考虑双边定价的P2P网络借贷拍卖机制设计
2020-11-07周正龙胡凤英李延晖
周正龙,胡凤英,李延晖
考虑双边定价的P2P网络借贷拍卖机制设计
周正龙1,胡凤英2,李延晖1
(1. 华中师范大学 信息管理学院,湖北 武汉 430079;2.中南大学 商学院,湖南 长沙 410083)
本文基于P2P网络借贷的双边市场特征,提出一种考虑双边定价的P2P网络借贷拍卖机制,旨在激励借贷双方自觉地报告自己的真实类型,进而提高整个机制的效率。同时,该机制在激励参与人披露其真实信息以及降低借款人支付成本方面具有一定优势,是对现有交易机制的一种改进与补充。进一步研究结果显示,在不考虑违约率的情形下,该拍卖机制满足双边激励相容性、个体理性和弱预算平衡等特征;而在考虑违约率的情形下,该拍卖机制满足双边激励相容性,但不满足个体理性和弱预算平衡特征。对比发现,考虑违约率的拍卖机制更实用于实际经济环境,但受到违约率的影响无法实现机制的效率最大化,因此需要尽量降低借款人的违约率,从而有利于提高机制对资源的配置效率。
P2P网络借贷;拍卖机制;激励相容性;个体理性;弱预算平衡
0 引言
早在公元前500年,拍卖就被用于出售各种物品。无论是艺术品还是古董,都会在拍卖会上落槌卖出,包括现在的许多商品,比如烟草、鱼、鲜花、废金属等,都可以通过拍卖的方式卖出去,甚至于一些公用事业的债券也可以通过拍卖卖给投资公司。而在当今时代,拍卖机制的形式逐渐被细分,不同领域逐渐形成自己的拍卖形式。例如,在政府采购合同中,通常采取一级价格密封拍卖、二级价格密封拍卖、英式拍卖以及荷兰式拍卖的形式进行交易[1-2];在多属性拍卖中,通常采取第一评分拍卖(first-score auction)、第二评分拍卖(second-score auction)以及第二评分优先供应拍卖(second-preferred-offer auction)[3-4]。因此,在P2P网络借贷市场中,简单地复制这些拍卖机制并不能有效解决P2P网络借贷的资源配置问题,无法使得资源配置达到帕累托状态。
目前国外文献的研究主要集中于信用风险评价、借款人和贷款人行为等相关问题[5-11]。例如Guo 等[5]对不同跨度的贷款资金进行分析,并建模评估每笔贷款的信用风险问题; Liu 等[6]对贷款人和借款人的行为进行分析得到,贷款人和借款人会存在羊群效应、聚集效应和菱镜效应的现象。同样地,国内文献也主要侧重于风险控制、信用认证机制、法律监管等问题[12-13],而较少分析目前P2P网络借贷市场的拍卖机制。事实上,P2P网络借贷市场刚开始实施的交易模式是拍卖机制,而且这种拍卖机制不同于ebay的拍卖机制。所以,早期研究人员主要从拍卖竞价的影响因素展开分析,研究贷款人的个人、环境和社会等因素是否会对贷款人的投标策略产生显著的影响[14]。随后,一些研究人员将P2P网络借贷拍卖机制与网上传统拍卖机制进行比较研究,指出了P2P网络借贷拍卖机制与传统拍卖机制的显著差异性,其中最显著的不同是P2P网络借贷拍卖机制属于多个中标人机制,而传统拍卖机制属于单个中标人机制[15]。整体而言,拍卖方式比文字描述能更好地解决P2P借贷的资源配置和交易效率问题,拍卖方式能够更好地披露借款人信息,激励借款人在还款过程中履行借款约定,有良好信誉记录的借款人能够获得更低成本的借款[16-17]。
然而,不同P2P网络借贷市场存在不同的交易机制(总体上可以划分为三种不同机制,即考虑借款人定价的交易机制、考虑贷款人定价的拍卖机制以及考虑第三方平台定价的交易机制[11]),使得现有经典平台的交易机制在借贷双方的激励相容特征和机制效率方面存在一些不足。例如,Prosper平台的拍卖机制只能满足部分中标贷款人的激励相容性,无法满足最后一个成功贷款人的激励相容特征,因此Prosper拍卖机制的交易价格往往偏高,导致较少借款人参与拍卖,使得整个机制的效率偏低[18];而Prosper平台的标价机制(即考虑第三方平台定价的交易机制)主要依赖于第三方平台对借款人的评价,其交易价格一般等于借款人的真实价格,因此可以认为借贷双边都满足激励相容特征,但是这种机制需要第三方平台严格考察借款人类型,所花费的时间和成本较大,使得整个机制的效率不高,甚至会低于Prosper拍卖机制[19]。进一步地,拍拍贷平台的散标交易(即考虑借款人定价的交易机制)无法满足借款人的激励相容特征,难以获得借款人的真实信息,因此拍拍贷平台上的违约率往往偏高,导致较少贷款人参与拍卖,同样降低了整个机制的效率[20]。因此,可以基于P2P网络借贷的双边市场特征[21],对现有P2P网络借贷市场的交易机制进行改进,以激励交易参与者批露其真实信息。
鉴于此,论文提出一种考虑双边定价的P2P网络借贷拍卖机制,以满足借款人和贷款人的双边激励相容特征,提高整个机制的交易效率(这里的双边定价可以解释为,拍卖机制的交易价格由贷款人报价和借款人报价共同决定,因此该机制可以简称为双边拍卖机制)。相对于现有平台的交易机制而言,这个机制的最大特点是同时考虑了贷款人和借款人的报价,并满足借款人和贷款人的双边激励相容特征,进而使得借款人和贷款人在一定程度上把握了借贷的自主权,在实际运用中也容易采取这种机制。进一步地,论文提供的拍卖机制是对现有交易模式的一种创新,对于推动P2P网络借贷行业的健康发展具有重要意义。
1 标准双边拍卖机制设计
结合现有P2P网络借贷交易模式,论文从理论分析角度对考虑双边定价的P2P网络借贷拍卖机制进行详细研究,并讨论该机制的激励相容特征和参与人(包括贷款人和借款人)在该机制中的决策行为。与目前大多数采取借款人事前定价、贷款人拍卖定价以及第三方平台定价的机制相比,这类考虑双边定价的拍卖机制有利于激化贷款人之间的竞争,激励借贷双方披露自己的真实信息。这里可以将这类考虑双边定价的拍卖机制分为标准机制和拓展机制,其中标准机制是不考虑借款人违约率的拍卖机制,而拓展机制是考虑了借款人违约率的拍卖机制。这一节主要对标准机制进行详细分析。
1.1 变量假设
首先给出机制设计的相关假设,以便于后期在此基础上设计双边定价的拍卖机制。

