Application of a modified surgical position in anterior approach for total cervical artificial disc replacement
2020-04-22WenXiuHouHaoXuanZhangXiaWangHaiLingYangXiaoRongLuan
Wen-Xiu Hou,Hao-Xuan Zhang,Xia Wang,Hai-Ling Yang,Xiao-Rong Luan
Wen-Xiu Hou,Xia Wang,Xiao-Rong Luan,Third Ward of Orthopedics Department,Qilu Hospital,Shandong University,Jinan 250012,Shandong Province,China
Hao-Xuan Zhang,Department of Spine Surgery,Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital,The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University,Jinan 250014,Shandong Province,China
Hai-Ling Yang,Department of Nursing,Qilu Hospital,Shandong University,Jinan 250012,Shandong Province,China
Abstract
Key words: Anterior approach;Surgical position;Total cervical artificial disc replacement;Cervical spondylosis
INTRODUCTION
Artificial cervical disc prosthesis was designed by utilizing bionics technology,thus preserving the activity of the treated segment,and its design was first reported by Goffinet al[1]in 2002.Total cervical artificial disc replacement (TDR) has been considered a safe and effective alternative surgical treatment for cervical spondylosis and degenerative disc disease that have failed to improve with conservative methods[2-9].
Positioning the surgical patient is a critical part of the procedure.Appropriate patient positioning is crucial not only for the safety of the patient but also for optimizing surgical exposure,ensuring adequate and safe anesthesia,and allowing the surgeon to operate comfortably during lengthy procedures[10,11].
The surgical posture is the traditional position used in anterior cervical approach;in general,patients are in a supine position with a pad under their shoulders and a ring-shaped pillow under their head[12,13].The activity of the adjacent segment accelerates the degeneration of the adjacent layers and causes new symptoms[8,14-17].
To enable an improved TDR procedure,shorten the time of operation,reduce the incidence of perioperative complications,and improve the safety of the procedure,we planned to improve the traditional surgical position in anterior cervical approach.
In this study,a total of 48 cervical spondylosis patients who were treated by TDR with either the traditional or the modified surgical position were assessed.We comprehensively determined the clinical outcomes,including the blood pressure and heart rate before and after body positioning,position setting time,total operation time,and intraoperative blood loss.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
All patients were initially assessed and treated by trained nurses before being enrolled in this study.Patients received a diagnosis of cervical spondylosis of one segmental level that was supported by clinical symptoms and imaging data and had poor clinical outcomes even after previously undergoing strict conservative treatment for at least three months.
Study design and parameters
Forty-eight patients were divided into a traditional position group and a modified position group,with 24 patients in each group (Table 1).Perioperative parameters were retrospectively analyzed.
To assess the safety of the position setting process,blood pressure and heart rate were used,and these metrics were measured in all patients before and after the position setting process in both groups.In addition,the surgical position setting time was measured.After surgery,total operation time and intraoperative blood loss were recorded to evaluate the effects of surgical position on the safety of surgery.
Surgical position setting
Traditional position group:The traditional surgical position setting is shown in Figure 1A and B.After anesthesia intubation,the patient's head,neck,and shoulders were lifted,a shoulder pad was placed under the shoulders,and a ring-shaped pillow was placed under the head.Subsequently,the patient was positioned back on the table,and the height and position of the head,neck,and shoulder were checked until the neck was fully exposed.
Modified position group:The modified surgical position setting is shown in Figure 1C and D.After anesthesia intubation,a shoulder pad and a ring-shaped pillow were placed under the shoulder and head,respectively.Then,a soft pillow with a height of approximately 10 cm was placed under the patient's neck.The lower jaw was pulled in the rostral direction,both shoulders were pulled in the caudal direction,and tape was used to maintain the position.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as the mean ± SD.Statistical analyses were performed by the independent-samplest-test between two groups using SPSS (version 22.0,Chicago,IL),and categorical variables were analyzed by the Mann-WhitneyUtest.Differences ofP< 0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
General patient information
All patients who underwent single-level Mobi-C artificial disc replacement from September 2014 to September 2015 were included (28 males and 20 females).The average age was 45.7 years (range,25-65 years).Of the patients,8 had C3-C4 replacement,22 had C4-C5 replacement,and 18 had C5-C6 replacement.
