矩形hBN层状光栅中的Goos-Hänchen位移
2023-12-19招月金高周胜
招月,金高,周胜,2
矩形hBN层状光栅中的Goos-Hänchen位移
招月1,金高1,周胜1,2
(1. 哈尔滨师范大学 物理与电子工程学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150025;2. 广州航海学院 基础教学部,广东 广州 510725)
六方氮化硼(hBN)是一种天然的范德瓦尔斯双曲材料,在两个红外波长范围内表现出双曲色散关系,可用于加强光与物质的相互作用.在目前的工作中,设计了矩形层状光栅hBN(RLG)结构,通过数值模拟发现能够增大Goos-Hänchen(GH)位移的同时具有较高的反射率.利用电场分布直接揭示了GH位移增强归因于RLG结构中的高局域的电场.值得注意的是,GH峰值的频率和宽度也可以由入射光偏振,hBN层各向异性轴方向的高度和厚度等参数来调控.基于GH位移的RLG结构传感特性,灵敏度高达1.401 μm/ RIU.这些结果可以为高灵敏光学传感器、光学开关和光电子探测器的设计提供有益参考.
Goos-Hänchen位移;hBN光栅;光学传感器
在几何光学中,入射光束和反射光束严格满足反射定律,但在1947年,Goos和Hänchen[1]两位科学家在实验中首次发现光束在两种界面上发生全反射时,反射光束相对于几何光学反射光束会产生横向位移,后来人们把这种现象称为Goos-Hänchen(GH)位移[2].1948年Artmann[3]在物理上提出了稳态相位法,对这种现象做出了理论解释,同时还给出了求GH位移的公式
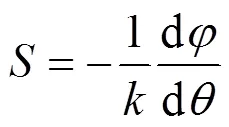
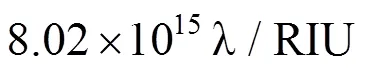
GH位移可以被介电光栅层中导模共振的激发增强[18-21].例如:LI[22]等研究了SLG、介电光栅、银膜和1DPC杂化结构中的GH位移,其GH位移可以被来自于金属层中的SPR和1DPC中的波导模式联合效应在特定角度下最大增大到波长的7430倍,证实了GH位移可以通过改变SLG的费米能量来调整.ZHU[23]等研究了单层二硫化钼和对称/不对称介电光栅组合结构中反射波的生长激素位移.当单层二硫化钼接到对称和非对称介电光栅层上时,GH位移可以被显著增强,其增强可归因于介电光栅层中导模共振的激发.单层二硫化钼不对称光栅实现了高达9490倍的波长.巨大的GH位移往往伴随着极低的反射率,这在一定程度上给研究造成了阻碍,这种情况一般采用弱测量的方法进行精密测量.弱测量是被Aharonov[24]等在1988年首次提出的,他们认为测量得到的弱值可以远远大于可观测量的范围.直到1991年,Ritchie[25]等在实验中验证了这一理论的正确性.弱测量为量子测量提供了新方法,更重要的是,弱测量的弱值放大效应为微弱信号的精密测量提供了崭新的思路.但是,对弱信号的捕捉、放大和检测也必然需要很大的工作量.
本文利用中心光束法,研究了矩形hBN层状光栅增强GH位移的可能性.研究发现,GH位移可以有效地被该结构增大,特别是在GH位移达到峰值时,相应波长上的反射率[26]也很高,这克服了GH值和反射率之间的困难.