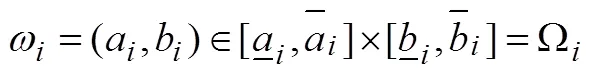
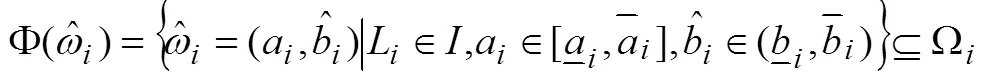
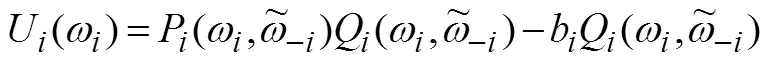
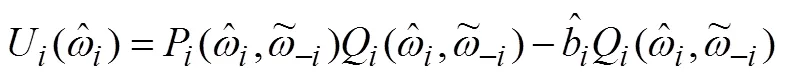

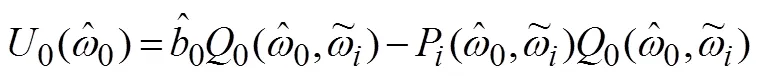
1.2 机制设计


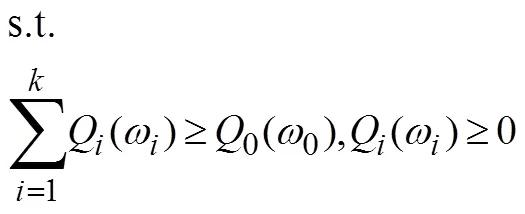
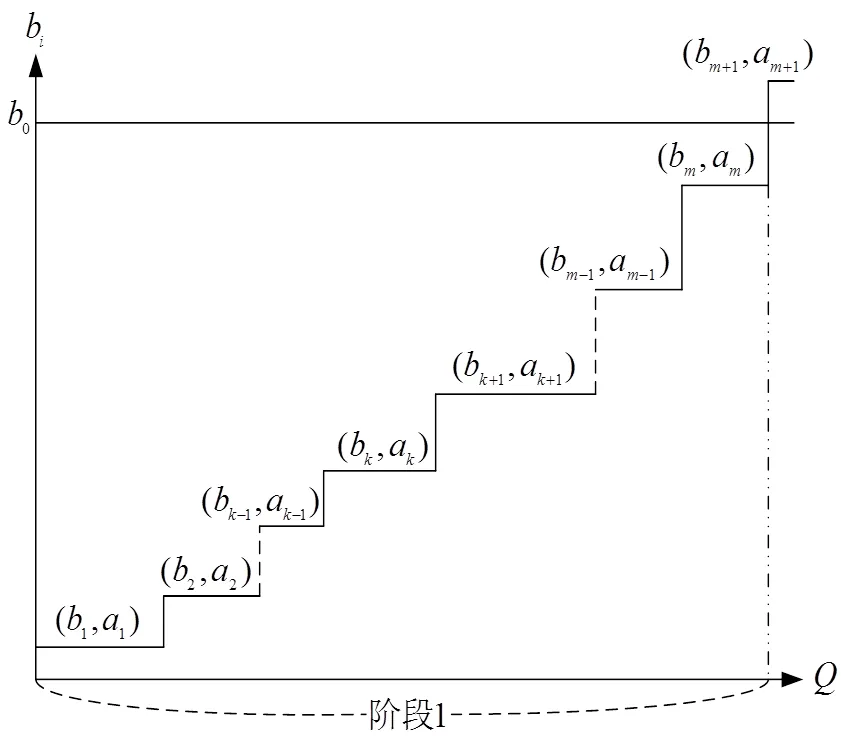
图1 阶段1的示意图
Figure 1 Sketch map of stage 1
(2)按照定义2选择活跃贷款人。如果阶段1中没有贷款人愿意参与拍卖或没有获得活跃贷款人,则视为拍卖失败;如果有足够的贷款人参与阶段1过程,并且能获得活跃贷款人集合,则进入阶段2。

