超声引导下平面内与平面外技术进行术中动脉穿刺置管研究
2017-05-10聂明辉张晓侠刘会玲李义学王晓岩
聂明辉+张晓侠+刘会玲+李义学+王晓岩+吴文瑛+冯佩明

(1. 承德醫学院附属医院超声科;2.承德医学院附属医院麻醉科,河北承德 067000)
[摘 要] 目的:探讨超声引导下平面内技术与平面外技术在术中动脉穿刺置管中的应用。方法:选择我院2015年7月~2016年8月择期手术患者122例,随机分为平面内技术组(A组,n=62)和平面外技术(B组,n=60)。A、B两组患者分别在超声引导下采用平面内技术和平面外技术进行桡动脉穿刺置管。记录每组患者超声定位时间、总穿刺时间、穿刺次数,首次穿刺成功例数及首二次穿刺成功例数,并分别于穿刺前(T1)和拔管后0.5h(T2)测量穿刺点桡动脉内径、桡动脉收缩期血流峰值流速及穿刺侧的无创动脉血压,记录两组患者并发症的发生情况。结果:两组患者总穿刺时间和穿刺次数相比差异无统计学意义,A组患者超声定位时间长于B组、首次成功穿刺例数少于B组,差异有统计学意义,P<0.05,但A组患者首二次穿刺成功率显著高于B组,差异有统计学意义,P<0.05;组内比较:两组患者T1时刻的桡动脉内径均大于T2时刻且桡动脉收缩期血流峰值流速均低于T2时刻,差异有统计学意义,P<0.05,两组患者T1和T2时刻MAP相比,差异无统计学意义;组间比较:T1和T2时刻两组患者桡动脉内径、收缩期血流峰值流速、MAP相比差异无统计学意义;A组患者血肿和桡动脉后壁穿透的发生率明显低于B组患者,差异有统计学意义,P<0.05。结论:平面内技术和平面外技术引导动脉穿刺置管对桡动脉血流动力学影响相似;与平面外技术相比,平面内技术超声定位时间长,但其首二次穿刺成功率高,并发症少。
[关键词] 超声引导;平面内技术;平面外技术;桡动脉穿刺
中图分类号:R445.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:2095-5200(2017)04-046-03
DOI:10.11876/mimt201704019
Ultrasound-guided in-plane and out-of-plane approaches for intraoperative artery cannulation NIE Minghui1,ZHANG Xiaoxia2,LIU Huiling1,LI Yixue1,WANG Xiaoyan1,WU Wenying1,FENG Peiming1. (1. Department of ultrasound,Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University Chengde 067000 China;2. Department of Anesthesiology, Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University Chengde 067000 China)
[Abstract] Objective: This study was designed to explore the application of ultrasound-guided in-plane and out-of-plane approaches for intraoperative artery cannulation. Methods: A total sampale of 122 patients who underwent elective surgery from July 2015 to August 2016 were randomly divided into in-plane group (group A, n=62) and out-of-plane group (group B, n=60). The patients of group A and group B underwent radial artery cannulation with ultrasound-guided in-plane and out-of-plane approaches. The length of ultrasonic positioning, the times of cannulation attempts, the total duration of cannulation, success rates at first-time attempt and the first two attempts were recorded. The radial artery diameter and peak systolic velocity, and noninvasive arterial blood pressure on the puncture side were measured at the points for cannulation before cannulation (T1) and 0.5 h after extubation (T2). The complication of the two groups was recorded. Results: There was no significant difference the total duration of cannulation and the times of cannulation attempts between the two groups. The length of ultrasonic positioning of group A was longer than that of the group B, the success rate at first-time attempt was less than that of the group B, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05), but the success rate at the first two attempts was significantly higher in group A than in group B. Compared with T2, the radial artery diameter of both two groups was greater at T1, and the peak systolic velocity of radial artery of both two groups was lower than that of T2, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in MAP between the two groups at T1 and T2. There was no significant difference in the radial artery diameter and peak systolic velocity, and MAP between the two groups of patients at T1 and T2. The incidence of hematoma and wall penetrating of radial artery in group A was significantly lower than those in group B, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusions Ultrasound-guided in-plane and out-of-plane approaches for intraoperative artery cannulation have similar effects on hemodynamics of radial artery. Compared: with out-of-plane approach, in-plane approach has longer ultrasonic positioning time, but its success rate at first two attempts is higher, and has less complications.
