甘丙肽及其受体亚型在人乳腺癌标本中的表达
2016-05-30邓佳卉徐志卿戚晓东
张 帅 邓佳卉 徐志卿 戚晓东*
(1.安徽医科大学北京军区总医院临床学院乳腺科,北京100700;2.首都医科大学三博脑科医院功能神经外科,北京 100093;3. 首都医科大学基础医学院神经生物学系,北京 100069)
甘丙肽及其受体亚型在人乳腺癌标本中的表达
张帅1邓佳卉2徐志卿3戚晓东1*
(1.安徽医科大学北京军区总医院临床学院乳腺科,北京100700;2.首都医科大学三博脑科医院功能神经外科,北京 100093;3. 首都医科大学基础医学院神经生物学系,北京 100069)
【摘要】目的 探索甘丙肽(galanin,GAL)及其受体亚型(galanin receptor1、2、3, GALR1、2、3)在乳腺癌及癌周组织中的表达情况,分析其与不同临床治疗方法的关系。方法qRT-PCR法检测乳腺癌及癌周组织的GAL及其3种受体亚型mRNA的表达情况。Western blotting分析GAL在乳腺癌及癌周组织中的表达情况。t检验分析不同术前处理组之间癌组织的GAL及其受体亚型表达的变化,而配对t检验用于分析同一术前处理组内癌组织和癌周组织之间GAL及其受体亚型表达的变化。结果在术前无治疗组中,癌组织GAL mRNA及GAL蛋白比癌旁组织高(P<0.05,P<0.01),而GALR1、GALR2、GALR3 mRNA比癌旁组织低(P<0.05,P<0.05,P<0.01)。经过新辅助化学治疗(neoadjuvant chemotherapy, NAC)与高强度聚焦超声射频消融术(high intensity focused ultrasound, HIFU)治疗后,癌组织与癌旁组织相比,GAL及其受体mRNA和蛋白差异无统计学意义,但是与术前无治疗组癌组织相比,GAL mRNA及GAL蛋白明显降低(P<0.05)。此外,经过NAC治疗后癌组织中GALR3 mRNA要明显高于术前无治疗组的癌组织(P<0.01)。结论GAL及其受体亚型在乳腺癌中存在异常表达,并与临床治疗方法有关,可能为乳腺癌的诊断、治疗及预后提供了新的生物学标志。
【关键词】乳腺癌;甘丙肽;甘丙肽受体亚型
乳腺癌是国内外女性最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,且其发病率仍呈上升趋势[1-2]。乳腺癌的综合治疗方案制定目前主要依据雌激素受体(estrogen receptor, ER)、孕激素受体(progesterone receptor, PR)、人表皮生长因子受体-2(human epidermal growth factor receptor-2, Her-2)、细胞增生核抗原(cell proliferation associated nuclear antigen, Ki-67)等分子标志物的检测。其中针对Her-2这一靶点而开发的曲妥珠单抗在临床的应用开启了乳腺癌的靶向治疗时代[3],但是针对三阴性乳腺癌和其他难治性乳腺癌,仍没有理想的治疗靶点和特异性药物,相关药物靶点的寻找和特异性药物的开发仍然是目前研究的热点之一。
