Effects of dietary fiber on human health
2022-11-26YangHeBixiangWangLiankuiWenFengzhongWangHansongYucDongxiaChenXinSuChiZhang
Yang He, Bixiang Wang, Liankui Wen*, Fengzhong Wang*,Hansong Yuc,*, Dongxia Chen Xin Su Chi Zhang
a Institute of Food Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), Beijing 100193, China
b Department of Food Science and Engineering, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun 130118, China
c Division of Soybean Processing, Soybean Research & Development Center, Chinese Agricultural Research System, Changchun 130118, China
Keywords:
Dietary fiber
Physicochemical properties
Human health
A B S T R A C T
Dietary fiber (DF) is believed to provide important health benefits and it has become a research hotspot.DF exists in most natural foods, including fruits (16.74%−91.24%), vegetables (6.53%−85.19%), grains (9.76%−69.20%)and so on.DF has different physicochemical properties such as water holding capacity (WHC) (2.01−25.03 g/g),water swelling capacity (WSC) (0.95−23.90 mL/g), oil holding capacity (OHC) (0.65−29.00 g/g),glucose adsorption capacity (GAC) (0.17−4.65 mmol/g), cholesterol adsorption capacity (CAC) (0.03−37.10 mg/g)and viscosity, which make it exhibits different physiological functions such as reducing the risk of obesity,diabetes, cancer, and intestinal diseases.On the basis of consulting related databases, the physicochemical properties of DF and its derived physiological functions are reviewed.It is found that DF has effect on the prevention and treatment of obesity due to good WHC, WSC, OHC and CAC.Good GAC can relieve the symptoms of diabetes.The physicochemical properties of WHC and WSC can reduce the risk of cancer.The WHC, WSC and viscosity are beneficial to intestinal health.
1.Introduction
Dietary fiber (DF) is the edible parts of plants, which can be completely or partially fermented in large intestine with undigested and unabsorbable in the human small intestine.It is the sum of carbohydrates and their analogues, including nondigestible polysaccharides, oligosaccharides, and associated plant substances [1].DF can be divided into soluble dietary fiber (SDF) and insoluble dietary fiber (IDF) base on its solubility in hot water.SDF is noncellulosic polysaccharide, including oligosaccharides and some indigestible polysaccharides (e.g., inulin, arabic gum, gum, pectins,galactomannan andβ-glucans).IDF includes cellulose, lignin, and some hemicelluloses [2-5].DF comes from a wide range of sources,including fruits, vegetables, grains, as well as others (Table 1).High viscosity SDF (such as pectin and oligosaccharide) is higher in apples, oranges, persimmons, pears, dried beans, cauliflower,carrots, and potatoes, etc.Pectin is a network of polygalacturonic acid composed ofD-galacturonic acid residues linked byα-1,4 glycosidic bonds, and has good viscosity and absorbability.So it has the property of adsorb glucose, cholesterol and heavy metals [6,7].Willats et al.[8]showed that the different degree of polymerization and complex side chain of pectin are important in anti-cancer activity and other biological activity characteristics,and its mechanism needs to be studied.Most IDF such as lignin,cellulose, and semi-fibers in grains (e.g., wheat, soybeans, mung beans and oats) are small in viscosity but have good swelling properties.Cellulose is a polymer-insoluble polysaccharide connected by glucose throughβ(1→4) glycosidic bonds and belongs to linear molecule.The adjacent cellulose chains have a stable fibrous structure by hydrogen bonding, which makes cellulose has water holding capacity (WHC), water swelling capacity (WSC), oil holding capacity (OHC), glucose adsorption capacity (GAC), and cholesterol adsorption capacity (CAC), etc.[9,10].

Table 1Summary of DF content and its physicochemical properties from different sources.
