集后装入样品袋中带回实验室经过自然风干后过筛待测。在已选择好的标准样方中,采用全株收割法对已选择好的标准样方中采集所有植被,分为残存棉花(地上、地下)、草本(地上)采集,共计525份植物样品,取部分样品带回实验室杀青后烘干和粉碎待检测使用。
1.2.3 测定指标
土壤碱解N采用碱解蒸馏法测定;植物全氮采用H2SO4-H2O2消煮法测定;土壤速效磷和植物的全磷采用0.5 mol/L NaHCO3浸提钼锑抗比色法测定;土壤速效钾和植物全钾采用NH4OAc浸提-火焰光度法测定;土壤有机质和植物有机碳采用H2SO4-K2Cr2O7外加热法测定[22]。
1.3 数据处理
运用SPSS26.0完成对土壤养分的描述性统计分析及独立样本Kruskal-Wallis统计分析,利用单因素LSD分析对棉花植被和草本层营养特征分析,用ArcGIS进行研究区的制作。
2 结果与分析
2.1 永久监测区退耕地初始年土壤养分特征
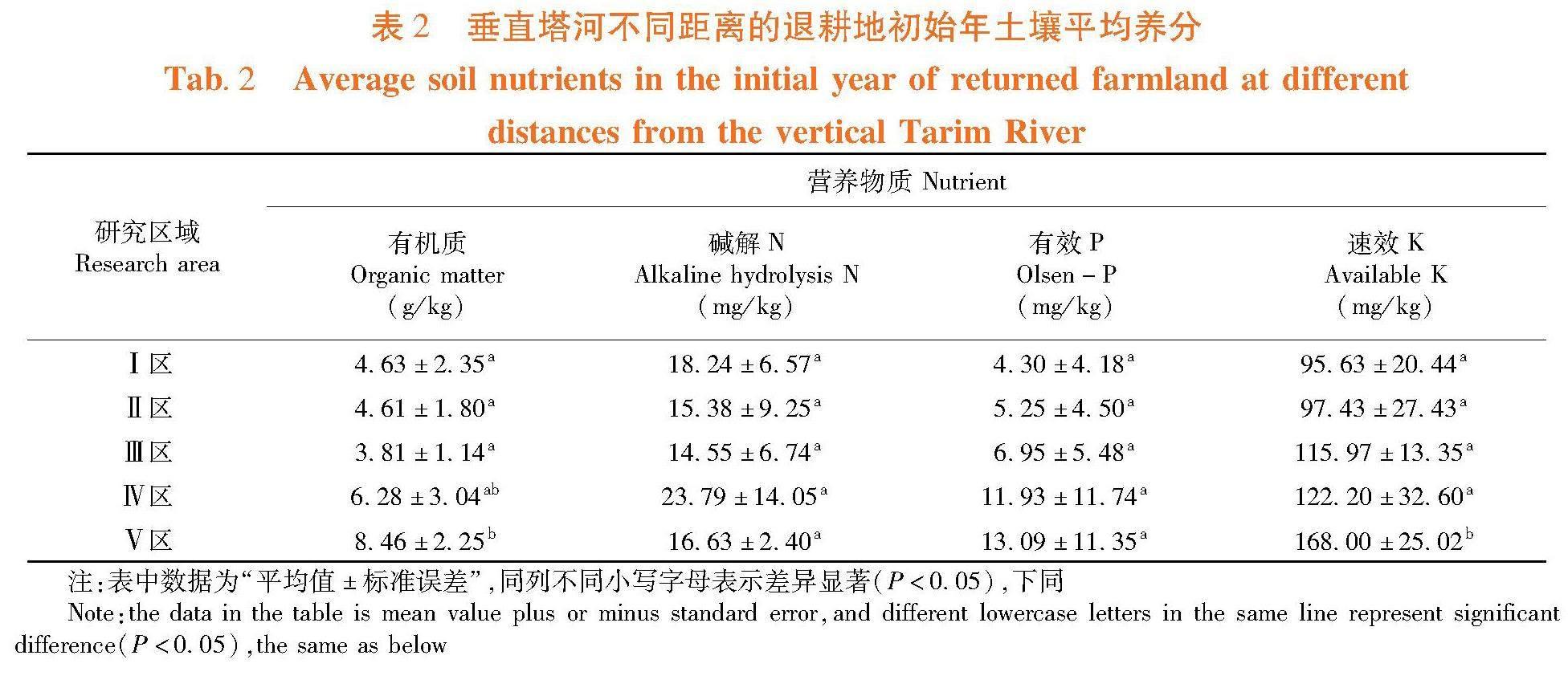
研究表明,5个监测区土壤各养分含量之间存在显著差异(P<0.05)。土壤有机质含量区间在3.81~8.46 g/kg,碱解N含量区间是14.55~23.79 mg/kg,有效P含量区间在4.30~13.09 mg/kg,速效K含量区间在95.63~168.00 mg/kg。5个不同监测区中土壤有机质含量由高到低依次是Ⅴ区>Ⅳ区>Ⅰ区>Ⅱ区>Ⅲ区,Ⅴ区(8.46 g/kg)比Ⅲ区(3.81 g/kg)高达55%;碱解 N含量由高到低依次是Ⅳ区>Ⅰ区>Ⅴ区>Ⅱ区>Ⅲ区,Ⅳ区(23.79 mg/kg)比Ⅲ区(14.55 mg/kg)高达39%;有效P和有机碳含量由高到低依次是Ⅴ>Ⅳ>Ⅲ>Ⅱ>Ⅰ。有效P和速效K含量分别在Ⅴ区(13.09、168.00 mg/kg)均比在Ⅰ区(4.30、95.63 mg/kg)中高,分别高出67%和43%。表2
有机质含量区间在2.21~10.75 g/kg,碱解N含量区间在4.37~44.53 mg/kg;有效P含量区间在0.67~25.02 mg/kg,速效K的含量区间在50.77~200.02 mg/kg,监测研究区的土壤养分均在土层垂直深度上有显著差异(P<0.05)。在不同样地中有机质和碱解N含量均在0~10 cm的土层中最高,有效P和速效K在0~20 cm的浅层土壤中高于深层土壤的养分含量。60~100 cm的土壤速效K、有机质和碱解N的含量均有小幅增加,有效P含量仅在Ⅳ区和Ⅴ区增加,且在Ⅰ区中呈现极显著(P<0.01)。
棉秆中养分含量在各样地中分布较均匀,但是根系在Ⅰ区和Ⅱ区全P和全K的含量远高于区于其他3个采样区的含量。表3
2.2 永久监测区退耕地初始年植物营养特征
2.2.1 残存棉秆及根系营养特征