甘丙肽(galanin,GAL)是一种由30个氨基酸残基构成的神经肽,已知的3种受体亚型(galanin receptor1、2、3,GALR1、2、3)均为G蛋白偶联型受体[4]。除在神经系统中广泛表达外,研究[5-6]显示GAL及其受体亚型在多种肿瘤中均有表达,且在诊断、治疗、预后和细胞生物学特性等方面扮演着重要的角色。然而,目前国内外针对GAL及其受体亚型与乳腺肿瘤的关系的研究仅有少量报道[7-8],在乳腺肿瘤及瘤周组织中的表达情况及与临床资料的关系尚未明确。本研究即对其在乳腺癌及癌周组织中的表达情况进行了检测,分析与不同临床治疗方法之间的关系。
1材料与方法
1.1临床标本
选取2015年2月至2015年10月于北京军区总医院乳腺中心术前经穿刺病理确诊为乳腺癌并行手术患者19例(表1)。均于术中切取肿瘤及瘤周乳腺组织标本,所取标本立即使用干冰冻存。本研究经医院伦理委员会批准,所有患者知情同意。
1.2主要试剂
RNA提取试剂盒(Qiagen公司,德国);荧光定量PCR试剂盒(ABI公司,美国);反转录试剂盒(Invitrogen公司,美国);BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(Pierce公司,美国),甘内肽小鼠抗人单克隆抗体(Sigma公司,美国),β-actin小鼠抗人单克隆抗体(Sigma公司,美国),HRP二抗(Amersham公司,美国),Western blotting相关试剂(普利莱基因技术有限公司,中国)。

表1 乳腺癌患者信息
ER:estrogen receptor; PR:progesterone receptor; Her-2:human epidermal growth factor receptor-2; Ki-67:cell proliferation associated nuclear antigen; HIFU:high intensity focused ultrasound; NAC:neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
1.3主要方法
1.3.1实时荧光定量PCR检测GAL及其受体GALR1、GALR2和GALR3 mRNA的量