1 理论模型
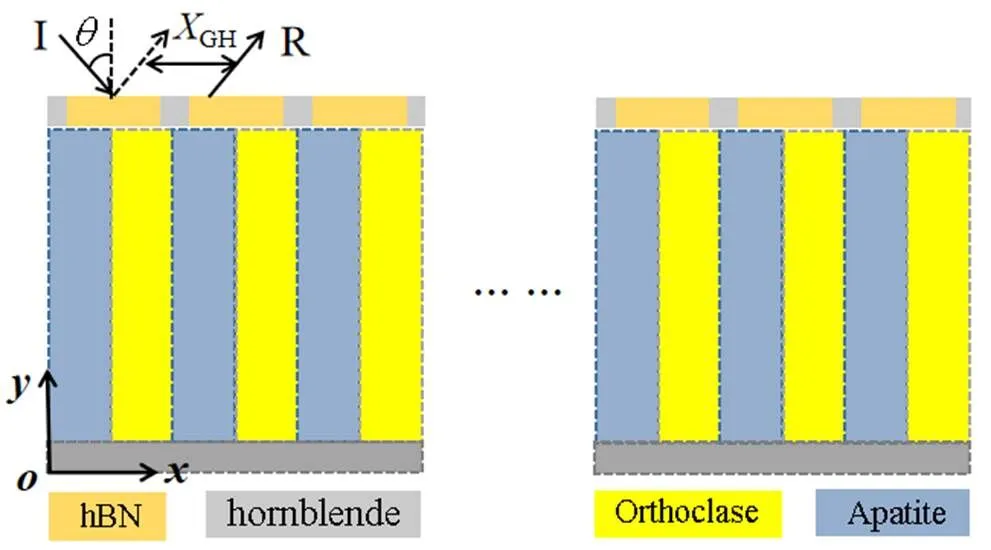
图1 矩形hBN层状光栅结构示意图
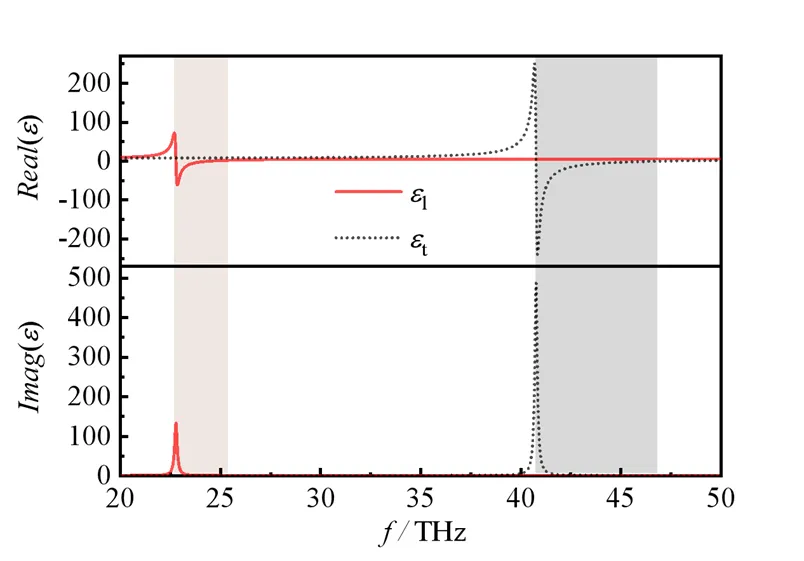
图2 不同频率情况下hBN的介电常数
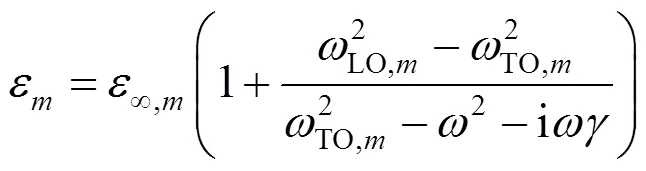
中心光束法是计算GH位移的一种有效方法.基于斯奈尔公式和有效的琼斯矩阵[29],它可以很容易地描述光束的波场变换和结构的接触面,并确定光束质心坐标.其计算公式可以表示为[30]
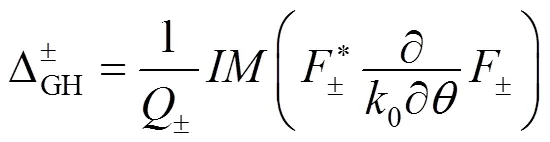
2 结果与讨论
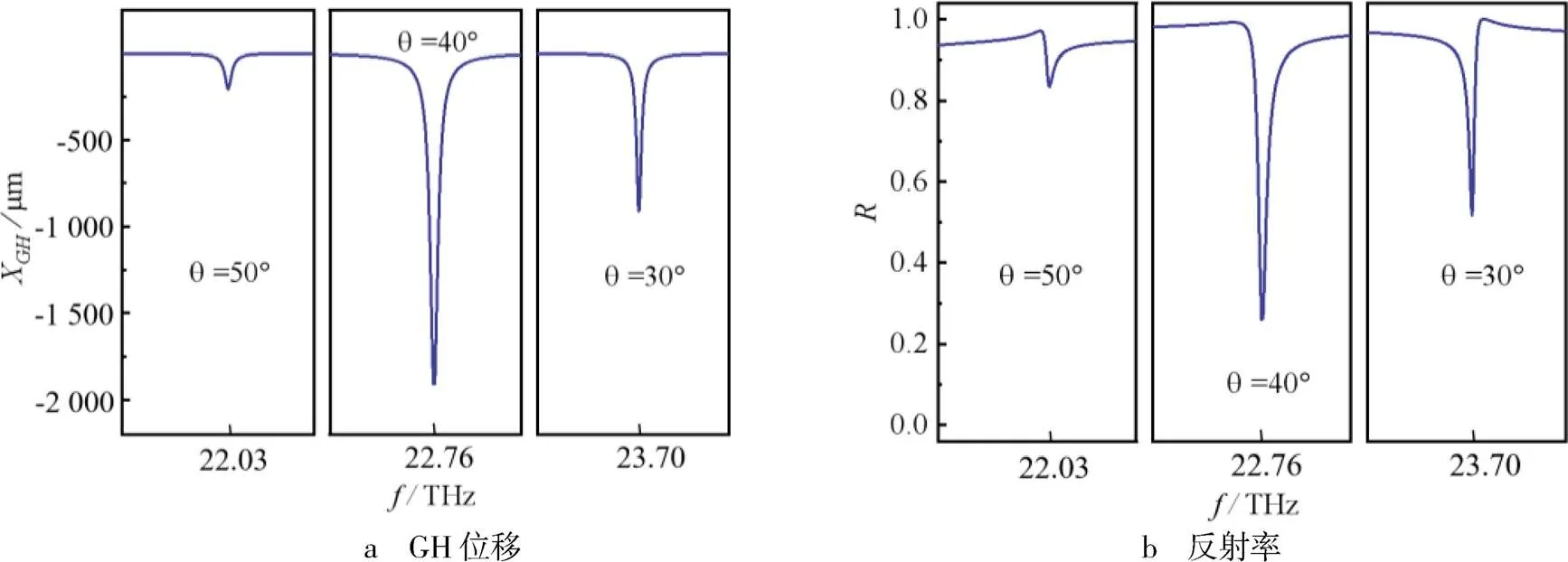
