点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中神经型一氧化氮合成酶的分布与定位
2021-04-15白帆孙敬锋张胜根韩卓然吕爱军胡秀彩
白帆 孙敬锋 张胜根 韩卓然 吕爱军 胡秀彩


摘要:【目的】研究點带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中的一氧化氮(NO)含量及神经型一氧化氮合成酶(nNOS)分布与活性,为深入揭示NO在点带石斑鱼神经系统中的作用机制打下基础。【方法】采用NADPH-d组织化学染色法、免疫组织化学法、蛋白免疫印迹(Western blotting)及Griess试剂法,对点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中nNOS的分布与活性及NO含量进行分析。【结果】经NADPH-d组织化学染色后,一氧化氮合成酶(NOS)阳性物质呈蓝色。在点带石斑鱼大脑中,NOS阳性物质位于神经元和神经纤维;在小脑中,NOS分布在颗粒层的颗粒细胞、分子层的神经纤维和浦肯野细胞层的浦肯野细胞;在视网膜中,NOS分布于色素上皮层、视锥视杆层、外核层、外网层、内核层、内网层、节细胞层和视神经纤维层。经免疫组织化学染色后,nNOS阳性物质呈深棕色。在大脑中,nNOS存在于神经元和神经纤维;在小脑中,nNOS分布在颗粒层、分子层和浦肯野细胞层;在视网膜中,nNOS分布在色素上皮层、视锥视杆层、外核层、外网层、内核层、内网层、节细胞层和视神经纤维层。Western blotting检测结果显示,点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中的nNOS在显色后的硝酸纤维素膜上均出现3条免疫印迹条带,对应分子量分别为80、120和130 kD。NO含量在点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中分别为17.601±1.743和13.624±1.249 ?mol/L,nNOS活性在脑组织和视网膜中分别为38.070±3.047和23.748±2.860 U/mg。【结论】在点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中均存在nNOS,推测nNOS在点带石斑鱼脑神经及视神经系统生理活动中发挥重要作用。脑组织中的NO含量和nNOS活性均显著高于视网膜,是由于脑组织作为重要的中枢神经,对机体生理功能起重要调节作用。
关键词: 点带石斑鱼;神经型一氧化氮合成酶(nNOS);脑组织;视网膜;免疫组织化学定位;NADPH-d组织化学染色
中图分类号: S965.334 文献标志码: A 文章编号:2095-1191(2021)12-3286-08
Immunohistochemical distribution and localization of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in brain and retina of Epinephelus coioides
BAI Fan, SUN Jing-feng*, ZHANG Sheng-gen, HAN Zhuo-ran, LYU Ai-jun, HU Xiu-cai
(College of Fisheries, Tianjin Agricultural University/Tianjin Key Lab of Aqua-ecology and
Aquaculture, Tianjin 300384, China)
Abstract:【Objective】The content of nitric oxide(NO), distribution and activity of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in brain and retina of Epinephelus coioides were studied to provide foundation for further revealing the mechanism of action of NO in the nervous system of E. coioides. 【Method】NADPH-d staining, immunohistochemical method, western blotting and Griess reaction were used to study the distribution, activity of nNOS and NO content in the brain and retina.【Result】The positive material of nitric oxide synthase(NOS) was stained blue using NADPH-d method. NOS positive materials were found in neurons and nerve fibers in the cerebrum. In the cerebellum, NOS was distributed in granular cells of the granular layer, nerve fibers of the molecular layer, and Purkinje cells of the Purkinje cell layer. In the retina, the NOS was found to be distributed in the pigment epithelium layer, rod and cone layer, outer nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, inner plexiform layer, ganglion cell layer and retinal nerve fiber layer. In addition, the immunohistochemical positive materials of nNOS were stained dark brown. In the cerebrum, nNOS was distributed in neurons and nerve fibers. In the cerebellum, nNOS was distributed in the granular layer, molecular layer and Purkinje cell layer. In the retina, nNOS was found to be distributed in the pigment epithelium layer, rod and cone layer, outer nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, inner plexiform layer, ganglion cell layer and retinal nerve fiber layer. The result of western blotting showed that there were three protein blotting bands on the nitrocellulose membrane after co-lor development for nNOS in the brain and retina, their corresponding molecular weights were 80, 120 and 130 kD, respectively. The NO content in brain and retina were 17.601±1.743 and 13.624±1.249 mol/L, respectively. The nNOS acti-vity in brain and retina were 38.070±3.047 and 23.748±2.860 U/mg, respectively. 【Conclusion】nNOS exists in brain and retina of E. coioides, and it is speculated that nNOS may play an important role in the cranial and visual nervous system physiological activity of fish. The NO content and nNOS activity in brain are significantly higher than those in retina, presumably because the brain is the important central nervous system and plays an important role in regulating the physiological functions of body.