图2 阶段2的示意图
Figure 2 Sketch map of stage 2
(3)在阶段2中,按照定义3选择中标贷款人,此时,如果贷款人的供给小于借款需求,则视为拍卖失败;如果贷款人的供给大于或等于借款需求,则视为拍卖成功,可以进一步制定相应的分配方案和支付方案。
(4)输出各个中标人的贷款数额和拍卖合同利率。
为了更清晰地观察这个机制的实施过程,可以通过图1和图2加以说明。
1.3 机制的特征分析

或者

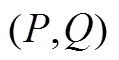
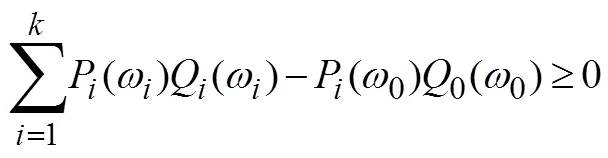
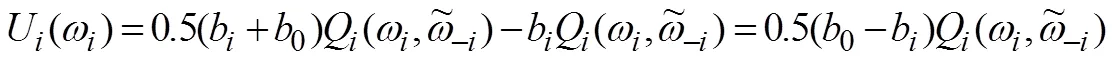
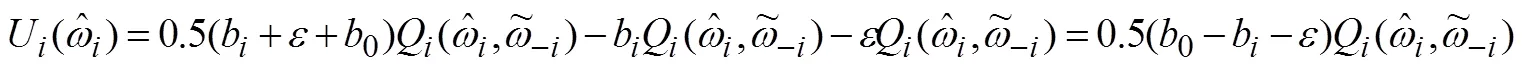
式(10)减去式(11)得到


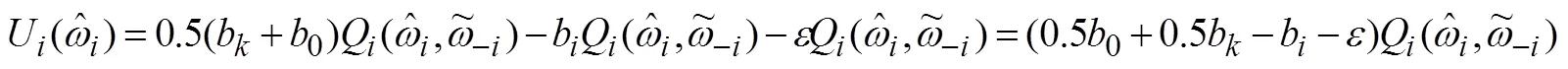

报告虚假类型时获得的效用为
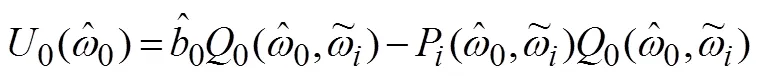

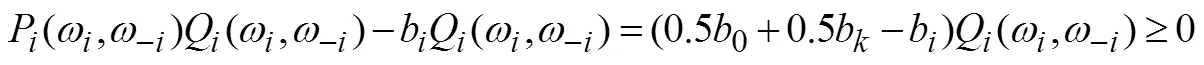
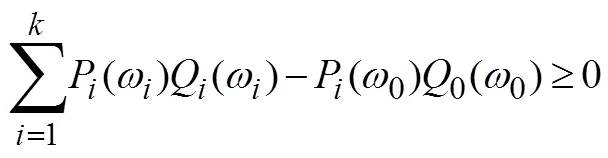
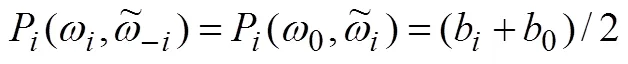

结合公式(7)可以得到,
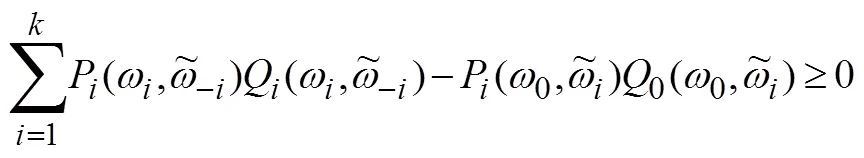
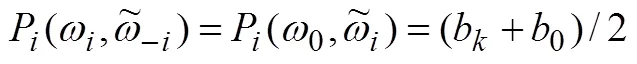
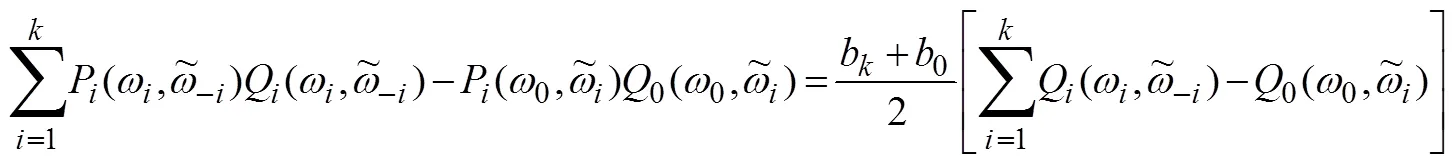
同样结合公式(7)可以得到,
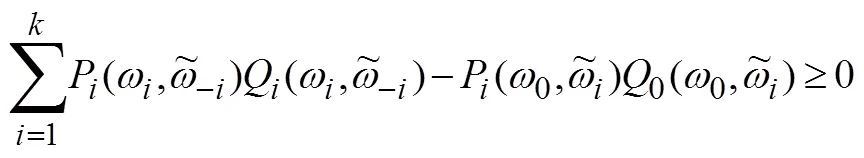
2 双边拍卖的拓展机制设计
接下来,论文进一步从理论分析角度对双边拍卖的拓展机制进行详细研究,重点讨论标准机制加入借款人违约率之后是否能继续满足双边激励相容性、参与人的个体理性、以及弱预算平衡等特征。在实际运行过程中势必会存在借款人违约的情况,因此拓展的拍卖机制更符合实际情况,具有重要的研究价值。
2.1 变量假设
相同的变量假设和规则与标准机制一致,不再重复定义。这里重点给出拓展机制特有的变量假设,以便于后期在此基础上设计双边定价的拍卖机制。
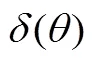
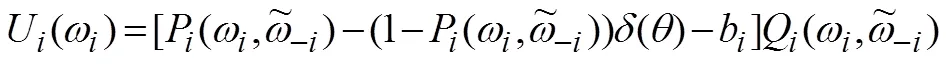
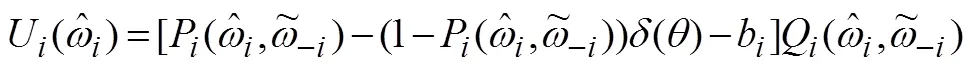