With the rapid development of modern society, many patients with chronic diseases are dramatically increasing, including obesity,diabetes, cancer, intestinal diseases, and other non-communicable diseases.The incidence of disease is increasing year by year worldwide, which further leads to an increase in mortality worldwide[11,12].The occurrence of chronic diseases not only increases the family and global economic burden, but also reduces the happiness index.Evidence suggests that DF can participate in human metabolism to prevent and treat these diseases (Fig.1) [13,14].Wei et al.[15]showed that 10 g/day increase in total fiber intake, the probability of suffering from metabolic syndrome is reduced by 11%.It has also been found that among the DF, cereal and fruit fiber can reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome.DF with different structures has different physicochemical properties, which play a vital role in regulating the health mechanism of human body.Studies believe that the physicochemical properties of DF such as WHC, WSC,OHC, GAC, CAC, and visibility are closely related to physiological functions.Therefore, the relationship between these physicochemical and physiological functions are discussed, and the product of DF in functional food in life are collected.These are expected to lay the foundation for the development of DF health food.

Fig.1 Metabolism of DF in human body and disease prevention.
2.Physicochemical properties
2.1 WHC
WHC is describe as mix 1 g of DF (dry basis) with water under specific conditions, and calculate the amount of water retained (g)after overnight [16].The WHC has a certain relationship with the structure of DF.When the contact area and the hydrophilic group of DF increase, water can be retained in the hydrophilic part or in the space of network fiber structure, which will improve the WHC.The WHC of DF ranges from 2.01 g/g to 25.03 g/g, among them,vegetable DF has the highest WHC (7.10−18.90 g), followed by fruits(3.38−13.08 g) and grains (2.01−6.23 g) (Table 1).Vegetable DF has high WHC due to its irregular, loose and porous surface, just as Xie et al.[17]studied that Angelica keiskei’s root DF has high WHC.Zheng et al.[18]reported that the DF content in coconut is (13.08 ±0.36) g, which is higher than that of most vegetables.This may be due to the DF structure of coconut is looser and more porous than most vegetables, which increases the surface area and facilitates water retention.In food research development and industrial production,processing and modification methods are often used to change the structure of DF to promote the desire for better physicochemical properties.DF has a good WHC, which is one of the main reasons for its role in improving human health.Firstly, DF has a lubricating effect after absorbing water, which can promote intestinal peristalsis and intestinal motility [19].Secondly, DF expands the volume of food after absorbing water, which can reduce food intake.DF is fermented in the intestine to produce SCFAs, which can promote the secretion of satiety hormones [20].Those will reduce the risk of obesity.Thirdly, DF can increase stool volume after absorbing water and swell, promote defecation while taking carcinogens away [21,22].At the same time, DF fermentation can regulate gut microbiota, so as to prevent diseases [23].
2.2 WSC
The method to determine WSC is to add DF sample (1 g) and water into the graduated cylinder overnight, and record the expansion volume [24].DF has WSC for the following reasons: 1) Water has surface tension strength, it can be maintained in the DF capillary structure.2) Hydrogen bonds and dipole hydrophilic groups bind to water.3) This is directly related to the contact area of DF.The WSC of DF ranges from 0.95 mL/g to 23.90 mL/g, of which WSC of vegetables DF is 5.35−18.70 g/g, the fruit DF is 3.20−10.17 g/g, and the grain DF is 0.95−7.54 g/g (Table 1).The WSC of coconut DF is the strongest to reach (10.17 ± 0.40) g/g, it exposes more hydrogen bonds and dipole forms [18].Xie et al.[25]reported that the WSC of DF from purple potatoes are related to processing conditions.High pressure homogenized DF has good WSC (18.30 mL/g), because the alteration of chemical and structural natures induced by high pressure treatments.Generally, the WSC of DF is beneficial to its functional properties for the same reasons as WHC.