Key words: Epinephelus coioides; neuronal nitric oxide synthase(nNOS); brain; retina; immunohistochemistry; NADPH-d staining
Foundation item: National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972840); Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (19JCZDJC34600); Scientific Research and Innovation Project of Tianjin Agricultural University (2019XY037)
0 引言
【研究意义】一氧化氮(Nitric oxide,NO)是一种信使分子,具有多种生物学功能,能介导血管内皮源性舒张,并参与免疫调节和免疫耐受(Seabra and Duran,2017;Alimoradi et al.,2019;Yu et al.,2019)。NO是由L-精氨酸末端胍基氧化产生,此反应主要依靠一氧化氮合成酶(Nitric oxide synthases,NOS)催化完成(Hedison et al.,2018)。根据组织表达及其功能的不同,可将NOS划分为3种:神经型一氧化氮合成酶(Neuronal nitric oxide synthase,nNOS)、诱导型一氧化氮合成酶(Inducible nitric oxide synthase,iNOS)和内皮型一氧化氮合成酶(Endothelial nitric oxide synthase,eNOS)(Bogdan,2015)。其中,nNOS主要在脑神经系统的神经元中表达,通过神经转运而引起血管和非血管平滑肌松弛,产生的NO参与大脑的发育、学习、扩展及记忆等过程(Luo and Zhu,2011;刁宏旺和李守林,2017;Chong et al.,2019)。因此,研究鱼类nNOS的分布及活性,可为揭示NO在鱼类神经系统中的作用机制提供理论依据。【前人研究进展】NO是神经元NMDA受体激活后产生的一种重要递质,可促使神经系统第二信使cGMP的产生,从而对神经系统产生影响(Zhang et al.,2017)。视网膜是鱼类产生视觉的部位,而NO是鱼类视网膜中重要的神经调节因子,通过影响突觸前和突触后的神经元以调节视觉信息处理(Neufeld et al.,2000;李超等,2014;Wang et al.,2018)。3种亚型NOS在视网膜中均有不同程度的表达,但nNOS是视觉反应的主要参与者(Vielma et al.,2012)。还原型辅酶Ⅱ依赖性黄递酶(NADPH-d)作为NOS的组织化学标记物,可间接反映NO的分布及活性,已广泛应用于NOS在神经系统中的定位研究,但NADPH-d组织化学染色无法直接区分NOS的3种亚型(Sun et al.,2020)。免疫组织化学法是通过抗原和抗体特异性结合区分不同亚型NOS(韩卓然等,2016),已有学者将这2种方法相结合用于神经系统中的nNOS定位研究。Sánchez-Islas和León-Olea(2001)通过分析nNOS在美西钝口螈(Ambystoma mexicanum)嗅上皮中的分布情况,发现其主要存在于嗅觉受体神经元;王平利等(2011)研究发现恒河猴(Macaca mulatta)纹状体中分布着大量的nNOS阳性神经元;Bombardi等(2013)研究证实nNOS在宽吻海豚(Tursiops truncatus)的脊髓中广泛表达;Chong等(2019)研究报道了nNOS在啮齿动物大脑不同区域的分布情况;López等(2019)通过研究澳大利亚肺鱼(Neoceratodus forsteri)氮能系统,并以此评估神经递质系统间的相互作用;Serenini等(2020)研究证实NO是肌肠神经细胞中重要的神经递质之一,在平滑肌松弛过程中发挥中介作用;Yan等(2021)研究发现NOS在大鼠成牙本质细胞中有表达。