床边检测NT-proBNP及cTnI对心源性呼吸困难的临床诊断价值
2016-11-12廖通张元春李焕轮古振拓潘朝庆卢丽华谭志伟黄锡藩
廖通,张元春△,李焕轮,古振拓,潘朝庆,卢丽华,谭志伟,黄锡藩
床边检测NT-proBNP及cTnI对心源性呼吸困难的临床诊断价值
廖通1,张元春1△,李焕轮1,古振拓1,潘朝庆1,卢丽华1,谭志伟2,黄锡藩2
目的探讨床边联合检测氨基末端B型钠尿肽原(NT-proBNP)和心肌肌钙蛋白I(cTnI)水平对心源性呼吸困难的诊断价值。方法选取以呼吸困难为主诉入院的患者120例,入院时立即行床边NT-proBNP、cTnI检测,NT-proBNP>300 ng/L或cTnI>0.16 μg/L定义为心源性呼吸困难。根据最后诊断将呼吸困难患者分为心源组(n= 68)和肺源组(n=52),同时选取30例健康体检人群作为对照组,对3组的NT-proBNP、cTnI水平进行分析。研究单独检测NT-proBNP、cTnI和NT-proBNP+cTnI联合检测诊断心源性呼吸困难的敏感度和特异度。结果肺源组及心源组的NT-proBNP及cTnI水平均高于对照组,且心源组高于肺源组(P<0.01)。NT-proBNP、cTnI单独检测诊断心源性呼吸困难的敏感度分别为67.65%和52.94%;两者联合检测提高至94.12%;NT-proBNP、cTnI单独检测时的特异度分别为70.00%和53.33%,联合检测提高至86.67%。NT-proBNP+cTnI联合检测的敏感度高于NT-proBNP、cTnI单独检测(P<0.05),检测特异度高于cTnI单独检测(P<0.05),与NT-proBNP单独检测差异无统计学意义。两者联合对心源性呼吸困难诊断的阳性预测值为94.12%(64/68),阴性预测值为86.67%(26/30)。结论床边联合检测NT-proBNP、cTnI在心源性呼吸困难快速诊断中具有重要的价值,两者联合检测能够提高其诊断的敏感度。
呼吸困难;诊断,鉴别;敏感性与特异性;氨基末端B型钠尿肽原;心肌肌钙蛋白I;肺源性呼吸困难;心源性呼吸困难
呼吸困难是内科常见危重症之一,发病率和死亡率较高,其中以心源性与肺源性呼吸困难最常见,较早的鉴别诊断尤为重要,但超声心动图、胸部X线片等常规检查受限于时间或地点,较难提供及时便利的诊断参考。心源性与肺源性呼吸困难临床表现往往有重叠性,彻底区分困难,因此,寻找能快速诊断的指标和方法具有重要的临床价值。人类B型钠尿肽(B-type natriuretic peptide,BNP)基因表达前体原在脱去N端的信号肽后成为B型钠尿肽前体(N-terminalpro-brainnatriureticpeptide,proBNP)。proBNP在分泌过程中或进入血液后可分解成BNP和N端脑钠肽激素原(N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide,NT-proBNP)。心肌肌钙蛋白I(cardiac troponin,cTnI)是心肌损伤的标志物已成为共识,心力衰竭时cTnI因心肌损伤及受损心肌细胞通透性可增加释放入血,可为心力衰竭的诊疗提供参考。有研究显示,BNP和NT-proBNP可用于充血性心力衰竭诊断、心源性与肺源性呼吸困难的鉴别诊断[1]。NT-proBNP与cTnI联合检测能否进一步提高心源性呼吸困难鉴别诊断的特异度及敏感度的相关研究少见。本研究旨在探讨联合检测cTnI对快速鉴别心源性呼吸困难的临床应用价值。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象选取2014年6月—2016年2月以呼吸困难为主诉于本院就诊的患者120例。呼吸困难诊断标准参照文献[2-3]:患者主观感到空气不足,呼吸费力;客观表现为患者呼吸活动用力,重者鼻翼扇动、张口耸肩、端坐呼吸,辅助呼吸肌也参与活动,呼吸频率>24次/min,呼吸深度与节律异常(速而浅或慢而深)。