上海某社区甲状腺结节人群随访结果分析
2020-12-10鲁青夏建兵陈海英金志萍
鲁青 夏建兵 陈海英 金志萍

摘 要 目的:通过对甲状腺结节患者的随访,评估甲状腺结节大小、性质的变化。方法:在社区451名常住居民中经甲状腺超声检测发现375例甲状腺结节患者,其中男性142例,平均年龄(65.3±8.1)岁,女性233例,平均年龄(62.8±8.3)岁。每年进行随访,为期3年。观察甲状腺结节的个数、结节大小以及对结节性质的初步判断。结果:在随访的3年中,在初次评估的375例甲状腺结节患者的977个甲状腺结节中,发现结节体积有增长的180个,占18.61%。有35例(9.33%)出现新增结节,有6例(1.60%)因发现甲状腺恶性肿瘤而进行了手术治疗。多元logistic回归分析显示,BMI、怀孕次数(女性)、脑力工作者与甲状腺结节体积增长有关(P<0.05)。结论:大多数甲状腺结节在3年随访期间基本保持结节体积及性质的稳定,并不会对甲状腺结节患者人群的正常生活带来影响。
关键词 甲状腺结节;社区;随访
中图分类号:R736.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-1533(2020)22-0039-04
Analysis of follow-up results of thyroid nodule population in a community in Shanghai
LU Qing1, XIA Jianbing2, CHEN Haiying1, JIN Zhiping3**(1. General Practice Department of Fengpu Community Health Service Center of Fengxian District, Shanghai 201401, China; 2. General Surgery Department of Fengcheng Hospital, Fengxian District, Shanghai 201411, China; 3. General Practice Department of Nanqiao Community Health Service Center of Fengxian District, Shanghai 201499, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: By following up patients with thyroid nodules, to evaluate the size and nature of thyroid nodules. Methods: Among 451 permanent residents in the community, 375 patients with thyroid nodules were detected by thyroid ultrasound, there were 142 males with an average age of (65.3 ± 8.1) years and 233 females with an average age of (62.8 ±8.3) years. The patients were followed up every year for 3 years. The number and size of thyroid nodules and the preliminary determination of the nature of nodules were observed. Results: During the 3 years of follow-up, among the 977 thyroid nodules in 375 patients with thyroid nodules in the initial evaluation, 180 nodules were found to have increased in volume, accounting for 18.61%. There were 35 cases (9.33%) with new nodules, and 6 cases (1.60%) underwent surgical treatment due to the discovery of thyroid malignant tumor. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that BMI, number of pregnancies (female), and mental workers were related to the increase in the volume of thyroid nodules (P <0.05). Conclusion: Most thyroid nodules remain stable in volume and nature during the 3-year follow-up period, and would not affect the normal life of thyroid nodules patients.
KEY WORDS thyroid nodule; community; follow-up
近年來,甲状腺结节的发病率持续上升。人群中甲状腺结节患病率可达到50%~80%左右,这一趋势可能与甲状腺超声检查分辨率及检查者水平的提高有关[1-3]。这一现象给甲状腺结节患者带来一定心理压力。社区层面对甲状腺疾病的管理未引起足够重视,多数甲状腺结节患者有一定恐慌情绪。但根据文献报道,绝大多数甲状腺结节为良性结节,对于人体影响甚小[4-6]。本研究旨在通过社区甲状腺结节患者的动态随访,观察甲状腺结节大小、性质的变化,以及影响甲状腺结节大小发生变化的相关因素,为甲状腺结节患者的随访管理提供依据。