图3 矩形hBN层状光栅结构GH位移和反射率随频率的变化
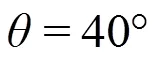
图4 矩形hBN层状光栅结构在不同频率下电场分布
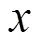
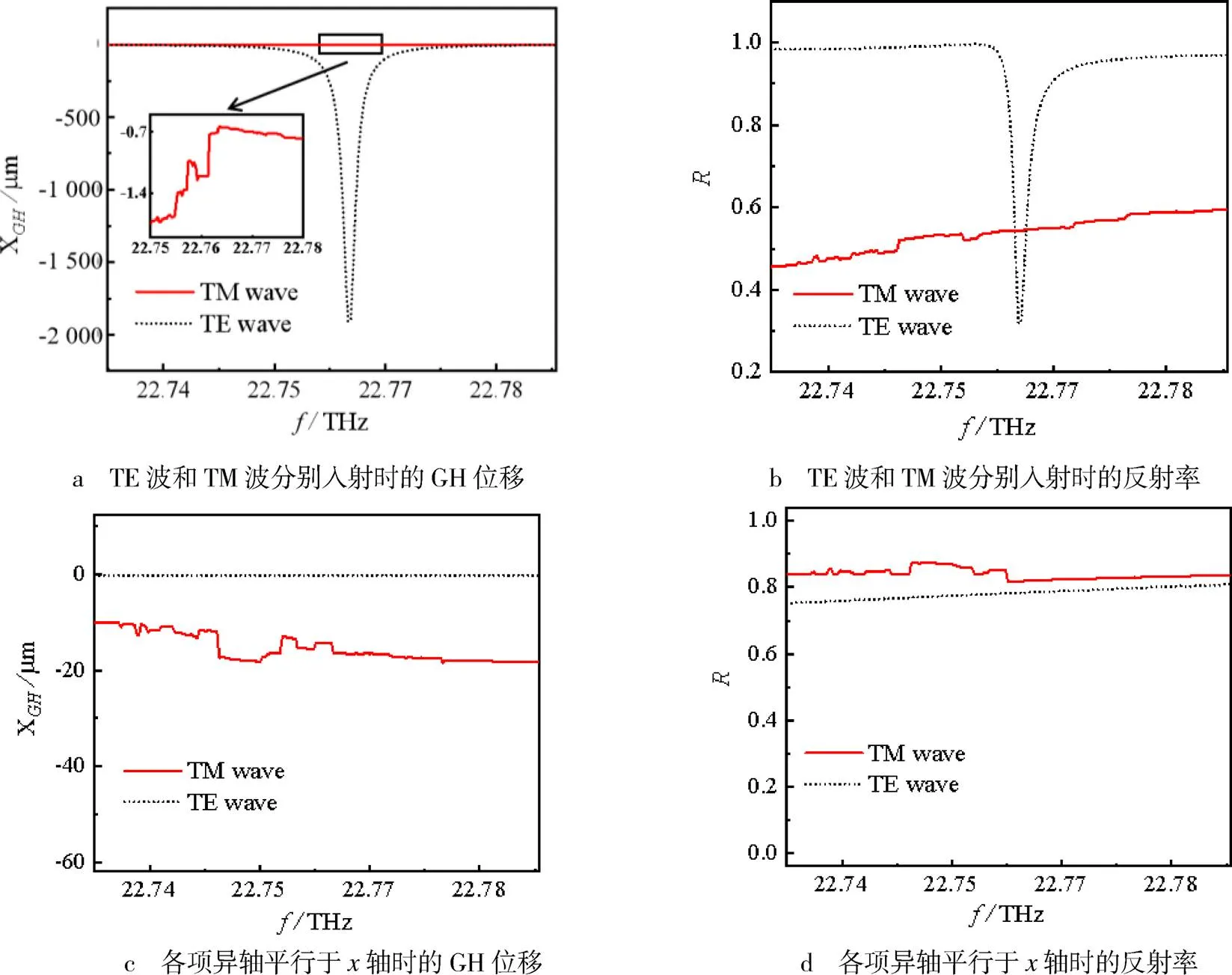
图5 横电(TE)波和横磁(TM)波分别入射及各项异轴平行于轴时的GH位移和反射率
注:黑色的虚线表示TE波;红色的实线代表TM波;插图显示了TM波在相应频率的局部放大图.
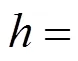
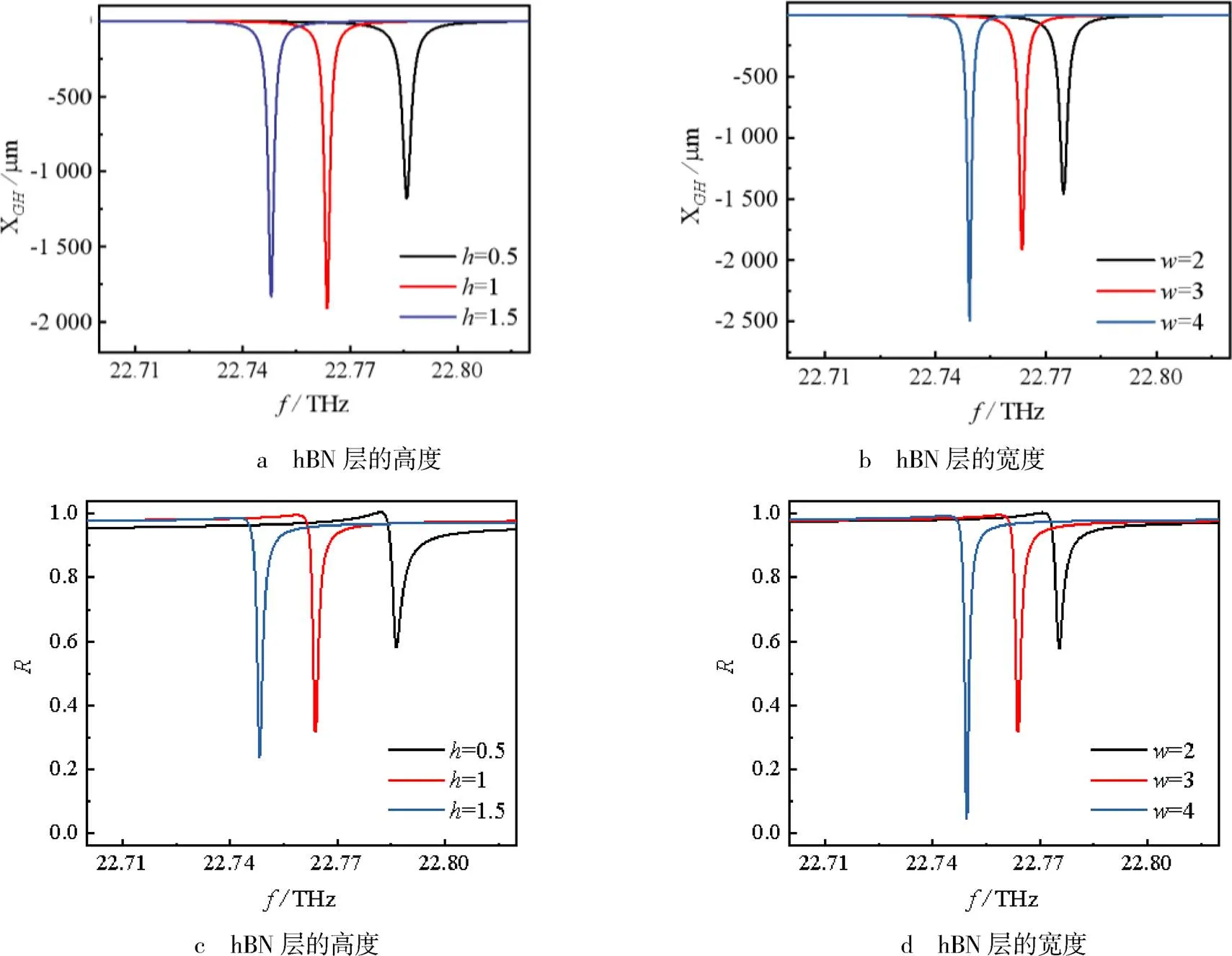