研究表明,塔河中下游退耕地5个永久监测研究区内残存棉秆和根系的养分含量。在棉秆中,全P含量区间是1.54~1.71 g/kg,全K含量区间是24.01~28.38 g/kg,全N含量区间是9.59~13.25 g/kg,有机碳含量区间是284.67~439.00 g/kg。在根系中,全P的含量区间是1.30~3.85 g/kg,全K含量区间是13.2~35.1 g/kg,全N含量区间7.73~13.1 g/kg,有机碳的含量区间277~420 g/kg。不同监测区中棉秆和根系的养分含量均有显著差异(P<0.05)。表4
2.2.2 退耕地初始年草本层营养特征
研究表明,全P含量区间在1.35~4.14 g/kg,全K的含量区间在16.4~41.67 g/kg,全N的含量区间在14.22~27.62 g/kg,有机碳的含量区间在247.57~333.33 g/kg,表明5个监测区草本层各养分含量之间存在显著差异(P<0.05)。其中全P和全K的含量在不同监测区之间的变化趋势一致,且全P和全K的含量由高到低依次是Ⅳ区>Ⅴ区>Ⅲ区>Ⅱ区>Ⅰ区,全N含量在不同样地中由高到低依次是Ⅰ区>Ⅳ区>Ⅴ区>Ⅱ区>Ⅲ区,有机碳在不同样地中由高到低依次是Ⅰ区>Ⅴ区>Ⅳ区>Ⅱ区>Ⅲ区。表5
3 讨 论
3.1
原初土壤环境的差异会导致群落演替过程中物种多样性的变化[23-25]、生物群落的发生、发育和演替的速度[26-28],是影响退化生态系统生态功能恢复与维持的关键因素之一[29]。研究中5个监测区初始年土壤各养分含量之间存在显著差异((P<0.05)),可能影响区域内胡杨、柽柳以及骆驼刺等不同生物群落的发生、发育,将对维持退化荒漠生态系统生态产生显著影响[30]。研究监测区域退耕地土壤平均养分含量(有机质5.108 g/kg,碱解N 17.11 mg/kg,有效P 8.61 mg/kg,速效K 108.99 mg/kg)高于天然胡杨幼龄林(有机质4.41 g/kg,碱解N 13.67 mg/kg,有效P 1.42 mg/kg,速效K 83.97 mg/kg),其中有效P含量接近于近熟林(9.84 mg/kg)[31],有机质含量接近于樟子松人工林中龄林[37]而低于油松天然次生林的有机质含量[32]。因人工施肥原因致使监测区域退耕地的初始年土壤养分含量较高,可能促进胡杨、柽柳等植物群落發生、发育和演替速度,从而减少了向顶级群落演替的时间[33]。因此,胡杨林退耕还林区域具备向顶级群落演替的土壤营养条件。
3.2