1 对象与方法
1.1 对象
从2015年9月1日起在上海奉贤区西渡、奉浦两个社区任选8个村(居)委中共451名常住居民,通过甲状腺超声检查检出375名甲状腺结节患者。对375名甲状腺结节患者每年随访复查一次,至2018年9月结束。在超声评估前检查血甲状腺功能指标,排除甲状腺功能异常者。
375例甲状腺结节患者的平均年龄(63.8±8.3)岁。其中男性142例,平均年龄(65.3±8.1)岁,女性233例,平均年龄(62.8±8.3)岁。
1.2 方法
甲状腺超声检查固定由3名甲状腺超声医生按照统一标准对甲状腺结节进行评估。检查采用多普勒超声,浅表部位采用12 MHz探头,深部组织采用7.5~10 MHz探头。超声检查者仔细测量并记录每个结节水平径、前后径及上下径。并且观察每个结节的内部情况(实性、海绵状、囊性、混合性),回声情况,结节边界情况以及结节周围血流情况等超声特征,并进行描述性统计[7]。若出现低回声,不规则边界,结节长径大于宽径,点状钙化,结节内点状血流等超声征象,则怀疑甲状腺结节性质问题,需转诊至上级医院进一步明确结节性质。甲状腺结节大小变化,采用甲状腺结节体积(三径相乘)变化超过50%来确定[8]。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 15.0软件进行统计分析。计数资料用百分率(%)表示,比较采用χ2检验。使用logistic回归方法分析影响甲状腺结节体积增长的相关因素。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
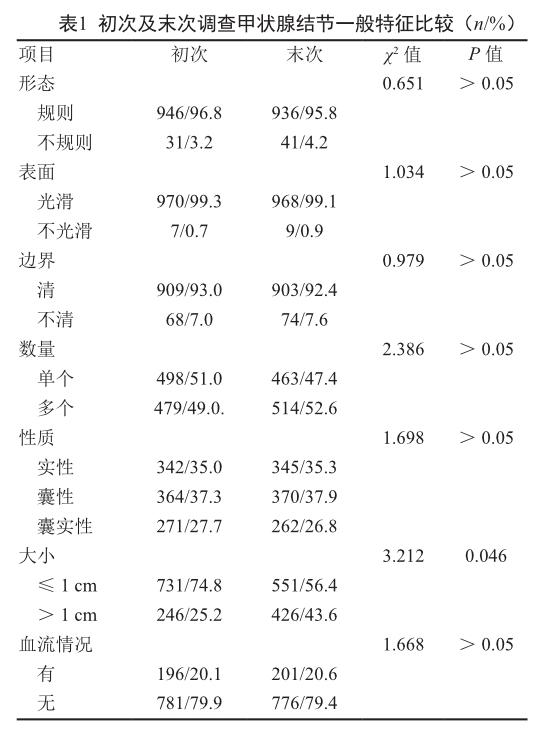
2.1 初次及末次调查甲状腺结节一般特征
初次评估甲状腺結节为977个,在随访过程中,发现体积增长的结节为180个,占所有结节的18.61%。有35人出现新增结节,占9.33%。有6人发现甲状腺恶性肿瘤,占1.60%,均进行了手术治疗。
大多数甲状腺结节形态规则,表面光滑,边界清楚。而对于结节性质来说,结节实性,囊性,囊实性各占约 1/3。在初次及末次调查甲状腺结节特征中发现,直径>1 cm的结节数量随着时间的推移出现增长,直径≤1cm的结节数量减少,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表1。
2.2 影响甲状腺结节体积增长的单因素分析
甲状腺结节体积增长与年龄、体重指数(BMI)、怀孕次数、职业、吸烟史、食海带类、食用加碘盐有关(P<0.05);与性别、饮酒史无关(P>0.05)。见表2。
2.3 影响甲状腺结节体积增长的多因素分析
以有无甲状腺结节体积增长为因变量,以年龄,BMI,怀孕次数(女性),职业,食用加碘盐,食海带类,吸烟史(男)为自变量进行多元logistic回归分析。结果显示,BMI、怀孕次数(女性)、脑力工作者与甲状腺结节体积增长相关(P<0.05);年龄、食用海带类、使用加碘盐、吸烟史与甲状腺结节体积增长无关(P>0.05)。见表3。
3 讨论
虽甲状腺结节患者日益增多,但尚未有直接证据证明何种因素与甲状腺结节发生密切相关;同时甲状腺结节如何发展,如何转归也是一个临床空白[9-10]。
本研究发现,BMI增高是甲状腺结节体积发生增大的危险因素之一。相关文献也有同样报道,这可能与人体内脂肪代谢,同时出现胰岛素抵抗现象,影响了下丘脑-垂体激素轴,促使甲状腺结节发生及生长有关[11-13]。本次研究发现,缺少体力活动(脑力工作者)的人群比较容易出现甲状腺结节体积增长的情况。这可能与工作压力大、长期处于精神紧张状态,易导致失眠、焦虑、免疫力下降和内分泌紊乱等因素有关。本研究还显示,女性怀孕次数的增加也是甲状腺结节体积增大的危险因素,这可能是怀孕次数的增加影响人体激素代谢的改变,与甲状腺激素之间存在一定相关性。普遍认为碘摄入可能是甲状腺结节发生及发展的重要环境因素,但本研究显示食海带类及摄入含碘盐与甲状腺结节的体积增大无明显相关性,这可能与本次研究对象的人体差异、样本量有限等因素有关。以往临床经验都认为,甲状腺结节体积会随着时间的推移而逐渐增长[14-15]。有作者认为大多数甲状腺结节体积会增长(39%~61.2%),但另一些研究却认为大多数甲状腺结节大小会保持稳定,甚至结节会缩小、消失[16-18]。这可能与既往研究绝大多数为回顾性研究有关。其次对于结节体积变化并没有统一标准,从而使得研究结果可能会出现较大的误差,得出并不一致的研究结果。目前广泛接受的是甲状腺结节体积大小发生50%的变化,这一变化衡量标准也被美国甲状腺协会指南所推荐[19, 7]。本次研究发现社区仅18.61%的甲状腺结节出现增大情况。因此,大多数的甲状腺结节还是相对稳定,没有必要引起过度的恐慌和临床干预。同时,基于超声诊断的良性甲状腺结节在一定随访期内大小变化相对稳定,对该人群可采取长期随访和相对保守的临床策略。
本研究存在一些不足。首先本研究为单中心研究,研究对象对总体的代表性相对有限;其次,所有结节的良恶性判断基于超声结果,可能存在数据测量结果的偏倚;第三,随访时间相对较短,样本量相对较小。要进一步证实以上结论还需有更大样本的多中心的队列研究来支持。
参考文献
[1] Davies L, Ouellette M, Hunter M, et al. The increasing incidence of small thyroid cancers: where are the cases coming from?[J]. Laryngoscope, 2010, 120(12): 2446-2451.