【本研究切入点】目前,针对nNOS的研究主要集中在哺乳动物(Anaeigoudari et al.,2016;Coelho et al.,2017;Zhang et al.,2018),仅在马苏大马哈鱼(Oncorhynchus masou)及大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus)等少数鱼类中有报道(Pushchina et al.,2012;韩卓然等,2016),而有关点带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides)脑组织和视网膜中nNOS分布及活性与NO含量的研究至今鲜见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】采用NADPH-d组织化学染色法、免疫组织化学法、蛋白免疫印迹(Western blotting)及Griess试剂法,对点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中nNOS的分布与活性及NO含量进行研究,为深入揭示NO在点带石斑鱼神经系统中的作用机制打下基础。
1 材料与方法
1. 1 试验材料
供试点带石斑鱼购自天津市海发珍品实业发展有限公司,平均体长20±1 cm、平均体重210±20 g;挑选健康无病的30尾点带石斑鱼备用。羊nNOS一抗(ab6175)和二抗(ab6746)购自英国Abcam公司;NO测定试剂盒购自碧云天生物技术研究所;NOS测定试剂盒和蛋白定量测试盒购自南京建成生物工程研究所。
1. 2 样品采集与处理
点带石斑鱼以三卡因(MS-222)进行麻醉,体表消毒后于冰盘上取出脑组织和视网膜,放入4%多聚甲醛中固定5 h,然后置于20%蔗糖溶液中至组织沉底,-80 ℃保存备用。
1. 3 NADPH-d组织化学染色
使用冰冻切片机(Thermo Microm HM 525)进行快速冷冻切片;切片(厚度7 ?m)以PBS(0.01 mol/L,pH 7.4)冲洗3次,每次5 min;然后在β-NADPH孵育液(0.3% Triton X-100,1 mg/mL NBT,0.6 mg/mL β-NADPH,0.1 mol/L PBS)中37 ℃孵育3 h,经脱水、透明及封片后进行镜检。阴性对照孵育液中不含β-NADPH。
1. 4 免疫组织化学定位
参照韩卓然等(2016)的方法进行免疫组织化学定位。在阻断内源性过氧化物酶活性后进行抗原修复,具体操作:将冷冻切片置于枸橼酸缓冲液(0.01 mol/L,pH 6.0)中煮沸15~20 min。以PBS(0.01 mol/L,pH 7.4)代替一抗用于阴性对照。
1. 5 Western blotting检测
将点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜样品分别置于匀浆器中,加入单去污剂裂解液(0.05 mol/L Tris HCl,8.76 mg/mL NaCl,1% Triton X-100,100 μg/mL PMSF),在冰上进行充分匀浆后,参照孙敬锋等(2017)的方法进行Western blotting检测。
1. 6 NO含量与nNOS活性测定
取点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜样品各100 mg,解冻后充分匀浆,分别采用蛋白定量测试盒(考马斯亮蓝法)测定蛋白含量,NO测定试剂盒(Griess试剂法)测定NO含量,NOS测定试剂盒(化学比浊法)测定nNOS活性,具体方法按试剂盒说明进行操作。
1. 7 统计分析
试验数据采用SPSS 16.0中的独立样本 t 检验进行差异显著性分析。
2 结果与分析
2. 1 NADPH-d组织化学染色结果
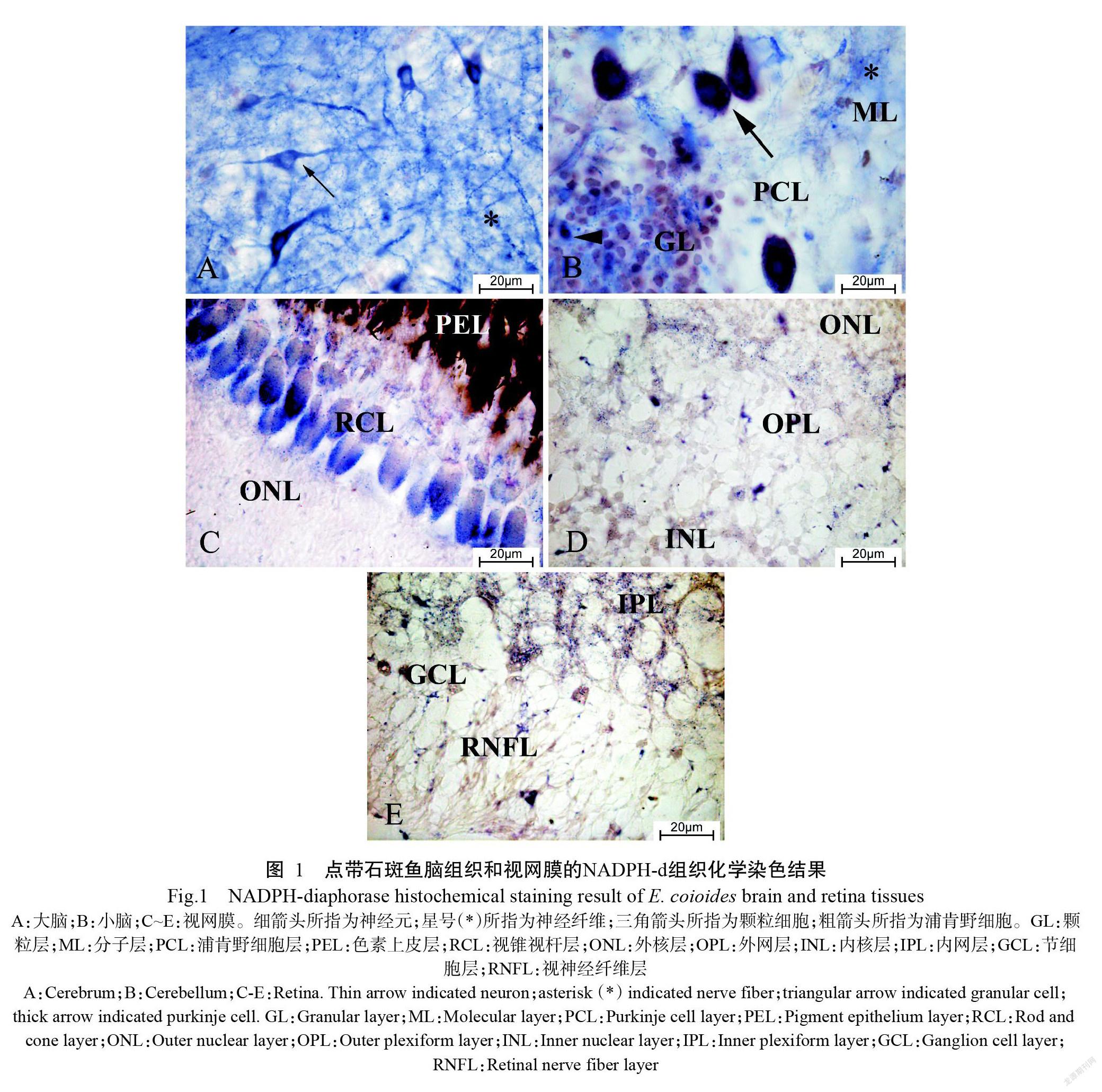
经NADPH-d组织化学染色后,NOS阳性物质呈蓝色。如图1-A所示,点带石斑鱼大脑中存在丰富的神经元和神经纤维,神经元细胞核淡染,呈梭形或多角形,还有一些呈卵圆形。小脑颗粒层中的阳性颗粒细胞及分子层中的阳性神经纤维均呈蓝色;浦肯野细胞中也存在NOS阳性反应(图1-B)。在视网膜中,色素上皮层和视锥视杆层可观察到大量蓝色颗粒(图1-C);此外,在外核层、外网层和内核层(图1-D),以及内网层、节细胞层和视神经纤维层均可观察到NOS阳性物质(图1-E)。
2. 2 免疫组织化学定位结果
经免疫组织化学染色后,nNOS阳性物质呈深棕色。在点带石斑鱼大脑中可观察到神经元(图2-A)和神经纤维(图2-B)nNOS阳性物质;在小脑颗粒层中有少量nNOS阳性颗粒细胞,分子层中有许多的nNOS阳性神经纤维,浦肯野细胞也呈现nNOS阳性反应(图2-C)。在视网膜中的色素上皮层、视锥视杆层、外核层和外网层(图2-D),以及内核层、内网层、节细胞層和视神经纤维层均呈明显的nNOS阳性反应(图2-E)。