按照Qiagen公司RNA提取试剂盒操作说明提取制备总RNA,应用反转录试剂盒合成cDNA。设计并验证人GAL及其受体引物(表2),引物均由Invitrogen公司合成。GAL及其受体GALR1、GALR2和GALR3表达用相对定量PCR的SYBR Green法检测,每例重复3次实验。以术前无治疗组的癌周组织mRNA的相对变化的倍数作为100%参照。

表2 甘丙肽及其受体引物
1.3.2蛋白质提取和Western blotting法检测GAL蛋白表达量
提取乳腺组织总蛋白,经BCA法定量,调整样本为相同蛋白浓度,取10 μL相同总量蛋白上样,经SDA-PAGE凝胶电泳,转至PVDF膜上,鼠抗人GAL (1∶100稀释),内参GAPDH (1∶5 000稀释),4 ℃孵育过夜,室温孵育二抗1 h,显影曝光并采集图像,通过Image J软件分析各条带灰度值。
1.4统计学方法

2结果
2.1乳腺癌组织中GALmRNA的表达
术前未经治疗的乳腺癌组织中GALmRNA表达显著高于癌旁组织(P<0.05),而经过新辅助化学治疗(neoadjuvant chemotherapy, NAC)或高强度聚焦超声射频消融术(high intensity focused ultrasound, HIFU)治疗的乳腺癌组织中GALmRNA表达与癌旁组织相比差异无统计学意义,但是明显低于未经治疗的乳腺癌组织(P<0.05),详见图1。
2.2GAL蛋白在乳腺癌组织中的表达
术前未经治疗的乳腺癌组织中GAL蛋白表达水平显著高于癌旁组织(P<0.01),而经过NAC或HIFU治疗的乳腺癌组织中GAL蛋白表达与癌旁组织相比差异无统计学意义,但是明显低于未经治疗的乳腺癌组织(P<0.05),详见图2。
2.3乳腺癌组织中GALR1 mRNA的表达
术前未经治疗的乳腺癌组织中GALR1 mRNA表达显著低于癌旁组织(P<0.05),而经过NAC或HIFU治疗的乳腺癌组织中GALR1 mRNA表达与癌旁组织相比差异无统计学意义(图3)。

图1 乳腺癌组织中GAL mRNA的表达
*P<0.05;#P<0.05; GAL:galanin; HIFU:high intensity focused ultrasound; NAC:neoadjuvant chemotherapy; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
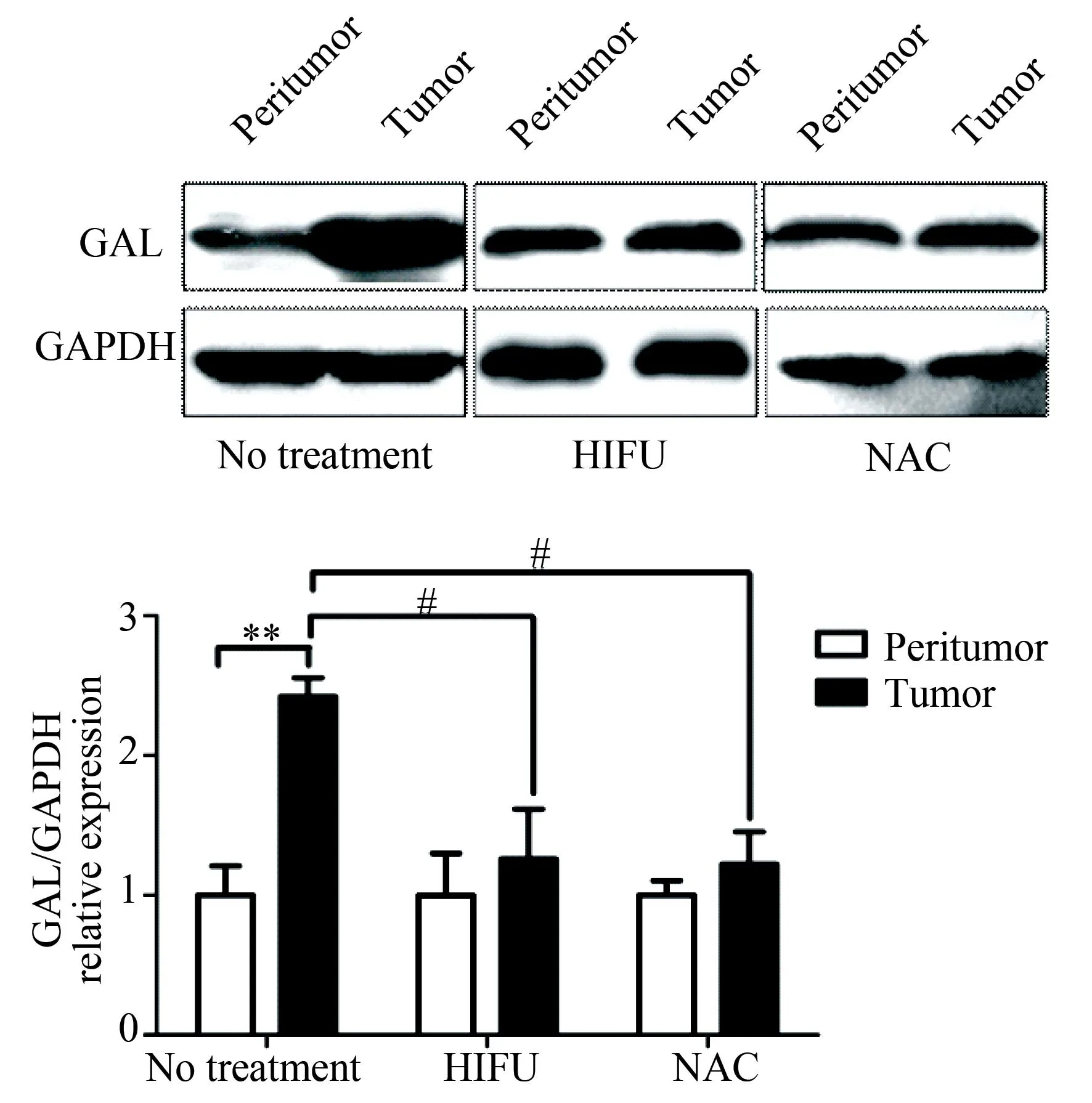
图2 Western blotting法检测乳腺癌组织中
**P<0.01;#P<0.05; GAL:galanin;HIFU:high intensity focused ultrasound; NAC:neoadjuvant chemotherapy; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.

