手足口病重症患儿营养素水平与病情的相关性分析
2016-04-15王晓波杜潘艳赵玉萍王宝林高翠红
王晓波 杜潘艳 赵玉萍 王宝林 高翠红 张 双
(唐山市妇幼保健院,唐山063000)
手足口病重症患儿营养素水平与病情的相关性分析
王晓波杜潘艳赵玉萍王宝林高翠红张双
(唐山市妇幼保健院,唐山063000)
[摘要]目的:探讨手足口病患儿外周血中营养素前白蛋白(PA)、纤维连接蛋白(FN)、视黄醇结合蛋白(RBP)、C-反应蛋白(CRP)、微量元素铁、锌及维生素D(VitD)水平与病情的相关性。方法:采用免疫比浊法检测PA、FN、RBP和CRP水平;采用火焰原子吸收法检测全血微量元素铁、锌水平;采用电化学发光法检测VitD水平。结果:重症组与普通组、对照组比较,PA、FN、RBP、铁、锌及VitD水平均低,CRP水平升高(P<0.05);普通组与对照组比较,PA 、FN和RBP水平均降低,CRP水平升高(P<0.05);铁、锌及VitD水平在普通组和对照组间无统计学意义(P>0.05)。重症恢复期PA、FN、RBP、铁、锌及VitD水平均高于急性期(P<0.01),但仍低于对照组(P<0.05);恢复期CRP水平与对照组无统计学意义(P>0.05)。PA、FN和RBP水平与手足口病病情呈显著负相关(P<0.05);而CRP与病情呈显著正相关(P<0.05);铁、锌、VitD水平与病情呈低度负相关(P<0.05)。结论:手足口病重症病例存在营养缺乏,临床应对其进行营养状态动态评估并适量补充营养。
[关键词]手足口病;重症;营养素;相关性
手足口病(Hand,foot and mouse disease,HFMD)是一种主要由肠道病毒引发的急性传染病。普通病例呈自限性,重症病例可合并神经系统、呼吸系统、循环系统等严重并发症[1]。低龄儿童是易感人群。有研究表明儿童体内营养素缺乏可影响免疫系统功能,容易发生感染性疾病[2,3]。本研究对本院确诊的手足口病患儿外周血中营养指标前白蛋白(Pre albumin,PA)、纤维连接蛋白(Fibronectin,FN)、视黄醇结合蛋白(Retinol binding protein,RBP)、C-反应蛋白(C- reactive protein,CRP)、微量元素铁(Iron)、锌(Zinc)及维生素D(Vitamin D,VitD)水平等进行总结分析,并探讨其与病情相关性。
1资料与方法
1.1研究对象病例组为2013年6月~2015年8月期间于本院儿科已确诊的手足口病病例381例,年龄4月~8岁,平均年龄(3.2±1.2)岁。根据《手足口病诊疗指南 (2010年版)》临床分类标准[4]表1病例组和对照组比较结果将病例分为普通组和重症组。普通组276例,男142例,女134例,平均年龄(3.4±1.1)岁;重症组105例,男56例,女49例,平均年龄(2.9±1.0)岁。对照组88例,为病例收集同期于儿童保健科体检的健康儿童,男47例,女41例,年龄4月~8岁,平均年龄(3.2±1.0)岁,且近1月内未发生过消化系统疾病。对照组与病例组间性别、年龄比较,均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
Tab.1Comparison between case group and control group

GroupsCasesPA(mg/L)FN(mg/L)RBP(mg/L)CRP(mg/L)Iron(mmol/L)Zn(μmol/L)VitD(nmol/L)Control88256.9±33.4236.6±38.939.4±8.21.7±0.98.4±2.289.4±8.341.6±8.4General276224.3±40.2217.3±44.734.6±10.515.5±9.28.2±2.386.8±17.938.2±16.6Severe105182.5±30.6168.6±43.926.7±9.445.4±19.76.7±2.670.4±12.831.5±12.7P1)<0.05P2)<0.05>0.05
Note:1)Comparison between the severe group and the general、control group;2)Comparison between the general group and control group.