[2] Sosa JA, Hanna JW, Robinson KA, et al. Increases in thyroid nodule fine-needle aspirations, operations, and diagnoses of thyroid cancer in the United States[J]. Surgery. 2013, 154(6): 1420-1426.
[3] Smith-Bindman R, Lebda P, Feldstein VA, et al. Risk of thyroid cancer based on thyroid ultrasound imaging characteristics: results of a population-based study[J]. JAMA Intern Med, 2013, 173(19): 1788-1796.
[4] 中華医学会内分泌学分会, 中华医学会外科学分会, 中国抗癌协会头颈肿瘤专业委员会, 等. 甲状腺结节和分化型甲状腺癌诊治指南[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2012, 39(17): 1249-1272.
[5] Mandel SJ. Diagnostic use of ultrasonography inpatients with nodular thyroid disease[J]. Endocr Pract. 2004, 10(3): 246-252.
[6] Gharib H, Papini E, Paschke R, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, Associazione Medici Endocrinologi, and European Thyroid Association Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Nodules[J]. Endocr Pract, 2010, 16(suppl 1): 1-43.
[7] Knudsen N, Bols B, Bülow I, et al. Validation of ultrasonography of the thyroid gland for epidemiological purposes[J]. Thyroid, 1999, 9(11): 1069-1074.
[8] Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, et al. Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid. 2009, 19(11): 1167-1214.
[9] 陈士伟, 孔凡国, 汤冬琴, 等. 浙江上海地区健康人群甲状腺结节发病情况分析[J]. 实验与检验医学, 2014, 32(2): 214-216
[10] 邱蕾, 孙明晓, 汪耀, 等. 中年至超高龄老年人甲状腺结节的发病特点[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2014, 30(2): 115-118.
[11] 余开选, 胡朝恩, 宋晓峰, 等. 260例中老年甲状腺结节患者3年超声观察结果分析[J]. 中华保健医学杂志, 2015, 17(4): 305-328.
[12] Sousa PA, Vaisman M, Carneiro JR, et al. Prevalence of goiter and thyroid nodular disease in patients with class III obesity[J]. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2013, 57(2): 120-125.
[13] Rendina D, De Filippo G, Mossetti G, et al. Relationship between metabolic syndrome and multinodular non-toxic goiter in an inpatient population from a geographic area with moderate iodine deficiency[J]. J Endocrinol Invest. 2012, 35(4): 407-412.
[14] Pacini F, Schlumberger M, Dralle H, et al. European consensus for the management of patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma of the follicular epithelium[J]. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006. 154(6): 787-803.
[15] Filetti S, Durante C, Torlontano M. Nonsurgical approaches to the management of thyroid nodules[J]. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2006, 2(7): 384-394.
[16] Quadbeck B, Pruellage J, Roggenbuck U, et al. Long-term follow-up of thyroid nodule growth[J]. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2002, 110(7): 348-354.
[17] Alexander EK, Hurwitz S, Heering JP, et al. Natural history of benign solid and cystic thyroid nodules[J]. Ann Intern Med. 2003, 138(4): 315-318.
[18] Erdogan MF, Gursoy A, Erdogan G. Natural course of benign thyroid nodules in a moderately iodine-deficient area[J]. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006, 65(6): 767-771.
[19] Brauer VF, Eder P, Miehle K, et al. Inter observer variation for ultrasound determination of thyroid nodule volumes[J]. Thyroid. 2005, 15(10): 1169-1175.
