风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置的设计与试验
2016-03-21左兴健武广伟付卫强李立伟魏学礼赵春江西北农林科技大学机械与电子工程学院杨凌712100国家农业智能装备工程技术研究中心北京100097农业部农业信息技术重点实验室北京100097农业智能装备技术北京市重点实验室北京100097
左兴健,武广伟,付卫强,李立伟,魏学礼,赵春江(1. 西北农林科技大学机械与电子工程学院,杨凌 712100; 2. 国家农业智能装备工程技术研究中心,北京 100097;3. 农业部农业信息技术重点实验室,北京 100097; 4. 农业智能装备技术北京市重点实验室,北京 100097)
风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置的设计与试验
左兴健1,2,3,4,武广伟2,3,4,付卫强2,3,4,李立伟2,3,4,魏学礼2,3,4,赵春江1,3※
(1. 西北农林科技大学机械与电子工程学院,杨凌 712100;2. 国家农业智能装备工程技术研究中心,北京 100097;3. 农业部农业信息技术重点实验室,北京 100097;4. 农业智能装备技术北京市重点实验室,北京 100097)
摘要:针对中国水稻施肥机械化程度低,传统撒施肥料利用率低、施肥量大的现状,结合侧深施肥农艺特点,对风送式排肥方法进行了理论分析,研制了风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置。该装置采用模块化设计与乘坐式插秧机配套使用,采用电机驱动排肥、风送肥料、全球定位系统(global position system,GPS)测速的工作原理,侧位深施化肥的施肥方式,采用车辆行驶速度与排肥驱动电机转速实时匹配的精准施肥控制方法。设备在黑龙江七星农场开展了田间实际作业试验。试验表明,该装置与插秧机配合使用时能一次性完成插秧与侧深精准施肥作业,当预置施肥量为300 kg/hm2,车辆稳定行驶速度为1 m/s时,施肥量偏差控制在5.82%以内,能够较好的满足实际生产需求。该研究为开展水稻变量施肥控制技术研究和水稻侧深施肥装置的研发提供了参考。
关键词:农业机械;设计;农作物;风送式;精准施肥;侧深施肥
左兴健,武广伟,付卫强,李立伟,魏学礼,赵春江. 风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(3):14-21.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.03.003http://www.tcsae.org