植被的恢复与重建是漫长的过程[34],其恢复效果主要通过不同年限来体现。土壤有机质含量和生物多样性指数随着退耕年限(1、2、4年)的增加而缓慢增加[35-36];退耕年限(1、8、20年)越长,有机质分解将释放出更多的养分元素,其中植被全N、全P的含量不断增加,土壤碱解N、速效P的含量也呈现出不同程度的上升趋势,从而使土地地力逐渐恢复[37];退耕地农田在转变为人工草地(1、6年)与次生草地(14、30年)的过程中,土壤有机碳的含量增幅可达70%左右[38]。关于胡杨林退耕地的研究均集中在综合生态效益评价研究上[39-41],且大多数研究退耕地的自然恢复时间均选择在退耕地1年以后。
研究监测区域的退耕地初始年的土壤及植被养分状况尤为重要是胡杨林植被恢复的基础,更具有代表性。
监测区位于轮台县与尉犁县胡杨重点公益林区1.07×104 hm2(16万亩)的退耕还林地中,面积约为200 hm2(3 000亩),规模之大而退耕地初始年作为研究起始年,
4 结 论
4.1
在垂直塔河的采样区中土壤养分含量在IV区V区高于其他三个区,草本层营养成分含量与土壤养分特征相符合,而棉秆中的营养成分含量相对较均匀,棉花根系中的营养含量与距离塔河的远近有关。距离塔河越近,根系营养含量受影响越大,根系养分含量越高。其原因可能是与水分有关,研究中Ⅰ区、Ⅱ区靠近塔河其根系养分含量显著高于其他区。
4.2
土壤速效K和有机质在不同监测研究区中差异显著(P<0.05),随采样点距离的增加,土壤有效P和速效K的含量呈逐渐增加的趋势,有机质和碱解N的含量呈先递减后增加的趋势,土壤养分含量主要集中在Ⅳ区和Ⅴ区。不同样地中的土壤养分均在土层垂直深度上有显著差异(P<0.05),速效钾除外。五个样区中土壤养分均集中在表层土壤,且均随着土层深度的增加,土壤养分含量呈逐渐递减的趋势,但在60~100 cm处有小幅增加。
参考文献(References)
[1]
曾勇,赵成义,李传金,等.塔里木河沿岸不同生境下胡杨(Populus euphratica)群落的空间分布格局及关联性[J].生态学质志,2019,38(11):3273-3282.
ZENG Yong,ZHAO Chengyi,LI Chuanjin,et al.Spatial distribution pattern and correlation of Populus euphratica community in different habitats along the Tarim River [J].Ecology,2019,38(11):3273-3282.
[2]劉加珍,陈亚宁,陈永金.塔里木河下游物种多样性恢复速率分析[J].干旱区地理,2008,31(6):870-877.
LIU Jiazhen,CHEN Yaning,CHEN Yongjin.Analysis of restoration rate of species diversity in the lower reaches of Tarim River [J].Arid Land Geography, 2008,31(6):870-877.