心功能不全所致心源性呼吸困难诊断标准参考文献[4]。肺源性呼吸困难参考中华医学会呼吸病学分会制定的慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊治指南(2013年修订版)诊断标准。肺源性呼吸困难52例(肺源组),男29例,女23例,年龄43~71岁,平均(63.18±11.40)岁,其中慢性阻塞性肺气肿25例,支气管哮喘17例,慢性支气管炎7例,胸腔积液3例;心源性呼吸困难68例(心源组),男41例,女27例,年龄43~75岁,平均(65.27±9.75)岁,其中冠心病27例、高血压性心脏病26例、老年退行性心瓣膜病6例、风湿性心脏病5例、扩张型心肌病4例。选择同期健康体检者30例为对照组,男18例,女12例,年龄40~78岁,平均(64.53± 8.72)岁。患者组排除标准:心脏结构异常、肾功能不全、肿瘤、内分泌疾病、肝脏及神经系统疾病者。3组性别(χ2= 0.27)及年龄(F=0.38)差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.2 方法所有研究对象入院后即刻抽取肘正中静脉血5 mL,使用Radiometer公司全自动的床旁快速免疫分析仪AQT90 FLEX检测NT-proBNP和cTnI。NT-proBNP>300 ng/L或cTnI>0.16 μg/L定义为心源性呼吸困难诊断指标阳性[5-6]。NT-proBNP+cTnI联合检测指符合上述一个即诊断为心源性呼吸困难。对心源组和对照组患者比较NT-proBNP、cTnI单独检测和NT-proBNP+cTnI检测的敏感度和特异度。
1.3 统计学方法采用SPSS 19.0统计软件进行处理。符合正态分布的计量资料采用均数±标准差示,多组均数比较采用单因素方差分析,分析前用Levene法检测方差齐性,方差齐时多重比较使用LSD-t法;方差不齐时的多重比较使用Dunnett's法;不符合正态分布的计量资料用M(P25,P75)表达,组间比较采用秩和检验;计数资料组间比较采用卡方检验。检验水准α=0.05。
2 结果
2.1 各组血NT-proBNP和cTnI的检测结果的比较肺源组及心源组的NT-proBNP及cTnI水平均高于对照组,且心源组高于肺源组(P<0.05),见表1。
Tab.1Comparison of NT-proBNP and cTnI between three groups表1 各组NT-proBNP和cTnI的检测结果比较

Tab.1Comparison of NT-proBNP and cTnI between three groups表1 各组NT-proBNP和cTnI的检测结果比较
**P<0.01;a与对照组比较,b与肺源组比较,P<0.05
组别对照组肺源组心源组F或Z n 30 52 68 NT-proBNP(ng/L)38.16±20.85 146.91±43.82a 842.59±309.80ab 1 141.37**cTnI(μg/L)0.03(0.02,0.15)0.50(0.20,1.00)a 18.80(16.80,23.70)ab 123.83**
2.2 NT-proBNP联合cTnI诊断心源性呼吸困难的临床价值NT-proBNP、cTnI单独检测及联合检测时的敏感度和特异度差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05);NT-proBNP+cTnI检测敏感度高于NT-proBNP、cTnI单独检测(χ2分别为15.41和29.62,P<0.05),检测特异度高于cTnI单独检测(χ2=7.94,P=0.005),与NT-proBNP单独检测差异无统计学意义(χ2=2.46,P=0.117)。NT-proBNP+cTnI对心源性呼吸困难诊断的阳性预测值为94.12%(64/68),阴性预测值为86.67%(26/30),见表2。