Zuo Xingjian, Wu Guangwei, Fu Weiqiang, Li Liwei, Wei Xueli, Zhao Chunjiang. Design and experiment on air-blast rice side deep precision fertilization device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(3): 14-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.03.003 http://www.tcsae.org
Email:zuo_xj@163.com
0 引 言
水稻是中国最主要的粮食作物,是种植面积最大、单产最高、总产量最多的粮食作物。施肥是水稻生产过程中一个重要作业环节,目前中国水稻生产过程中施肥环节一直沿用人工手撒施肥方式,施肥量大,且肥料在田间分布不均,秧苗吸肥量不一致,直接影响水稻产量[1]。水稻侧深施肥是在水稻机械插秧的同时将颗粒肥料(基肥和蘖肥)一次性施于秧苗侧位具有一定深度土壤中的施肥方式,肥料呈条带状施于耕层,距水稻根系近,利于根系吸收利用,提高肥料利用率[2-6]。
在国外,日本久保田、井关、洋马等公司在水稻侧深施肥设备方面进行了大量的研究工作,研发了安装有侧深施肥装置的水稻插秧机系列化产品,侧深施肥装置采用机械式传动方式,安装复杂,与中国现有插秧机配套性差,阻碍了侧深施肥技术的应用[7-8],国内水稻机械施肥环节主要利用水田拖拉机悬挂圆盘式撒肥机进行抛撒施肥以及利用旋耕施肥一体机在旋耕的同时将肥料施在碎土层,施肥量大,肥料分布不均匀。在已开展水稻侧深施肥装置的研究方面,缺乏风送式输送肥料方面的理论研究,还没有实现对电机排肥的精确控制,无法实现精准施肥作业[9-14]。在已开展的精准施肥技术及控制系统研究方面,主要是针对旱田作业环境开展基于处方图的精准施肥技术装备研究,已有的基于处方图的变量施肥控制方法不能满足插秧机水田环境下侧深精准施肥的要求[15-19]。
本文结合水稻侧深施肥农艺特点,开展了风送排肥理论和水田侧深精准施肥控制方法的研究。针对乘坐式插秧机设计了风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置,采用电机驱动排肥、风送肥料的原理,通过全球定位系统(global position system,GPS)数据计算得到车体行驶速度,根据车速变化实时调整施肥量,以期实现水田环境中的侧深精准施肥作业,提高施肥均匀性和肥料利用率。
1 施肥装置结构及工作原理
