消化性溃疡患者外周血细胞免疫及体液免疫功能变化分析
2016-07-25李国熊吴建良
吴 蓉,李国熊,李 丽,周 刚,吴建良,陈 晶
消化性溃疡患者外周血细胞免疫及体液免疫功能变化分析
吴 蓉,李国熊,李 丽,周 刚,吴建良,陈 晶
310015浙江省杭州市,杭州师范大学附属医院消化内科
【摘要】目的探讨消化性溃疡患者外周血细胞免疫及体液免疫功能的变化及临床意义。方法选择2014年1月—2015年1月杭州师范大学附属医院门诊及住院的连续经胃镜确诊的消化性溃疡患者122例为溃疡组,另选择同期体检中心体检健康者70例为对照组,溃疡组患者根据是否感染幽门螺杆菌分为幽门螺杆菌阳性亚组(Hp+亚组)85例和幽门螺杆菌阴性亚组(Hp-亚组)37例,根据是否出血分为出血亚组58例和未出血亚组64例。检测外周血细胞免疫指标(包括CD3、CD4、CD8、CD4/CD8、CD19、CD56)及体液免疫指标(IgG、IgA、IgM、IgE、C3、C4)水平,出血亚组中30例大便隐血试验阳性患者大便隐血试验转阴后复查外周血细胞免疫指标及体液免疫指标。结果溃疡组患者外周血CD3、CD4、CD4/CD8、CD19、CD56、C3、C4水平较对照组降低,IgG水平较对照组升高(P<0.05);Hp+亚组患者外周血CD3、CD4、CD8、CD19、IgM、IgE水平较Hp-亚组升高,CD4/CD8较Hp-亚组降低(P<0.05);出血亚组患者外周血CD3、CD4水平、CD4/CD8较未出血亚组降低(P<0.05)。大便隐血试验阳性患者转阴后外周血CD3、CD4、CD8、CD19、CD56、C3、C4水平较治疗前升高,IgG、IgM水平较治疗前降低(P<0.05)。结论消化性溃疡患者存在免疫功能调节紊乱,幽门螺杆菌感染可促使机体产生强烈的免疫反应,急性出血后免疫功能处于抑制状态,止血后免疫功能有所恢复。
【关键词】消化性溃疡;幽门螺杆菌;消化性溃疡出血;细胞免疫;体液免疫
吴蓉,李国熊,李丽,等.消化性溃疡患者外周血细胞免疫及体液免疫功能变化分析[J].中国全科医学,2016,19(20):2481-2485.[www.chinagp.net]
WU R,LI G X,LI L,et al.Changes of cellular immune function and humoral immune function in peripheral blood of patients with peptic ulcer[J].Chinese General Practice,2016,19(20):2481-2485.
消化性溃疡是一种多发病、常见病,好发于胃和十二指肠。免疫因素是否参与了消化性溃疡的发生与发展,是目前国内外研究的焦点之一[1-2],且一直存在争议,免疫功能调节具有双向性,其亢进或低下与消化性溃疡的关系尚不清楚[3]。为此,本研究检测消化性溃疡患者外周血细胞免疫指标及体液免疫指标,观察消化性溃疡患者与体检健康者、是否感染幽门螺杆菌及是否出血与免疫功能指标的关系以及出血恢复期免疫功能指标的变化,探讨消化性溃疡与细胞免疫指标及体液免疫指标之间的关系。
1资料与方法
1.1临床资料选择2014年1月—2015年1月杭州师范大学附属医院门诊及住院的连续经胃镜确诊的消化性溃疡患者122例为溃疡组,其中男85例,女37例;年龄23~90岁,平均年龄(53.1±16.8)岁;胃溃疡50例,十二指肠球部溃疡52例,复合性溃疡20例;病程1个月~3年,平均病程(1.1±0.8)年。排除肝硬化或伴食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血、门静脉高压性胃病出血、恶性肿瘤、自身免疫性疾病、高血压、糖尿病、冠心病以及变态反应性疾病者。另选择同期体检中心体检健康者70例为对照组,其中男50例,女20例;年龄21~86岁,平均年龄(52.4±18.1)岁。对照组与溃疡组性别、年龄、体质指数、吸烟率、饮酒率比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表1)。本研究获得杭州师范大学附属医院医学伦理委员会批准,受试者均签署知情同意书。
表1对照组与溃疡组一般资料比较
Table 1Comparison of general data between control group and ulcer group

