k元(n-1)方体子网络可靠性的近似评估方法
2024-01-09冯凯李建德姬张建
冯凯,李建德,姬张建
元(-1)方体子网络可靠性的近似评估方法
冯凯*,李建德,姬张建
(山西大学 计算机与信息技术学院,太原 030006)(∗通信作者电子邮箱fengkai@sxu.edu.cn)
多处理器系统互连网络的拓扑性质对系统功能的实现起着重要的作用。元方体网络的子网络可靠性是以元方体为拓扑结构构建的多处理器系统处理计算任务时需要考虑的一个重要因素。为了精确高效地度量概率故障条件下元方体中元(-1)方体子网络的可靠性,提出基于反向传播(BP)神经网络的元(-1)方体子网络可靠性的近似评估方法。首先,利用蒙特卡洛仿真方法和元(-1)方体子网络可靠性的已有上下界给出用于训练BP神经网络的数据集的生成方法;其次,基于生成的训练数据集构造用于评估元(-1)方体子网络可靠性的BP神经网络模型;最后,对BP神经网络模型得出的元(-1)方体子网络可靠性的近似评估结果进行了分析,并与近似计算公式和基于蒙特卡洛的评估方法的结果进行了对比。与近似计算公式相比,所提方法得出的结果更为精确;与基于蒙特卡洛的评估方法相比,所提方法的评估耗时平均减少了约59%。实验结果表明,所提方法在兼顾精度和效率方面具有一定优势。
多处理器系统;互连网络;元方体;子网络可靠性;反向传播神经网络
0 引言
科学与工程计算领域的许多问题都有庞大的信息量和计算量,如流体动力学分析、社会经济预测、材料建模与设计等,这些课题对计算性能提出了极高的要求。为了满足人们对计算能力日益增长的需求,利用以某种模式连接的多处理器分摊任务进行协同并行计算是一种有效的解决方案,多处理器系统应运而生。随着多处理器系统规模的不断增大,系统功能的实现越来越依赖于它的支撑通信和数据交互的连接模式(即系统的互连网络,其中系统中的处理器用点表示,处理器之间的通信线路用边表示)。
对于一些特定的用户任务,多处理器系统只需指派系统的某个子网络(具有与系统互连网络相同的拓扑性质,但规模较小的网络)执行,不仅可以减少资源消耗,还可以避免大规模网络有效性较差的缺点。由于实际构建的大规模多处理器系统中发生故障是不可避免的,网络中较小规模子网络的可靠性研究对系统实际应用至关重要。

1 准备工作
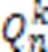
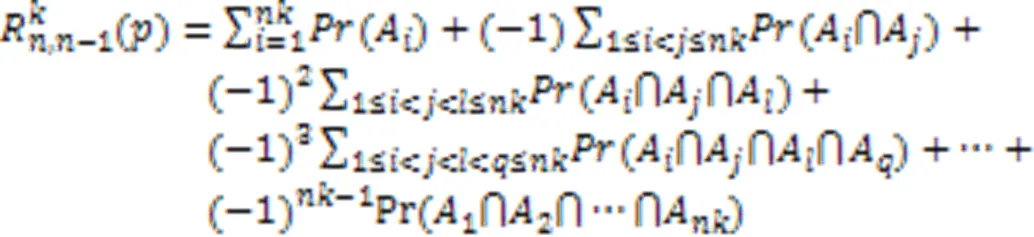




