东海沉积物中多溴联苯醚的分布特征研究
2016-06-07林匡飞于慧娟赵建华蔡友琼刘莉莉中国水产科学研究院东海水产研究所农业部水产品质量安全风险评估实验室上海00090华东理工大学国家环境保护化工过程环境风险评价与控制重点实验室上海0037
周 鹏,林匡飞,于慧娟,赵建华,蔡友琼,刘莉莉*(.中国水产科学研究院东海水产研究所,农业部水产品质量安全风险评估实验室,上海 00090;.华东理工大学,国家环境保护化工过程环境风险评价与控制重点实验室,上海 0037)
东海沉积物中多溴联苯醚的分布特征研究
周 鹏1,林匡飞2,于慧娟1,赵建华2,蔡友琼1,刘莉莉2*(1.中国水产科学研究院东海水产研究所,农业部水产品质量安全风险评估实验室,上海 200090;2.华东理工大学,国家环境保护化工过程环境风险评价与控制重点实验室,上海 200237)
摘要:采集分析了中国东海28个表层沉积物和7个柱状沉积物.结果表明,东海表层沉积物中除BDE-209外∑PBDEs的浓度范围为0.20~2.09ng/g dw,BDE-209的浓度范围为0.57~2.87ng/g dw,在总PBDEs中所占浓度百分比为57.9%~76.7%;接下来分别是BDE-99和BDE-47,所占比例分别为11.7%~21.5%和7.1%~17.4%.表层沉积物中PBDEs分布呈现出(离海岸线)由近及远浓度越来越低的趋势,由北到南浓度上升的趋势.东海柱状沉积物中PBDEs浓度随着深度加深呈现出先上升后下降的趋势,很好的反映出了PBDEs在中国大陆的使用历史和现状.表层沉积物TOC含量在0.54%~0.88%之间,柱状沉积物TOC的含量在0.62%~0.88%之间,而且不管是表层沉积物(R2=0.723,P< 0.01)还是柱状沉积物(R2=0.595, P<0.01),PBDEs浓度和TOC含量之间有较强的线性关系,表明沉积物中TOC含量是影响PBDEs分布的一个重要因素.
关键词:多溴联苯醚;东海;沉积物;分布;TOC
* 责任作者, 副教授, lilyliu@ecust.edu.cn
溴代阻燃剂(BFRs)因阻燃效率高、相对用量少、对复合材料的力学性能几乎无影响,成为目前世界上产量最大和应用较广泛的有机阻燃剂之一[1].多溴联苯醚(PBDE)是常用的溴代阻燃剂[2].其中, PBDEs是一类具有长期残留性、生物富集性和潜在致畸性的持久性有机物(POPs),随着溴原子个数的增加,其化学亲脂疏水性增强,蒸汽压逐渐降低[3].尽管五溴联苯醚(Penta-BDEs)和八溴联苯醚(Octa-BDEs)于2009年被加入到POPs禁令清单,但之前生产的产品寿命尚未终止,且Deca-BDEs仍在生产和使用,其通过含有PBDEs产品的生产、使用及处置等环节被释放到环境中[4].近年来,随着PBDEs被作为高效阻燃剂的广泛应用,其带来的环境问题和生物毒性也越来越引起关注.针对典型高污染区中PBDEs的研究已有许多,尤其是在BFRs生产、使用的企业和电子电器设备拆解、处置区域附近的土壤、大气等环境和生物体中均检测到较高浓度的PBDEs[5-7].
近年来,海洋地区POPs的污染程度日益引起人们的注意.由于PBDEs具有一定的挥发性,能够通过“蚱蜢跳效应”迁移到偏远地区,并能在低温环境中通过冷凝结效应而沉降[8],汇集到河流,然后通过地表径流最终汇集到湖泊海洋沉积物中[9].因此,其对环境和生态的影响已经不再局限于人类生产和居住的区域,在南北极和各大陆沿海地区等极少人类活动的地区也已检出PBDEs[10-12].海洋地区沉积物中PBDEs可能来自大气传输和沉降,之后被海洋动植物吸收富集到体内,而人类可能通过食用海洋生物富集PBDEs[13-14].因此,研究大陆沿海地区沉积物中PBDEs的污染水平和分布对评价PBDEs对人类和生物健康有重要意义.