[3]Gamfeldt L,Snll T,Bagchi R,et al. Higher levels of multiple ecosystem services are found in forests with more tree species[J].Nature Communications,2013,4:1340.
[4]马博虎,刘毅,李世清,等.黄土高原生态环境建设与土壤质量演变[J].生态经济,2007,23(3):39-46.
MA Bohu,LIU Yi,LI Shiqing,et al.Ecological Environment Construction and Soil Quality Evolution on the Loess Plateau [J].Ecological Economy,2007,23(3):39-46.
[5]韩新辉,杨改河,徐丽萍,等.黄土高原林(草)生态工程作用机理及模型验证[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2008,36(7):118-126.
HAN Xinhui,YANG Gaihe,XU Liping,et al.Mechanism and model validation of forest(grass) ecological engineering on the Loess Plateau [J].Journal of Northwest A&F University(Natural Science Edition), 2008,36(7):118-126.
[6]邵新庆,石永红,韩建国,等.典型草原自然演替过程中土壤理化性质动态变化[J].草地学报,2008,16(6):566-571.
SHAO Xinqing,SHI Yonghong,HAN Jianguo,et al.Dynamic changes in soil physicochemical properties during natural succession of typical grasslands [J].Journal of Grassland Science,2008,16(6):566-571.
[7]温仲明,焦峰,刘宝元,等.黄土高原森林草原区退耕地植被自然恢复与土壤养分变化[J].应用生态学报,2005,16(11):2025-2029.
WEN Zhongming,JIAO Feng,LIU Baoyuan,et al.Natural vegetation restoration and soil nutrient changes in the abandoned farmland in the Forest steppe area of the Loess Plateau [J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005,16(11):2025-2029.
[8]杨玉海,陈亚宁,李卫红.新疆塔里木河下游土壤特性及其对物种多样性的影响[J].生态学报,2008,28(2):602-611.
YANG Yuhai,CHEN Yaning,LI Weihong.Soil characteristics in the lower reaches of the Tarim River in Xinjiang and their impact on species diversity [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2008,28(2):602-611.
[9]邓铭江.塔里木河生态输水与生态修复研究与实践[J].中国水利,2022,(19):29-32.
DENG Mingjiang.Research and Practice on Ecological Water Transport and Ecological Restoration of the Tarim River [J].China Water Conservancy,2022,(19):29-32.
[10]陈亚宁,李卫红,陈亚鹏,等.塔里木河下游断流河道输水的生态响应与生态修复[J].干旱区研究,2006,23(4):521-530.
CHEN Yaning,LI Weihong,CHEN Yapeng,et al.Ecological response and ecological restoration of water transport in the interrupted river channels of the lower reaches of the Tarim River [J].Arid Zone Research,2006,23(4):521-530.
[11]李卫红,陈亚鹏,张宏峰,等.塔里木河下游断流河道应急输水与地表植被响应[J].中国沙漠,2004,24(3):301-305.
LI Weihong,CHEN Yapeng,ZHANG Hongfeng,et al.Emergency water supply and surface vegetation response in the downstream of the Tarim River in the cut off channel [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2004,24(3):301-305.
[12]古丽努尔·沙布尔哈孜,尹林克,严成.塔里木河下游人工胡杨林生态恢复过程的初步研究[J].干旱区地理,2004,27(3):384-387.
Gulinuer Shabuerhazi,YIN Linke,YAN Cheng.Preliminary study on the ecological restoration process of artificial Populus euphratica forest in the lower reaches of the Tarim River [J].Arid Land Geography,2004,27(3):384-387.
[13]汪飞.尉犁县退耕还林综合效益评价研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2009.
WANG Fei.Research on the Comprehensive Benefit Evaluation of Returning Farmland to Forests in Yuli County [D].Urumqi: Xinjiang University,2009.
[14]Lei J,Du H L,Duan A G,et al.Effect of stand density and soil layer on soil nutrients of a 37-year-old Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation in Naxi,Sichuan Province,China[J].Sustainability,2019,11(19):5410.
[15]古麗努尔·沙布尔哈孜,尹林克,热合木都拉·阿地拉.塔里木河中下游退耕还林还草综合生态效益评价研究[J].水土保持学报,2004,18(5):80-83.