组别例数性别(男/女)年龄(岁)体质指数(kg/m2)吸烟〔n(%)〕饮酒〔n(%)〕对照组7050/2052.4±18.123.3±5.634(48.6)37(52.9)溃疡组12285/3753.1±16.822.4±4.860(49.2)58(47.5)χ2(t)值0.066-1.051a0.374a0.0070.503P值0.7980.3220.7230.9350.478
注:a为t值;吸烟定义为:每天吸烟不少于1支,持续1年,或总量不少于18包/年;饮酒定义为:每周饮酒不少于2次,白酒不少于50 g/次或者其他酒类不少于500 ml/次
1.2分组溃疡组患者根据是否感染幽门螺杆菌分为幽门螺杆菌阳性亚组(Hp+亚组)85例和幽门螺杆菌阴性亚组(Hp-亚组)37例,幽门螺杆菌测定采用胃黏膜组织切片苏木素-伊红(HE)染色法和14C呼气试验,其中一项阳性即为幽门螺杆菌感染;根据是否出血分为出血亚组58例和未出血亚组64例,入院前有呕血和/或排柏油样大便,呕吐物或大便隐血试验阳性判断为出血。Hp+亚组与Hp-亚组患者性别、年龄、体质指数、吸烟率、饮酒率、疾病种类、病程比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表2)。出血亚组与未出血亚组患者性别、年龄、体质指数、吸烟率、饮酒率、疾病种类、病程比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表3)。
1.3检测方法清晨空腹抽取溃疡组患者及对照组受试者外周静脉血2 ml加入乙二胺四乙酸二钾(EDTA-K2)抗凝管中,充分混匀后进行细胞免疫指标检测,同时抽取4 ml全血,3 500 r/min离心10 min(离心半径20.8 cm),分离血清,进行体液免疫指标检测。使用FACS Clibur 流式细胞仪(美国BD公司)和Cell Quest软件测定受试者外周血细胞免疫指标〔包括T淋巴细胞(CD3)、辅助性T细胞(CD4)、抑制性T细胞(CD8)、CD4/CD8、B淋巴细胞(CD19)、自然杀伤细胞(CD56)〕水平。采用Immage双光径浊度分析仪(美国Beckman-Coulter公司)测定血清体液免疫指标(包括免疫球蛋白IgG、IgA、IgM、IgE,补体C3、C4)水平。出血亚组中30例大便隐血试验阳性患者大便隐血试验转阴后复查外周血细胞免疫指标及体液免疫指标。
1.4治疗患者均予抑制胃酸、补液治疗,合并大出血休克患者输注红细胞悬液200~400 ml。Hp+亚组患者予抗幽门螺杆菌四联疗法,使用泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊(杭州中美华东制药有限公司,药品生产批号131104)40 mg口服,2次/d;胶体果胶铋胶囊(浙江得恩德制药有限公司,药品生产批号20131017)0.2 g口服,3次/d;克拉霉素分散片(江苏扬子江药业集团有限公司,药品生产批号1406041)0.5 g口服,2次/d;阿莫西林胶囊(香港澳美制药厂,药品生产批号19961)1.0 g口服,2次/d。青霉素过敏者予呋喃唑酮片(天津力生制药股份有限公司,药品生产批号1404009)0.1 g口服,2次/d替代治疗2周,停用抗生素,4周后复查胃镜及14C呼气试验。
2结果
2.1对照组与溃疡组外周血细胞免疫指标及体液免疫指标比较溃疡组外周血CD3、CD4、CD4/CD8、CD19、CD56、C3、C4水平较对照组降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);溃疡组外周血IgG水平较对照组升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);对照组与溃疡组外周血CD8、IgA、IgM、IgE水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表4)。
2.2Hp+亚组与Hp-亚组患者外周血细胞免疫指标及体液免疫指标比较Hp+亚组患者外周血CD3、CD4、CD8、CD19、IgM、IgE水平较Hp-亚组升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Hp+亚组患者外周血CD4/CD8较Hp-亚组降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Hp+亚组与Hp-亚组外周血CD56、IgG、IgA、C3、C4水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表5)。
2.3出血亚组与未出血亚组患者外周血细胞免疫指标及体液免疫指标比较出血亚组患者外周血CD3、CD4水平、CD4/CD8较未出血亚组降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);出血亚组与未出血亚组外周血CD8、CD19、CD56、IgG、IgA、IgM、IgE、C3、C4水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表6)。
2.4大便隐血试验阳性患者治疗前及转阴后外周血细胞免疫指标及体液免疫指标比较大便隐血试验阳性患者转阴后外周血CD3、CD4、CD8、CD19、CD56、C3、C4水平较治疗前升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);转阴后外周血IgG、IgM水平较治疗前降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);治疗前与转阴后外周血CD4/CD8、IgA、IgE水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表7)。
3讨论
淋巴细胞在免疫应答中起核心作用,T淋巴细胞亚群是构成机体免疫防御系统的重要细胞,免疫球蛋白及补体与淋巴细胞同样是机体免疫防御机制的重要组成部分,在体液免疫中起着重要作用。目前消化性溃疡病因尚未完全明了,较为明确的病因是幽门螺杆菌感染,幽门螺杆菌感染是否使机体免疫功能紊乱,导致消化性溃疡的发生,目前的研究结果并不一致[1-3]。

