白藜芦醇对mmLDL损伤小鼠肠系膜动脉内皮依赖性舒张功能的作用
2020-05-06罗宏丽刘露吴知桂
罗宏丽 刘露 吴知桂
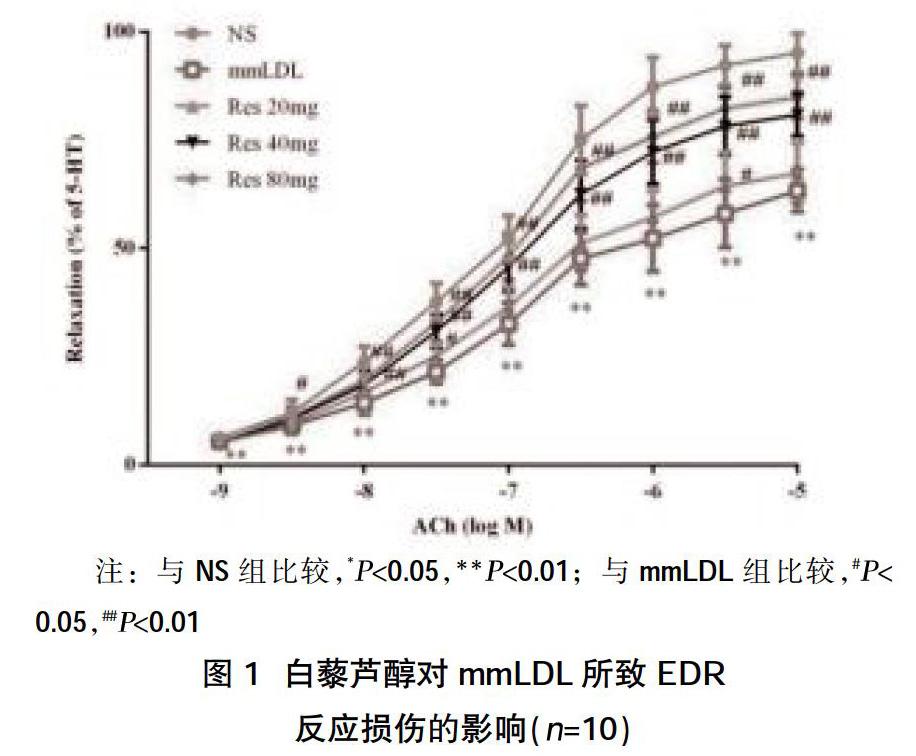

摘要:目的 探讨白藜芦醇对弱氧化低密度脂蛋白(mmLDL)所致小鼠肠系膜动脉内皮依赖性舒张(EDR)功能损伤的保护作用及可能机制。方法 将50只小鼠随机分为5组,即对照组(NS组)、mmLDL组(1 mg/kg,尾静脉注射,q12 h)及低、中、高剂量白藜芦醇组(Res组)(mmLDL 1 mg/kg,尾静脉注射,q12 h+Res 20,40,80 mg/kg,腹腔注射,q12 h)。72 h后检测各组肠系膜动脉环EDR功能及血清中NO、IL-1β、TNF-α水平和NOS活性。结果 白藜芦醇中、高剂量组明显减轻mmLDL对小鼠肠系膜动脉内皮依赖性舒张反应的抑制, ACh 产生的最大舒张率(Emax)为(80.88±5.05)%、(84.92±4.82)%,与mmLDL组比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),但中、高剂量组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);腹腔注射白藜芦醇后,NO途径和EDHF途径内皮依赖性舒张曲线均产生了明显的增强作用,Emax为(42.51±5.18)%、(47.41±5.76)%,与mmLDL组比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);mmLDL使小鼠血清中NO水平和NOS活性降低(P<0.01),炎症因子IL-1β和TNF-α水平显著性升高(P<0.01);给予白藜芦醇干预后,NO水平和NOS活性显著升高(P<0.05),IL-1β和TNF-α水平显著降低(P<0.01)。结论 白藜芦醇缓解mmLDL对小鼠肠系膜动脉EDR功能的损伤呈剂量依赖性,且减弱了mmLDL损伤NO-、EDHF途径的作用,该作用可能与促进内皮细胞合成、释放NO,减少炎症因子IL-1β、TNF-α有关。
关键词:白藜芦醇;弱氧化低密度脂蛋白;小鼠;肠系膜动脈;内皮依赖性舒张
Abstract:Objective To investigate the protective effect and possible mechanism of resveratrol on weakly oxidized low-density lipoprotein (mmLDL) -induced endothelium-dependent relaxation (EDR) function damage in mice mesenteric artery.Methods 50 mice were randomly divided into 5 groups, namely control group (NS group), mmLDL group (1 mg / kg, tail vein injection, q12 h) and low, medium and high dose resveratrol group (Res group) (mmLDL 1 mg / kg, tail vein injection, q12 h + Res 20, 40, 80 mg / kg, intraperitoneal injection, q12 h). After 72 h, the mesenteric artery ring EDR function, serum NO, IL-1β, TNF-α levels and NOS activity were detected in each group.Results The resveratrol medium and high dose groups significantly reduced the inhibition of mmLDL on the mesenteric artery endothelium-dependent relaxation response in mice. The maximum relaxation rate (Emax) produced by ACh was (80.88 ± 5.05)%, (84.92 ± 4.82)%, and compared with the mmLDL group, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.01), but compared with the middle and high dose groups, the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05); after intraperitoneal injection of resveratrol, the endothelium dependence of NO pathway and EDHF pathway the diastolic curve produced obvious enhancement effect, Emax reached (42.51 ± 5.18)%, (47.41 ± 5.76)%, compared with the mmLDL group, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.01); mmLDL caused the NO level in serum and NOS activity were decreased (P<0.01), the levels of inflammatory factors IL-1β and TNF-α were significantly increased (P<0.01); after intervention with resveratrol, NO levels and NOS activity were significantly increased (P<0.05), IL-1β and TNF-α levels were significantly reduced (P<0.01).Conclusion Resveratrol relieves the damage of mmLDL to the mesenteric artery EDR function in a dose-dependent manner, and attenuates the effect of mmLDL on the NO- and EDHF pathways. This effect may be related to promoting endothelial cell synthesis and release of NO, and reducing the inflammatory factor IL- 1β, TNF-α related.
2.3血清中NO、IL-1β、TNF-α含量和NOS活性 mmLDL使小鼠血清中NO水平和NOS活性降低(P<0.01),炎症因子IL-1β和TNF-α水平显著性升高(P<0.01);给予白藜芦醇干预后,NO水平和NOS活性显著升高(P<0.05),IL-1β和TNF-α水平显著降低(P<0.01),见表1。
3讨论
本研究显示白藜芦醇能明显对抗mmLDL所诱导的EDR功能的降低,并呈剂量依赖性。由于中、高剂量组对血管的舒张反应无明显差异,所以在研究保护机制的试验中仅设置了中剂量组。EDR主要由NO-、PGI2-和EDHF 3条途径构成,既往研究已经发现mmLDL对小鼠肠系膜动脉EDR的损伤主要与NO-和EDHF途径受损有关[11],因此本研究在探究白藜芦醇对其损伤的保护作用时也主要考察了这两条途径。试验结果发现,腹腔注射白藜芦醇后,NO途径和EDHF途径内皮依赖性舒张曲线均产生了明显的增强作用,表明白藜芦醇的血管内皮保护作用与这两条途径有关。
研究表明[12],白藜芦醇的血管舒张作用是通过调节血管舒张剂NO和血管收缩剂血管内皮素-1的生成,并增强NO的活性实现的。王召军等[7]发现白藜芦醇能呈浓度依赖性的舒张离体人肺内小动脉,其作用机制可能与促进NO的释放有关。Nagaoka T等[13]研究发现,白藜芦醇能够通过内皮依赖和非内皮依赖的舒张离体猪的视网膜动脉,其中内皮依赖性舒张主要通过细胞外调节蛋白激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinase,ERK)1/2通路增加NOS活性,提高NO浓度使血管舒张。本实验发现,白藜芦醇干预后,能使mmLDL降低的NO水平和NOS活性显著升高,表明白藜芦醇可能通过促进内皮细胞合成、释放NO而发挥保护mmLDL对EDR功能损伤的作用。
TNF-α属于Th1型促炎性细胞因子,主要由巨噬细胞、成纤维细胞、白细胞等分泌,在调节系统性炎症反应过程中发挥着重要作用[14]。IL-1β由激活的巨噬细胞分泌,是重要炎症反应启动因子,通过刺激炎症及免疫相关蛋白表达,在免疫调节中发挥重要作用。研究发现[15],白藜芦醇在体外能抑制IL-6基因的表达、蛋白合成和分泌,且能抑制IL-8和粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的释放;在体内,可抑制由TNF-α或脂多糖刺激引起的内皮血管细胞黏附分子-1 和细胞内黏附分子-1 的表达,从而抑制白细胞在血管壁的聚集,减轻炎症反应,阻止组织损伤[16]。本研究发现,尾静脉注射mmLDL后造成血清中炎症因子IL-1β、TNF-α的含量显著升高;而腹腔注射白藜芦醇后,能显著抑制mmLDL上调血清中IL-1β、TNF-α的浓度水平;表明对mmLDL所致小鼠肠系膜动脉EDR功能损伤的保护作用与减少炎症因子IL-1β、TNF-α有关。
综上所述, 白藜芦醇剂量依赖性的拮抗mmLDL对血管内皮以及内皮依赖性舒张功能的损伤作用,减弱了mmLDL损伤NO-、EDHF途径的作用,可能是通过促进内皮细胞合成、释放NO,下调炎症因子TNF-α 和IL-1β表达,缓解mmLDL对血管内皮细胞和内皮依赖性舒张功能的损伤作用。
参考文献:
[1]查晴,曹丽娟,王燕萍.oxLDL通过TLR4诱导脂质累积和炎症反应促进动脉粥样硬化的分子机制[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2017,37(5):611-615.