中国东海是世界上最大的大陆架之一,中国境内有多条大型河流的河水最终汇入其中,包括长江、钱塘江、瓯江、闽江等.而这些河流流经的沿海省份(上海、浙江和福建等)的工业化和城市化都非常高,有大量的电子、印染和石油化工等企业聚集[15].因此,含有大量污染物的、中国大陆的生产生活废水会随着这些河流的河水一起汇入到中国东海,使得中国东海成为这些污染物的一个汇[16].另外一方面,中国东海处于中国大陆的下风向因此又会有部分的污染物随着大气颗粒物的沉降一起进入到中国东海[17-18].而在中国沿海省份的聚集着大量使用PBDEs的生产企业,这些PBDEs和有可能随着污水的排放和大气颗粒物的沉降一起进入到中国东海,然后通过环境介质的重新分配和交换吸附进入到中国东海沉积物[19].因此,为了了解中国东海沉积物中PBDEs的污染现状和特征,我们对中国东海进行了采样和分析,为以后的研究提供基础数据.
1 材料与方法
1.1 样品信息
样品是参加“国家自然科学基金委员会2013年东海科学考察实验室研究6~7月航次”所采集的.采集时间为2013年6月21日~7月15 日,核心采样区域经度范围122°10’E~125°02’E,纬度范围26°48’N~32°00’N,见图1,各采样点具体经纬度见表1.本次考察共采集每个断面前4个站点的表层沉积物,共28个表层沉积物样品;柱状沉积物7个(每个断面的第一个站点采集15~ 30cm不等的柱状沉积物,然后每3cm分割,分开保存).
1.2 样品前处理
将所有底泥样品解冻后干燥,拣出碎石和碎壳等杂质,过200目筛,备用.底泥样品与无水硫酸钠充分混匀,加入回收率指示物13C-PCB-141和13C-BDE-209,研磨除去多余水分,用40mL丙酮/正己烷混合液 (1:1,V:V)索氏提取8h,索氏抽提采用瑞士BUCHI抽提系统B-811,加入干净的铜片除硫.然后将提取液浓缩定容至5.0~6.0mL,转移到30mL玻璃离心管中,加入约5mL浓硫酸,静置后离心,反复加入少量浓硫酸和正己烷2~4 遍,转移上清液至10mL量筒中,氮吹至1.0~2.0mL,用70mL正己烷/二氯甲烷混合液(1:1/V:V) 经多段硅胶柱净化,淋洗液经旋转蒸发和氮吹浓缩,定容至1.0mL正己烷中,经0.45µm 的PTFE膜过滤后,GC /MS检测分析.
1.3 样品分析和质量控制
使用配有Triplus自动进样器的GC6890-MS5975C(安捷伦科技有限公司)分析PBDEs,采用负化学电离源(NCI)并选择离子模式(SIM)进行检测.采用不分流进样模式,进样1µL,甲烷为反应气,高纯氩气(纯度99.99%)为载气,流速为1.5mL/min,进样口温度设为280℃.采用DB-5MS毛细管柱(30m×0.25mm×0.25µm)对Di-BDEs到Hepta-BDEs进行分离,升温程序为:100℃保持1min,再以30℃/min 的速度升温至220℃,停留2min,以3℃/min的速度升温至280℃,停留5min.选择m/z为79、81作为定性定量离子;对Octa-BDEs、Nona-BDEs和BDE-209采用DB-5HT毛细管柱(15.0m×0.25mm×0.1µm)进行分离,升温程序为:100℃保持1min,以8℃/min的速度升温至300℃,保持5min,320℃后运行2min.选择m/z 为79、81和486.7、487.7作为定性定量离子.