Gulinuer Shabuerhazi,YIN Linke,Rehemudula Adila.Study on the Comprehensive Ecological Benefit Evaluation of Returning Farmland to Forests and Grassland in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Tarim River [J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2004,18(5):80-83.
[16]李裕元,邵明安.黄土高原气候变迁、植被演替与土壤干层的形成[J].干旱区资源与环境,2001,15(1):72-77.
LI Yuyuan,SHAO Mingan.Climate change,vegetation succession,and formation of soil dry layer on the Loess Plateau [J].Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2001,15(1):72-77.
[17]刘加珍,陈亚宁,李卫红,等.塔里木河下游植物群落分布与衰退演替趋势分析[J].生态学报,2004,24(2):379-383.
LIU Jiazhen,CHEN Yaning,LI Weihong,et al.Analysis of distribution and decline succession trend of plant community in the lower reaches of Tarim River [J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2004,24(2):379-383.
[18]徐海量,宋郁东,陈亚宁,等.应用因子分析研究塔里木河下游生态环境的退化[J].干旱区地理,2005,28(1):21-25.
XU Hailiang, SONG Yudong,CHEN Yaning,et al.Study on the degeneration of ecological environment in the lower reaches of the Tarim River by using factor analysis [J].Arid Land Research,2005,28(1):21-25.
[19]Clements F E.Nature and structure of the climax.[J] .Eco.,1936,24:252-284.
[20]Holdridge.L if e z one ecology.San Jose,Costa Rica: T ropical science center,1967.
[21]史军辉,刘茂秀,王新英,等.塔里木河胡杨林生长过程土壤层碳氮磷化学计量变化特征及与其叶含量的相关性[J].新疆农业科学,2019,56(10):1879-1887.
SHI Junhui,LIU Maoxiu,WANG Xinying,et al.Characteristics of stoichiometric changes in soil carbon,nitrogen,and phosphorus during the growth process of Populus euphratica forests in the Tarim River and their correlation with leaf content [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,2019,56(10):1879-1887.
[22]鲍士旦.土壤农化分析(第三版)[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000.
BAO Shidan.Soil Agrochemical Analysis(Third Edition) [M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2000.
[23]韩路,王海珍,彭杰,等.塔里木荒漠河岸林植物群落演替下的土壤理化性质研究[J].生态环境学报,2010,19(12):2808-2814.
HAN Lu,WANG Haizhen,PENG Jie,et al.Study on soil physical and chemical properties under succession of plant community in Tarim desert riparian forest [J].Journal of Ecological Environment, 2010,19(12):2808-2814.
[24]Knops J M H,Tilman D.Dynamics of soil nitrogen and carbon accumulation for 61 years after agricultural abandonment [J]. Ecology, 2000, 81(1):88.
[25]左小安,趙学勇,赵哈林,等.沙地退化植被恢复过程中灌木发育对草本植物和土壤的影响[J].生态环境学报,2009,18(2):643-647.
ZUO Xiaoan,ZHAO Xueyong,ZHAO Halin,et al.The impact of shrub development on herbaceous plants and soil during the restoration of degraded vegetation in sandy land [J].Journal of Ecology and Environment,2009,18(2):643-647.
[26]张兆彤,王金满,张佳瑞.矿区复垦土壤与植被交互影响的研究进展[J].土壤,2018,50(2):239-247.
ZHANG Zhaotong,WANG Jinman,ZHANG Jiarui.Research progress on the interaction between soil and vegetation in mining area reclamation [J].Soils,2018,50(2):239-247.
[27]吴彦,刘庆,乔永康,等.亚高山针叶林不同恢复阶段群落物种多样性变化及其对土壤理化性质的影响[J].植物生态学报,2001,25(6):648-655.
WU Yan,LIU Qing,QIAO Yongkang,et al.Change of community species diversity in different restoration stages of subalpine coniferous forest and its impact on soil physical and chemical properties [J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2001,25(6):648-655.
[28]温仲明,焦峰,赫晓慧,等.黄土高原森林边缘区退耕地植被自然恢复及其对土壤养分变化的影响[J].草业学报,2007,16(1):16-23.