[2]Chen G,Chen XL,Xu CB,et al.Toll-like receptor protein 4 monoclonal antibody inhibits mmLDL-induced endothelium-dependent vasodilation dysfunction of mouse mesenteric arteries[J].Microvascular Research,2020(127):103923.
[3]Schnack L,Sohrabi Y,Lagache SMM,et al.Mechanisms of Trained Innate Immunity in oxLDL Primed Human Coronary Smooth Muscle Cells[J].Front Immunol,2019(10):13.
[4]Chen G,Wang JJ,Xu CB,et al.Minimally Modified LDL-Induced Impairment of Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation in Small Mesenteric Arteries of Mice[J].J Vasc Res,2016,53(1-2):58-71.
[5]过华蕾,邵畅,龚仪棠.白藜蘆醇对抗氧化型低密度脂蛋白诱导的内皮细胞损伤及其机制[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2016,26(8):699-702.
[6]李国洪,金美娟,王新鸣,等.白藜芦醇对氧化型LDL所致血管内皮细胞损伤的保护作用[J].解放军医学杂志,2008,33(6):719-721.
[7]王召军,邓春玉,邝素娟,等.白藜芦醇对离体人肺内小动脉血管张力的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2015,35(4):540-543
[8]Zeng ZS,Lin J,Xu CB,et al.Minimally modified low-density lipoprotein upregulates the ETB and α1 receptors in mouse mesenteric arteries in vivo by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway[J].J Pharm Pharmacol,2019,71(6):937-944.
[9]郭立军,江高峰,李海鹏,等.mmLDL对小鼠肠系膜动脉α1受体介导的血管收缩及相关蛋白表达影响的研究[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(6):827-833.
[10]刘阳,林杰,秦旭平,等.mmLDL激活ERK1/2通路上调小鼠肠系膜动脉ET_B受体的研究[J].湘南学院学报(医学版),2018,20(2):1-6.
[11]陈根,秦旭平,林杰,等.弱氧化低密度脂蛋白对小鼠肠系膜动脉内皮依赖性舒张功能的影响及机制[J].药学学报,2013,48(11):1657-1664.
[12]杨菊红,王楠,李京艳,等.白藜芦醇对高脂处理人脐静脉内皮细胞SIRT1表达、eNOS活性及NO分泌的影响[J].中国药房,2009,20(13):981-983.
[13]Nagaoka T,Hein TW,Yoshida A,et al.Resveratrol, a component of red wine, elicits dilation of isolated porcine retinal arterioles:Role of nitric oxide and Potassium channels[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2007,48(9):4232-4239.
[14]Kalliolias GD,Ivashkiv LB.TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies[J].Nat Rev Rheumatol,2016,12(1):49-62.
[15]Ozcan Cenksoy P,Oktem M,Erdem O,et al.A potential novel treatment strategy:Inhibition of angiogenesis and inflammation by resveratrol for regression of endometriosis in an experimental rat model[J].Gynecol Endocrinol,2015,31(3):219-224.
[16]Dull AM,Moga MA,Dimienescu OG,et al.Therapeutic Approaches of Resveratrol on Endometriosis via Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Angiogenic Pathways[J].Molecules,2019,24(4):667-687.
收稿日期:2020-01-27;修回日期:2020-02-03
編辑/肖婷婷