表2重症组急性期与恢复期比较结果
Tab.2Comparison between acute phase and convalescence of severe group
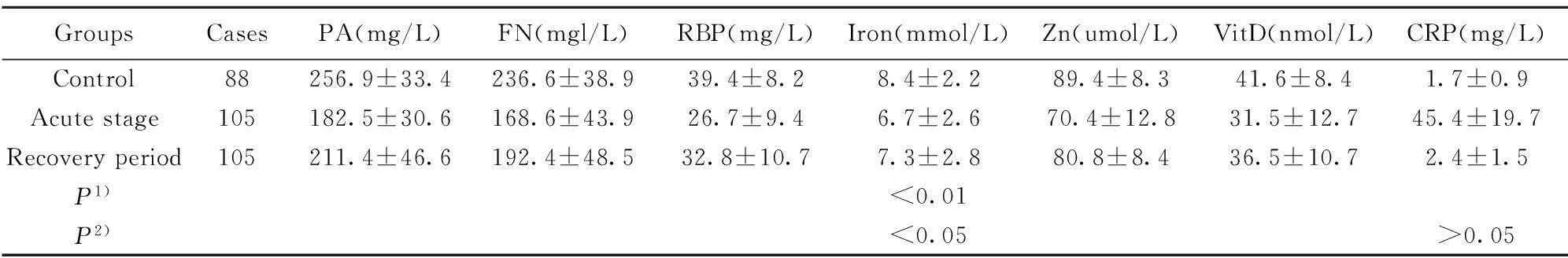
GroupsCasesPA(mg/L)FN(mgl/L)RBP(mg/L)Iron(mmol/L)Zn(umol/L)VitD(nmol/L)CRP(mg/L)Control88256.9±33.4236.6±38.939.4±8.28.4±2.289.4±8.341.6±8.41.7±0.9Acutestage105182.5±30.6168.6±43.926.7±9.46.7±2.670.4±12.831.5±12.745.4±19.7Recoveryperiod105211.4±46.6192.4±48.532.8±10.77.3±2.880.8±8.436.5±10.72.4±1.5P1)<0.01P2)<0.05>0.05
Note:1)Comparison of convalescence and acute phase;2)Comparison of convalescence and control group.
1.2实验方法采集研究对象入院12 h内及重症患儿恢复期空腹静脉血3管,一管肝素锂抗凝2 ml,采用火焰原子吸收法检测全血微量元素铁、锌水平,试剂由北京博晖公司提供;两管无抗凝剂3 ml,分离血清,其中1管采用免疫比浊法检测PA、FN、RBP、CRP水平,试剂由南京波音特生物科技公司提供;另1管采用电化学发光法检测维生素D水平,试剂为德国罗氏诊断公司提供。

2结果
2.1病例组和对照组比较结果重症组与普通组、对照组比较,患儿PA、FN、RBP、铁、锌及VitD水平均低,CRP水平升高,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);普通组与对照组比较,PA、FN和RBP水平均降低,CRP水平升高,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);微量元素铁、锌及VitD水平在普通组和对照组间无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。
表3营养素与HFMD病情相关性
Tab.3Correlation between nutrients and state of HFMD
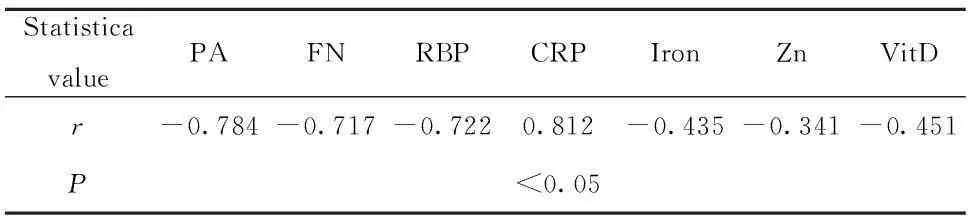
StatisticavaluePAFNRBPCRPIronZnVitDr-0.784-0.717-0.7220.812-0.435-0.341-0.451P<0.05
2.2重症组急性期与恢复期比较结果重症组患儿恢复期与急性期比较,PA、FN、RBP、铁、锌及VitD水平均升高(P<0.01);但这些指标水平均低于对照组(P<0.05);恢复期CRP水平降低,与对照组无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。
2.3营养素与HFMD病情相关性PA、 FN、RBP水平与HFMD病情呈显著负相关(P<0.05);而CRP与病情呈显著正相关(P<0.05);铁、锌、VitD水平与病情呈中度负相关(P<0.05)。见表3。