用上述色谱及质谱方法测得样品中13CPCB-141和13C-PBDE-209 2种替代物的回收率分别为84.5%±10.5%和78.0%±8.5%.每16个样品为1个批次,每个批次样品同时做方法空白、空白加标和基质加标,以控制整个分析过程的准确度和精密度.数据未进行回收率矫正.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 东海表层沉积物中TOC含量和BFRs的浓度如表1所示,东海表层沉积物中TOC含量在0.54%~0.88%之间,这个结果整体在Kao等人的报道结果之间.而对比世界其他海域 (例如亚马逊三角洲TOC含量为0.6% ± 0.1%[20],密西西比三角洲TOC含量为0.71% ± 0.27%[21],世界海域表层沉积物TOC平均含量为0.75%[22]),中国东海沉积物中TOC含量与之相当.根据Kao等[23]和Wang等[16]提供的13C同位素数据,运用TOC同位素平衡模型计算得出,长江是长江三角洲和东海主要的有机物来源,其贡献量达到沉积物重量的26%~54%.
东海表层沉积物中PBDEs的浓度如表1所示.其中∑PBDEs的浓度范围为0.20~2.09ng/g dw, BDE-209的浓度范围为0.57~2.87ng/g dw.然而,本文所检测出的BDE-209浓度较Chen 等[24]2006年的检测结果(0.16~95ng/g dw)要低许多.可能是因为采样点离海岸线的距离差异,本研究的采样点离海岸线较远,因而受到内陆排放的影响可能就小很多.还有另外一个原因可能是由于欧盟于2006年推出了RoHS指令,商业Deca-BDE被禁用,因而导致市面上的PBDEs使用量大为减少[25].
为了考察东海沉积物中PBDEs浓度和TOC含量之间的关系,对表层沉积物中PBDEs浓度和TOC含量进行线性拟合,所得拟合结果如图2所示.从图2可以看出,东海沉积物中PBDEs浓度和TOC含量之间的线性关系非常好(R2=0.723, P<0.01),这进一步验证了东海沉积物中PBDEs浓度分布的一个重要影响因素是沉积物中TOC含量.

图2 东海表层沉积物中PBDEs浓度和TOC直接的关系Fig.2 The correlations between PBDEs concentrations and TOC% in the surface sediments from the ECS
2.2 东海表层沉积物中PBDEs迁移特征
东海各个断面采样点的表层沉积物中的PBDEs浓度如图3所示.从图3可以看出,所有断面离陆地最近的采样点的表层沉积物中的PBDEs浓度都是最高的,随着离陆地距离越远,其浓度也随之降低,这充分说明了东海表层沉积物中PBDEs主要来自于内陆江河的直接排放.例如,位于杭州湾的断面1和断面2主要受钱塘江的影响,而断面5和断面6主要受从浙江台州入海的瓯江影响.
另外从图3可以看出,BDE-209在所有PBDEs中所占浓度百分比范围为57.9%~76.7%,接下来分别是BDE-99和BDE-47,所占比例范围分别为11.7%~21.5%和7.1%~17.4%,这说明BDE-209是所有PBDEs同系物中最为主要的同系物.虽然BDE-209是主要同系物,但是BDE-209所占比重只有57.9%~76.7%,比太湖[26]以及其他的有关沉积物文献报道结果低出许多.可能是因为东海表层沉积物中PBDEs主要来源于两方面,一方面是来源于内陆河流颗粒物的输送,其颗粒物中BDE-209所占比例为90%以上[27].另外一方面是来源于内陆空气中颗粒物的沉降,而空气颗粒物中吸附的PBDEs中低溴代的PBDEs所占比例要比河流颗粒物中所占比例高出许多[28].东海表层沉积物主要来之于空气颗粒物沉降和河流颗粒物的输送,所以其中BDE-209所占比例介于空气颗粒物和河流颗粒物之间.