1.1施肥装置结构
该装置采用模块化整体式设计,包括一体化安装底座、测速模块、施肥控制器、车载控制终端、作业状态传感器、排肥驱动电机、肥箱、排肥器、鼓风机、风管、排肥管、排肥口,底座通过螺栓或其他连接紧固件固定在插秧机踏板上,该装置能与不同品牌、不同型号插秧机配套使用。该装置与插秧机配套使用结构简图如图1所示,主要技术参数如表1所示。
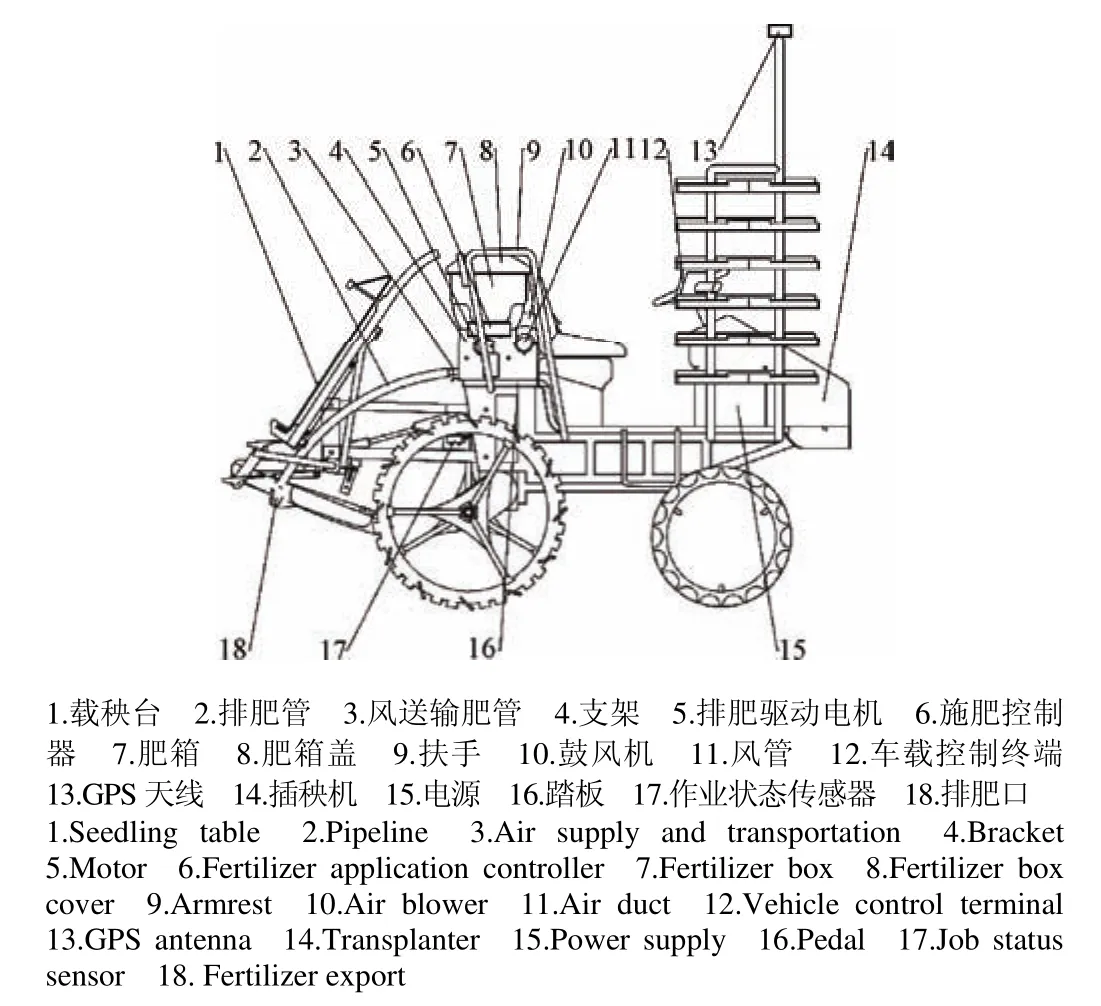
图1 施肥装置与插秧机配套使用结构简图Fig.1 Supporting use of fertilizing device and transplanting machine structural diagram
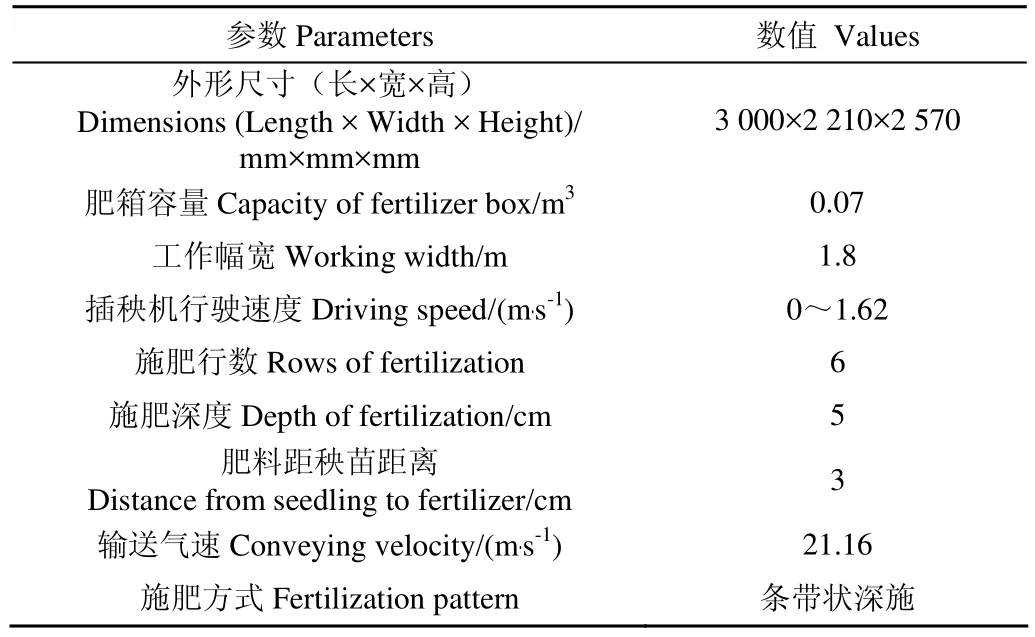
表1 风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置主要技术参数Table 1 Main technical parameters of rice side deep precision fertilization device based on wind feed type
1.2一体化安装底座及肥箱结构
为简化安装方式,提高施肥装置的通用性,底座与肥箱采用一体化结构设计。肥箱采用轻质透明塑料肥箱,肥箱底部横截面为顶大底小的倒梯形状,肥箱通过支架安装在底座上,底座一端固定风机,一端支架固定排肥驱动电机及施肥控制器。一体化安装底座及肥箱如图2所示。
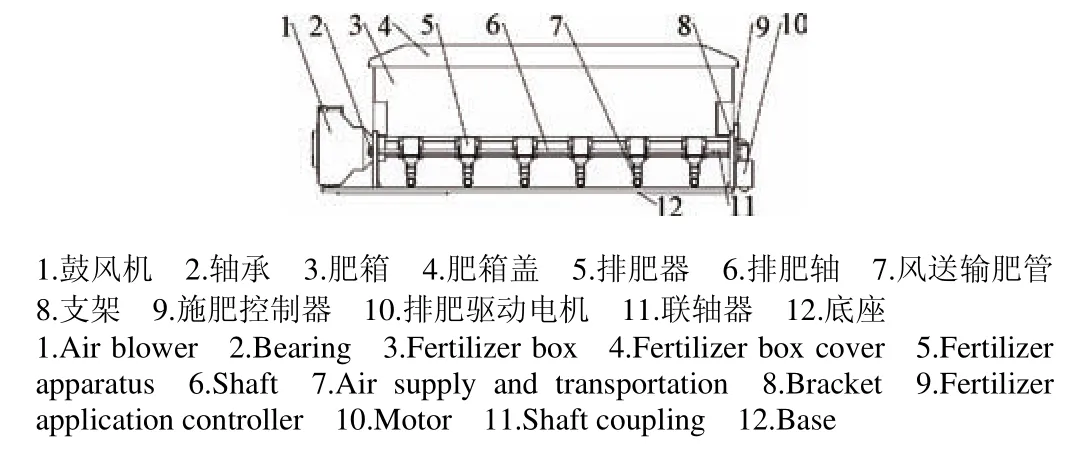
图2 一体化安装底座及肥箱结构示意图Fig.2 Structure of integrated installation base and fertilizer box
1.3工作原理
施肥装置采用电机驱动排肥、风送肥料的工作原理。施肥作业时,车载控制终端设定目标施肥量,排肥驱动电机带动排肥轮转动进行排肥,鼓风机强制气吹输送肥料。施肥深度及肥料距秧苗之间的距离通过排肥口与滑动板之间的距离来进行调整。采用车辆行驶速度与排肥驱动电机转速实时匹配的施肥控制方法,利用GPS数据计算得到插秧机行进速度,采用作业状态传感器感知插秧机工作状态,根据插秧机作业速度,实时控制施肥量。田间作业时,排肥口在秧苗侧边3 cm处划出一道深5 cm的矩形沟槽,排肥器排出的肥料在风力和重力的作用下,经风送输肥管、排肥管、排肥口,下落至已划沟槽的底部,最后,在覆土板作用下将肥料覆盖于沟槽中[10-14]。施肥原理图如图3所示。

图3 施肥原理图Fig.3 Fertilization principle diagram