表2 Hp+亚组与Hp-亚组患者一般资料比较
注:a为t值;Hp+亚组为幽门螺杆菌阳性亚组,Hp-亚组为幽门螺杆菌阴性亚组

表3 出血亚组与未出血亚组患者一般资料比较
注:a为t值
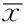
表4 对照组与溃疡组外周血细胞免疫指标及体液免疫指标比较( ±s)
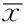
Table 5Comparison of the indexes of cellular immune function and humoral immune function in peripheral blood between Hp+ subgroup and Hp- subgroup

组别例数CD3(×106/L)CD4(×106/L)CD8(×106/L)CD4/CD8CD19(×106/L)CD56(×106/L)IgG(g/L)IgA(g/L)IgM(g/L)IgE(U/ml)C3(g/L)C4(g/L)Hp+亚组851159±518727±356433±2711.91±0.78233±123211±13011.91±2.822.36±0.791.21±0.77193±730.91±0.220.22±0.07Hp-亚组37780±323534±220255±1482.55±1.40168±83196±10912.90±3.942.50±1.050.93±0.46175±820.84±0.200.21±0.07t值5.2824.0105.123-2.8944.1020.852-1.362-0.8142.5921.9311.4300.718P值<0.001<0.001<0.0010.006<0.0010.3920.1620.4030.0140.0480.1550.474

Table 6Comparison of the indexes of cellular immune function and humoral immune function in peripheral blood between bleeding subgroup and non-bleeding subgroup

组别例数CD3(×106/L)CD4(×106/L)CD8(×106/L)CD4/CD8CD19(×106/L)CD56(×106/L)IgG(g/L)IgA(g/L)IgM(g/L)IgE(U/ml)C3(g/L)C4(g/L)出血亚组58848±515532±361314±1811.85±0.85181±108173±9612.21±3.502.42±1.081.07±0.68275±1280.84±0.220.22±0.06未出血亚组641127±473730±291396±2982.35±1.19221±120226±13712.18±3.082.35±0.701.12±0.70146±940.91±0.200.21±0.07t值-2.316-2.453-1.402-2.017-1.446-1.9050.0490.328-0.2851.477-1.303-0.523P值0.0240.0170.1660.0480.1530.0610.9610.7440.7770.1460.1970.602