表1 东海表层沉积物中PBDEs同系物浓度和TOC含量Table 1 The concentration of PBDEs congeners and TOC in surface sediment of East China Sea
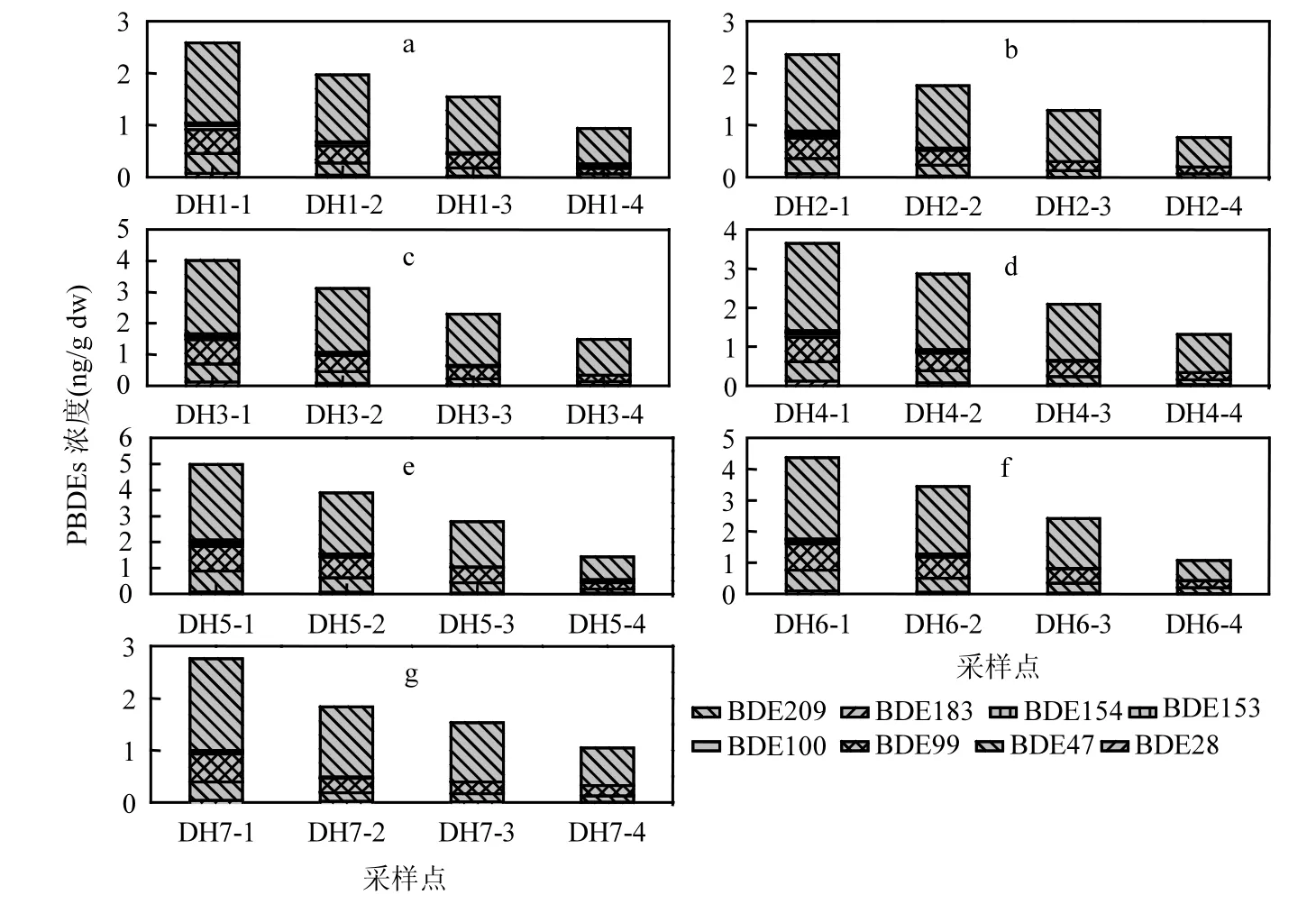
图3 东海表层沉积物中PBDEs的浓度Fig.3 The concentration of PBDEs in surface sediment of East China Sea
2.3 东海柱状沉积物中PBDEs的浓度分布
东海柱状沉积物中PBDEs的浓度和TOC含量见表2和图4.从表2和图4可以看出,东海柱状沉积物中PBDEs浓度总体呈现出先上升后下降的趋势,当沉积物深度到达15cm以后,PBDEs浓度已检测不到或者低于检出限.以DH1-1柱状沉积物为例,表层0~3cm沉积物中PBDEs总浓度为2.58ng/g dw,随着深度继续加深3~6、6~9、9~12、12~15cm沉积物中PBDEs总浓度依次为3.04、1.81、0.74和0.33ng/g dw.这一现象和中国大陆使用PBDEs的方式非常吻合.随着20世纪70年末改革开放的开始,中国制造业开始迅猛发展,PBDEs开始进入中国市场并被使用到相关产品中[2],因此在大约15cm深处的沉积物开始有PBDEs的检出,随后其浓度大量增加,并在3~6cm深处的沉积物浓度达到最高.之后浓度略有下降,这是因为2006年前后随着欧美等国家相继推出类似于RoHS指令这样的法规之后,PBDEs的使用量开始明显下降,但是市场上2006年之前的产品仍含有大量的PBDEs,因此沉积物中PBDEs只是出现了略微的下降趋势.

表2 东海柱状沉积物中PBDEs浓度和TOC含量Table2 The concentration of PBDEs and TOC in core sediment from ECS

续表2

