miR-122-5p对类风湿关节炎滑膜细胞增殖与凋亡的影响及其机制
2022-05-06郭占非吴洁杨学华许振丹范文强高晓
郭占非 吴洁 杨学华 许振丹 范文强 高晓








[摘要]目的研究miR-122-5p对类风湿关节炎(RA)滑膜细胞增殖、凋亡的影响及其机制。方法运用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)分别检测正常关节滑膜细胞、RA滑膜细胞中miR-122-5p以及盘状结构域受体激酶(DDR2)的表达。实验分为阴性对照(miR-NC)组(转染mimic NC序列)、miR-122-5p寡核苷酸模拟物(miR-122-5p)组(转染miR-122-5p模拟物mimics)、miR-122-5p特异性寡核苷酸抑制剂阴性对照(anti-miR-NC)组、miR-122-5p特异性寡核苷酸抑制剂(anti-miR-122-5p)组、miR-122-5p+pcDNA组(共转染miR-122-5p mimics和空载体(pcDNA))、miR-122-5p+pcDNA-DDR2组(共转染miR-122-5p mimics和DDR2过表达载体(pcDNA-DDR2)),用脂质体法转染至RA滑膜细胞。采用Western blot方法检测细胞中DDR2、P21和Survival的蛋白表达,MTT法检测细胞增殖,流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡,双荧光素酶报告基因检测实验检测细胞中miR-122-5p与DDR2的结合力。结果与正常滑膜细胞相比较,RA滑膜细胞中miR-122-5p的表达显著降低,DDR2的表达显著升高(t=27.714~48.853,P<0.001)。过表达miR-122-5p可抑制RA滑膜細胞增殖,促进其凋亡(t=16.716~121.500,P<0.001)。miR-122-5p可抑制野生型DDR2细胞的荧光活性。过表达DDR2可以逆转miR-122-5p对RA滑膜细胞的增殖抑制和凋亡促进作用(t=106.335~327.990,P<0.001)。结论miR-122-5p可抑制RA滑膜细胞的增殖,促进其凋亡,其机制可能与靶向DDR2有关。
[关键词]关节炎,类风湿;微RNAs;盘状结构域受体2;细胞增殖;细胞凋亡
[中图分类号]R593.22;R342.2[文献标志码]A[文章编号]2096-5532(2022)02-0289-05
doi:10.11712/jms.2096-5532.2022.58.074[开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)]
[网络出版]https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/37.1517.R.20220412.1535.005.html;2022-04-1409:13:38
EFFECT OF MIR-122-5P ON THE PROLIFERATION AND APOPTOSIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS SYNOVIAL CELLS AND ITS MECHANISM GUO Zhanfei, WU Jie, YANG Xuehua, XU Zhendan, FAN Wenqiang, GAO Xiao (Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The Fourth Clinical College of Xinxiang Medical College, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang 453000, China)
[ABSTRACT]ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of miR-122-5p on the proliferation and apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial cells and it mechanism.MethodsQuantitative real-time PCR was used to measure the expression of miR-122-5p and DDR2 in normal synovial cells and RA synovial cells. The experiment was divided into negative control (miR-NC) group (transfected with mimic NC sequence), miR-122-5p oligonucleotide analogue group (transfected with miR-122-5p mimics), miR-122-5p specific oligonucleotide inhibitor negative control (anti-miR-NC) group, miR-122-5p specific oligonucleotide inhibitor (anti-miR-122-5p) group, miR-122-5p+pcDNA group (co-transfected with miR-122-5p mimics and empty vector pcDNA), and miR-122-5p+pcDNA-DDR2 group (co-transfected with miR-122-5p mimics and DDR2 overexpression vector pcDNA-DDR2), and RA synovial cells were transfected by lipofection. Western blot was used to measure the protein expression of DDR2, P21, and Survi-val; MTT assay was used to measure cell proliferation; flow cytometry was used to measure cell apoptosis; dual-luciferase reporter assay was used to measure the binding force of miR-122-5p and DDR2.ResultsCompared with the normal synovial cells, the RA synovial cells had a significant reduction in the expression of miR-122-5p and a significant increase in the expression of DDR2 (t=27.714-48.853,P<0.001). Overexpression of miR-122-5p inhibited the proliferation and promoted the apoptosis of RA synovial cells (t=16.716-121.500,P<0.001), and miR-122-5p could inhibit the fluorescence activity of wild-type DDR2 cells. Overexpression of DDR2 reversed the effect of miR-122-5p in inhibiting the proliferation and promoting the apoptosis of RA synovial cells (t=106.335-327.990,P<0.001). ConclusionThis experiment shows that miR-122-5p can inhibit the proliferation and promote the apoptosis of RA synovial cells, possibly by targeting DDR2.