Tab.1 Validity analysis on upper and lower bounds of

2 本文方法
2.1 方法介绍
BP神经网络是处理非线性问题的有效工具,可以通过监督学习解决回归问题。BP神经网络的结构分为输入层、隐藏层和输出层,它利用链式法则通过反向传播更新网络参数,以减小损失函数数值,完成模型的训练。Hornik等[23]在理论上证明,构造一个3层神经网络能够以任意精度逼近任何非线性函数。给定训练集,BP神经网络可以以较高精度实现从输入到输出的映射功能。
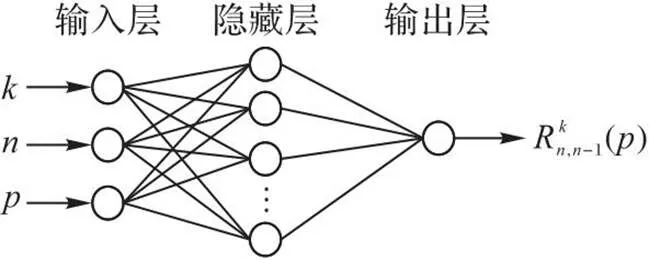
图1 用于评估子网络可靠性的 BP神经网络结构
2.2 数据集生成方法
算法1 训练数据集生成算法。
10) else
19) end if
20) end for
24) else
26) end if
27) end for
29) end if
30) end for
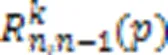

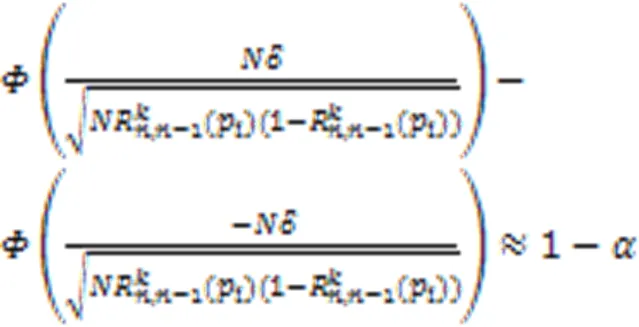
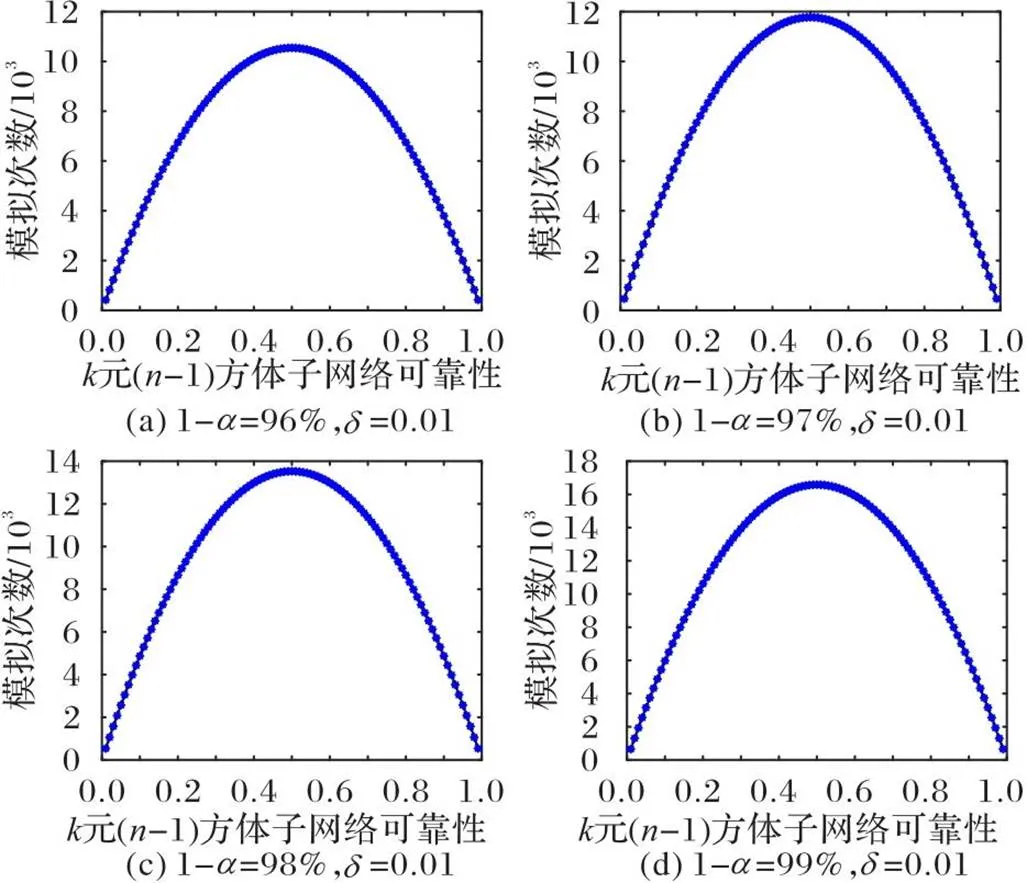
图2 不同置信度下最小模拟次数计算结果
2.3 BP神经网络模型
2.3.1隐层节点数的选择