2.3 OHC
The method to determine OHC is to mix sample (1 g) with soybean oil, leave it to stand for reaction, and centrifuge to retain the amount of oil [26].The OHC of DF is mainly related to the total charge density,hydrophobicity, surface properties and treatment conditions.The OHC of DF ranges from 0.65 g/g to 29.00 g/g.In general, the OHC of vegetable DF (1.01−25.8 g/g) is higher than fruit DF (0.65−9.91 g/g)and cereal DF (0.96−29.00 g/g) (Table 1).Among them, walnut powder has the largest OHC, it has more porous and honey comb like [27].Yu et al.[28]proposed that the OHC of carrot DF is significantly improved because the enzyme treatment exposed more hydrophilic groups and the cellular network structure.Zhao et al.[29]showed that the OHC (1.72 g/g) of super fine grinding rice bran IDF is significantly lower than that of fine IDF (2.09 g/g) and crude DF(2.96 g/g).As the particle size of superfine grinding decreases, the honeycomb structure of IDF disappears, which makes the OHC decrease.The OHC of DF is also the basis of important functional properties.DF can absorb fat and reduce the intake of excess calories in the body, which can prevent the occurrence of obesity [30].
2.4 GAC
GAC is describe as the mix DF (1 g ) and 100 mL glucose solution(5−200 mmol/L) in an enzyme reactor and mix the amount of glucose retained by centrifugation [31].GAC of DF is related to its physical properties, because glucose can adhere to the network structure of DF and reduce the contact with human intestinal tract [32].The GAC of DF in food is from 0.17 mmol/g to 4.65 mmol/g, and studies on GAC mainly focus on vegetable DF (Table 1).Huang et al.[33]found that GAC of garlic stems DF increased after ultrasonic treatment, which is due to the increase of honey-comb network structure.Yu et al.[28]reported that IDF extracted from carrot using a complex enzyme method (2.43 mmol/g), and GAC exhibits a significantly improved with the high hydrostatic pressure (2.63 mmol/g).The GAC of DF is related to the glucose metabolism function.This is because DF can absorb sugars, and produce SCFAs through fermentation in the body,which can prevent the diabetes [34,35].
2.5 CAC
CAC is expressed as the mass of cholesterol absorbed by 1 g of sample.CAC of DF is divided into physical and chemical adsorption.Physical adsorption is mainly related to the particle size, specific surface area, porosity and reaction temperature of DF [36-38].Chemical adsorption is related to the DF charge and hydrophobic group.CAC ranges from 0.03 mg/g to 37.10 mg/g, and the major studies of CAC focus on vegetables DF (12.94−37.10 mg/g) (Table 1).Bamboo shoot shell DF can bind or adsorb bile acids and cholesterol(12.94 mg/g), thereby reducing cholesterol [39].Liu et al.[40]showed that SDF in soybean hulls has good viscosity, which can enhance the CAC (7.62 mg/g), thereby reducing blood cholesterol levels.DF with good CAC can prevent and treat obesity disease.DF can absorb cholesterol, and the SCFAs produced by fermentation can participate in body metabolism and improve dyslipidemia, which are the reasons for preventing obesity [38,41].
2.6 Viscosity
Viscosity is the relationship between fluid flow and the force directed on the fluid, and it can be affected by many factors, such as chemical composition, structure, particle size, surface area and processing conditions.Gallaher et al.[42]used whole oatmeal or instant oatmeal to make muffins and fed to rats, and the viscosity of the intestinal contents supernatant is measured.The results showed that the viscosity of whole oatmeal (about 225 cP) is significantly higher than eating instant oatmeal (about 110 cP).The reason is that more viscosity fiber such asβ-glucan in whole oats, andβ-glucan has more hydrophilic groups, which promotes the increase of the water film thickness of the intestinal mucosa, thereby increasing the viscosity of supernatant intestinal contents.Ullah et al.[43]found that the viscosity of okara stability increased after thermal pre-treatment.The viscosity of DF can prevent obesity and diabetes by delaying fat formation and gastric emptying, and increasing insulin sensitivity.