There was no significant difference in sex,age,history,treated segment,anesthesia,or surgical staff between the two groups (P> 0.05).
Blood pressure and heart rate before and after body positioning
In the traditional position group,the blood pressure was 124.76 ± 15.3 mmHg before body positioning and 126.69 ± 18.7 mmHg after body positioning (Figure 2A).The average heart rate was 76.36 ± 14.2 bpm and 78.01 ± 13.8 bpm in the traditional position group before and after body posture,respectively (Figure 2B).
In the modified position group,the blood pressure before body positioning was 128.43 ± 18.8 mmHg,and it was 129.33 ± 17.1 mmHg after body positioning (Figure 2A).The average heart rate was shown to be 82.61 ± 15.0 bpm and 83.25 ± 14.4 bpm in the modified position group before and after body posture,respectively (Figure 2B).
Blood pressure and heart rate before and after body positioning were not significantly different within each group or between the two groups (P> 0.05).
Surgical position setting time and total operation time
The surgical position setting time was 1.85 ± 0.49 min in the traditional position group,and it was 4.57 ± 0.67 min in the modified position group (Figure 3).A statistically significant increase was observed in the modified position group compared with the traditional position group (P< 0.05).
The total operation time was significantly shorter in the modified position group(82.05 ± 12.4 min) than in the traditional position group (95.78 ± 14.5 min) (P< 0.05)(Figure 3).
Intraoperative blood loss
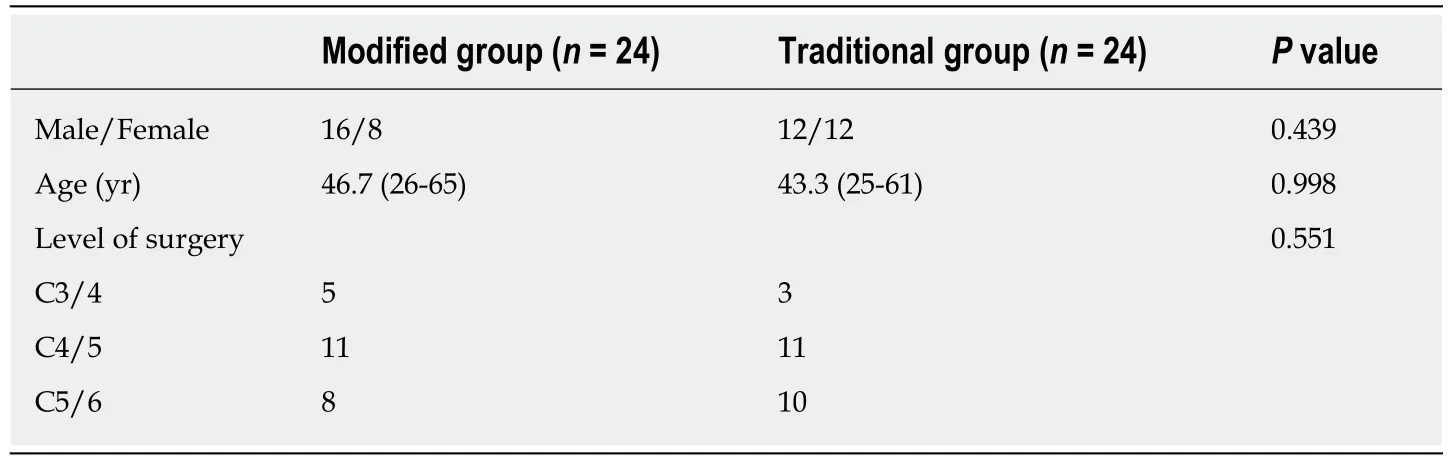
Table1 Demographic characteristics of the patients
The intraoperative blood loss in the modified position group (20 ± 8.1 mL) was significantly lower than that in the traditional position group (27 ± 7.5 mL;P< 0.05)(Figure 4).