[KEY WORDS] arthritis, rheumatoid; microRNAs; discoidin domain receptor 2; cell proliferation; apoptosis
类风湿关节炎(RA)是一种影响多个关节的全身自身免疫性疾病,其可导致关节中滑膜细胞的增殖,而血管翳的形成可能导致潜在的软骨破坏和骨侵蚀,以及促炎细胞因子的过量产生,加快破坏进程的发展[1-2]。RA的发病原因与其他自身免疫性疾病一样,病因复杂多样。临床上的药物以抑制免疫反应、减轻炎症为主,不能达到根治的目的,而且长期使用对机体产生的副作用较大[3-4]。因此,提高RA的治疗效果成为该领域的一大难题。miRNA是由长度为20个左右的核苷酸组成的短链内源性非编码的微小RAN分子,在机体各种疾病的发生中具有举足轻重的作用[5]。据报道,miRNA在RA中也具有调控作用[6],其中包括miR-122-5p[7]。盘状结构域受体激酶(DDR2)属于受体激酶酪氨酸的一种,大量研究显示,其在RA中具有重要的促炎作用[8]。本研究拟以RA病人滑膜细胞为研究对象,检测miR-122-5p和DDR2在滑膜细胞的表达,并观察调控 miR-122-5p和DDR2表达对该细胞增殖、凋亡的影响,揭示miR-122-5p与DDR2的靶向关系,旨在为RA的治疗提供新的作用靶点。
1材料与方法
1.1实验材料
本文所用組织标本,均来自新乡市中心医院接受手术治疗的8例RA病人及意外交通事故导致关节粉碎性骨折的5例病人。DMEM培养液、胰蛋白酶购自GIBCO公司;胎牛血清购自杭州四季青公司;甲基噻唑基四唑(MTT)试剂购自美国Sellect公司;Lipofectamine2000、逆转录试剂盒购自大连Takara公司;Trizol液购自北京百奥莱博;十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶(SDS-PAGE)试剂盒、增强型化学发光试剂(ECL)发光液和放射免疫沉淀试验(RIPA)蛋白裂解液等均购自碧云天生物技术公司;双荧光素酶报告基因检测试剂盒购自美国Promega公司;Annexin V-FITC/PI凋亡检测试剂盒购自北京索莱宝公司。
1.2实验方法
1.2.1细胞的分离、培养及分组处理按照梁晓辉等[9]报道的方法,取新鲜滑膜组织剪碎,用DMEM培养液和胰蛋白酶消化后进行分离培养RA滑膜细胞和正常滑膜细胞。将miR-122-5p寡核苷酸模拟物(miR-122-5p mimics)及阴性对照mimic NC序列(miR-NC)、miR-122-5p特异性寡核苷酸抑制剂(anti-miR-122-5p)及其阴性对照(anti-miR-NC)、miR-122-5p mimics+空载体(pcDNA)、miR-122-5p mimics+DDR2过表达载体(pcDNA-DDR2)用脂质体LipofectamineTM2000转染至RA滑膜细胞。转染6 h后,更换培养液继续培养48 h,分别标记为miR-NC组(A组)、miR-122-5p组(B组)、anti-miR-NC组(C组)、anti-miR-122-5p组(D组)、miR-122-5p+pcDNA组(E组)和miR-122-5p+pcDNA-DDR2组(F组)用于后续实验。
1.2.2实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)法检测细胞中miR-122-5p和DDR2的表达Trizol法提取细胞样本总RNA,并用Nano-Drop 2000微量分光光度计进行RNA定量。DNase Ⅰ 消化RNA中可能污染的DNA。采用逆转录试剂盒合成模板链cDNA。按扩增反应体系进行PCR,每个样品重复3次,取平均值,反应结束后分析Ct值,以2-△△Ct法计算miR-122-5p和DDR2的相对表达水平。
1.2.3Western blot法检测细胞中DDR2、P21和Survival的蛋白表达收集细胞,加入裂解液,冰上裂解20~30 min。以12 000 r/min离心10 min,取上清置于EP管,加入5×SDS上样缓冲液,沸水煮沸10 min。电泳后将蛋白转移至PVDF膜,50 g/L脱脂奶粉将膜封闭2 h;洗膜,加入一抗,4 ℃过夜孵育;洗膜,加二抗,4 ℃孵育2 h。加发光液,曝光。以GAPDH为内参照,以目的条带与GAPDH条带灰度值的比值表示目的蛋白的相对表达。