图3 不同隐层节点数下BP神经网络的预测精度对比
2.3.2初始学习率的选择

从图4可以看出,对于不同的训练数据集,不同初始学习率对BP神经网络模型训练时长的影响均不明显。本文选取初始学习率为0.15。

图4 不同初始学习率下BP神经网络的训练时间对比
2.3.3模型结果分析

表2 不同数据集的测试集上的均方根误差的平均值

图5 BP神经网络模型的评估结果
2.3.4对比实验结果
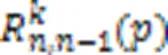

图6 不同评估结果与真值的对比
表3两种方法的评估时长及RMSE

Tab.3 Evaluation time and RMSE of two methods
3 结语
随着多处理器系统应用领域的不断扩大,系统互连网络的设计需求日趋多样化,许多新型互连网络拓扑结构被相继提出。利用基于BP神经网络的子网络可靠性的近似评估方法对新型互连网络的子网络可靠性进行评估值得进一步研究,这将有助于新型互连网络在多处理器系统中的应用和推广。
[1] DAS C R, KIM J. A unified task-based dependability model for hypercube computers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 1992, 3(3): 312-324.
[2] CHANG Y, BHUYAN L N. A combinatorial analysis of subcube reliability in hypercubes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 1995, 44(7): 952-956.
[3] WU X, LATIFI S. Substar reliability analysis in star networks [J]. Information Sciences, 2008, 178(10): 2337-2348.
[4] LIN L, XU L, ZHOU S, et al. The reliability of subgraphs in the arrangement graph[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2015, 64(2): 807-818.
[5] LI X, ZHOU S, XU X, et al. The reliability analysis based on subsystems of (,)-star graph[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2016, 65(4): 1700-1709.
[6] HUANG Y, LIN L, WANG D. On the reliability of alternating group graph-based networks[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2018, 728: 9-28.
[7] ZHANG Q, XU L, ZHOU S, et al. Reliability analysis of subsystem in dual cubes [J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2020, 816: 249-259.
[8] FENG K, MA X, WEI W. Subnetwork reliability analysis of bubble-sort graph networks[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2021, 896: 98-110.
[9] LV M, FAN J, FAN W, et al. Fault diagnosis based on subsystem structures of data center network BCube [J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2022, 71(2): 963-972.
[10] LIU X, ZHOU S, LIU J, et al. Reliability analysis of the cactus-based networks based on subsystem[J]. The Computer Journal, 2022,2022: No.bxac163.
[11] ANDERSON E, BROOKS J, GRASSL C, et al. Performance of the CRAY T3E multiprocessor [C]// Proceedings of the 1997 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing. New York: ACM, 1997: 1-17.
[12] ADIGA N R, BLUMRICH M A, CHEN D, et al. Blue Gene/L torus interconnection network[J]. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 2005, 49(2/3): 265-276.
[13] FENG K, JI Z, WEI W. Subnetwork reliability analysis in-ary-cubes [J]. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 2019, 267: 85-92.
[14] LV Y, FAN J, HSU D F, et al. Structure connectivity and substructure connectivity of-ary-cube networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 433/434: 115-124.
[15] LIU A, WANG S, YUAN J, et al. The h-extra connectivity of-ary-cubes[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2019, 784: 21-45.
[16] WANG S, ZHANG G, FENG K. Fault tolerance in-ary-cube networks [J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2012, 460: 34-41.
[17] YANG Y, LI J, WANG S. Embedding various cycles with prescribed paths into-ary-cubes[J]. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 2017, 220: 161-169.
[18] 冯凯,李婧.元方体的子网络可靠性研究[J]. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(7): 31-36.(FENG K, LI J. Study on subnetwork reliability of-ary-cubes [J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(7): 31-36.)
[19] LV M, FAN J, CHEN G,et al. The reliability analysis of-ary-cube networks [J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2020, 835: 1-14.
[20] CHEN X B. Paired 2-disjoint path covers of faulty-ary-cubes[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2016, 609(Pt 2): 494-499.