2 排肥覆土部件设计
2.1排肥口设计
排肥口通过螺栓固定于插秧机滑动板上。作业过程中滑动板底部的根茬、杂草在通过排肥口时被楔形块压入泥浆或随泥浆分流到排肥口两侧,两侧泥浆无法快速弥合划出的矩形沟槽,为排肥口肥料的排出创造了条件。楔形块按照船形铲式开沟器原理进行设计,迎面切角为35°,排肥口底部与滑动板之间的距离为5 cm,排肥口中心与秧爪之间的距离为3 cm,从而保证定位施肥。排肥口安装位置及结构如图4所示。

图4 排肥口结构示意图Fig.4 Structure of fertilizer outlet
2.2覆土装置
覆土装置如图5所示,包括滑动板,板式覆土板。覆土板通过预留孔安装在滑动板上,覆土板设置在左右排肥口的正后方,两覆土板呈V形结构,板长不超过100 mm,过长刮伤秧苗,过短覆土能力差。两覆土板板间夹角为120°,夹角过小覆土能力差,夹角过大易壅土堵塞,覆土板与地面夹角为60°。
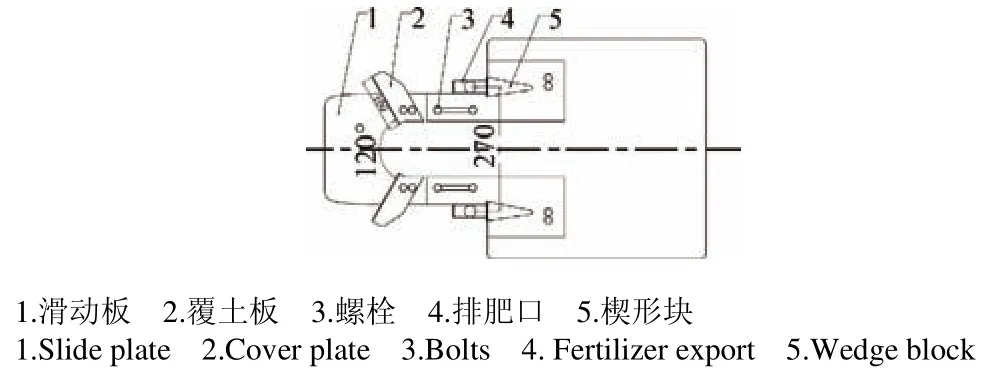
图5 覆土装置结构示意图Fig.5 Structure of trenching and casing soil
3 气力输送系统
3.1气力输送系统结构及工作原理
风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置是侧深施肥技术应用的载体,气力输送系统是实现水田环境中稳定排肥的关键。水田施肥,排肥管路长且曲折,传统的凭重力排肥效果不佳,水和泥浆会影响肥料从排肥管排出,有时会倒灌进排肥管阻碍肥料正常排出,造成堵塞。本装置采用开放式气力输送肥料的方法[20-21]。
本施肥装置气力输送系统气源压力低于0.1 MPa,采用正压压送式气力输送系统[20-21]。系统主要由鼓风机、风速调节开关、风管、风送输肥管、排肥器、料斗、排肥管组成。图6为气力输送系统简图,气源设在系统前端,系统工作时,肥料经排肥器下落至风送输肥管,鼓风机将具有一定压力的压缩气体通入风送输肥管,在文丘里效应的作用下,风送输肥管进料口呈负压,气流沿进气口通向出气口,与被输送的颗粒肥料混合,颗粒肥料在输送管中以流动的气体为载体,经排肥管、排肥口在气流和重力的双重作用下落入下肥口划出的位于已插秧苗侧位具有一定深度的矩形沟槽内[22-24]。

图6 气力输送系统Fig.6 Pneumatic conveying system
3.2气力输送系统主要参数
3.2.1空气流量
为保证颗粒肥料在输肥管路中顺利输送而不被堵塞,颗粒肥料和空气要保持适当的混合浓度比,本输送系统属于低压系统,生产率较小,混合浓度比取0.6[20],空气流量为

