多学科联合治疗对肥胖患儿炎症因子及胰岛素抵抗的影响
2021-09-28陈琦俞碧君齐茵琳庞福珍许光敏
陈琦 俞碧君 齐茵琳 庞福珍 许光敏

[關键词] 多学科联合治疗;肥胖症;炎症因子;胰岛素抵抗
[中图分类号] R711.75 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)22-0057-05
Effects of multidisciplinary combined therapy on inflammatory factors and insulin resistance in obese children
CHEN Qi1 YU Bijun2 QI Yinlin1 PANG Fuzhen1 XU Guangmin1
1.Department of Pediatrics, Tiantai Branch, Zhejiang Provincial People′s Hospital, Tiantai 317200, China; 2.International Medical Center (House of Elite Physicians), Tiantai Branch, Zhejiang Provincial People′s Hospital, Tiantai 317200, China
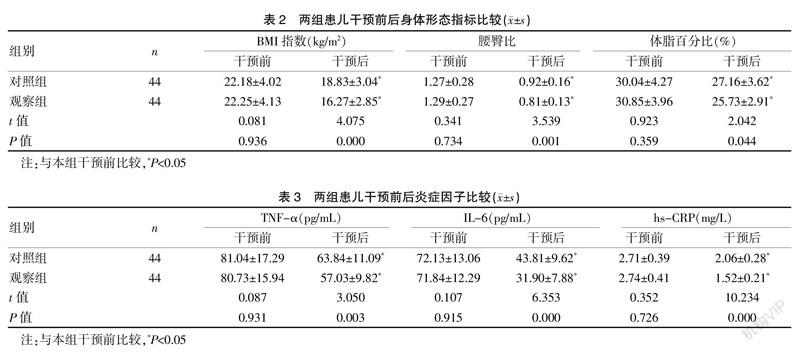
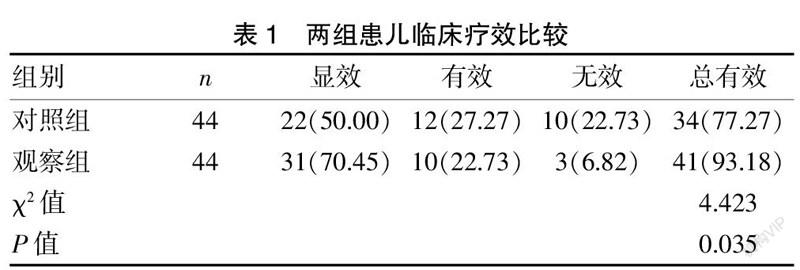
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effects of multidisciplinary combined therapy on inflammatory factors and insulin resistance in obese children. Methods A total of 88 obese children who were treated in our hospital from February 2017 to August 2019 were selected as the research objects and divided into the observation group (n=44) and the control group (n=44) according to the random number table method. The control group was treated with conventional therapy, while the observation group was treated with multidisciplinary combined therapy led by the pediatrician. The clinical efficacy, body shape index, inflammatory factors and insulin resistance of the two groups were compared. Results The total effective rate in the observation group was 93.18%, which was higher than that of 77.27% in the control group, with significant difference (P<0.05). After intervention, BMI, waist-hip ratio and body fat percentage in both groupswere significantly lower than those before intervention,and the decrease in the observation group was higher than that in the control group, with significant difference (P<0.05); the levels of TNF-α,IL-6 and hs-CRP in the two groups were significantly lower than those before intervention, and the decrease in the observation group was higher than that in the control group, with significant difference (P<0.05); the levels of FINS,CLU and HOMA-IR in the two groups were significantly lower than those before intervention, and the decrease in the observation group was higher than that in the control group, with significant difference(P<0.05). Conclusion Compared with conventional therapy, multidisciplinary combined therapy can significantly improve the efficacy of obese children, reduce BMI, waist-hip ratio, body fat percentage and insulin resistance index, and relieve inflammation.