[21] 谢丽霞,王志华. 基于布谷鸟搜索优化BP神经网络的网络安全态势评估方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2017, 37(7): 1926-1930.(XIE L X, WANG Z H. Network security situation assessment method based on cuckoo search optimized back propagation neural network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2017, 37(7): 1926-1930.)
[22] 戴宏亮,罗裕达. 基于蝙蝠算法优化反向传播神经网络模型的无线网络流量预测[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(S1):185-188.(DAI H L, LUO Y D. Wireless network traffic prediction based on bat algorithm optimized back propagation neural network model[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(S1): 185-188.)
[23] HORNIK K, STINCHCOMBE M, WHITE H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators[J]. Neural Networks, 1989, 2(5): 359-366.
[24] 盛骤,谢式千,潘承毅. 概率论与数理统计[M]. 4版. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2008: 119-126.(SHENG Z, XIE S Q, PAN C Y. Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2008: 119-126.)
Approximate evaluation method of-ary(-1)-cube subnetwork reliability
FENG Kai*, LI Jiande, JI Zhangjian
(,,030006,)
The implementation of the functions of a multiprocessor system relies heavily on the topological properties of the interconnection network of this system. The subnetwork reliability of-ary-cube network is an important factor that needs to be taken into account when the computing tasks are processed by the multiprocessor systems constructed with-ary-cube as topological structure. In order to accurately and efficiently measure the reliability of the-ary (-1)-cube subnetwork in a-ary-cube under the probabilistic fault condition, an approximate method to evaluate the reliability of-ary (-1)-cube subnetwork based on the Back Propagation (BP) neural network was proposed. Firstly, the generation method for dataset to train BP neural network was given by the aid of the Monte Carlo simulation method and the known upper and lower bounds on the reliability of the-ary (-1)-cube subnetwork. Then, the BP neural network model for evaluating the reliability of the-ary (-1)-cube subnetwork was constructed on the basis of the generated training dataset. Finally, the approximate evaluation results of the-ary (-1)-cube subnetwork reliability obtained by the BP neural network model were analyzed and compared with the results obtained by the approximate calculation formula and the evaluation method based on Monte Carlo simulation. The results obtained by the proposed method were more accurate compared with the approximate calculation formula, and the evaluation time of the proposed method was reduced by about 59% on average compared with the evaluation method based on Monte Carlo simulation. Experimental results show that the proposed method has certain advantages in balancing accuracy and efficiency.
multiprocessor system; interconnection network;-ary-cube; subnetwork reliability; Back Propagation (BP) neural network
This work is partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61502286), Basic Research Program of Shanxi Province (20210302123438).
FENG Kai, born in 1987, Ph. D., associate professor. His research interests include fault tolerance of interconnection network, graph theory and its applications.
LI Jiande, born in 1997, M. S. candidate. His research interests include fault tolerance of interconnection network.
JI Zhangjian, born in 1983, Ph. D., associate professor. His research interests include pattern recognition, machine learning.
TP393.02
A
1001-9081(2023)12-3875-07
10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022111719
2022⁃11⁃18;
2023⁃04⁃10;
2023⁃04⁃30。
国家自然科学基金资助项目(61502286);山西省基础研究计划项目(20210302123438)。
冯凯(1987—),男,山西临汾人,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向:互连网络的容错性、图论及其应用;李建德(1997—),男,山西太原人,硕士研究生,CCF会员,主要研究方向:互连网络的容错性;姬张建(1983—),男,陕西澄城人,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向:模式识别、机器学习。
