超声椭圆振动和微量润滑耦合切削Inconel718的性能研究
2020-07-04林靖朋王大中
林靖朋 王大中

摘要:本文利用仿真軟件AdvantEdge研究了微量润滑量(MQL)和超声椭圆振动(UEV)切削对加工性能的影响,与常规切削(CT)相比,显著降低了切削力和切削温度。同时比较了UEV车削条件下不同喷嘴角度对加工性能的影响。不同的喷嘴角度会影响温度和应力的变化,选择合适的喷嘴角度有利于提高工件的表面质量,提高刀具的使用寿命。
关键词: 超声椭圆振动; 微量润滑; 喷嘴角度; 车削
【Abstract】In this paper, the simulation software AdvantEdge is used to study the effect of micro-lubrication (MQL) and ultrasonic elliptical vibration (UEV) cutting on machining performance.Compared with conventional cutting (CT), cutting force and cutting temperature are significantly reduced.The effects of different nozzle angles on machining performance under UEV turning conditions are also compared.Different nozzle angles affect changes in temperature and stress, selecting the proper nozzle angle is conducive to improving the surface quality of the workpiece and increasing the service life of the tool.
【Key words】 ultrasonic elliptical vibration; minimal lubrication; nozzle angle; turning
0 引 言
镍基高温合金具有优异的高温强度,化学稳定性、耐蚀性、抗热震性等性能,广泛用于航空航天、能源和化学领域、燃气轮机、火箭发动机和核反应堆等[1]。 Inconel718的常规车削(CT)工艺中的主要问题是切削力高和切削温度高,这会加剧刀具磨损并降低加工质量[2]。
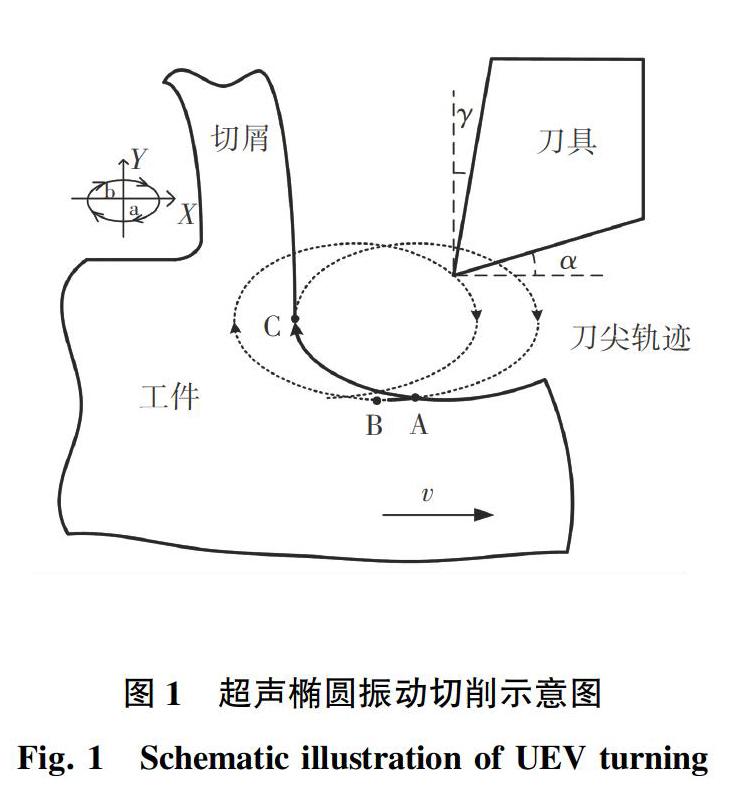
超声椭圆振动(UEV)车削Inconel718可以降低切削力和温度,提高工件的表面质量,并延长刀具和工件的使用寿命[3]。超声振动车削,也称为超声辅助车削,是一种基于普通车削加工在一个方向或多个方向上施加频率超过20 KHz的周期性振动的加工技术。 UEV车削示意图如图1所示。
绿色制造和可持续发展已成为新时代机械制造业的主要发展趋势之一,如何最大限度地减少切削液的危害并确保加工质量已成为当前国内外机械制造业面临的主要问题[4]。目前,金属切削领域有许多冷却和润滑方法,例如液氮冷却、低温冷却、空冷、喷雾冷却和微量润滑(MQL)[5]。 MQL是指使用非常少量的切削液,通常为100 ml / h或更少,其使用量约为传统湿切削液的六十分之一[6]。 MQL可以显著减少切削液的使用,大大减少传统泛流冷却对环境造成的危害[7]。本文将MQL与超声振动耦合车削,研究了不同喷嘴位置对切削性能的影响。
1 实验设置
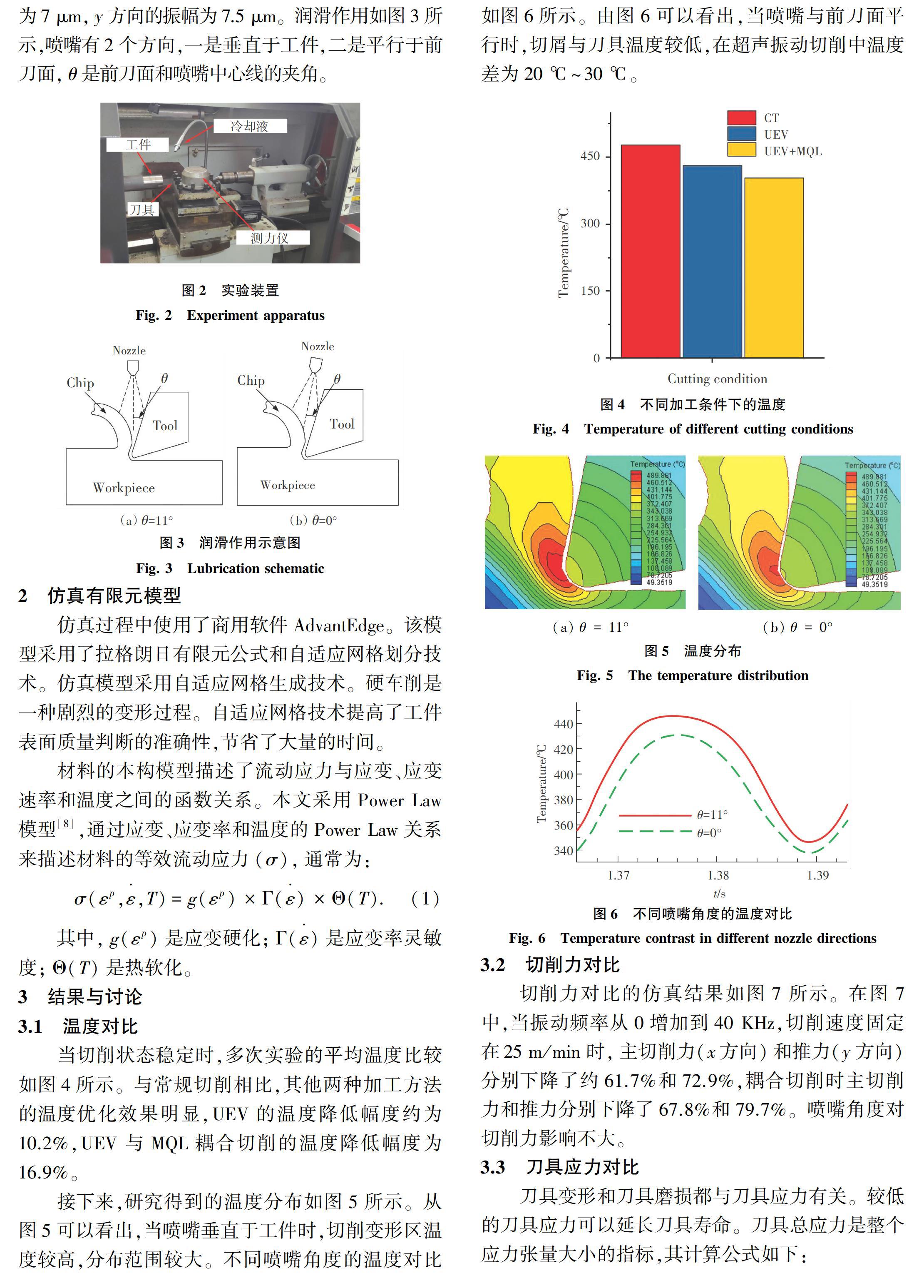
实验装置如图2所示。工件材料选用Inconel718,材料加工选用11°前角和10°后角的CBN刀具。切削速度(25 m/min),进给量(0.005 mm/r),背吃刀量(0.005 mm)。刀具的振动频率是40 KHz,x方向的振幅为7 μm,y方向的振幅为7.5 μm。润滑作用如图3所示,喷嘴有2个方向,一是垂直于工件,二是平行于前刀面,θ是前刀面和喷嘴中心线的夹角。
2 仿真有限元模型
仿真过程中使用了商用软件AdvantEdge。该模型采用了拉格朗日有限元公式和自适应网格划分技术。仿真模型采用自适应网格生成技术。硬车削是一种剧烈的变形过程。自适应网格技术提高了工件表面质量判断的准确性,节省了大量的时间。
4 结束语