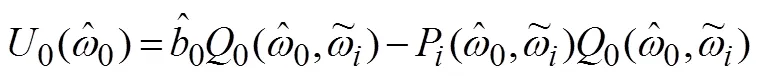

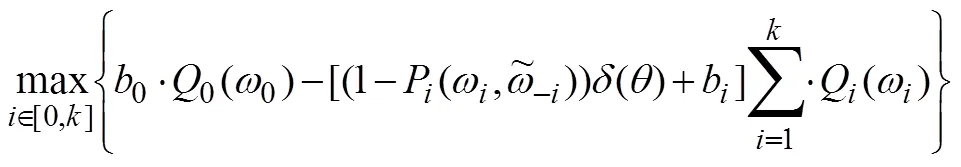
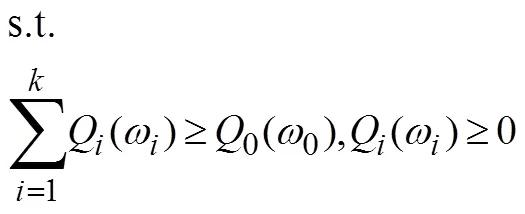
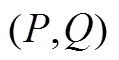
(2)按照定义2选择活跃贷款人。如果阶段1中没有贷款人愿意参与拍卖或没有获得活跃贷款人,则视为拍卖失败;如果有足够的贷款人参与阶段1过程,并且能获得活跃贷款人集合,则进入阶段2。
(3)在阶段2中,按照定义3选择中标贷款人,此时,如果贷款人的供给小于借款需求,则视为拍卖失败;如果贷款人的供给大于或等于借款需求,则视为拍卖成功,可以进一步制定相应的分配方案和支付方案。
(4)输出各个中标人的贷款数额和拍卖合同利率。
2.2 拓展机制的特征分析
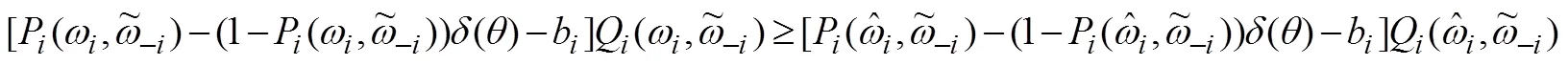
或者

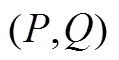
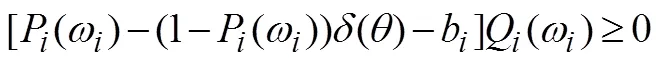
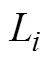
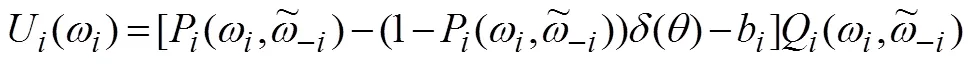
报告虚假类型时获得的效用为
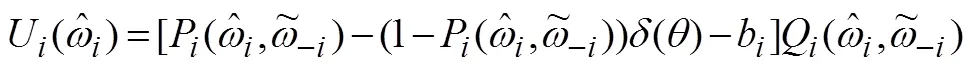
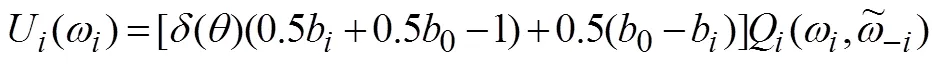
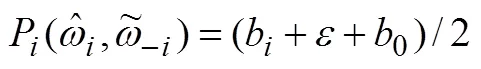
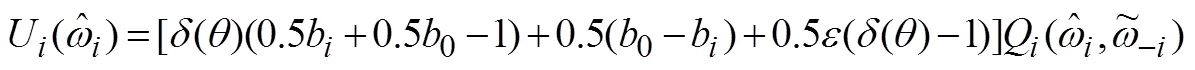
式(26)减去式(27)得到