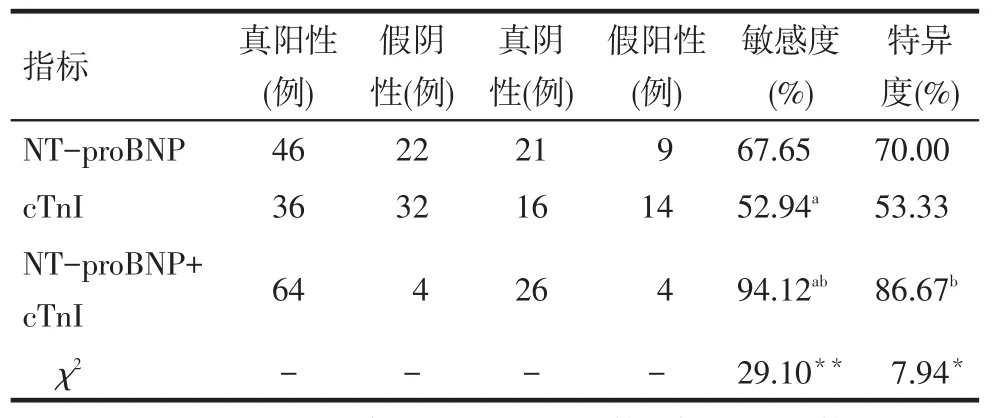
Tab.2Comparison of NT-proBNP,cTnI and combined detection results表2 NT-proBNP、cTnI单独及联合检测结果比较
3 讨论
呼吸困难是中老年患者急诊最常见的病症之一,但以心源性和肺源性呼吸困难最为多见,两者在临床表现上有一定的重叠,快速准确鉴别难度较大[7]。当心室容量增加、心脏压力负荷加重、心肌缺血、室壁肌张力增加时心肌细胞的基因被激活,生成含有134个氨基酸的蛋白质,该蛋白质的信号肽被切除后成为含108个氨基酸的proBNP,并被迅速分泌入血,很快以1∶1的比例降解为BNP和NT-proBNP,促进尿、尿钠的排泄和血管扩张[8]。与BNP相比,NT-proBNP的半衰期长,稳定性好,分子质量大,易于测定。研究认为,NT-proBNP<100 ng/L基本可排除心源性呼吸困难[9]。另有研究认为,NT-proBNP水平可以反映急性心肌缺血的严重程度和范围[10]。
目前,关于NT-proBNP在急性呼吸困难鉴别诊断中作用的研究较多。陈红兴等[2]对呼吸困难患者行床边检测NT-proBNP后发现,心源性呼吸困难者的NT-proBNP(2 026.4±122.7)ng/L水平明显高于肺源性呼吸困难者(191.8±28.12)ng/L,且急性心力衰竭程度越重,其水平越高。但该研究未涉及NT-proBNP对心源性呼吸困难检验的敏感度和特异度,且选择的心源性患者均为心衰患者。同时国内外医学界一致认定,NT-proBNP≥2 000 ng/L时即可以确诊为急性心力衰竭[11]。
cTn在评估心肌损伤中具有较高敏感度及特异度,近几年来已经逐渐取代肌酸激酶(CK)及其同工酶(CK-MB)在心肌梗死(MI)诊断中的地位,成为临床评估心肌损伤的主要标志物。cTnI作为cTn的一个亚型,与其他亚型相比具有高度的组织特异性,成为心肌损伤最敏感的标志物[12]。cTnI逐渐成为心肌梗死早期诊断的常用指标[13]。cTnI比传统的心肌酶更特异和敏感,被认为是目前最好的心肌损伤标志物,被誉为心肌损伤的“金标准”[14]。
由于每项指标判断疾病的敏感度和特异度不同,其单独检测时存在一定的局限性,如一些特异性较强的指标,不够敏感,易漏诊,从而使患者错过最佳治疗时机;一些高敏感度指标的特异度低,易误诊,给患者带来精神和心理负担,因而联合检测对疾病的诊断和判断预后显得尤为重要[15]。本研究结果显示,在心源性呼吸困难中,NT-proBNP+cTnI检测的敏感度均高于各单独检测,特异度比单独检测cTnI要高,表明这两项指标对心源性呼吸困难诊断均有重要价值,且可以互补。联合检测的阴性预测值为86.67%,提示对于联合指标为阴性的患者,基本可以排除心源性呼吸困难,两者联合检测对心源性呼吸困难诊断的阳性预测值为94.12%,两者阳性基本排除肺源性呼吸困难,具有重要的临床诊断价值。
综上所述,利用床边快速免疫分析仪检测NT-proBNP及cTnI对心源性呼吸困难的诊断具有重要价值,两者联合检测能够提高其诊断的敏感度。
[1]Maries L,Manitiu I.Diagnostic and prognostic values of B-type natriuretic peptides(BNP)and N-terminal fragment brain natriuretic peptides(NT-pro-BNP)[J].Cardiovasc J Afr,2013,24(7):286-289.doi:10.5830/CVJA-2013-055.