图3 乳腺癌组织中GALR1 mRNA的表达
*P<0.05; GALR:galanin receptor;HIFU:high intensity focused ultrasound; NAC:neoadjuvant chemotherapy; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
2.4乳腺癌组织中GALR2 mRNA的表达
术前未经治疗的乳腺癌组织中GALR2 mRNA表达显著低于癌旁组织(P<0.05),而经过NAC或HIFU治疗的乳腺癌组织中GALR2 mRNA表达与癌旁组织相比差异无统计学意义(图4)。

图4 乳腺癌组织中GALR2 mRNA的表达
*P<0.05; GALR:galanin receptor; HIFU:high intensity focused ultrasound; NAC:neoadjuvant chemotherapy; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
2.5乳腺癌组织中GALR3 mRNA的表达
术前未经治疗的乳腺癌组织中GALR3 mRNA表达显著低于癌旁组织(P<0.01),而经过NAC或HIFU治疗的乳腺癌组织中GALR3 mRNA表达略低于癌旁组织但差异无统计学意义,经过NAC治疗后癌组织中GALR3 mRNA要明显高于术前无治疗组的癌组织(P<0.01),详见图5。
3讨论
研究[4]显示多种非神经内分泌肿瘤中都有神经肽及其受体表达。这些肽和受体为肿瘤的诊断、同位素示踪和具有细胞毒性的肽类似物治疗提供了分子学依据。其表达与肿瘤的分化程度及侵袭性相关,其促进或者抑制癌细胞增生活性的作用,有指导治疗的价值。
GAL在不同肿瘤中有着不同的表达情况与临床意义。如Kim等[6]报道结肠腺癌中GAL与GALmRNA要高于癌旁组织,且其表达会随着肿瘤大小的增长与分期的增加而明显升高,并与患者预后相关。Sugimoto等[9]报道头颈部鳞癌中GALmRNA水平是升高的。目前针对GAL及其受体系统与乳腺癌关系的研究很少,Ormandy等[7]报道甘丙肽基因定位于11q13,该位点在乳腺癌中常发生扩增。本研究中,在术前无治疗组的癌组织中GAL及GALmRNA水平比癌周组织的要高,其可能与基因扩增有关。
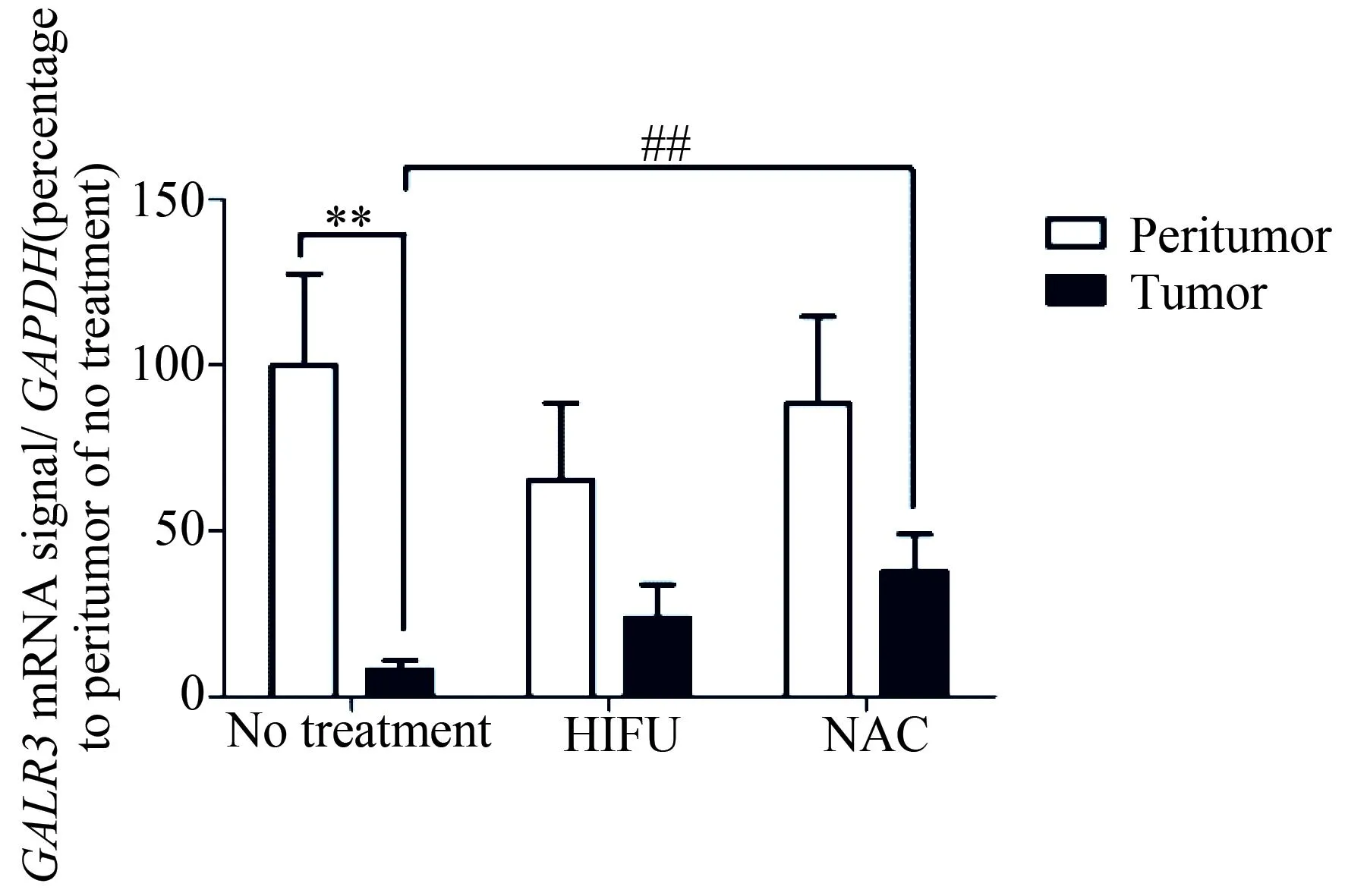
图5 乳腺癌组织中GALR3 mRNA的表达
**P<0.01;##P<0.01; GALR:galanin receptor; HIFU:high intensity focused ultrasound; NAC:neoadjuvant chemotherapy; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Chung等[8]在乳腺癌及多种其他癌细胞系中发现GAL受体基因-GALR2基因启动子存在过度甲基化的现象,这部分解释了GALR2的mRNA显著低于癌旁组织的原因。在人头颈部鳞癌中,GALR1[10]及GALR2[11]分别被证明有抑制细胞增生和诱导凋亡的作用,本研究中GAL及GALmRNA升高并伴随受体mRNA表达降低的现象,是否因为配体的高表达而引起受体的代偿性下调,或由于受体的下调而导致配体的代偿性高表达,及其与癌细胞增生或凋亡的关系,值得进一步的研究。
乳腺癌有多个亚克隆细胞群,不同的细胞群对不同治疗方案有不同的敏感性,因此在治疗过程中,肿瘤分子表达的特征可能发生改变[12]。