与常规切削相比,UEV车削温度降低了10.2%,UEV 与 MQL耦合切削温度降低了16.9%;UEV车削的主切削力和推力分别降低61.7%和72.9%,UEV与MQL耦合切削的主切削力和推力分别降低67.8%和79.7%。当喷嘴角与前刀面平行时,工件和刀具温度较低,刀具应力较小。喷嘴角度对切削力影响不大。为了提高工件质量和刀具寿命,有必要选择合适的喷嘴角度。
参考文献
[1] CHOUDHURY I A , ELBARADIE M A. Machinability of nickel-base super alloys: A general review[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1998, 77(1-3): 278.
[2]LI Huaizhong , ZENG H, CHEN Xiaoqi. An experimental study of tool wear and cutting force variation in the end milling of Inconel 718 with coated carbide inserts[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2006, 180(1-3): 296.
[3]WANG Fei, LIU Yonghong, SHEN Yang, et al. Machining performance of Inconel 718 using high current density electrical discharge milling[J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes ,2013,28:1147.
[4]BOSWELL B , ISLAM M N, DAVIES I J, et al. A review identifying the effectiveness of minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) during conventional machining[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology ,2017,92:321.
[5]JIA Dongzhou, ZHANG Dongkun, ZHANG Yanbin, et al. Experimental verification of nanoparticle jet minimum quantity lubrication effectiveness in grinding[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research,2018, 16:2758.
[6]TAWAKOLI T , HADAD M J, SADEGHI M H. Influence of oil mist parameters on minimum quantity lubrication – MQL grinding process[J].International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2010,50:521.
[7]HEE P K, OLORTEGUI-YUME J, YOON M C, et al. A study on droplets and their distribution for minimum quantity lubrication (MQL)[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2010,50(9): 824.
[8]JIANG Zenghui, WANG Xiaoliang, ZHANG Jianhai, et al. Finite element analysis of surface residual stress of titanium alloy TC4 based on high speed cutting[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2012, 500:157.