[Key words] ultrasound guidance; in-plane approach; out-of-plane approach; radial artery
动脉穿刺是临床上常用的有创穿刺技术。成功的动脉穿刺是抢救危重患者的基础,通畅的动脉通路不仅可以持续监测有创动脉血压、监测动脉血气而且可以进行血液透析等治疗操作[1]。桡动脉是动脉穿刺的常用部位之一。传统的桡动脉穿刺技术通过盲探触摸桡动脉搏动进行穿刺,常因定位不准、进针角度方向的差异而导致穿刺失败[2]。随着超声技术的发展,超声引导下的血管穿刺技术也广泛应用于临床麻醉中[3]。超声引导下的血管穿刺技术主要包括平面内技术和平面外技术,因此本研究将探讨超声引导下平面内技术与平面外技术在术中动脉穿刺置管中的应用,为临床麻醉中超声引导下桡动脉穿刺置管提供参考。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择我院2015年7月~2016年8月的择期手术患者122例,18~65岁,ASA I~II级,随机分为平面内技术组(A组,n=62)和平面外技术(B组,n=60)。排除动脉粥样硬化、周围血管疾病、尺动脉疾病、Allen试验阴性者等不适宜行桡动脉穿刺的患者。本研究经我院伦理委员会批准且所有患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 方法
两组患者清醒进入手术室后,吸氧2L/min,持续监测心电图、脉搏氧饱和度、无创动脉血压,开放上肢外周静脉,镇静镇痛。患者穿刺前均进行Allen试验,结果为阳性者选择左手进行穿刺。所有患者取平卧位,穿刺侧手臂外展90°,手掌向上平放于搁手板上,手腕背侧垫纱布卷背伸30°~60°并固定,常规碘伏消毒前臂掌侧腕关节皮肤,铺巾,穿刺部位使用2%利多卡因局部麻醉。使用Sonosite Micromaxx便携式超声仪(美国,Sono Site公司),探头频率选择6~13MHz,超声探头涂上耦合剂后采用一次性无菌保护套套扎。A、B两组患者分别采用平面内技术和平面外技术在手腕横纹处探查桡动脉,选择最佳穿刺点,具体操作方法如下。A组:将探头与桡动脉走形垂直采用短轴切面确定桡动脉的位置,并移动超声探头使其处于画面中间,再将探头与桡动脉平行以长轴切面再次确定桡动脉的位置,左右移动超声使其对准桡动脉的中间位置,右手持动脉穿刺针以30°~45°向超声和皮肤交点处穿刺,当超声图像中出现完整的进针声影后缓慢进针并观察穿刺针尾端若见回血后,边向近心端进针边退针芯,待套管进入桡动脉后固定接压力传感器监测血压。B组:以短轴切面确定桡动脉的位置,将桡动脉调整至画面中点,以同样角度进针穿刺,见穿刺针回血后置入套管并固定连接压力传感器监测血压。两组患者均由相同操作者进行桡动脉穿刺,穿刺两次不成功者则更换操作者并交替采用平面内、外法改变引导方式,四次不成功者则为操作失败。进针一次未成功则记一次穿刺。手术结束后,两组患者均拔出动脉导管并以加压包扎按压15min。
1.3 观察指标
分别于穿刺前和拔管后0.5h测量穿刺点桡动脉内径、桡动脉收缩期血流峰值流速及穿刺侧的无创动脉血压,记录每组患者超声定位时间、总穿刺时间、穿刺次数,首次穿刺成功例数、首二次穿刺成功例数以及两组患者并发症(血肿、桡动脉后壁穿透)的发生情况。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS19.0统计学软件进行统计学分析,计量资料采用t检验或方差分析,计数资料采用χ2检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组患者一般情况比较
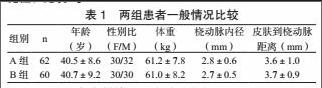
两组患者一般情况(年龄、性别比、体重、桡动脉内径和皮肤到桡动脉距离)相比差异无统计学意义,具有可比性,见表1。
2.2 两组患者穿刺情况及桡动脉指标