2. 3 Western blotting检测结果
经Western blotting检测,结果发现点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中的nNOS分别在硝酸纤维素膜上出现3条免疫印迹条带(图3)。根据蛋白分子量标准Marker迁移率,计算得到对应的蛋白分子量分别为80、120和130 kD。
2. 4 NO含量及nNOS活性测定结果
由图4可看出,点带石斑鱼脑组织中NO含量为17.601±1.743 ?mol/L,视网膜中NO含量为13.624±1.249 ?mol/L,即脑组织中的NO含量显著高于视网膜(P<0.05,下同)。由图5可看出,点带石斑鱼脑组织中nNOS活性为38.070±3.047 U/mg,视网膜中nNOS活性为23.748±2.860 U/mg,即脑组织中的nNOS活性显著高于视网膜。
3 讨论
NO是一种简单的双原子分子,参与体内信号转导,在多种器官、系统和组织中发挥重要作用(Wang et al.,2018;Tejero et al.,2019)。NOS是NO合成过程中的关键酶,由于NO不稳定,因此主要通过观察NOS分布及活性对NO进行定位研究(刘鹏等,2009;高川等,2020)。本研究采用NADPH-d组织化学染色法定位NOS,但无法直接鉴别NOS的亚型,故同时采用免疫组织化学法定位nNOS。nNOS结构域高度保守,在不同物种中均含有氧化蛋白域、还原蛋白域及钙调素(CaM)结合位点等结构域(张湑泽等,2014)。nNOS的基因编码区(CDS)高度保守,人类和鼠的nNOS氨基酸序列相似性为93%,鼠和牛的nNOS氨基酸序列相似性为98%(杜滨,2012)。经BLAST比对分析发现,羊nNOS抗体作为抗原肽的第1409~1429位氨基酸序列高度保守,故本研究以羊nNOS抗体检测点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中的nNOS分布情况。
经NADPH-d染色后,发现在点带石斑鱼大脑皮质的神经元和神经纤维及小脑皮质颗粒层、分子层和浦肯野细胞层中均存在NOS,与Schober等(1993)对虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mickiss)、Holmqvist等(1994)对大西洋鲑(Salmo salar)的研究结果相似。Villani和Guarnieri(1996)利用NADPH-d组织化学染色法对金鱼(Carassius auratus)视网膜中的NOS进行定位,结果表明NOS主要分布在内核层、节细胞层、内网层和外网层。除此之外,本研究还在点带石斑鱼视网膜的色素上皮层、视锥视杆层、外核层和视神经纤维层中发现NOS阳性表达,造成这种差异的原因可能是鱼的种类不同。鉴于NOS的3种亚型无法通过NADPH-d组织化学染色进行直接鉴别,本研究同时采用免疫组织化学法定位nNOS,结果发现nNOS位于点带石斑鱼大脑皮质的神经元和神经纤维及小脑皮质颗粒层、分子层和浦肯野细胞层中,与NADPH-d组织化学染色结果一致,且nNOS阳性神经元主要呈梭形,与Jadhao和Malz(2004)在伯氏妊丽鱼(Haplochromis burtoni)脑组织中的观察结果相似。已有研究证明,NO是视网膜中生理及病理过程的重要活性介质(Vielma et al.,2012)。经免疫组织化学染色后,在点带石斑鱼视网膜中深棕色的nNOS阳性物质主要分布在色素上皮层、视锥视杆层、外核层、外网层、内核层、内网层、节细胞层和视神经纤维层,与NADPH-d组织化学染色显示的NOS分布部位一致,但NADPH-d组织化学染色的外核层、外网层、内核层、内网层、节细胞层和视神经纤维层颜色较弱,究其原因可能是NADPH-d组织化学染色定位的是NOS(包含3种NOS亚型),而免疫组织化学只定位nNOS。在点带石斑鱼的脑组织和视网膜中均存在nNOS,故推测nNOS产生的NO可作为神经递质介导并参与神经系统的信息传递和生理调节过程。