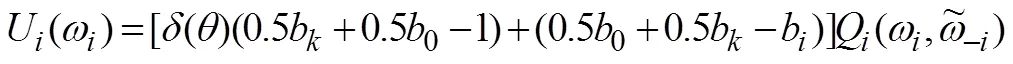
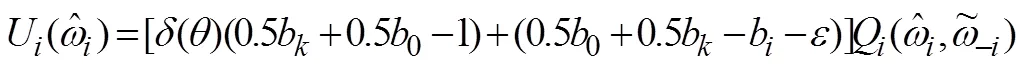
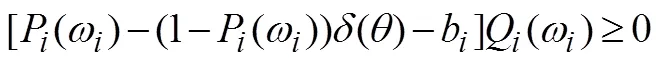
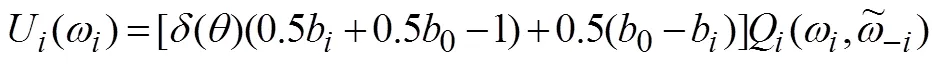
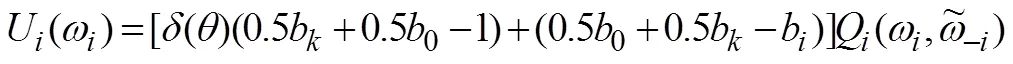
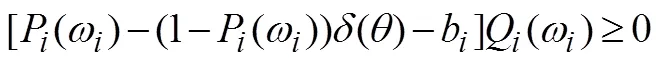
证毕。
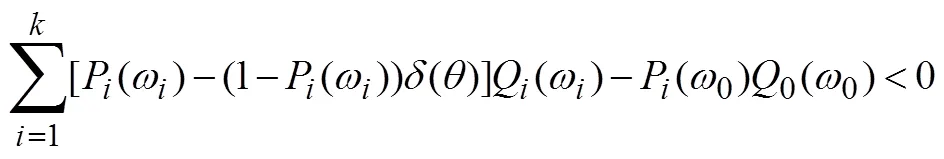