3.DF and human health
3.1 DF and obesity
In recent years, obese patients have been increasing year by year all over the world.According to statistics from 200 countries, the global prevalence of obesity has increased from 3.2% in 1975 to 10.8% in 2014 in men.At the same time, the data suggests an increase from 6.4% of women to 14.9% [61].In 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults aged 18 were overweight, of which more than 650 million were obese, and more than 340 million children and adolescents aged 5−19 were overweight or obese.The increasing number of obese patients poses a threat to human health worldwide, increases the global burden, and becomes a challenge for human [62].Reducing obese patients has become an urgent problem.Adequate intake of DF has been shown to play an important role in preventing obesity.
DF can block the fat absorption and reduce energy intake by regulating food intake, digestion, absorption and metabolism.The main weight loss mechanism of DF is as follows: 1) The viscosity of SDF such as gum and gum arabic is high, which can slow down the migration of nutrients.DF has galacturonic acid structure,which has a high viscosity [30].At the same time, DF has good WHC, OHC and CAC, which can enhance the adsorption of fat.In addition, the network structure of IDF makes it have better CAC [63].Mandimika et al.[38]described that broccoli DF contains sticky pectin, which reduces the intake of dietary fat, and enhances the removal of cholesterol and bile acid from enterohepatic circulation,thereby reducing blood cholesterol levels.Luo et al.[39]found that bamboo shoot shell contained a large amount of IDF, which can bind or adsorb bile acids and cholesterol, leading to a reduction of cholesterol in various pools.2) DF has good WSC, which can enhance satiety and reduce food intake.Lambert et al.[20]found that the intake of DF will absorb water and increase satiety, which can delay nutrients absorption and effectively reduce energy intake.3) DF produces SCFAs through intestinal microbial fermentation,while promotes the secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and YY peptide (PYY).GLP-1 is released from intestinal L-cells, which promotes insulin secretion and pancreatic cell proliferation, controls glycogen synthesis in muscle cells, and enhances satiety [64].PYY is an intestinal secretion hormone with anti-obesity effect, which has the effect of suppressing appetite and reducing food intake [65].Chang et al.[41]reported that the IDF of pear pomace can dilute energy, increase energy consumption, and promote GLP-1 and PYY secretion after intestinal fermentation, thereby reducing fat cells and effectively improves obesity.
All in all, the improvement of obesity by DF mainly comes from the physicochemical properties such as WHC, WSC, OHC, CAC and viscosity, which delay the absorption of fat from food.Both SDF and IDF have the effects of reducing obesity, which is better requires a lot of experimental researches.
3.2 DF and diabetes
In the past few decades, the incidence of diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, is the highest, accounting for 90% of all diseases.It has grown very rapidly, and the number of patients with diabetes has continued to increase globally.It was 151 million in 2000 and 285 million in 2010.The global prevalence of diabetes is expected to be 7.8% by 2030 [66].The increase in the number of diabetic patients also increases the global economic burden.These issues make it urgent for us to prevent and treat type 2 diabetes as soon as possible.Studies have found that DF has an important role in the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The mechanism of DF lowering blood glucose is as follows: 1)The network structure of DF can form a physical barrier and delay the diffusion of glucose.Fibrous particles act as a physical barrier to glucose molecules and entrapment of glucose in the fiber-forming network.When the structure of DF becomes loose and porous, and more surface functional groups are exposed, the interaction between DF and glucose will be enhanced, and the GAC will be improved.Srichamroen et al.[67]and Ashutosh et al.[68]reported that DF from sunflower seeds, tamarind and cassia seeds has a positive effect on retarding glucose diffusion.In addition, DF extracted from potatoes by Cheng et al.[34]has a significant effect on slowing the diffusion of glucose.It is due to the porous of DF and the exposure of surface functional groups, which enhances the interaction between DF and glucose.Millet IDF can delay glucose absorption and help better control serum glucose level, which is mainly caused by the physical barrier of IDF [69].2) Viscous fibers can delay gastric emptying and increase the sensitivity of insulin to hypoglycaemic effects.Bobboi et al.[70]noted that the viscosity of ingested guar gum can reduce the postprandial hyperglycemia.3) DF is fermented by the gut microbiota to produce SCFAs, thereby stimulate the secretion of satiety hormone(GLP-1 and PYY), those hormones help to increase insulin secretion and control the blood glucose level.Zhao et al.[35]reported that acetic acid and butyric acid can improve glucose homeostasis by inducing GLP-1 and PYY intestinal production, thereby stimulating insulin secretion.