1.2.4MTT实验检测细胞增殖调整细胞密度至10/L,然后接种至96孔板中,取适量的细胞(每孔1 000个),每孔加入MTT溶液(5 g/L)20 μL,孵育4 h。终止细胞培养,弃去培养液上清,然后每孔加入150 μL的DMSO,振荡使结晶充分融解,在490 nm波长处检测细胞吸光度(OD490)。细胞增殖能力与细胞的吸光度值呈正比。
1.2.5流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡按照Annexin V-FITC/PI凋亡检测试剂盒说明书步骤进行操作,用500 μL的结合缓冲液悬浮细胞,首先加入5 μL的Annexin V-FITC避光反应20 min,然后再加入5 μL的PI避光反应20 min,最后在1 h内上流式细胞仪结束检测。细胞凋亡率(%)=早期凋亡率+晚期凋亡率。
1.2.6双荧光素酶报告基因检测实验检测细胞miR-122-5p与DDR2的结合力将荧光素酶报告载体(psiCHECK2-DDR2-WT,psiCHECK2-DDR2-MUT)分别加入用脂质体法转染miR-122-5p mi-mics和miR-NC的 RA滑膜细胞,培养6 h后,更换新鲜培养液继续培养,转染48 h。按照双荧光素酶报告基因检测试剂盒说明书进行操作。结果以海肾荧光素酶的发光强度与萤火虫荧光素酶发光强度的比值表示miR-122-5p与DDR2的结合力。
1.3统计学处理
采用SPSS 21.0软件进行统计学分析。计量资料数据用x±s表示,多组间均数比较采用单因素方差分析,两组比较采用t检验,不同组别、不同时间及其二者交互的细胞活性比较采用析因设计方差分析。以P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2.1miR-122-5p和DDR2在RA滑膜细胞表达
qRT-PCR和Western blot检测结果显示,与正常滑膜细胞组相比较,RA滑膜细胞组细胞中miR-122-5p表达显著降低,DDR2 的mRNA和蛋白表达均显著升高(t=27.714~48.853,P<0.001)。见图1和表1。
2.2过表达miR-122-5p对RA滑膜细胞增殖和凋亡的影响
MTT法和流式细胞术检测细胞增殖与凋亡结果显示,不同时间、不同组别及其二者交互作用下OD比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.001)。与miR-NC组相比较,miR-122-5p组RA滑膜细胞中miR-122-5p表达显著升高,48、72 h时细胞增殖显著降低、细胞凋亡率显著升高,P21和Survival蛋白表达均显著降低(t=16.716~121.500,P<0.001)。见图2和表2。
2.3miR-122-5p与DDR2的结合力检测
miR-122-5p靶向DDR2的生物信息学预测显示,DDR2与miR-122-5p的5′端存在8个互补的核苷酸序列(见图3)。双荧光素酶报告基因检测实验结果显示,与miR-NC组相比,miR-122-5p组WT-DDR2细胞的荧光活性显著降低(t=100.623,P<0.001),MUT-DDR2细胞的荧光活性无显著变化。见表3。与anti-miR-NC组(1.00±0.01)相比,anti-miR-122-5p组(1.89±0.13)细胞中DDR2蛋白表达显著升高,与miR-NC组(1.01±0.01)相比,miR-122-5p组(0.21±0.02)细胞中DDR2蛋白表达显著降低(F=969.103,P<0.001)。见图4。
2.4DDR2过表达对miR-122-5p调控RA滑膜细胞增殖和凋亡的影响
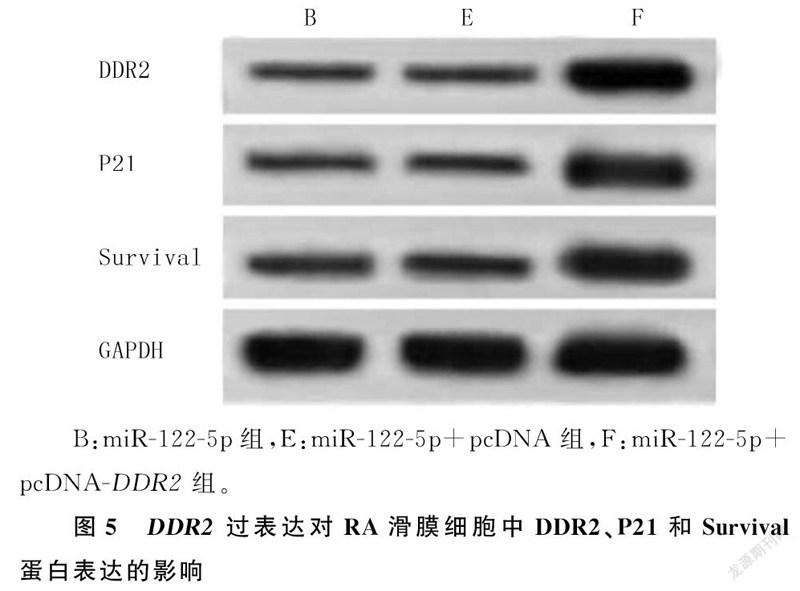
不同时间、不同组别及二者交互作用下OD490比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。与miR-122-5p+pcDNA组相比,miR-122-5p+pcDNA-DDR2组细胞中DDR2蛋白表达显著升高,48、72 h时细胞增殖显著升高、细胞凋亡率显著降低,P21和Survival蛋白表达均显著升高(t=106.335~327.990,P<0.001)。见表4和图5。
3讨论