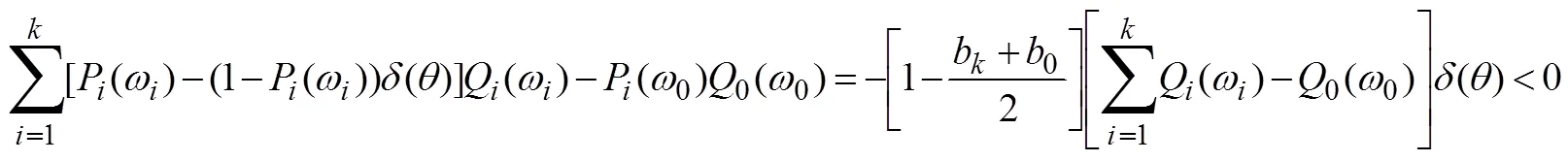
3 算例分析与比较

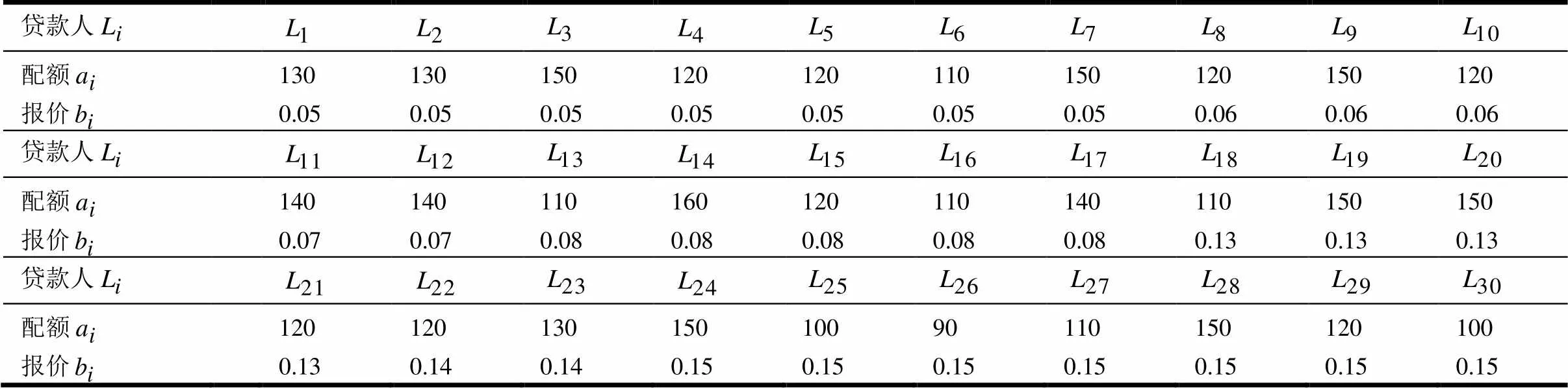
表1 所有活跃贷款人的配额和报价

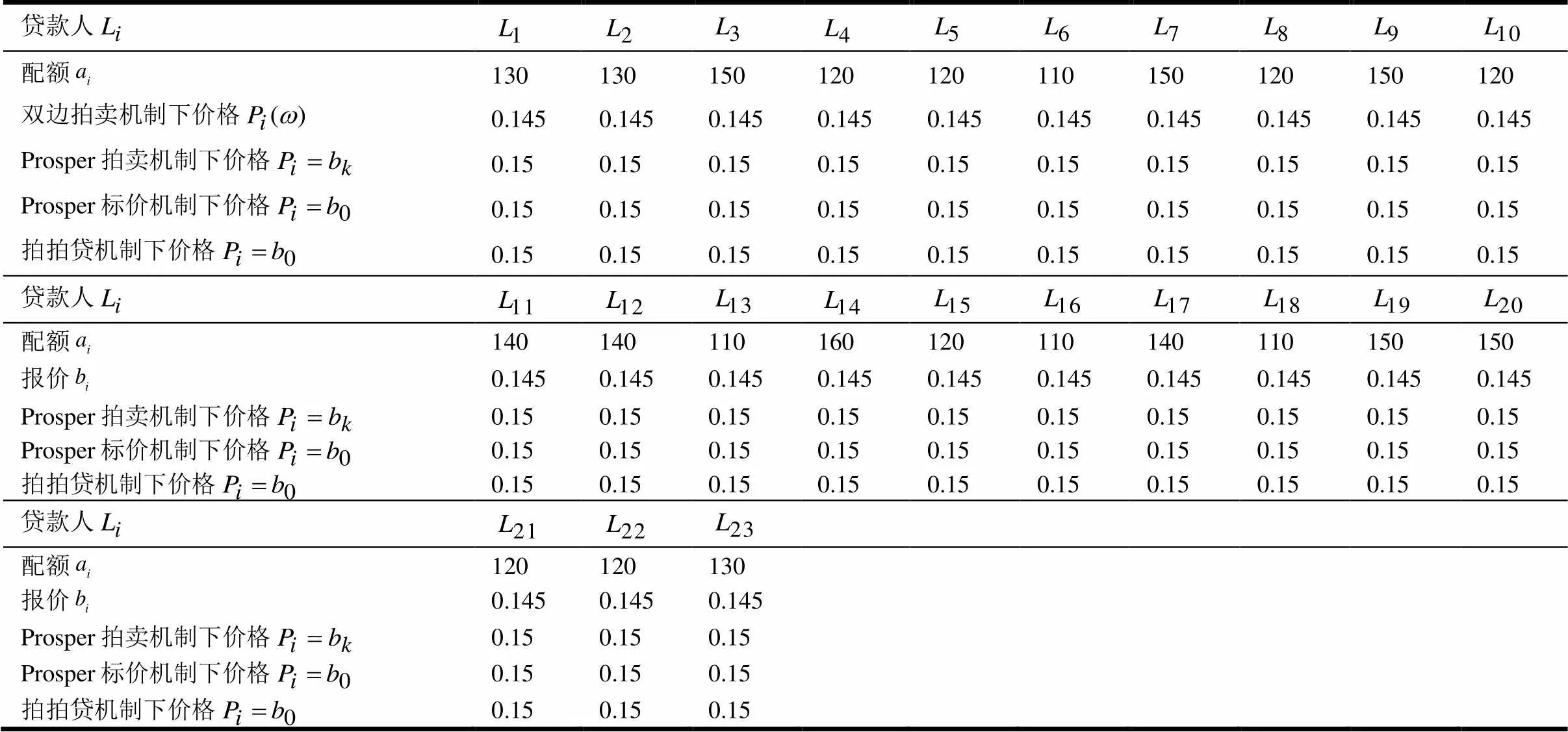
表2 不同机制下的配置信息


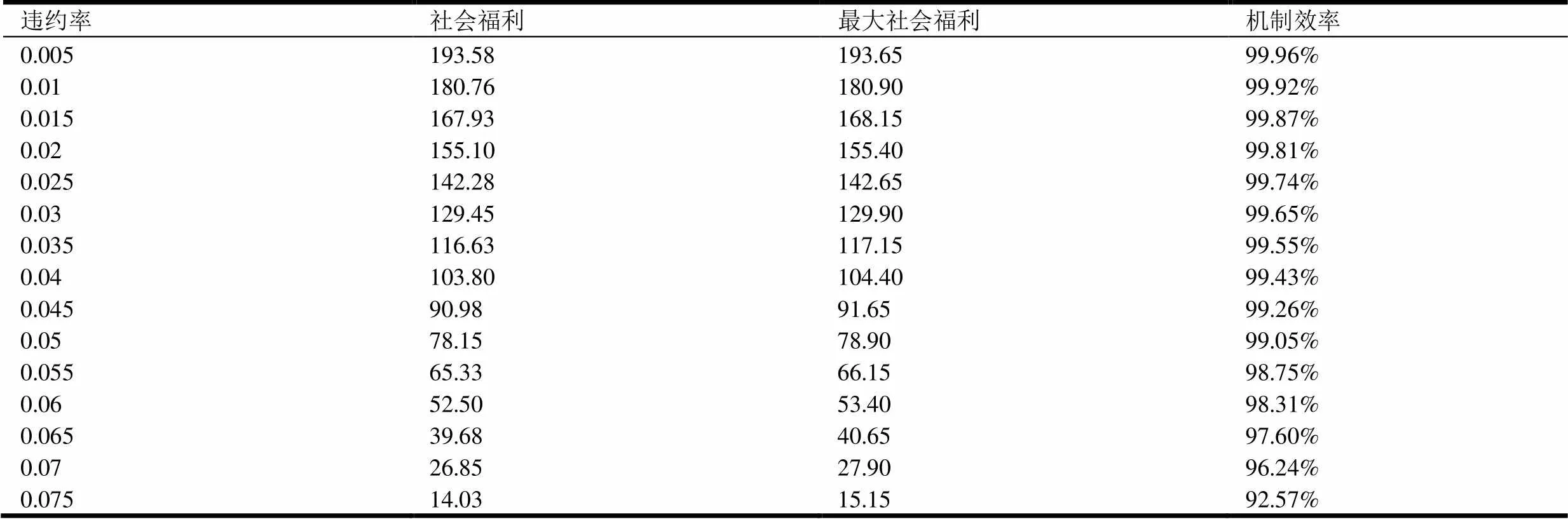
表3 机制的社会福利和效率
结合表3可以说明,本文设计的双边拍卖机制对资源的配置是富有效率的,并且随着借款人违约率的不断降低,机制对资源的配置效率越高。因此,在实际应用过程中应当尽量降低借款人的违约率,这样不仅可以更好地激励借贷双方揭露自己的真实类型,而且有利于提高资源配置的效率。需要指出的是,市场效率的损失源于信息不对称的P2P网络借贷市场中,拍卖组织者为了激励借款人和贷款人报告自己的真实类型,需要提供一定的信息租金给赢得拍卖的贷款人。在有个体理性和弱预算平衡的约束条件下,这样做的直接结果是减少市场交易量,从而导致少量效率的损失。
4 研究结论
论文以P2P网络借贷市场为研究背景,提出一种考虑双边定价的P2P网络借贷拍卖机制,以满足借款人和贷款人的双边激励相容特征(即满足借贷双方自觉地报告自己的真实类型),以提高整个机制的效率,同时也对现有P2P网络借贷平台的交易模式提供了一种新的设计思路。相对于现有平台的拍卖机制而言,这个机制的最大特点是同时考虑了贷款人和借款人的报价,进而使得借款人和贷款人在一定程度上把握了借贷的自主权,所以在实际运用中也容易采取这种机制。在拍卖机制设计上,通过两种方式进一步展开,即不考虑借款人违约率的双边拍卖机制设计(即标准机制)和考虑借款人违约率的双边拍卖机制设计(即拓展机制)。随后对两种机制分别进行激励相容性、个体理性和弱预算平衡等特征分析。结果显示,标准机制满足双边激励相容性、个体理性和弱预算平衡等特征;拓展机制满足双边激励相容性、但不满足个体理性和弱预算平衡等特征。这说明,拓展双边定价的拍卖机制在揭示参与人真实类型时无法保证个人理性和弱预算平衡,即参与人报告其真实类型不是最优的,无法实现拓展机制的全社会福利最大化,存在效率损失。通过算例分析也指出,其市场效率的损失源于信息不对称的P2P网络借贷市场中,拍卖组织者为了激励借款人和贷款人报告自己的真实类型,需要提供一定的信息租金给赢得拍卖的贷款人。在有个体理性和弱预算平衡的约束条件下,这样做的直接结果是减少市场交易量,从而导致少量效率的损失。
整体而言,本文提出的双边拍卖机制在激励参与人披露其真实信息以及降低借款人支付成本方面具有一定优势,并且可以有效地实现资源配置。因此,鉴于中国不成熟的信用评级体系,可以采用该拍卖机制以提高P2P网络借贷市场的交易效率。当然,本文设计的拍卖机制只是对现有机制提出了初步的改进思路,尚存在一些局限。特别地,为了清楚地刻画和比较不同P2P网络借贷市场的交易机制,论文仅考虑了机制的特征性质,没有对机制的市场效率进行建模分析。因此可以进一步对双边拍卖机制的市场效率进行拓展和理论分析,给出具体的数学表达方式,这样有利于比较不同交易机制的市场效率问题。面临着现实市场的需求,深入研究这些问题具有重要的理论和现实意义,这些也将作为日后继续研究的工作。
[1] Duenyas I, Hu B, Beil D R. Simple auctions for supply contracts [J]. Management Science, 2013, 59(10): 2332-2342.
[2] Li W, Larson M, Hu C, et al. Secure multi-unit sealed first-price auction mechanisms [J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2016, 9(16): 3833-3843.
[3] Papakonstantinou A, Bogetoft P. Multi-dimensional procurement auction under uncertain and asymmetric information [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 258(3): 1171-1180.
[4] Huang M, Qian X, Fang S C, et al. Winner determination for risk aversion buyers in multi-attribute reverse auction [J]. Omega, 2016(59): 184-200.
[5] Yanhong Guo, Wenjun Zhou, Chunyu Luoa, etc. Instance-based credit risk assessment for investment decisions in P2P lending [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016(249): 417-426.
[6] De Liu, Daniel J. Brass, Yong Lu, etc. Friendships in Online P2P Lending: Pipes, Prisms, and Relational Herding [J]. MIS Quarterly, 2015, 39(3): 729-742.
[7] M. Malekipirbazari, V. Aksakalli. Risk assessment in social lending
via random forests [J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015(42): 4621-4631.
[8] Milad Malekipirbazari, Vural Aksakalli. Risk assessment in social lending via random forests [J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015(42): 4621-4631.
[9] Lauri Puro, Jeffrey E. Teich, Hannele Wallenius, Jyrki Wallenius. Borrower Decision Aid for people-to-people lending [J]. Decision Support Systems, 2010(49): 52-60.
[10] Eunkyoung Lee, Byungtae Lee. Herding behavior in online P2P lending: An empirical investigation [J]. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 2012(11): 495-503.
[11] Ma B, Zhou Z, Hu F. Pricing mechanisms in the online Peer-to-Peer lending market[J]. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 2017(26): 119-130.
[12] 陈冬宇, 朱浩, 郑海超. 风险、信任和出借意愿——基于拍拍贷注册用户的实证研究[J]. 管理评论, 2014,26(1):150-158.