WEN Zhongming,JIAO Feng,HE Xiaohui,et al.Natural restoration of vegetation on abandoned farmland in the forest edge area of the Loess Plateau and its impact on soil nutrient changes [J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2007,16(1):16-23.
[29]王凯博,陈美玲,秦娟,等.子午岭植被自然演替中植物多样性变化及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J].西北植物学报,2007,27(10):2089-2096.
WANG Kaibo,CHEN Meiling,QIN Juan,et al.Shangguan Zhouping.Changes in plant diversity and their relationship with soil physicochemical properties during natural vegetation succession in Ziwuling [J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2007,27(10):2089-2096.
[30]刘鸿雁,黄建国.缙云山森林群落次生演替中土壤理化性质的动态变化[J].应用生态学报,2005,16(11):2041-2046.
LIU Hongyan,HUANG Jianguo,JI Yunshang.Dynamics of soil properties under secondary succession forest communities in Mt.Jinyuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2005,16(11):2041-2046.
[31]王新英,史军辉,刘茂秀.塔里木河流域不同龄组胡杨林土壤理化性质及相关性[J].东北林业大学学报,2016,44(9):63-68.
WANG Xinying,SHI Junhui,LIU Maoxiu.Soil physicochemical properties and correlation of Populus euphratica forests of different age groups in the Tarim River Basin [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2016,44(9):63-68.
[32]牛沙沙,周永斌,刘丽颖,等.不同林龄樟子松人工林土壤理化性质[J].东北林业大学学报,2015,43(2):47-50,62.
NIU Shasha,ZHOU Yongbin,LIU Liying,et al.Soil physicochemical properties of Pinus sylvestris plantations of different ages [J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2015,43(2):47-50,62.
[33]赵伟红,康峰峰,韩海荣,等.冀北辽河源地区不同林龄油松天然次生林土壤理化特征的研究[J].西北林学院学报,2014,29(3):1-8.
ZHAO Weihong,KANG Fengfeng,HAN Hairong,et al.Study on soil physicochemical characteristics of natural secondary forests of Pinus tabulaeformis at different ages in the Liaohe River source area of northern Hebei [J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2014,29(3):1-8.
[34]温仲明,焦锋,卜耀军,等.植被恢复重建对环境影响的研究进展[J].西北林学院学报,2005,20(1):10-15.
WEN Zhongming,JIAO Feng,BU Yaojun,et al.Research progress on the impact of vegetation restoration and reconstruction on the environment [J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2005,20(1):10-15.
[35]張久丹,李均力,包安明,等.2013-2020年塔里木河流域胡杨林生态恢复成效评估[J].干旱区地理,2022,45(6):1824-1835.
ZHANG Jiudan,LI Junli,BAO Anming,et al.Effectiveness assessment of ecological restoration of Populus euphratica forest in the Tarim River Basin during 2013-202[J].Arid Land Geography,2022,45(6):1824-1835.
[36]朱成刚,艾克热木·阿布拉,李卫红,等.塔里木河下游生态输水条件下胡杨林生态系统恢复研究[J].干旱区地理,2021,44(3):629-636.
ZHU Chenggang,Aikeremu Abula,LI Weihong,et al.Study on the restoration of Populus euphratica forest ecosystem under ecological water transport conditions in the lower reaches of the Tarim River [J].Arid Land Geography, 2021,44(3):629-636.
[37]田洪艳,郭平,周道玮.草原开垦对草原土壤及植被的扰动生态学作用[J].干旱区研究,2001,18(3):67-71.
TIAN Hongyan,GUO Ping,ZHOU Daowei.Ecological disturbance effects of grassland reclamation on grassland soil and vegetation [J].Arid Zone Research, 2001,18(3):67-71.
[38]郑秋红,张宏,贾海坤等.怀来盆地弃耕地自然恢复过程中土壤养分动态[J].生态与农村环境学报,2006,22(1):24-28.
ZHENG Qiuhong,ZHANG Hong,JIA Haikun,et al.Soil nutrient dynamics during the natural restoration of abandoned farmland in the Huailai Basin [J].Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2006,22(1):24-28.