Table 7Comparison of the indexes of cellular immune function and humoral immune function in peripheral blood of patients with positive fecal occult blood testing results between before treatment and after their testing results turned negative
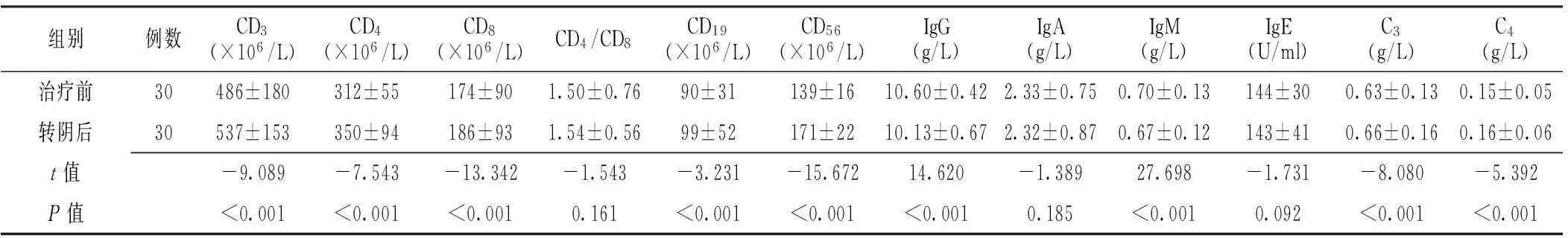
组别例数CD3(×106/L)CD4(×106/L)CD8(×106/L)CD4/CD8CD19(×106/L)CD56(×106/L)IgG(g/L)IgA(g/L)IgM(g/L)IgE(U/ml)C3(g/L)C4(g/L)治疗前30486±180312±55174±901.50±0.7690±31139±1610.60±0.422.33±0.750.70±0.13144±300.63±0.130.15±0.05转阴后30537±153350±94186±931.54±0.5699±52171±2210.13±0.672.32±0.870.67±0.12143±410.66±0.160.16±0.06t值-9.089-7.543-13.342-1.543-3.231-15.67214.620-1.38927.698-1.731-8.080-5.392P值<0.001<0.001<0.0010.161<0.001<0.001<0.0010.185<0.0010.092<0.001<0.001

综上所述,本研究结果说明免疫功能参与了消化性溃疡的发生、发展,临床可通过调节免疫功能达到治愈和预防消化性溃疡的目的。关于免疫功能紊乱与消化性溃疡之间的关系,尚待大样本研究进一步证实。
作者贡献:吴蓉进行课题设计与实施、资料收集整理、撰写论文、成文并对文章负责;李丽、周刚、吴建良、陈晶进行课题实施、评估、资料收集;李国熊进行质量控制及审校。
本文无利益冲突。
参考文献
[1]NISHIMOTO T,SATOH T,TAKEUCHI T,et al.Critical role of CD4(+)CD25(+)regulatory T cell in preventing murine autoantibody-mediated thrombocytopenia[J].Exp Hematol,2012,40(4):279-289.
[2] 徐勤燕,金文涛.消化性溃疡患者血清IL-2、IL-18和Gas检测的临床意义[J].放射免疫学杂志,2012,25(5):492-494.
XU Q Y,JIN W T.Clinical significance of changes on serum IL-2,IL-18 and Gastrin levels in patients with peptic ulcer[J].Journal of Radioimmunology,2012,25(5):492-494.


[4]聂韶华,祝扬,张敏,等.HP(+)DU患者外周血淋巴细胞亚群与胃粘膜组织急性炎症的关系[J].世界华人消化杂志,2000,8(5):590-592.
[5] CHENG H H,TSENG G Y,YANG H B,et al.Increased numbers of Foxp3-positive regulatory T cells in gastritis,peptic ulcer and gastric adenocarcinoma[J].World J Gastroenterol,2012,18(1):34-43.
[6]KINDLUND B,SJÖLING A,HANSSON M,et al.FOXP3-expressing CD4(+) T-cell numbers increase in areas of duodenal gastric metaplasia and are associated to CD4(+) T-cell aggregates in the duodenum of Helicobacter pylori-infected duodenal ulcer patients[J].Helicobacter,2009,14(3):192-201.