3讨论
手足口病起病急,病情发展迅猛,控制不及时容易发展成重症病例,甚至危及生命。HFMD的发生发展与机体免疫水平密切相关[5],而人体免疫水平的高低受多种因素影响,其中营养因素起着非常重要的作用,是维持人体正常免疫功能和健康的物质基础。营养失调会对人体免疫系统造成很大损伤。有研究显示在发展中国家入院或重症监护病房存在急性或慢性营养不良的患儿可达53%[6]。
PA、FN、RBP对于急性营养不良具有早期诊断价值,能及时反映患者肠外营养状况及恢复[7,8]。微量元素铁、锌和VitD在调节和介导免疫反应的过程中有着重要的作用,营养素缺乏影响机体免疫功能[9-11]。本研究中HFMD病患儿,尤其是重症病例营养素水平均低,与病情严重程度呈负相关,提示手足口病存在营养素缺乏,营养素水平可能影响机体正常的免疫功能。住院期间患儿受多种因素影响,营养状况进一步恶化,易导致病情加重,而病情恶化又会影响营养素的摄入、合成和吸收[3]。因此重症患儿住院期间营养风险筛查和营养评估至关重要。
CRP作为非特异性急性炎性反应标记物,在急性应激反应状态下,肝脏优先合成CRP而减少合成白蛋白、前白蛋白[12]。有研究用CRP与PA的比值作为评估消化系统手术成功的指标[13]。本研究中CRP水平与HFMD病情呈显著正相关,提示CRP不仅可以判断疾病的严重程度[14],还可以间接反映患者营养状况。
本研究中重症患儿恢复期营养素水平均高于急性期,提示临床应对重症病例进行营养状态动态评估,有助于监测病情。重症患儿恢复期营养素水平仍低于健康儿童,可能由于病毒对患儿机体造成炎性反应,尽管处于恢复期,但仍会影响机体对营养素的吸收和合成。
综上所述,手足口病重症患儿存在营养素缺乏状况,在疾病的诊疗过程中进行定期、动态评估并及时给予补充,可利于监测病情及改善预后。
参考文献:
[1]Ma E,Chan KC ,Cheng P,etal.The Enterovirus 71 epidemic in 2008 --public health implications for Hong Kong[J].Int Infection Dis,2010,14(9):e775-e780.
[2] Mao S,Zhang A,Huang S.Meta-analysis of Zn,Cu and Fe in the hair of Chinese children with recurrent respiratory tract infection[J].Scand J Clin Lab Invest,2014 ,74(7):561-567.
[3]Krawinkel MB.Interaction of nutrition and infections globally:an overview[J].Ann Nutr Metab,2012,61(Suppl 1):39-45.
[4]卫生部办公厅关于印发《手足口病诊疗指南(2010年版)》的通知[EB/OL].(2010-04-06)[2010-06-01]http://www.moh.gov.cn/publicfiles/business/ht mlfiles/mohyzs/s3586/202004/46884.htm.