3.3 DF and cancer
Cancer is one of the main public problems that seriously threaten the health of human beings [71].Therefore, the prevention of cancer is urgent.The occurrence of cancer is closely related to eating habits,and high DF diet can effectively prevent the occurrence of a variety of cancers (Table 2).
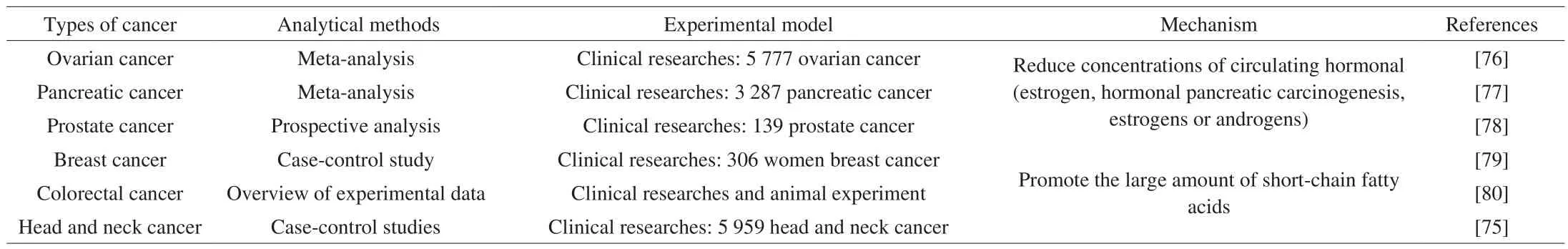
Table 2Effect of DF in some types of cancer.
The mechanism of DF to prevent cancer is mainly reflected in the following aspects.1) DF has WHC and SWC, which can increase stool volume, accelerate defecation time, and reduce the concentration of carcinogens in the intestine.Dahl et al.[21]reported that DF can reduce the risk of colorectal cancer because the increased fecal bulk and decreased transit time, thereby reducing the carcinogens concentration of colorectal epithelium.2) DF can reduce the concentration of circulating hormones and increase excretion.The prevention mechanism of ovarian cancer and breast cancer is mainly to inhibit the secretion of hormones and reduce the bioavailability of hormones.Ho et al.[72]studies showed that DF in fruits and vegetables prevents female breast cancer by inhibiting estrogen enzymes and reducing estrogen secretion.In addition,Xu et al.[73]reported that intaking DF can reduce steroid hormones and help regulate insulin growth factor, thereby reducing the risk of ovarian cancer.For every 5 g/day DF increase, the risk of ovarian cancer is reduced by 3% (relative risk, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.95–0.99).3) DF fermentation produces SCFAs such as butyrate, which can inhibit histone deacetylase and related signaling pathways in cultured cancer cells, and promote cancer cell apoptosis [74].Studies by Kawakita et al.[75]showed that DF seems to have anti-inflammatory effects through the production of SCFAs by gut bacteria with antiproliferation and pro-apoptotic properties, resulting in reducing the risk of cancer.
3.4 DF and intestinal disease
The gastrointestinal system is the largest barrier tissue of the human body.In a healthy state, the intestinal environment can play a key role in promoting food digestion and affecting the mucosal immune system through symbiotic microbiota.Imbalance of the gut microbiota may cause damage to the intestinal barrier, thereby increasing the susceptibility to certain diseases [23].The incidence of intestinal diseases is closely related to lifestyle and diet.People who consume more DF can regulate the gut microbiota, prevent constipation, and maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier,thereby promoting intestinal health.