Chen D Y, Zhu H, Zheng H C. Perceive risk, trust, and willingness to lend: An empirical study based on the users of PPDai.com[J]. Management Review, 2014,26(1):150-158.
[13] 曾建光. 网络安全风险感知与互联网金融的资产定价[J].经济研究, 2015, 50(7): 131-145.
Zeng J G. Network security risk perception and asset pricing of internet finance[J].Economic Research Journal, 2015(7): 131-145.
[14] Rafaeli S, Noy A. Social Presence: Influence on Bidders in Internet Auctions [J]. Electronic Markets, 2005, 15(2): 158-175.
[15] Puro L, Teich J E, Wallenius H, et al. Bidding strategies for real-life small loan auctions [J]. Decision Support Systems, 2011, 51(1): 31-41.
[16] Einav L, Farronato C, Levin J. Peer-to-peer markets [J]. Annual Review of Economics, 2016(8): 615-635.
[17] Gomez Lemmen Meyer, Ana. Pricing Mechanisms in Peer-to-Peer Online Credit Markets [Z]. Job Market Paper, Stanford University, 2015.
[18] Chen N, Ghosh A, Lambert N S. Auctions for social lending: A theoretical analysis [J]. Games and Economic Behavior, 2014(86): 367-391.
[19] Wei Z, Lin M. Market mechanisms in online peer-to-peer lending[J]. Management Science, 2016, 63(12): 4236-4257.
[20] 周正龙, 马本江, 胡凤英. 中国P2P网络借贷平台的动态逆向拍卖机制[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2017, 37(2): 409-417.
Zhou Z L, Ma B J, Hu F Y. Dynamic reverse auction mechanism on online P2P lending of China[J]. Systems Engineering - Theory & Practice, 2017, 37(2): 409-417.
[21] 邱甲贤, 聂富强, 童牧, 胡根华. 第三方电子交易平台的双边市场特征——基于在线个人借贷市场的实证分析[J]. 管理科学学报,2016(1):47-59.
Qiu J X, Nie F Q, Tong M, et al. Two-sided characteristics of the third-party electronic market: Evidencefrom online peer-to-peer lending marketplace[J]. Journal of Management Sciences in China, 2016(1):47-59.
[22] Huang P, Scheller–Wolf A, Sycara K. Design of a multi–unit double auction e–market [J]. Computational Intelligence, 2002, 18(4): 596-617.
Auction mechanism of online P2P lending based on bilateral pricing
ZHOU Zhenglong1, HU Fengying2, LI Yanhui1
(1. School of Information Management, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, China;2. Business School, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
P2P online lending is part of financial activities. It operates through an Internet platform and uses "crowd wisdom" to allow multiple lenders to conduct transactions with borrowers who want to obtain funds. However, the current domestic and foreign research mainly focuses on risk control, credit authentication, legal supervision and other issues, but less involved in the P2P online lending market transaction mechanism. In addition, the frequent transaction problems of the existing platforms reflect the shortcomings of the existing transaction mechanism in terms of disclosing information and improving transaction efficiency. In view of this, based on the bilateral market characteristics of P2P online lending, this paper proposes a P2P online lending auction mechanism that considers bilateral pricing, and improves the existing P2P online lending market trading mechanism to encourage transaction participants to disclose their true information. Improve the transaction efficiency of the entire mechanism. Compared with the trading mechanism of the existing platform, the biggest feature of this mechanism is that it considers the bidding of the lender and the borrower at the same time, and meets the bilateral incentive compatibility characteristics of the borrower and the lender, so that the borrower and the lender to a certain extent, we have grasped the autonomy of borrowing and lending, and it is easy to adopt this mechanism in practical use. At the same time, this mechanism is of great significance for promoting the healthy development of the P2P online lending market.