[5] Zhang Y,Liu H,Wang L,Yang F,etal.Comparative study of the cytokine/chemokine response in children with differing disease severity in enterovirus 71- induced hand,foot,and mouth disease[J].PLoS One,2013,8(6):e67430.
[6] Bhutta ZA,Salam RA.Global nutrition epidemiology and trends[J].Ann Nutr Metab,2012,61(Suppl 1):19-27.
[7]Xu D,Li J,Song Y,etal.Laparoscopic surgery contributes more to nutritional and immunologic recovery than fast-track care in colorectal cancer[J].World J Surg Oncol,2015,13(1):18.
[8]Feferbaum R,Delgado AF,Zamberlan P,etal.Challenges of nutritional assessment in pediatric ICU[J].Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care,2009,12(3):245-250.
[9]Cassat JE,Skaar EP.Iron in infection and immunity[J].Cell Host Microbe,2013,13(5):509-519.
[10]Nishida K.New knowledge from past decade:role of zinc in immune system[J].Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi,2013,68(3):145-152.
[11]Lang PO,Samaras N,Samaras D,etal.How important is vita min D in preventing infections?[J].Osteoporos Int,2013 ,24(5):1537-1553.
[12] Mehta NM,Compher C;A.S.P.E.N.Board of Directors.A.S.P.E.N.Clinical Guidelines:nutrition support of the critically ill child[J].JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr,2009 ,33(3):260-276.
[13]Harriman S,Rodych N,Hayes P,etal.The C-reactive protein:prealbu min ratio as a predictor of successful surgical closure of gastrointestinal fistulas[J].Am Surg,2015,1(2):73-77.
[14]Page AL,de Rekeneire N,Sayadi S,etal.Diagnostic and prognostic value of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in malnourished children[J].Pediatrics,2014,133(2):e363-370.
[收稿2015-09-11修回2015-09-21]
(编辑倪鹏)
Correlation of nutrient levels and state of severe cases with HFMD
WANGXiao-Bo,DUPan-Yan,ZHAOYu-Ping,WANGBao-Lin,GAOCui-Hong,ZHANGShuang.
TangshanWomenandChildrenHealth-CareHospital,Tangshan063000,China
[Abstract]Objective:To detect the levels of PA,FN,RBP,CRP,Iron,Zinc,VitD in peripheral blood of children with HFMD and to explore the relationship between them and the disease.Methods: The levels of PA,FN,RBP and CRP were detected by immune turbidimetric assay;and the levels of Iron and Zinc were detected by flame atomic absorption spectrometry;while the levels of VitD were detected by electro chemilumin escence.Results: The levels of PA,FN,RBP,Iron,Zinc and VitD in the severe group were lower than those in other groups,while the levels of CRP were higher than those in other groups(P<0.05);and the levels of PA,FN and RBP in the general group were lower than that in the control group,while the levels of CRP were higher than that in the control group(P<0.05).And no significance were found of the levels of Iron,Zinc and VitD in the general group and the control group(P>0.05).The levels of PA,FN,RBP,Fe,Zn and VitD in the convalescence were higher than those in the acute phase of the severe cases(P<0.01),and lower than those in the control group(P<0.05);And no statistical significance were found of the levels of CRP between the convalescent phase of severe cases and the control group(P>0.05).There were negative correlation between the levels of PA,FN,RBP and the state of HFMD(P<0.05),while there were positive correlation between the levels of CRP and the state of HFMD(P<0.05).And there were low negative correlation between the levels of Iron,Zinc,VitD and the state of HFMD(P<0.05),respectively.Conclusion: There were nutritional deficiency in severe cases of HFMD,and the nutritional status should be assessed dynamically,then proper amount of nutrition should be supplement.
[Key words]HFMD;Severe cases;Nutrients;Correlation
中图分类号R725.1
文献标志码A
文章编号1000-484X(2016)03-0414-03
作者简介:王晓波(1976年-),男,主管检验师,主要从事临床儿科检验研究。
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2016.03.026