DF fermentationin vivocan promote the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, which play a vital role in preventing and treating diseases.Kang et al.[81]reported that the Konjaku flour (KF) supplementation significantly reduces the obese mice weight.This is because the KF boosts the abundances of some obesity-related beneficial microorganisms (such asMegasphaera elsdenii) in the gut microbiota of high fat diet mice, while reduces those of harmful microorganisms (such asAlistipes,Alloprevotella,Bacteroides acidifaciens, andParabacteroides goldsteinii).In addition, we found that soybean IDF can prevent obesity in mice on a high-fat diet by regulating the gut microbiota.Soybean IDF intake can increase the potential beneficial bacteriaLactobacillales,Lactobacillus, Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group related to obesity.The abundance ofBacteroides_acidifacienssignificantly reduced the weight of mice on a high-fat diet.Zhang et al.[82]showed that inulin treatment can promote the abundance of probiotic bacteriaLactobacillus,Lachnospiraceae,Phascolarctobacterium, andBacteroidesin diabetic rats.Faraz et al.[83]found that high DF diet can promote beneficial bacteria, resulting in protecting effect on colon cancer.Alfa et al.[84]found that resistant starch can improve the gut microbiota of middle-aged and elderly people, stimulate the growth of Bacteroidetes, and change the ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes and the relative abundance of butyric acid.
DF has good WHC and SWC, which can relieve functional constipation and promote gastrointestinal digestion.Chao et al.[19]showed that DF with WHC and SWC can increase defecation and help to relieve constipation symptoms in children.In patients with non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease, a DF-rich diet improves esophageal motility and reduces the frequency of gastroesophageal reflux and heartburn per week [22].
DF has the effect of promoting intestinal health, because it can protect the intestinal barrier and enhance the intestine length.The SCFAs produced by DF fermentation can inhibit inflammatory factors, thereby protecting the integrity of the intestinal barrier.Chapman et al.[85]studies reported that increased concentration of butyric acid has an effect on alleviating ulcerative colitis.SCFAs fermented by inulin in the colon can reduce mucosal proinflammatory cytokines, which show a lower degree of mucosal damage and a decrease in the sting of crypt damage [86].Zohre et al.[87]reported that the intake of cooked pea DF increases the abundance ofLachnospiraceaein the intestine.Higher butyrate-producing promotes the Muc2 and Muc4 expression of the main components in the intestinal mucus layer, so it is important for the protective function of this layer.The length of the colon affects the effect of DF fermentation, which the increase of the colon length can shorten the fermentation time and increase the degree of fermentation.Dert et al.[88]reported that intestinal diseases can shorten the length of the colon.Our team studies found that the intake of soybean IDF can increase the colon length of mice,significantly improve the intestinal damage of high-fat diet in mice,and make the colon epithelial cells of mice intact and goblet cells intact and uniform.
A number of studies have found that SCFAs produced by DF through the fermentation of gut microbiota can prevent and improve the occurrence of obesity, diabetes, cancer and intestinal diseases.The effect of DF on prevention and treatment diseases is related with the SCFAs (Fig.2).DF is fermented by gut microbiota to produce SCFAs, and SCFAs can promote the increase of PYY, GLP-1 and insulin sensitivity, cancer cell apoptosis and intestinal integrity, which is conducive to disease prevention and treatment.

Fig.2 The effect of DF on prevention and treatment diseases is related with the SCFAs.
3.5 Other functions
In recent years, with the deepening of researches, some other functions of DF have been discovered, including reducing heavy metal toxicity, the risk of cardiovascular and female diseases, and improving allergic symptoms such as rhinitis.
DF is a natural chelating agent, which can complex with lead ions to form a precipitate, so it can effectively prevent the absorption of lead in the gastrointestinal tract.DF can delay or reduce the absorption of heavy metals and carcinogens in the intestine.The laxative effect of DF, the residence time of feces and harmful substances in the intestine is shortened, which greatly reduces the harm of harmful substances to the human body, thereby reducing the risk of pathological changes in cancer [89].SDF contains some carboxyl side chain groups, which can reduce the toxicity of heavy metals.IDF has a network structure that forms physical adsorption,indicating that IDF can hinder the absorption of lead ions and reduce the risk of lead poisoning.Khotimchenko et al.[90]showed that low-esterified pectin, high-esterified pectin and pectin calcium gel particles have good adsorption of lead ions.Wang et al.[91]studied that soybean IDF exhibits higher lead (II) ion adsorption capacity, and adsorption occurs on the surface of fiber particles.