GALR1[13]和GALR2[14]与结肠癌对特定化学治疗药物的敏感性有关,HIFU治疗也会改变癌细胞的分子表达特征[15],这可能解释了在NAC与HIFU组癌组织中3种受体亚型的mRNA虽然降低但差异无统计学意义,GAL及GALmRNA升高但差异亦无统计学意义,且明显低于术前无治疗组的现象。此外,本研究发现经过NAC治疗后癌组织中GALR3 mRNA要明显高于术前无治疗组的癌组织,GALR3是否也与乳腺癌化学治疗敏感性有关,尚需要进一步研究。综上,笔者推测GAL及其受体系统参与了乳腺癌对不同治疗方案反应的差异性,但其表达情况及与临床治疗方法的关系仍需进一步探讨,相关的研究具有一定的临床指导意义。
总之,本研究显示了GAL及其受体亚型在乳腺癌中存在差异表达,且与临床治疗方法相关,该研究可能为乳腺癌的诊断、治疗及预后提供了新的资料。考虑到本研究样本量较少,与患者临床及病理资料的相关性未能明确,今后,本课题组将进一步收集样本,完善患者临床及病理资料,进一步阐明GAL及其受体亚型在乳腺癌中表达的临床意义。
4参考文献
[1] DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2013 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2014, 64(1): 52-62.
[2] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade P D, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-132.
[3] Ahmed S, Sami A, Xiang J. HER2-directed therapy: current treatment options for HER2-positive breast cancer [J]. Breast Cancer, 2015, 22(2):101-116.
[4] Lang R, Gundlach A L, Kofler B. The galanin peptide family: receptor pharmacology, pleiotropic biological actions, and implications in health and disease [J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2007, 115(2):177-207.
[5] Rauch I, Kofler B. The galanin system in cancer [J]. EXS, 2010, 102: 223-241.
[6] Kim K Y, Kee M K, Chong S A, et al. Galanin is up-regulated in colon adenocarcinoma [J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2007, 16(11): 2373-2378.
[7] Ormandy C J, Lee C S, Ormandy H F, et al. Amplification, expression, and steroid regulation of the preprogalanin gene in human breast cancer [J]. Cancer Res, 1998, 58(7): 1353-1357.