miRNA在包括RA的多种疾病中具有重要的作用[10]。如miR-146a、miR-203和miR-223等在关节炎中均发挥重要的调控作用[11-13]。WANG等[14]使用miRNA阵列技术筛选RA病人血浆中的差异miRNA,发现miR-122-3p的表达水平明显降低。张莹莹等[15]研究也发现,miR-122-3p在RA病人血浆中异常降低。研究显示,ANRIL可以通过miR-122-5p/DUSP4轴调节骨关节炎滑膜细胞的增殖和凋亡[16-22]。但关于miR-122-5p在RA中的作用及其对滑膜细胞的影响尚未见报道。本研究检测了RA病人滑膜细胞中miR-122-5p的表达,研究结果显示,miR-122-5p低表达。进一步过表达miR-122-5p后的结果显示,RA滑膜细胞活性降低,细胞凋亡率显著升高,P21和Survival蛋白表达均显著降低,说明过表达miR-122-5p可抑制RA滑膜细胞增殖、促进其凋亡。这为RA病人滑膜病变机制提供了基础,也为miRNA在RA中的诊断和治疗研究及应用提供参考依据。
DDR2为酪氨酸激酶受体家族成员之一,其在RA滑膜组织中的表达异常升高,对软骨细胞具有破坏作用[23]。抑制DDR-2可降低关节炎模型小鼠炎症反应和关节破坏严重程度[24-27]。此外,研究发现DDR2-CYR61-MMP1信号通路通过调节滑膜细胞的迁移和侵袭,促进RA的骨侵蚀[28]。本文研究结果也显示,RA滑膜细胞中DDR2高表达,与文献报道结果相一致[23],这为探索DDR2在RA中的功能提供了体外研究的理论依据。本实验结果还表明,miR-122-5p靶向负调控DDR2的表达,以及过表达DDR2可抑制miR-122-5p对RA滑膜细胞的增殖抑制和凋亡促进作用,这说明不仅miR-122-5p可靶向调控DDR2的表达,而且DDR2也可逆向调控miR-122-5p的表达,从而发挥对RA的调控功能。这为miR-122-5p在RA治疗中的潜在价值开发提供了更充分的理论依据。
综上所述,miR-122-5p可抑制RA滑膜细胞增殖、促进其凋亡,其机制可能与miR-122-5p靶向调控DDR2有关,本研究结果为RA治疗提供了新的方向。但miR-122-5p上游基因是如何调控其表达及其在RA发生发展过程中的作用机制尚未明确。
[参考文献]
[1]WASSERMAN A M. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. American Family Physician, 2011,84(11):1245-1252.
[2]鮑晓,何成松. 沉默TLR4对类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞增殖和侵袭的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2019,54(2):187-190.
[3]PISETSKY D S. Advances in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: costs and challenges[J]. North Carolina Medical Journal, 2017,78(5):337-340.
[4]SHIM J W, PARK M J. Arthroscopic synovectomy of wrist in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Hand Clinics, 2017,33(4):779-785.
[5]LU M, ZHANG Q P, DENG M, et al. An analysis of human microRNA and disease associations[J]. PLoS One, 2008,3(10): e3420.
[6]MURATA K, YOSHITOMI H, TANIDA S, et al. Plasma and synovial fluid microRNAs as potential biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis[J]. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 2010,12(3): R86.