DISCUSSION
Artificial cervical disc prosthesis was designed to reconstruct or maintain the height of the intervertebral disc,maintain the regular activity of the cervical spine,and create favorable conditions for the recovery of function of the spinal cord after the spinal cord compression was removed[4,18-20].
An appropriate surgical position is crucial for the operation.Improvement in the patient's surgical status facilitates the surgeon's procedure and reduces the amount of bleeding and the incidence of complications,thus creating essential conditions for successful implementation of the disc and recovery of the patient[10,11].
In this study,48 cases of cervical disc replacement with Mobi-C prosthesis were included.Compared with patients in the traditional surgical position,patients in the modified surgical position had more satisfactory clinical outcomes,and the advantages are as follows.
对此,采访中,多地纪检干部也向本刊记者表示,对于群众身边的形式主义、官僚主义等直观的或“变种”的“四风”问题,纪委监委会严查不松劲。“对顶风违纪问题加大监督检查力度,严查快办,并实行责任倒查,严肃追究党组织主体责任和纪检组织的监督责任,同时对典型问题通报曝光,形成有力震慑。”近来,各地通过不断丰富监督检查手段,通过常规检查、大数据筛查、群众监督等方式,密切关注“四风”隐形变异、改头换面等新动向,其目的都是很明确的,那就是严防“四风”反弹回潮。
To facilitate the operation and select the appropriate type of prosthesis in TDR,the patient is typically placed in the supine-neutral surgical position to maintain the natural curve of the cervical spine[8,21-27].Because only the shoulder pad and ringshaped pillow were placed under the shoulders and head,respectively,the neck of the patient was not supported in the traditional surgical position during anterior cervical approach.However,in the modified position,the shoulder pad and ringshaped pillow were placed under the shoulders and head,respectively,and a soft pillow with a height of approximately 10 cm was placed under the patient's neck so that the patient was in the supine-neutral surgical position during the surgery.
Patients with the modified surgical position are fixed firmly and securely
During a cervical surgical procedure,slight activity of the patient can have serious consequences,including cervical displacement and injuries of the blood vessels and the spinal cord[15,23,28-32].In the modified position,the lower jaw and both shoulders were pulled in the rostral and the caudal directions,respectively,and wide tape was used for auxiliary fixation.Thus,the cervical spine and other parts of the patient were securely fixed,allowing a successful surgery and guaranteeing the safety of the patients.
Reduced total operative time and intraoperative blood loss
The total operation time was significantly shorter in the modified position group than in the traditional position group.Intraoperative blood loss in the modified position group was significantly lower than that in the traditional position group.
The modified surgical position needs more surgical position setting time.However,the total operation time was shortened,and intraoperative blood loss was reduced in patients with the modified surgical position compared with patients with the traditional position.A shorter operation time results in a lower operation risk,and a smaller amount of bleeding during the operation can not only help the surgeon's activity but also reduce the risk of injury in patients,which is beneficial to the healing process.
In this study,the modified surgical position in anterior approach was successfully designed for TDR.The results indicated that the modified surgical position had no adverse effects on the blood pressure and heart rate of the patient.The modified surgical position reduces the total operation time and intraoperative blood loss,although it consumes more surgical position setting time;these results suggest that the modified position is beneficial to the operation of the surgeons,and it is worthy of application and widespread use in TDR.