Kim等(1999)采用Western blotting检测NOS在大鼠、小鼠、豚鼠及兔子视网膜中的表达情况,结果均获得1条分子量为155 kD的免疫印迹条带。孙敬锋等(2017)通过研究nNOS在毛蚶(Scapharca kagoshimensis)外套膜和鳃组织中的表达情况,发现有2条nNOS免疫反应条带,对应的分子量分别为120和80 kD。本研究利用Western blotting对点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中的nNOS进行检测分析,结果获得3条免疫印迹条带,对应的蛋白分子量分别为80、120和130 kD。nNOS在进化过程中高度保守,在不同物种的不同组织器官中均有分布,但其蛋白分子量存在差异。在点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中均出现3条不同分子量的nNOS免疫印迹条带,究其原因可能是nNOS存在不同的修饰和剪接作用下并非以单一形式存在,但具体作用机制还需进一步探究。
NO含量变化在机体生理机能中发挥重要作用,免疫调节、血小板凝集反应及神经信号传递等生理过程均伴随有低水平的NO,而许多疾病的产生和发展与机体体内稳定的NO含量变化有关(张胜根等,2011;Akanji et al.,2020)。在正常生理状况下,nNOS可在组织器官内低水平表达(Robbins and Grisham,1997)。张胜根等(2011)研究表明,在半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis Gunther)不同组织器官中均能检测到NO和NOS,但不同组织器官中的NO含量和NOS活性存在明显差异。本研究结果显示,点带石斑鱼脑组织中的NO含量和nNOS活性均显著高于视网膜,推测脑组织作为重要的中枢神经,含有丰富的nNOS,产生的NO可调节机体的生理功能。
4 结论
在点带石斑鱼脑组织和视网膜中均存在nNOS,推测nNOS在点带石斑鱼脑神经及视神经系统生理活动中发挥重要作用。脑组织中的NO含量和nNOS活性均显著高于视网膜,是由于脑组织作为重要的中枢神经,对机体生理功能起重要调节作用。
参考文献:
韩卓然,石洪玥,孙敬锋,王一泽,邢克智. 2016. 神经型一氧化氮合酶在大菱鲆脑组织中的分布及定位[J]. 南方农业学报,47(2):296-300. [Han Z R,Shi H Y,Sun J F,Wang Y Z,Xing K Z. 2016. Distribution and immunohistochemical localization of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in brain tissue of Scophthalmus maximus[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,47(2):296-300.] doi:10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2016.02.296.
高川,徐丽娟,席健峰,姜良勇,周奎臣. 2020. 一氧化氮与代谢综合症相关性的研究进展[J]. 山东化工,49(9):98-99. [Gao C,Xu L J,Xi J F,Jiang L Y,Zhou K C. 2020. Research progress on the relationship between nitric oxi-de and metabolic syndrome[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry,49(9):98-99.] doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2020. 09.037.
刁宏旺,李守林. 2017. 诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)与神经源性膀胱的关系研究[J]. 臨床小儿外科杂志,16(6):612-616. [Diao H W,Li S L. 2017. Relationship between inducible nitric oxide synthase(iNOS) and neurogenic bladder[J]. Journal of Clinical Pediatric Surgery,16(6):612-616.] doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-6353.2017.06.020.