两组患者总穿刺时间和穿刺次数相比差异无统计学意义,A组患者超声定位时间长于B组、首次成功穿刺例数少于B组,差异有统计学意义,P<0.05,但A组患者首二次穿刺成功率显著高于B组,差异有统计学意义,P<0.05,见表2。
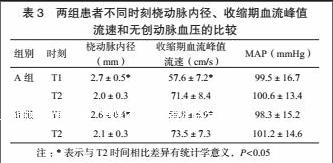
两组组内比较:T1时刻的桡动脉内径均大于T2时刻且桡动脉收缩期血流峰值流速均低于T2时刻,差异有统计学意义,P<0.05,两组患者T1和T2时刻MAP相比,差异无统计学意义;组间比较:T1和T2时刻两组患者桡动脉内径、收缩期血流峰值流速、MAP相比差异无统计学意义,见表3。
A组患者血肿2例、桡动脉后壁穿透3例;B组分别为9例、12例,A组并发症发生率明显低于B组患者,差异有统计学意义,P<0.05。
3 讨论
传统的桡动脉穿刺常采用盲探触摸桡动脉搏动的方法,虽然简单易行,但对操作者的技术要求较高[4]。对于肥胖、心律失常、低血压以及桡动脉解剖异常的患者,桡动脉穿刺常存在较大的困难[5-6]。反复穿刺会引起桡动脉痉挛和血肿的形成进一步加大穿刺的难度[7]。超声引导下血管穿刺不仅可以清楚分辨血管和穿刺针的相对位置而且可以在直视下调整进针的角度和方向,减少盲探操作的不确定性,提高穿刺的成功率[8]。
平面内技术和平面外技术是超声引导下血管穿刺常用的技术,二者各有优劣。平面内技术中,穿刺针和血管长轴在同一平面且在穿刺过程中可以动态观察二者的关系,能够减少穿刺针对血管壁造成的损伤[8];平面外技術中可以直接观察进针的方向和血管腔之间的关系,提高穿刺的速度[9]。本研究中两组患者桡动脉内径和皮肤到桡动脉距离相比差异无统计学意义,具有可比性。A组患者超声定位时间长于B组,表明平面外技术更容易找到桡动脉,这是由于平面外技术引导下腕部横断面超声范围较宽,更容易发现桡动脉的搏动,而平面内技术下超声范围小,只能在短轴法下找到动脉然后再旋转超声探头寻找[11-12],因此需要时间更长。A组首次成功穿刺例数少于B组,可能的原因有:平面内技术引导下由于超声断层图的切片厚度的影响,声像图上可能存在临近靶区结构的回声,干扰操作者的判断,误认为穿刺针在血管内,反复穿刺操作时间延长[13];平面外技术下能够清楚的判断进针方向和桡动脉最大径角度的关系,随时调整进针方向,避免临床上动脉穿刺时常出现针尾喷血而置管不畅的情况[14],减少操作时间;由于桡动脉位置较表浅以及穿刺针穿刺过程中的推挤等均可能引起平面内技术下图像的移位,影响穿刺的效果和时间。A患者首二次穿刺成功率显著高于B组,是由于在平面内技术引导下穿刺失败时,交替使用平面外技术能够清晰显示桡动脉截面与针尖的相对位置,稍微调整角度则可以顺利进行[15],而平面外技术由于针尖和超声探头垂直,当针尖进入皮下后调整超声探头后仍难以分辨[16],所以首二次穿刺成功率低。由于平面外技术失败后超声影响难以分辨,需要多次调整穿刺针多因此也会引起桡动脉的多处损伤,所以B组并发症的发生率要高于A组。由于穿刺损伤可能引起患者血管痉挛、局部血肿挤压动脉、局部血管内膜增生以及新鲜血栓的形成,使血管内径减小,所以T1时刻的桡动脉内径均大于T2时刻,而为了满足远端肢体的血供,血液流速代偿性增加,所以两组桡动脉收缩期血流峰值流速低于T2时刻。
總之,平面内技术和平面外技术引导动脉穿刺置管对桡动脉血流动力学影响相似;与平面外技术相比,平面内技术超声定位时间长,但其首二次穿刺成功率高,并发症少。
参 考 文 献
[1] Stone MB, Moon C, Sutijono D, et al. Needle tip visualization during ultrasound-guided vascular access: short-axis vs long axis approach[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2010,28(3):343-347.