图4 东海柱状沉积物中PBDEs浓度和同系物组成Fig.4 The concentration and congeners contribution of PBDEs in core sediment form ECS
就不同柱状沉积物之间比较来说,其PBDEs浓度总体呈现出的分布趋势和表层沉积物是一致的,即位于瓯江入海口的DH 5-1柱状沉积物中PBDEs浓度最高.其原因如2.2节所述,主要是因为瓯江受浙江台州等废旧电子电器拆解行业污染严重,其输送至东海的颗粒物中PBDEs含量较钱塘江高.
柱状沉积物Core DH 1-1、DH2-1、DH3-1、DH4-1、DH5-1、DH6-1和DH7-1中TOC的含量分别在0.62%~0.78%、0.68%~0.82%、0.64%~0.77%、0.63%~0.73%、0.73%~0.88%、0.74%~0.88%和0.63%~0.75%之间(表2).此外,柱状沉积物中PBDEs浓度和TOC含量之间有较强的线性关系(R2=0.595,P<0.01,图5),这进一步说明沉积物中PBDEs分布和TOC含量有较大的关系.

图5 东海柱状沉积物中PBDEs浓度(ng/g dw)和TOC含量(%)之间的关系Fig.5 The correlations between PBDEs concentrations and TOC% in the core sediments from the ECS
3 结论
3.1 东海表层沉积物中TOC含量在0.54%~0.88%之间;其中∑PBDEs的浓度范围为0.20~2.09ng/g dw,BDE-209的浓度范围为0.57~2.87ng/g dw.东海沉积物中PBDEs浓度和TOC含量之间的线性关系非常好(R2=0.723,P<0.01).3.2 东海表层沉积物中BDE-209在所有PBDEs中所占浓度百分比范围为57.9%~76.7%,接下来分别是BDE-99和BDE-47,所占比例范围分别为11.7%~21.5%和7.1%~17.4%.其分布呈现出(离海岸线)由近及远浓度越来越低的趋势;由北到南浓度上升的趋势.