杜滨. 2012. 中国卤虫一氧化氮合成酶基因的克隆及表达模式研究[D]. 大连:辽宁师范大学. [Du B. 2012. Molecular cloning and the preliminary function of the nitric oxi-de synthase from brine shrimp—Artemia sinica[D]. Dalian:Liaoning Normal University.] doi:10.7666/d.Y2234542.
李超,王亮,覃乐政,张秀梅. 2014. 4种岩礁性鱼类视网膜感光细胞和最小分辨角的比较[J]. 水产学报,38(3):400-409. [Li C,Wang L,Qin L Z,Zhang X M. 2014. Comparison study of four species of coral-reef teleosts (Scorpaeniformes) with photoreceptor cells and the angle of minimum resolution[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,38(3):400-409.] doi:10.3724./SP.J.1231.2014.49000.
刘鹏,伟忠民,佟宇. 2009. NO、NOS对学习记忆和神经毒性作用的研究进展[J]. 辽宁医学院学报,30(4):369-372. [Liu P,Wei Z M,Tong Y. 2009. The research of NO and NOS effects on learning memory and neurological toxicity[J]. Journal of Liaoning Medical University,30(4):369-372.] doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-0424.2009.04.034.
孙敬锋,王一泽,吕爱军,Yeong Yik Sung,董少杰,郭永军,邢克智. 2017. 毛蚶外套膜和鳃组织中神经型一氧化氮合酶免疫组织化学定位研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,(3):115-120. [Sun J F,Wang Y Z,Lü A J,Sung Y Y,Dong S J,Guo Y J,Xing K Z. 2017. Immunohistochemical localization of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in mantle tissue of Scapharca kagoshimensis[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology,(3):115-120.] doi:10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2017.03.016.
王平利,程树军,李玉谷,黄韧,张媛,李楚宣. 2011. 恒河猴纹状体一氧化氮合酶阳性神经元的形态学观察[J]. 郑州牧业工程高等专科学校学报,31(3):6-9. [Wang P L,Cheng S J,Li Y G,Huang R,Zhang Y,Li C X. 2011. Morphological observation of the neurons containing NOS in the striatum of rhesus monkey(Macaca mulatta)[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou College of Animal Husbandry Engineering,31(3):6-9.] doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-3111. 2011.03.003.