图6 不同参数下GH位移和反射率随频率的变化
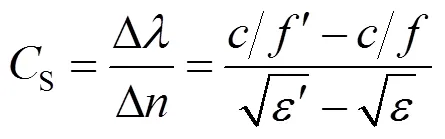
式中:定义为峰值波长;在的条件下,;为光在空气中的速度;,为入射波频率;,为上方空间的介电常数,折射率与介电常数的关系为.在从左侧入射的情况下,对介电常数很敏感(见图7).本文分析了RLG结构在GH位移中的作用,以探讨其在传感器中的潜在应用.利用灵敏度因子对该传感器的性能进行了表征.当介电常数从1.001到1.01,扫描间隔为0.00 1时,寻找GH位移最大最高的灵敏性,其灵敏度可达到.值得注意的是,空气的介电常数为1,温度可以改变其介电常数.
3 结语
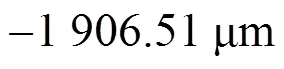
[1] Goos F,Hanchen H.Ein neuer und fundamentaler versuch zurtotalreflexion[J].Ann Pays,1947,436(7):333-346.
[2] Goos F,Lindberg-Hänchen H.Neumessung des strahlversetzungseffektes bei totalreflexion[J].Annalen der Physik,1949,440(3):251-252.
[3] Artmann K.Berechnung der Seitenversetzung des totalreflektieren Strahles[J].Ann Phys,1948,437(1/2):87.