3.3 东海柱状沉积物中PBDEs浓度呈现出先上升后下降的趋势.柱状沉积物TOC的含量在0.62%~0.88%之间,而且柱状沉积物中PBDEs浓度和TOC含量之间有较强的线性关系(R2=0.595, P<0.01).
参考文献:
[1] 朱婧文,刁 硕,刘成斌.溴代阻燃剂 [J].科技信息, 2012, (25):26.
[2] De Wit C A.An overview of brominated flame retardants in the environment [J].Chemosphere, 2002,46:583-624.
[3] Fu J, Suuberg E M.Vapor pressure of solid polybrominated diphenyl ethers determined via Knudsen effusion method [J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2011,30:2216-2219.
[4] Streets S S, Henderson S A, Stoner A D, et al.Partitioning and bioaccumulation of PBDEs and PCBs in Lake Michigan [J].Environmental Science and Technology, 2006,40:7263-7269.
[5] 田 慧,郭 强,毛潇萱,等.广州地区典型多溴联苯醚迁移和归趋行为模拟 [J].中国环境科学, 2014,34(3):758-765.
[6] Jin J, Wang Y, Liu W, et al.Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in atmosphere and soil of a production area in China: levels and partitioning [J].Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011,23:427-433.
[7] Yang S, Wang S, Liu H, et al.Tetrabromobisphenol A: tissue distribution in fish, and seasonal variation in water and sediment of Lake Chaohu, China [J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2012,19:4090-4096.
[8] Zheng X, Liu X, Jiang G, et al.Distribution of PCBs and PBDEs in soils along the altitudinal gradients of Balang Mountain, the east edge of the Tibetan Plateau [J].Environmental Pollution, 2012,161:101-106.
[9] Allsopp M, Erry B, Santillo D, et al.POPs in the Baltic: a review of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the Baltic Sea [R].Greenpeace International, 2001.
[10] Wang X P, Gong P, Yao T D, et al.Passive air sampling of organochlorine pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers across the Tibetan Plateau [J].Environmental Science and Technology, 2010,44:2988-2993.
[11] Möller A, Xie Z, Sturm R, et al.Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and alternative brominated flame retardants in air and seawater of the European Arctic [J].Environmental Pollution, 2011,159:1577-1583.
[12] 耿大玮,李英明,张 庆.南极乔治王岛大气中PCBs和PBDEs的污染水平及分布规律 [R].上海:第六届全国环境化学学术大会, 2011.
[13] Muir D C, Backus S, Derocher A E, et al.Brominated flame retardants in polar bears (Ursus maritimus) from Alaska, the Canadian Arctic, East Greenland, and Svalbard [J].Environmental Science and Technology, 2006,40:449-455.
[14] Parolini M, Guazzoni N, Binelli A, et al.Polybrominated diphenyl ether contamination in soil, vegetation, and cow milk from a high-mountain pasture in the Italian Alps [J].Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2012,63:29-44.
[15] Cai M, Zhao Z, Yang H, et al.Spatial distribution of per-and polyfluoroalkyl compounds in coastal waters from the East to South China Sea [J].Environmental Pollution, 2012,161:162-169.
[16] Wang X C, Sun M Y, Li A C.Contrasting chemical and isotopic compositions of organic matter in Changjiang (Yangtze River) estuarine and East China Sea shelf sediments [J].Journal of Oceanography, 2008,64:311-321.
[17] Guo Z, Lin T, Zhang G, et al.High-resolution depositional records of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the central continental shelf mud of the East China Sea [J].Environmental Science and Technology, 2006,40:5304-5311.
[18] Hu L, Lin T, Shi X, et al.The role of shelf mud depositional process and large river inputs on the fate of organochlorine pesticides in sediments of the Yellow and East China Seas [J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2011,38(3):246-258.
[19] Bettina H, Hermann F, Wolfgang V L, et al.Effects of chain length, chlorination degree, and structure on the octanol− water partition coefficients of polychlorinated n-alkanes [J].Environmental Science and Technology, 2011,45:2842-2849.