[7]FILKOVÁ M, JNGEL A, GAY R E, et al. microRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. BioDrugs, 2012,26(3):131-141.
[8]SU J, YU J T, REN T T, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 2 is associated with the increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 2009,330(1/2):141-152.
[9]梁晓辉,朱平,杨勇,等. 中性粒细胞增强类风湿关节炎滑膜细胞产生基质金属蛋白酶及其细胞侵袭力[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2007,23(9):827-830.
[10]STANCZYK J, PEDRIOLI D M, BRENTANO F, et al. Altered expression of microRNA in synovial fibroblasts and synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2008,58(4):1001-1009.
[11]李力,罗晓星. 类风湿关节炎患者关节液中miRNA表达谱研究及其临床意义[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2017,21(13):51-55.
[12]STANCZYK J, OSPELT C, KAROUZAKIS E, et al. Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2011,63(2):373-381.
[13]SHIBUYA H, NAKASA T, ADACHI N, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-223 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium controls osteoclast differentiation[J]. Modern Rheumatology, 2013,23(4):674-685.
[14]WANG W H, ZHANG Y Y, ZHU B, et al. Plasma micro-RNA expression profiles in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Oncotarget, 2015,6(40):42557-42568.
[15]張莹莹. 类风湿关节炎患者血浆microRNA表达谱研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2014.
[16]LI X, HUANG T L, ZHANG G D, et al. LncRNA ANRIL impacts the progress of osteoarthritis via regulating proliferation and apoptosis of osteoarthritis synoviocytes[J]. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 2019,23(22):9729-9737.
[17]HAN K, WANG F R, YU M Q, et al. LncRNA MEG3 in-hibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of synovial cells in rats with knee osteoarthritis by regulating PTEN[J]. Europeanreview for medical and pharmacological sciences, 2020,24(10):5242-5248.
[18]唐占英,褚立希,胡志俊. 力学刺激对膝骨关节炎软骨细胞作用的分子生物学机制进展[J]. 河北医学, 2019,25(2):332-335
[19]LONG H, LI Q, XIAO Z P, et al. LncRNA MIR22HG promotes osteoarthritis progression via regulating miR-9-3p/ADAMTS5 pathway[J]. Bioengineered, 2021,12(1):3148-3158.
[20]CHEN Z B, CAO W L, SU K, et al. MIR22HG inhibits cell growth, migration and invasion through regulating the miR-24-3p/p27kip1 axis in thyroid papillary carcinomas[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019,23(13):5851-5862.
[21]ZHANG H D, JING S F, WANG X X, et al. Effects of ACE2/GHRL axis on proliferation, apoptosis and inflammatory factor levels of synovial cells in osteoarthritis[J]. Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering, 2022,12(7):1342-1347.
[22]LI W, WANG B, WEI C, et al. LncRNA GACAT3 con-tributes to osteoarthritis progression by suppressing growth and inducing apoptosis of chondrocytes through miR-195/TGF-β/Smad5 axis[J]. Archives of Medical Science, 2021. doi:10.5114/aoms/130391.
[23]ZHAO W, ZHANG C, SHI M, et al. The discoidin domain receptor 2/annexin A2/matrix metalloproteinase 13 loop promotes joint destruction in arthritis through promoting migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes[J]. Arthritis & Rheumatology (Hoboken, N J), 2014,66(9):2355-2367.
[24]MU N, GU J T, HUANG T L, et al. Blockade of discoidin domain receptor 2 as a strategy for reducing inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis via altered interleukin-15 and dkk-1 signaling in fibroblast-like synoviocytes[J]. Arthritis & Rheumatology (Hoboken, N J), 2020,72(6):943-956.
[25]KIM J J, DAVID J M, WILBON S S, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 activation links extracellular matrix to podocyte lipotoxicity in Alport syndrome[J]. EBioMedicine, 2021,63(5):103162. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103162.
[26]SANNOMIYA Y, KASEDA S, KAMURA M, et al. The role of discoidin domain receptor 2 in the renal dysfunction of alport syndrome mouse model[J]. Renal Failure, 2021,43(1):510-519.
[27]MOUSSA C E H, HEBRON M, LONSKAYA I. A novel discoidin domain receptor inhibitor reduces neuropathology and attenuates inflammation in Alzheimer and Parkinson models[J]. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, July, 2017,13(7 Supple):P228-P229.
[28]HUANG T L, MU N, GU J T, et al. DDR2-CYR61-MMP1 signaling pathway promotes bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis through regulating migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes[J]. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 2017,32(2):407-418.
(本文編辑于国艺)