[2] Velasco A, Ono C, Nugent K, et al. Ultrasonic evaluation of the radial artery diameter in a local population from texas[J]. J Invasive Cardiol, 2012,24(7):339-341.
[3] Shioh AL, Savel RH, Paulin LM, et al. Ultrasound-guided catheterization of the radial artery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Chest, 2011,139(2):524-529.
[4] Ganesh A, Kaye R, Cahill AM, et al. Evaluation of ultrasound-guided radial artery cannulation in children[J]. Pediatr Crit Care Med, 2009,10(1):45-48.
[5] Troianos CA, Hartman GS, Glas KE, et al. Guidedlines for performing ultrasound guided vascular cannulation: recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2011,24(12):1291-1318.
[6] Yildirim V, Ozal E, Cosar A, et al. Direct versus guidewire-assisted pediatric radial artery cannulation technique[J]. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth, 2006,20(1):48-50.
[7] Levin PD, Sheinin O, Gozal Y. Use of ultrasound guidance in the insertion of radial artery catheters[J]. Crit Care Med, 2003, 31(2):481-484.
[8] Shioh AL, Savel RH, Paulin LM, et al. Ultrasound-guided catheterization of the radial artery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of radomized controlled trials[J]. Chest, 2011,139(3):524-529.
[9] Chittoodan S, Breen D, ODonnell BD, et al. Long versus short axis ultrasound guided approach for internal jugular vein cannulation: a prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. Med Ultrason, 2011, 13(1): 21-25.
[10] Quan Z, Tian M, Chi P, et al. Modified short-axis out-of-plane ultrasound versus conventioanl long-axis in-plane ultrasound to guide radial artery cannulation: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Anesth Analg, 2014,119(1):163-169.
[11] Brzezinski M, Luisetti T, London MJ. Radial artery cannulation: a comprehensive review of recent anatomic and physiologic investigations[J]. Anesth Analg, 2009, 109(6):1763-1781.
[12] Nie B, Zhou YJ, Li GZ, et al. Clinical study of arterial anatomic variations for trasradial coronary procedure in chinese population[J]. Chin Med J, 2009,122(18):2097-2102.
[13] Mahler SA, Wang H, Lester C, et al. Short- vs Long- axis approach to ultrasound guided peripheral intravenous access: a prospective randomized study[J]. Am J Emerg Med. 2011,29(9):1194-1197.
[14] Ball RD, Scouras NE, Orebaugh S, et al. Randomized, prospective, observational simulation study comparing resident needle-guided vs free-hand ultrasound techniques for central venous catheter access[J]. Br J Anaesth. 2012,108(1):72-79.
[15] Moon CH, Blehar D, Shear MA, et al. Incidence of posteriar vessel wall puncture during ultrasoung-guided vessel cannulation in a simulated model[J]. Acad Emerg Med, 2010,17(10):1138-1141.
[16] Michaedl B, Cynthia Moon, Darrell Sutijono, et al. Needle tip visualization during ultrasound-guided vascular access: short-axis vs long-axis approach[J]. American J Emerg Med, 2010,28(4):343-347.
基金項目:承德市科学技术研究与发展计划项目,编号201606A027。
第一作者:聂明辉,本科,主治医师,研究方向:超声临床,Email:xuxy1696@126.com。
通讯作者:吴文瑛,本科,副主任医师,研究方向:超声临床,Email:zzzzuf@126.com。