[2]Chen HX,Ni HF.Application of rapid bedside detection blood ntprobnp in differential diagnosis of dyspnea in the emergency department[J].Journal of Radioimmunology,2011,24(4):419-421.[陈红兴,倪海芳.床边快速检测全血NT-proBNP在急诊呼吸困难鉴别诊断中的应用[J].放射免疫学杂志,2011,24(4): 419-421].doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-9810.2011.04.036.
[3]Lei L.Clinical value of B-type natriuretic peptide combined with CA125 detection in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea[J]. Chinese Journal of the Frontiers of Medical Science,2015,7(11): 152-154.[雷磊.B型钠尿肽和CA125联合检测在呼吸困难鉴别诊断中的临床价值[J].中国医学前沿杂志,2015,7(11): 152-154].
[4]Jiang TT.The translational application of brain natriuretic peptide measurements in pulmonary and cardiac dyspnea[D].Hefei:the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University,2013:10-11.[蒋婷婷.血浆脑钠肽测定在肺源性和心源性呼吸困难鉴别诊断中的应用[D].合肥:安徽医科大学第一附属医院,2013:10-11].
[5]TanY,Zeng XF,Li JM,et al.Clinical differential diagnosis valueof detecting blood BNP,hs-CR and cTnI levels in patients with dyspnea[J].J Mod Lab Med,2012,27(4):38-43.[谈昀,曾宪飞,李军民,等.血BNP,hs-CRP和cTnI水平在呼吸困难患者中的临床鉴别诊断价值[J].现代检验医学杂志,2012,27(4): 38-43].doi:10.3969/J.issn.1671-7414.2012.04.015.
[6]Zhu XP,Wang CG.The application of combined detection of the NT-pro BNP and cTnI in the diagnosis and treatment of acute heart failure patients[J].Laboratory Medicine,2013,28(1):30-32.[朱笑频,王成刚.NT-proBNP和cTnI联合检测在急诊心力衰竭患者诊治中的应用[J].检验医学,2013,28(1):30-32].doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673.8640.2013.01.007.
[7]Hunt SA,Abraham WT,Chin MH,et al.ACC/AHA2005 guideline update for the diagnosis and management of chronic heart failure in the adult[J].Circulation,2005,112(12):1825-1852.doi:10.1161/ CIRCULATIONAHA.105.167587.
[8]Chen H,Zhou YY,Dai YD.Clinical Application Progress of NT-proBNP[J].Labeled Immunoassays and Clin Med,2015,22(1): 69-71.[陈华,周懿忆,戴屹东.NT-proBNP的临床应用进展[J].标记免疫分析与临床,2015,22(1):69-71].doi:10.11748/ bjmy.issn.1006-1703.2015.01.022.
[9]Sturgess DJ,Venkatesh B.Plasma free cortisol and B-type natriuretic peptide in septic shock[J].Anaesth Intensive Care,2012,40(1):95-98.
[10]Shao ML,Huang CX,Li Z.Effects of glutamine and valsartan on the brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide of patients with chronic heart failure[J].Pak J Med Sci,2015,31(1):82-86.doi:10.12669/pjms.311.6302.
[11]Zhang JW.Diagnostic value of combined detection of serum CTGF and NT-proBNP in heart failure[J].Journal of Clinical Emergency(China),2013,10(2):62-64[张俊威.联合检测CTGF和NT-proBNP在心衰诊断中的应用价值[J].临床急诊杂志,2013,10(2):62-64].
[12]Qiu J,Wu G.Progress in clinical application of cTnI in percutaneous coronary intervention related myocardial infarction[J].Chin Heart J,2016,28(3):362-365.[邱珺,吴刚.cTnI在PCI相关心肌梗死中的临床应用进展[J].心脏杂志,2016,28(3):362-365].