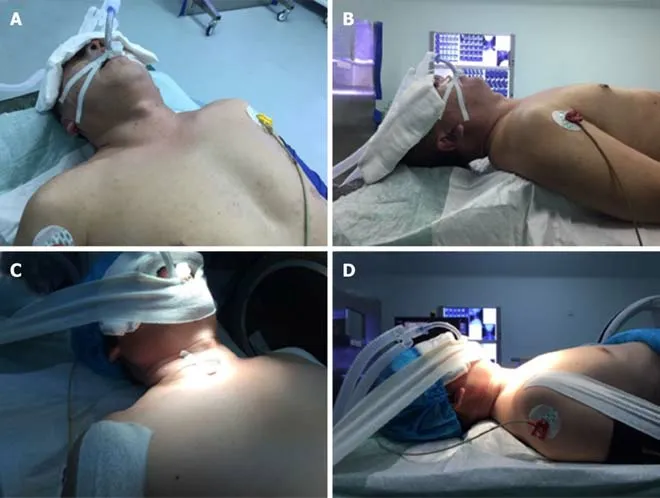
Figure1 Surgical position setting.
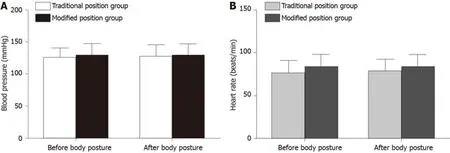
Figure2 Patients' blood pressure and heart rate before and after body positioning.

Figure3 Position setting time and total operation time in the two groups.
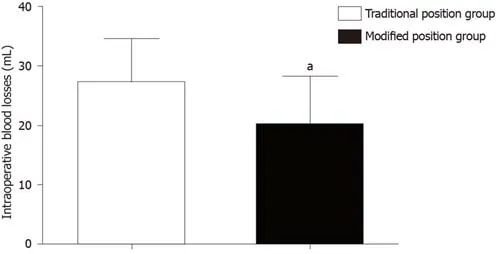
Figure4 lntraoperative blood losses in the two groups.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Total cervical artificial disc replacement (TDR) has been considered a safe and effective alternative surgical treatment for cervical spondylosis and degenerative disc disease that have failed to improve with conservative methods.
Research motivation
Positioning the surgical patient is a critical part of the procedure.Appropriate patient positioning is crucial not only for the safety of the patient but also for optimizing surgical exposure,ensuring adequate and safe anesthesia,and allowing the surgeon to operate comfortably during lengthy procedures.The surgical posture is the traditional position used in anterior cervical approach;in general,patients are in a supine position with a pad under their shoulders and a ring-shaped pillow under their head.The activity of the adjacent segment accelerates the degeneration of the adjacent layers and causes new symptoms.
Research objectives
To investigate the clinical outcomes of the use of a modified surgical position versus the traditional surgical position in anterior approach for TDR.
Research methods
In the modified position group,patients had a soft pillow under their neck,and their jaw and both shoulders were fixed with wide tape.The analyzed data included intraoperative blood loss,position setting time,total operation time,and perioperative blood pressure and heart rate.
Research results
Blood pressure and heart rate were not significantly different before and after body positioning in both groups.Compared with the traditional position group,the modified position group showed a statistically significantly longer position setting time.However,the total operation time and intraoperative blood loss were significantly reduced in the modified position group compared with the traditional position group.
Research conclusions
The clinical outcomes indicated that total operation time and intraoperative blood loss were lower in the modified position group than in the traditional position group,thus reducing the risks of surgery while increasing the position setting time.
Research perspectives
The modified surgical position is a safe and effective method to be used in anterior approach for TDR surgery.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Role of oxysterol-binding protein-related proteins in malignant human tumours
- Oncogenic role of Tc17 cells in cervical cancer development
- Acute distal common bile duct angle is risk factor for postendoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis in beginner endoscopist
- Three-dimensional computed tomography mapping of posterior malleolar fractures
- Potential role of the compound Eucommia bone tonic granules in patients with osteoarthritis and osteonecrosis:A retrospective study
- Prognostic factors for overall survival in prostate cancer patients with different site-specific visceral metastases:A study of 1358 patients