[4] Das C M,Kang L,Hu D,et al.Graphene Coated Gold Chips for Enhanced Goos Hanchen Shift Plasmonic Sensing[J].Physica Status Solidi(a),2021,218(8):2000690.
[5] Olaya C M,Hayazawa N,Balois-Oguchi M V,et al.Molecular Monolayer Sensing Using Surface Plasmon Resonance and Angular Goos-Hänchen Shift[J].Sensors,2021,21(13):4593.
[6] ZHANG Xiangli,WANG Yuhan,ZHAO Xiang,et al.Fano resonance based on long range surface phonon resonance in the mid-infrared region[J].IEEE Photonics Journal,2019,11(2):1-8.
[7] Petrov N I,Sokolov Y M, Stoiakin V V,et al.Observation of Giant Angular Goos-Hanchen Shifts Enhanced by Surface Plasmon Resonance in Subwavelength Grating[C]//Photonics MDPI,2023,10(2):180.
[8] Jahani D,Akhavan O,Hayat A,et al.Optical Goos Hänchen effect in uniaxially strained graphene[J].JOSA A,2023,40(1):21-26.
[9] YU Tianyi,LI Honggen,CAO Zhang,et al.Oscillating wave displacement sensor using the enhanced Goos Hänchen effect in a symmetrical metal-cladding optical waveguide[J].Optics Letters,2008,33(9):1001-1003.
[10] Wan R G,Zubairy M S.Tunable and enhanced Goos-Hänchen shift via surface plasmon resonance assisted by a coherent medium[J].Optics Express,2020,28(5):6036-6047.
[11] ZHOU Xiang,LIU Shuoqing,DING Yiping,et al.Precise control of positive and negative Goos-Hänchen shifts in graphene[J].Carbon,2019,149: 604-608.
[12] HAN Lei,PAN Jianxing,WU Cuiming,et al.Giant Goos-Hänchen shifts in Au-ITO-TMDCs-graphene heterostructure and its potential for high performance sensor[J].Sensors,2020,20(4):1028.
[13] Ogawa S,Fukushima S,Shimatani M.Extraordinary optical transmission by hybrid phonon plasmon polaritons using hBN embedded in plasmonic nanoslits[J].Nanomaterials,2021,11(6):1567.
[14] SONG Haoyuan,ZHOU Sheng,SONG Yuling,et al.Tunable propagation of surface plasmon-phonon polaritons in graphene-hBN metamaterials[J].Optics & Laser Technology,2021,142:107232.
[15] LI Yubo,SONG Haoyuan,ZHANG Yuqi,et al.Tunable enhanced spatial shifts of reflective beam on the surface of a twisted bilayer of hBN[J].Chinese Physics B,2022,31(6):064207.
[16] YUE Qinxin,ZHEN Weiming,DING Yiping,et al.Giant Goos-Hänchen shifts controlled by exceptional points in a PT-symmetric periodic multilayered structure coated with graphene[J].Optical Materials Express,2021,11(12):3954-3965.
[17] DU Xiaodong,DA Haixia.Large and controlled Goos Hänchen shift in monolayer graphene covered multilayer photonic crystals grating[J].Optics Communications,2021,483:126606.
[18] LI Tingwei,DA Haixia,DU Xiaoming,et al.Giant enhancement of Goos Hänchen shift in graphene-based dielectric grating[J].Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics,2020,53(11):115108.
[19] ZHANG Changwei,YE Hong,LI Zhengyang,et al.Giant and controllable Goos Hänchen shift of monolayer graphene strips enabled by a multilayer dielectric grating structure[J].Applied Optics,2022,61(3):844-850.
[20] MA Shanshan,ZHU Xiaojun,LU Delian,et al.Dual dielectric grating-assisted enhancement of Goos-Hänchen shift in monolayer graphene[J].Physica Scripta,2022,97(8):085504.
[21] WU Feng,LUO Ma,WU Jiaju,et al.Dual quasibound states in the continuum in compound grating waveguide structures for large positive and negative Goos-Hänchen shifts with perfect reflection[J].Physical Review A,2021,104(2):023518.
[22] LI Zhengyang,ZHANG Changwei,YE Hong,et al.Enhanced Goos-Hänchen shift of graphene via hybrid structure with dielectric grating,metallic layer and photonic crystal[J].Physica E:Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures,2022,142:115272.