[20] Aller R C, Blair N E.Sulfur diagenesis and burial on the Amazon shelf: Major control by physical sedimentation processes [J].Geo-Marine Letters, 1996,16:3-10.
[21] Lin S, Morse J W.Sulfate reduction and iron sulfide mineral formation in Gulf of Mexico anoxic sediments [J].American Journal of Science, 1991,291:55-89.
[22] Berner R A.Burial of organic carbon and pyrite sulfur in the modern ocean: its geochemical and environmental significance [J].Am.J.Sci., 1982,282:451-473.
[23] Kao S, Lin F, Liu K.Organic carbon and nitrogen contents and their isotopic compositions in surficial sediments from the East China Sea shelf and the southern Okinawa Trough [J].Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2003,50: 1203-1217.
[24] Chen S J, Gao X J, Mai B X, et al.Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface sediments of the Yangtze River Delta: levels, distribution and potential hydrodynamic influence [J].Environmental Pollution, 2006,144:951-957.
[25] De Wit C A, Herzke D, Vorkamp K.Brominated flame retardants in the Arctic environment–trends and new candidates [J].Science of the Total Environment, 2010,408:2885-2918.
[26] Qiu X, Zhu T, Hu J.Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and other flame retardants in the atmosphere and water from Taihu Lake, East China [J].Chemosphere, 2010,80:1207-1212.
[27] Carlsson P, Herzke D, Wedborg M, et al.Environmental pollutants in the Swedish marine ecosystem, with special emphasis on polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE), Chemosphere, 2011,82:1286-1292.
[28] Deng W J, Zheng J S, Bi X H, et al.Distribution of PBDEs in air particles from an electronic waste recycling site compared with Guangzhou and Hong Kong, South China [J].Environ.Int., 2007,33:1063-1069.
The distribution of polybrominated piphenyl rther in the sediment of East China Sea.
ZHOU Peng1, LIN Kuang-fei2, YU Hui-juan1, ZHAO Jian-hua2, CAI You-qiong1, LIU Li-li2*(1.Laboratory of Quality and Safety Risk Assessment for Aquatic Products (Shanghai), Ministry of Agriculture, East China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Science, Shanghai 200090, China;2.East China University of Science and Technology, State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Environmental Risk Assessment and Control on Chemical Process, Shanghai 200237, China).China Environmental Science, 2016,36(1):149~156
Abstract:In this study, 28surface sediment and 7core sediment samples were collected from the East China Sea (ECS) to determine the distribution properties of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs).The concentrations of total PBDEs (excepted BDE-209) in surface sediment samples were in the range of 0.20~2.09ng/g dw.Among the detected congeners, BDE-209 was the predominant congener with the corresponding concentration ranging from 0.57~2.87ng/g dw (57.9%~76.7% of total PBDEs), followed by BDE-99 and BDE-47.Moreover, the concentrations of PBDEs decreased with the increase of distance between sampling sites and coastline and increased from the north to south.The distribution trends of PBDEs in core sediment samples from the ECS matched well with the application history and status of PBDEs products in China.The ratios of total organic carbon (TOC) in the surface and core sediment samples were ranged from 0.54%~0.88% and 0.62%~0.88% respectively.And the correlations between TOC and PBDEs in both surface (R2=0.723, P< 0.01) and core (R2=0.595, P<0.01) sediment samples indicated that TOC might be one of the impact factors for the characteristics of PBDEs distribution in sediment.
Key words:polybrominated diphenyl ethers;East China Sea;sediment;distribution;total organic carbon
中图分类号:X55
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1000-6923(2016)01-0149-08
收稿日期:2015-05-20
基金项目:环保公益性行业科研专项(201309047,201309030);国家自然科学基金(41001316,41371467,40901148);中央高校基本科研业务费(NO.WB1214059)
作者简介:周 鹏(1988-),男,江西贵溪人,助理研究员,博士,主要从事水产品检测、POPs污染分析及源解析研究.发表论文4篇.