[13]Chen M,Dai H.Early diagnostic value of cardiac troponinI,creatine kinase-mb and high-sensitivity C reactive protein in acute myocardial infarction[J].Anhui Medical Journal,2013,34(10):1481-1483.[陈明,戴红.cTnI、CK-MB和hs-CRP在急性心肌梗死早期诊断中的价值[J].安徽医学,2013,34(10): 1481-1483].doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0399.2013.10.015.
[14]Liu H,Li Y,Xu SW,et al.Clinical value of combined detection of CK-MB,MYO,cTnI and plasma NT-proBNP in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction[J].Hainan Med J,2015,26(23): 3496-3499.[刘欢,李艳,许淑文,等.血清CK-MB、MYO、cTnI和血浆NT-proBNP联合检测诊断急性心肌梗死的临床价值[J].海南医学,2015,26(23):3496-3499].doi:10.3969/j. issn.1003-6350.2015.23.1266.
[15]Li J.Comparison of the value of myocardial enzymes and cardiac troponin in the diagnosis of myocardial injury[J].Medical Information,2014,28(9):393-396.[李军.心肌酶与肌钙蛋白在诊断心肌损伤时的价值比较[J].医学信息,2014,28(9):393-396].doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2014.09.473.
(2016-03-04收稿2016-04-22修回)
(本文编辑陆荣展)
The clinical value of bedside testing of plasma levels of NT-proBNP and cTnI in the rapid diagnosis of cardiac dyspnea
LIAO Tong1,ZHANG Yuanchun1△,LI Huanlun1,GU Zhentuo1,PAN Chaoqing1,LU Lihua1,TAN Zhiwei2,HUANG Xifan2
1 Department of Cardiology,Dalang Hospital,Dongguan,Guangdong 523770,China;2 Department of Cardiology,Xinxing People's Hospital△
ObjectiveTo explore the diagnostic value of combined bedside detection of aminoterminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide(NT-proBNP)and cardiac troponin I(cTnI)in the diagnosis of cardiac dyspnea.MethodsA total of 120 patients with dyspnea admitted in our department from June 2014 to February 2016 were included in this study.At the time of admission,NT-proBNP and cTnI levels were measured by bedside test.Values of NT-proBNP>300 ng/L or cTnI>0.16 μg/L were defined as positive for cardiac dyspnea.According to the final diagnosis,patients were divided into two groups: cardiac dyspnea group(n=68)and pulmonary dyspnea group(n=52).At the same time,30 healthy people were selected as control group.Values of NT-proBNP and cTnI were used for statistical analysis between the three groups.The sensitivity and specificity of NT-proBNP,cTnI and cTnI+NT-proBNP were compared between three groups.ResultsThe levels of NT-proBNP and cTnI were significantly higher in pulmonary dyspnea group and cardiac dyspnea group than those in the control group,and the levels were significantly higher in cardiac dyspnea group than those of pulmonary dyspnea group(P<0.01). The detection sensitivity of NT-proBNP and cTnI alone was 67.65%and 52.94%,combined detection of both was up to 94.12%.The specificity of NT-proBNP and cTnI detection alone was 70.00%and 53.33%,respectively,and combined detection of both was up to 86.67%.The sensitivity of NT-proBNP+cTnI was significantly higher than that of NT-proBNP and cTnI alone(P<0.05),but there was no significant difference in the specificity between combined detection andindividual detection of NT-proBNP.The positive predictive value of the combined detection in the diagnosis of cardiac dyspnea was 94.12%(64/68),and the negative predictive value was 86.67%(26/30).ConclusionBedside detection with combination of cTnI and NT-proBNP has important clinical application value in the rapid diagnosis of cardiac dyspnea,which is a rapid clinical testing method.
dyspnea;diagnosis,differential;sensitivity and specificity;N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide;cardiac troponin;pulmonary dyspnea;cardiac dyspnea
R441.8,R446
A
10.11958/20160114
2014年云浮市医药卫生科研课题资助项目(2014B54)
1广东省东莞市大朗医院心血管内科(邮编523770);2广东省云浮市新兴县人民医院
廖通(1982),男,主治医师,学士,主要从事心血管内科的临床诊疗工作
△通讯作者E-mail:yczhang8101@163.com