張胜根,邢克智,孙敬锋,王庆奎,马倩倩. 2011. 半滑舌鳎组织器官中一氧化氮含量和一氧化氮合酶活性的测定[J]. 安徽农业科学,39(12):7295-7297. [Zhang S G,Xing K Z,Sun J F,Wang Q K,Ma Q Q. 2011. Determination of nitric oxide production and nitric oxide synthase activity in organizations of half-smooth tongue-sole(Cynoglossus semilaevis Gunther)[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,39(12):7295-7297.] doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.12.137.
张湑泽,谢玲,郭新异,陈桂华,林恭华,都玉蓉,庞礴,郭松长. 2014. 高原鼢鼠神经型一氧化氮合酶基因编码区序列克隆与分析[J]. 兽类学报,34(1):17-27. [Zhang X Z,Xie L,Guo X Y,Chen G H,Lin G H,Du Y R,Pang B,Guo S C. 2014. CDS cloning and sequence analysis of neuronal nitric oxide synthase(nNOS) from plateau zokor (Myospalax baileyi)[J]. Acta Theriologica Sinica,34(1):17-27.] doi:10.16829/j.slxb.2014.01.003.
Akanji M A,Adeyanju A A,Rotimi D,Adeyemi O S. 2020. Nitric oxide balance in health and diseases:Implications for new treatment strategies[J]. The Open Biochemistry Journal,14(1):25-32. doi:10.2174/1874091X0201401 0025.
Alimoradi H,Greish K,Gamble A B,Giles G I. 2019. Controlled delivery of nitric oxide for cancer therapy[J]. Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology,7(4):279-303. doi:10.2174/2211738507666190429111306.
Anaeigoudari A,Soukhtanloo M,Shafei M N,Sadeghnia H R,Reisi P,Beheshti F,Behradnia S,Mousavi S M,Hosseini M. 2016. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase has a role in the detrimental effects of lipopolysaccharide on spatial me-mory and synaptic plasticity in rats[J]. Pharmacological Reports,68(2):243-249. doi:10.1016/j.pharep.2015.09. 004.
Bogdan C. 2015. Nitric oxide synthase in innate and adaptive immunity:An update[J]. Trends in Immunology,36(3):161-178. doi:10.1016/j.it.2015.01.003.
Bombardi C,Grandis A,Gardini A,Cozzi B. 2013. Nitrergic neurons in the spinal cord of the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus)[J]. Anatomical Record,296(10):1603-1614. doi:10.1002/ar.22766.
Chong P S,Poon C H,Fung M L,Guan L,Steinbusch H W M,Chan Y S,Lim W L,Lim L E. 2019. Distribution of neuronal nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in adult male Sprague-Dawley rat brain[J]. Acta Histochemica,121(8):151437. doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2019.08.004.
Coelho C H,Martins T F,Oliveira-Pelegrin G R,da Rocha M J A. 2017. Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase activity does not alter vasopressin secretion in septic rats[J]. Pituitary,20(3):333-339. doi:10.1007/s11102-017-0786-x.
Hedison T M,Hay S,Scrutton N S. 2018. Trapping methods for probing functional intermediates in nitric oxide synthases and related enzymes[J]. Frontiers in Bioscience,23(10):1874-1888. doi:10.2741/4678.
Holmqvist B I,Ostholm T,Alm P,Ekstr?m P. 1994. Nitric oxide synthase in the brain of a teleost[J]. Neuroscience Letters,171(1-2):205-208. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(94)90640-8.
Jadhao A G,Malz C R. 2004. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-diaphorase activity in the brain of a cichlid fish,with remarkable findings in the entopeduncular nucleus:A histochemical study[J]. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy,27(2):75-86. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2003.12.001.
Kim I B,Lee E J,Kim K Y,Ju W K,Oh S J,Joo C K,Chun M H. 1999. Immunocytochemical localization of nitric oxide synthase in the mammalian retina[J]. Neuroscience Letters,267(3):193-196. doi:10.1016/s0304-3940(99)00363-8.