[39]王雷涛,尹林克,孙霞,等.塔里木河中下游退耕还林还草地的评价方法研究[J].干旱區研究,2005,22(4):537-540.
WANG Leitao,YIN Linke,SUN Xia,et al.Study on the evaluation method of returning farmland to forests and grasslands in the middle and lower reaches of the Tarim River [J].Arid Zone Research,2005,22(4):537-540.
[40]李春香,戴乐,吴晓菊.塔里木河中下游退耕还林还草工程生态经济效益评价[J].湖北农业科学,2012,51(19):4440-4442.
LI Chunxiang,DAI Le,WU Xiaoju.Ecological and economic benefits evaluation of the project of returning farmland to forests and grasslands in the middle and lower reaches of the Tarim River [J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2012,51(19):4440-4442.
[41]孟林,尹林克,白根本,等.塔里木河中下游退耕还林还草适宜区域界定与优化布局模式研究[J].草业学报,2003,12(6):36-41.
MENG Lin,YIN Linke,BAI Gengen,et al.Study on the definition and optimized layout model of suitable areas for returning farmland to forests and grasslands in the middle and lower reaches of the Tarim River [J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2003,12(6):36-41.
Numerical analysis of soil and vegetation nutrient characteristics in the initial year of returning farmland in the core area of Tarim River Populus euphratica forest
ZHANG You 1,2,3,LIU Maoxiu2,4,SHI Junhui 2,4,WANG Xinying 2,4,Aijier Abula 2,4,ZHANG Yan3
(1. College of Resources and Environment,Xinjiang Agricultural University,Urumqi 830052,China; 2.Research Station of Riparian Populus Euphratica Forest Ecosystem Positioning and Monitoring in Tarim River of Xinjiang,Urumqi 830046,China; 3.Research Institute of Soil,Fertilizer and Agricultural Water Conservation,Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Urumqi 830091,China; 4.Institute of Afforestation and Desertification Control,Xinjiang Academy of Forestry,Urumqi 830046)
Abstract:【Objective】 To preliminarily study the nutrient characteristics of soil and vegetation in the initial year of the abandoned land in the core area of Populus euphratica public welfare forest in the middle and lower reaches of the Tahe River in the hope of providing basic data support for the ecological restoration of the abandoned land in the area.
【Methods】 The soil and vegetation in the core area of Populus euphratica forest in the middle and lower reaches of the Tahe River were taken as the research object in the initial year of returning farmland.The "S" shaped distribution method,field standard whole tree harvesting method,and multi-point mixing method were used to collect vegetation and soil samples,and indoor analysis methods were used to measure vegetation and soil nutrients.
【Results】 (1)The soil nutrient content and the accumulation of vegetation nutrient components were concentrated in Zone IV and Zone V.(2)At the vertical depth of the soil,nutrients were concentrated in the surface soil,and as the soil depth increased,the soil nutrient content decreased in sequence.However,at the 60-100 cm soil layer,there was a slight increase.There was significant difference in soil nutrient content between different soil layers and depths(P<0.05).(3)And there were significant differences in the total N,total P,total K,and organic carbon content of residual cotton(cotton stalks,roots) and herbaceous plants in different fields(P<0.05).
【Conclusion】 This study indicates that the initial annual soil nutrient content of the abandoned land in the core area of the Populus euphratica forest nature reserve is high,which is conducive to the occurrence and development of desert vegetation communities and improve the community succession rate,and it is of great significance for the vegetation restoration and environmental changes in the abandoned land of the Populus euphratica forest in Tahe,as well as the relationship between ecological transition zone vegetation restoration and regional ecological stability.
Key words:Populus euphratica forest; returned farmland; initial year; nutrient characteristics
Fund projects:Autonomous Region Financial Forestry Development Subsidy Project (XJLYKJ-2022-1); Autonomous Region Finance Forestry Development Subsidy Project (XJLYKJ-2023-27)
Correspondence author:LIU Maoxiu (1976-), female, from Sichuan,associate researcher, research direction: desertification control and vegetation restoration,(E-mail)402622019@qq.com
Zhang Yan(1965-), female, from Tianjin,researcher, research direction: soil and plant nutrition and fertilization technology,(E-mail)yanzhangxj@163.com