Soliman et al.[92]found that DF can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.This is because SCFAs produced by DF fermentation can increase the degree of acidification of the environment in the colon cavity, while low pH can reduce the solubility of free bile acids and their conversion to secondary bile acids, and increase bile excretion [93].
Nagata et al.[94]reported that soybean DF reduces menstrual pain, the reason is that DF intake can inhibit estrogen enzymes and reduce the secretion of estrogen and steroid hormones, thereby reducing dysmenorrhea and helping to reduce the risk of illness.
Zhang et al.[95]found that DF has a significant inhibit allergic rhinitis complicated with allergic inflammation of asthma.The results showed that proper fiber intake can regulate gut microbiota and maintain immune stability to prevent and treat allergic diseases.
DF has good physicochemical and functional properties, so it plays an important role in the development of functional foods,food packaging and the protection of beneficial active substances.Furthermore, DF functional food has the effect of lowering blood fat and blood sugar, and good food properties of beverages and jam products, bakery, meat, and other products, including taste, color,hardness, texture, gel capacities and mechanical properties, which because DF has the good physicochemical properties (Table 3).

Table 3The products of DF in functional food.
4.Conclusion and future research
These physicochemical properties of DF include WHC(2.01−25.03 g/g), WSC (0.95−23.90 mL/g), OHC (0.65−29.00 g/g),GAC (0.17−4.65 mmol/g), CAC (0.03−37.10 mg/g) and viscosity,which play a vital role in preventing diseases.Good WHC, WSC,OHC, and CAC have an effect on obesity; viscosity and GAC have the greatest impact on diabetes; adsorption capacity has an effect on cancer; WHC, WSC and viscosity have benefits for intestinal health.DF is also widely used in functional foods.In this review, DF from fruits have the high content, which are easy to obtain and inexpensive.The DF from grains and beans also has the above advantages.Those can be used as a good source of DF in the future for the development of health food.
However, there are also shortcomings of DF studies in some aspects.First of all, the different polymerization degree of DF may have a preventive effect on different diseases, especially the polymerization degree of DF from different sources is also different.The polymerization degree of different DFs is still unclear on the disease prevention mechanism, so the structure of different polymerization degrees of DF from different sources is necessary for further research on disease prevention.Secondly, the prevention of diseases by DF is not limited to those mentioned in this review.In particular, the prevention and treatment of other diseases by regulating the gut microbiota requires a lot of experimental researches.Third, the intake of DF and the type of DF will have an impact on the prevention and treatment of diseases.It is necessary to study the dosage and type (SDF or IDF) of DF in the prevention and treatment of diseases to determine the optimal intake of different types.After the above problems are solved, DF will be more conducive to the prevention and alleviation of human diseases, while promoting the development of human health.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-04).And we also thank the National Engineering Laboratory for Wheat and Corn Deep Processing of China, and the Key Laboratory for Agricultural Product Deep Processing for support.
杂志排行
食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- Tea polyphenol - gut microbiota interactions: hints on improving the metabolic syndrome in a multi-element and multi-target manner
- Resveratrol and its derivates improve inflammatory bowel disease by targeting gut microbiota and inflammatory signaling pathways
- Milled flaxseed-added diets ameliorated hepatic inflammation by reducing gene expression of TLR4/NF-κB pathway and altered gut microbiota in STZ-induced type 1 diabetic mice
- Fermented soy whey induced changes on intestinal microbiota and metabolic influence in mice
- Effects of soy hull polysaccharide on dyslipidemia and pathoglycemia in rats induced by a high-fat-high-sucrose diet
- Chinese Torreya grandis cv.Merrillii seed oil affects obesity through accumulation of sciadonic acid and altering the composition of gut microbiota