López J M,Morona R,González A. 2019. Pattern of nitrergic cells and fibers organization in the central nervous system of the Australian lungfish,Neoceratodus forsteri (Sarcopterygii:Dipnoi)[J]. Journal of Comparative Neurology,527(11):1771-1800. doi:10.1002/cne.24645.
Luo C X,Zhu D Y. 2011. Research progress on neurobiology of neuronal nitric oxide synthase[J]. Neuroscience Bulletin,27(1):23-35. doi:10.1007/s12264-011-1038-0.
Neufeld A H,Shareef S,Pena J. 2000. Cellular localization of neuronal nitric oxide synthase(NOS-1) in the human and rat retina[J]. The Journal of Comparative Neurology,416(2):269-275. doi:10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(20000110)416:2<269::aid-cne11>3.0.co;2-2.
Pushchina E V,Varaksin A A,Obukhov D K. 2012. Gaseous transmitters in the brain of the masu salmon,Oncorhynchus masou (Salmoniformes,Salmonidae)[J]. Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology,48(1):101-114. doi:10.1134/s0022093012010112.
Robbins R A,Grisham M B. 2006. Nitric oxide[J]. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology,29(6):857-860. doi:10.1016/s1357-2725(96)00167-7.
Sánchez-Islas E,León-Olea M. 2001. Histochemical and immunohistochemical localization of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the olfactory epithelium of the axolotl,Ambystoma mexicanum[J]. Nitric Oxide,5(4):302-316. doi:10.1006/niox.2001.0347.
Schober A,Malz C R,Meyer D L. 1993. Enzymehistochemical demonstration of nitric oxide synthase in the dience-phalon of the rainbow trout(Oncorhynchus mickiss)[J]. Neuroscience Letters,151(1):67-70. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(93)90047-o.
Seabra A B,Duran N. 2017. Nanoparticulated nitric oxide donors and their biomedical applications[J]. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry,17(3):216-223. doi:10.2174/1389557516666160808124624.
Serenini G F,Beltrami J M,Ger?nimo E,Favetta P M,Legnani N G E,Otutumi L K,Martins L A,Germano R M. 2020. Quantification of the neurons of myenteric plexus of the bat Molossus rufus[J]. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira,40(6):493-500. doi:10.1590/1678-5150-PVB-6381.
Sun H J,Gao W T,Li H M,Ma X L. 2020. Comparative study of the distribution of NOS-positive neurons in pigeon intestine[J]. Anatomia Histologia Embryologia,49(4):563-570. doi:10.1111/ahe.12562.
Tejero J,Shiva S,Gladwin M T. 2019. Sources of vascular nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species and their regulation[J]. Physiological Reviews,99(1):311-379. doi:10. 1152/physrev.00036.2017.
Vielma A H,Retamal M A,Schmachtenberg O. 2012. Nitric oxide signaling in the retina:What have we learned in two decades?[J]. Brain Research,1430:112-125. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.10.045.
Villani L,Guarnieri T. 1996. Localization of nitric oxide synthase in the goldfish retina[J]. Brain Research,743(1-2):353-356. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(96)01103-1.
Wang Q M,Zhao X Y,Wang Z,Yang X B. 2018. Expression of nitric oxide synthase in the retina of monocular deprivation amblyopia rats[J]. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences,22(7):1879-1883. doi:10.26355/eurrev_201804_14708.
Yan T,Kong Y,Fan W G,Kang J,Chen H L,He H W,Huang F. 2021. Expression of nitric oxide synthases in rat odontoblasts and the role of nitric oxide in odontoblastic differentiation of rat dental papilla cells[J]. Deve-lopment,Growth & Differentiation,63(7):354-371. doi:10.1111/dgd.12745.
Yu B L,Ichinose F,Bloch D B,Zapol W M. 2019. Inhaled nitric oxide[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology,176(2):246-255. doi:10.1111/bph.14512.
Zhang J,Han Y,Wang Y,Cheng X,Wang C J. 2018. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition reduces brain damage by promoting collateral recruitment in a cerebral hypoxia-ischemia mice model[J]. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences,22(10):3166-3172. doi:10.26355/eurrev_201805_15077.
Zhang N,Diao Y,Hua R R,Wang J,Han S,Li J F,Yin Y L. 2017. Nitric oxide-mediated pathways and its role in the degenerative diseases[J]. Frontiers in Bioscience,22(5):824-834. doi:10.2741/4519.
(責任编辑 陈德元)