This auction mechanism is implemented through the following two stages. In phase 1, the borrower first announces a loan demand and sealed quotation, and then all lenders provide the loan amount and sealed quotation they are willing to supply within the specified time. The loan amount at this stage is accumulated by "how much is received ", and the quotations of all participants are sorted by "increasing prices", and active lenders are selected according to relevant definitions. In phase 2, the winning bidders are selected from the active lenders according to the relevant definitions, and the corresponding distribution plan and payment plan are formulated.
In the analysis of the characteristics of the auction mechanism, this paper studies the incentive compatibility, individual rationality and weak budget balance. The results show that an auction mechanism that does not consider the borrower's default rate (that is, the standard mechanism) satisfies the characteristics of bilateral incentive compatibility, individual rationality, and weak budget balance; however, an auction mechanism that considers the borrower's default rate (that is, the expansion mechanism) only meets the characteristics of bilateral incentive compatibility, dissatisfaction with individual rationality, and weak budget balance. This shows that the expansion mechanism cannot guarantee individual rationality and weak budget balance when revealing the true types of participants, and it cannot maximize the social welfare of the expansion mechanism (there is a loss of efficiency).
Through the analysis of examples, it is pointed out that the auction mechanism that considers the default rate is more practical in the actual economic environment, but the efficiency of the mechanism cannot be maximized by the impact of the default rate. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the default rate of the borrower as much as possible, which is conducive to increase the configuration efficiency of mechanism. Further, in the analysis of examples, this paper compares the difference between the bilateral auction mechanism and the existing mechanism. The results show that the bilateral auction mechanism has certain advantages in encouraging participants to disclose their true information and reduce the cost of borrower’s payment, which can be used as a supplement and improvement to the existing mechanism.
Online P2P lending; Auction mechanisms; Incentive compatibility; Individual rationality; Weak budget balance
F830;F724.59
A
1004-6062(2020)06-0138-010
10.13587/j.cnki.jieem.2020.06.014
2018-06-28
2018-11-19
Supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (71471073) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2017zzts050)
2018-06-28
2018-11-19
国家自然科学基金资助项目(71471073);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(2017zzts050)
周正龙(1989—),男,贵州毕节人;博士,华中师范大学讲师,硕士生导师;研究方向:金融工程、电子商务与运营管理。
中文编辑:杜 健;英文编辑:Boping Yan