[23] ZHU Xiaojun,LU Delian,MA Shanshan,et al.Guided mode resonance-driven giant Goos–Hänchen shift in monolayer MoS2based dielectric grating structure[J].Physica B:Condensed Matter,2022,643:414173.
[24] Aharonov Y,Albert D Z,Vaidman L.How the result of a measurement of a component of the spin of a spin-1/2 particle can turn out to be 100[J].Physical Review Letters,1988,60(14):1351.
[25] Ritchie N W M,Story J G,Hulet Randall G Realization of a measurement of a“weak value”[J].Physical Review Letters,1991, 66(9):1107.
[26] LU Delian,MA Shanshan,ZHU Xiaojun,et al.Temperature controllable Goos Hänchen shift and high reflectance of monolayer graphene induced by BK7 glass grating[J].Nanotechnology,2022,33(48):485201-485209.
[27] Glover P W J.Geophysical Properties of the Near Surface Earth:Electrical Properties-ScienceDirect[J].Treatise on Geophysics (Second Edition),2015,11:89-137.
[28] Ogawa S,Fukushima S,Shimatani M.Extraordinary optical transmission by hybrid phonon plasmon polaritons using hBN embedded in plasmonic nanoslits[J].Nanomaterials,2021,11(6):1567.
[29] Mishalov V D,Bachinsky V T,Vanchuliak O Y,et al.Jones matrix mapping of polycrystalline networks of layers of main types of amino acids[C]//Photonics Applications in Astronomy,Communications,Industry,and High-Energy Physics Experiments,2019.
[30] FU Shufang,WANG Xiangguang,ZHAN Yuqi,et al.Spin-splitting in a reflective beam off an antiferro magnetic surface[J].Optics Express,2021,29,39125-39136.
[31] Haneef M,Bacha B A,Khan H,et al.Surface plasmon polariton at the interface of dielectric and graphene medium using Kerr effect[J].Chinese Physics B. 2018,27(11):114215.
[32] ZHANG Jing,JIANG Bo,SONG Yibin,et al.Surface phonon resonance enhanced Goos-Hänchen shift and its sensing application in the mid-infrared region[J].Optics Express,2021,29(21/11):32973-32982.
Goos-Hanchen shift in rectangular hBN layered gratings
ZHAO Yue1,JIN Gao1,ZHOU Sheng1,2
(1. School of Physics and Electronic Engineering,Harbin Normal University,Harbin 150025,China;2. Department of Basic Teaching,Guangzhou Navigation University,Guangzhou 510725,China)
hBN is a van der Waals material which is expected to a naturally occurring hyperbolic material,exhibits natural hyperbolic dispersion relations in tworangesofinfrared wavelengths that can strengthen light-matter interactions.In the present work,a rectangular laminar grating hBN(RLG)structure is designed,which is found to be able to increase the Goos-Hänchen(GH)shift with high reflectivity through numerical simulations.The electromagnetic field distribution in this structure directly reveals that enhanced GH shift can be attributed to electric field of the high localization in the RLG structure.It is worth noting that the frequency and width of the GH peak can also be regulated by parameters such as incident light polarization,height and thickness of the direction of the anisotropic axis of the hBN layer.In addition,the structure-sensing properties based on the GH shift was evaluated with a sensitivity of up to 1.401 μm/ RIU.The increased and controlled GH shift in the RLG structure shows promise for the applications,such as,optical sensors,optical switches and optoelectronic detectors.
Goos-Hänchen shift;hBN gratings;optical sensors
1007-9831(2023)11-0032-07
O43∶TB32
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9831.2023.11.007
2023-09-17
哈尔滨师范大学研究生课程建设项目;哈尔滨师范大学研究生创新项目(HSDSSCX2022-49)
招月(1999-),女,黑龙江绥化人,在读硕士研究生,从事微纳光学研究.E-mail:2291346449@qq.com
周胜(1978−),男,黑龙江哈尔滨人,教授,硕士生导师,从事微纳光学研究.E-mail:zhousheng_wl@126.com