[8] Chung W, Kwabi-Addo B, Ittmann M, et al. Identification of novel tumor markers in prostate, colon and breast cancer by unbiased methylation profiling [J]. PLoS One, 2008, 3(4): e2079.
[9] Sugimoto T, Seki N, Shimizu S, et al. The galanin signaling cascade is a candidate pathway regulating oncogenesis in human squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 2009, 48(2): 132-142.
[10] Kanazawa T, Iwashita T, Kommareddi P, et al. Galanin and galanin receptor type 1 suppress proliferation in squamous carcinoma cells: activation of the extracellular signal regulated kinase pathway and induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors [J]. Oncogene, 2007, 26(39): 5762-5771.
[11] Kanazawa T, Misawa K, Misawa Y, et al. G-protein-coupled receptors: next generation therapeutic targets in head and neck cancer? [J]. Toxins (Basel), 2015, 7(8): 2959-2984.
[12] Norum J H, Andersen K, Sorlie T. Lessons learned from the intrinsic subtypes of breast cancer in the quest for precision therapy [J]. Br J Surg, 2014, 101(8): 925-938.
[13] Stevenson L, Allen W L, Turkington R, et al. Identification of galanin and its receptor GalR1 as novel determinants of resistance to chemotherapy and potential biomarkers in colorectal cancer [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18(19): 5412-5426.
[14] Kim J C, Lee H C, Cho D H, et al. Genome-wide identification of possible methylation markers chemosensitive to targeted regimens in colorectal cancers [J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2011, 137(10): 1571-1580.
[15] Huang X, Yuan F, Liang M, et al. M-HIFU inhibits tumor growth, suppresses STAT3 activity and enhances tumor specific immunity in a transplant tumor model of prostate cancer [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(7): e41632.
编辑孙超渊
Expression of galanin and its receptor subtypes in human breast cancer
Zhang Shuai1,Deng Jiahui2,Xu Zhiqing3,Qi Xiaodong1*
(1.DepartmentofBreast,theMilitaryGeneralHospitalofBeijing,ClinicalSchoolofAnhuiMedicalUniversity,Beijing100700,China; 2.DepartmentofFunctionalNeurosurgery,SanboBrainHospital,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100093,China; 3.DepartmentofNeurobiology,SchoolofBasicMedicalSciences,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100069,China)
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo determine the expression of galanin(GAL) and galanin receptor 1、2、3 (GALR1、2、3) in breast cancer and the paired peritumoral tissues; To analyze the relationship between the different clinical therapies and the expression of galanin and its receptor subtypes. MethodsqRT-PCR was performed to detect the mRNA level of galanin and its three receptor subtypes in breast cancer and the paired peritumoral tissues. Western blotting was carried out to detect the GAL protein level in breast cancer and the paired peritumoral tissues. t-test was used to analyze the expression of galanin and its three receptor subtypes in cancer tissues of different groups; while paired t-test was performed to analyze the expression of galanin and its three receptor subtypes in breast cancer and the paired peritumoral tissues of the same group. ResultsThe GAL mRNA and protein levels of cancer tissues were higher than the paired peritumoral tissues in the group of no preoperative treatment (P<0.05, P<0.01), whereas the mRNA levels of GALR1, GALR2 and GALR3 were lower than the paired peritumoral tissue (P<0.05, P<0.05, P<0.01). In the NAC and HIFU groups, there were no significant differences in GAL protein, GAL and its receptors mRNA levels between the cancer and the paired peritumoral tissues (P<0.05, P<0.05, P<0.01). However, the GAL protein and GAL mRNA levels were lower than the group of no preoperative treatment (P<0.05). In addition, the GALR3 mRNA level was higher than the group of no preoperative treatment in the NAC group (P<0.01). ConclusionThe abnormal expression of galanin and its receptor subtypes in breast cancer was relevant to different clinical therapies, which might be used as a potential biomarker for breast cancer diagnosis, therapy and prognosis.
【Key words】breast cancer; galanin; galanin receptor subtypes
(收稿日期:2016-03-10)
【中图分类号】R 739.9
[doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2016.02.020]
*Corresponding author, E-mail:qixiaodongbj@sina.com
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(31171032)。This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(31171032).
网络出版时间:2016-04-1221∶13网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3662.r.20160412.2113.032.html
· 基础研究 ·