[8] RAGHAVAN S,QUIDING-JRBRINK M.Immune modulation by regulatory T cells in Helicobacter pylori-associated diseases[J].Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets,2012,12(1):71-85.
[9] COOK K W,LETLEY D P,INGRAM R J,et al.CCL20/CCR6-mediated migration of regulatory T cells to the Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa[J].Gut,2014,63(10):1550-1559.
[10] GRAY B M,FONTAINE C A,POE S A,et al.Complex T cell interactions contribute to Helicobacter pylori gastritis in mice[J].Infect Immun,2013,81(3):740-752.
[12] 刘建生,肖红兵,傅极.消化性溃疡出血期血清免疫球蛋白、补体和C-反应蛋白变化的意义[J].内科急危重症杂志,2001,7(3):126-127.
LIU J S,XIAO H B,FU J.Significance of changes in serum immunoglobulins,complements and C-reactive protein in peptic ulcer with hemorrhage[J].Journal of Internal Intensive Medicing,2001,7(3):126-127.
[13] 周鹏志,潘浩霖,陈安薇.消化性溃疡并出血患者外周血T淋巴细胞亚群及NK细胞的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2002,12(13):15-16.
ZHOU P Z,PAN H L,CHEN A W.Subclasses of T lymphocyte and natural kill cells from patients with peptic ulcer and gastrointinal bleeding[J].China Journal of Modern Medicine,2002,12(13):15-16.
[15] 王海滨,张景萍,郭峰,等.血细胞天然免疫粘附肿瘤细胞的现象及意义[J].中华微生物和免疫学杂志,2001,21(3):263-265.
WANG H B,ZHANG J P,GUO F,et al.The phenomena and the significance of erythrocytes lymphocytes and granulocytes immune-adhering tumor cells in self-plasma[J].Chinese Journal of Microbiology and Immunology,2001,21(3):263-265.
(本文编辑:陈素芳)
Changes of Cellular Immune Function and Humoral Immune Function in Peripheral Blood of Patients With Peptic Ulcer
WURong,LIGuo-xiong,LILi,etal.
DepartmentofGastroenterology,theAffiliatedHospitalofHangzhouNormalUniversity,Hangzhou310015,China
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo investigate the changes of cellular immune function and humoral immune function in peripheral blood of patients with peptic ulcer and the clinical significance.MethodsFrom January 2014 to January 2015,we enrolled 122 patients who were definitely diagnosed as peptic ulcer in the Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University as ulcer group,and enrolled 70 healthy people who received physical examination as control group.According to whether infection of helicobacter pylori occurred,the patients in ulcer group were divided into helicobacter pylori positive subgroup(Hp+subgroup)(n=85) and helicobacter pylori negative subgroup(Hp-subgroup)(n=37),and were divided into bleeding subgroup(n=58) and non-bleeding subgroup(n=64) according to whether bleeding occurred.The indexes of cellular immune function(including CD3,CD4,CD8,CD4/CD8,CD19and CD56) and indexes of humoral immune function(including IgG,IgA,IgM,IgE,C3 and C4) in peripheral blood were detected.In bleeding subgroup,30 patints who had positive results in fecal occult blood testing received reexamination of the indexes of immune function and humoral immune function in peripheral blood after fecal occult blood testing showed negative results.ResultsThe levels of CD3,CD4,CD4/CD8,CD19,CD56,C3 and C4 in peripheral blood were lower in ulcer group than those in control group,the levels of IgG in peripheral blood was higher in ulcer group than that in control group(P<0.05);the levels of CD3,CD4,CD8,CD19,IgM and IgE in peripheral blood were higher in Hp+ subgroup than those in Hp- subgroup,the CD4/CD8 in peripheral blood was lower in Hp+ subgroup than that in Hp- subgroup(P<0.05);the levels of CD3,CD4 and CD4/CD8 in peripheral blood were lower in bleeding subgroup than those in non-bleeding subgroup(P<0.05).The levels of CD3,CD4,CD8,CD19,CD56,C3 and C4 in peripheral blood were higher in patients who had positive results in fecal occult blood testing first but later turned negative than those before treatment(P<0.05);the levels of IgG,IgM in peripheral blood were lower in patients who had positive results in fecal occult blood testing first but later turned negative than those before treatment(P<0.05).ConclusionPatients with peptic ulcer have disorder in immune function,and infection of helicobacter pylori may induce strong immune reactions.Acute hemorrhage may cause a inhibitory state of immune function which may be relieved after hemostasis.
【Key words】Peptic ulcer;Helicobacter pylori;Peptic ulcer hemorrhage;Cellular immunity;Humoral immunity
通信作者:李国熊,310015浙江省杭州市,杭州师范大学附属医院消化内科;E-mail:guoxiongli849@hotmail.com
【中图分类号】R 573.1
【文献标识码】B
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.20.025
(收稿日期:2015-11-12;修回日期:2016-03-20)
·临床诊疗提示·