式中Q为空气流量,m3/s;W为输送机构生产率,t/h;γ为空气容重,γ=1.2 kg/m3;μ为混合浓度比。
插秧机作业效率为0.2~0.61 hm2/h,按最大作业效率0.61 hm2/h、施肥量300 kg/hm2计算,可知输送机构生产率W为0.183 t/h,经计算,空气流量Q为250 m3/h。
3.2.2输送气速
输送气速是评价系统输送性能的重要指标,此速度必须保证颗粒肥料能在输肥管中正常运输。因输肥管有高低起伏,速度过低容易造成管道堵塞,速度过高不但浪费能量,还会增加肥料对管道的磨损,同时加剧颗粒肥料的破损,降低肥料缓释效应[21,25]。由于输送气速为

式中V*为输送气速,m/s;VL为肥料悬浮速度,m/s;k为速度系数(一般为1.5~2.5,与物料浓度,管道复杂性有关。)
本研究通过悬浮试验,实测得到悬浮速度为10.58m/s,由于水稻侧深施肥所用缓释复合肥料体积、密度大,风送管道长,速度系数k等于2为宜[20-21],输送气速V*为21.16 m/s。
本文同时在静止条件下,当排肥口处于水及泥浆环境中,进行了排肥试验。本对水及泥浆没过排肥口1、2、3、4、5 cm进行了排肥试验,并用太仓华裕控制设备有限公生产的基于热膜风速原理的风速传感器测定了水及泥浆不堵塞排肥口的临界风速。试验数据如图7所示。试验表明输送气速能满足排肥要求。
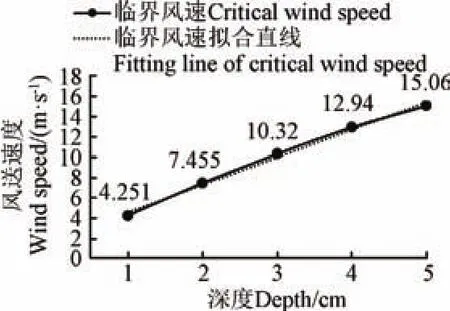
图7 临界风速图Fig.7 Critical wind speed chart
3.2.3风送输肥管结构设计
为实现风送系统肥料进口无空气泄漏,设计了如图8所示风送输肥管,该管由进料口、入口圆筒段、圆锥收缩段、圆筒形喉部、圆锥扩散段、出口圆筒段组成。鼓风机排出的气流通过入口圆筒段,以很高的速度经过圆筒形喉部,该高速气流通过圆筒形喉部时在文丘里效应的作用下在进料口形成负压,从而使进料口无气体外泄[26]。
输肥管路内径由空气消耗量和输送气速共同决定,内径为式中d1为输肥管内径,m。

计算可得输肥管内径d1为26.5 mm,由于与风送输肥管对接的标准钢丝骨架塑料软管内径为25、32 mm,本设备选用接近理论直径的内径为25 mm的钢丝骨架塑料软管,适当减小输肥管内径有助于提高风速,降低堵塞。根据经典文丘里管设计方法对风送输肥管进行设计,收缩角为21°,当扩散角为8°时,圆锥扩散段压差最小[27-28],当节流比为0.7时收缩段压差较小,所以喉部直径为d2= 17.5 mm,喉段长度常为0.5 d2或者d2,为保证肥料入口空间,该管喉部长度为d2=17.5 mm[27-28]。
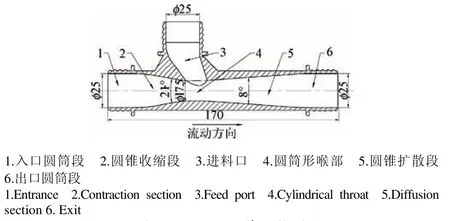
图8 风送输肥管结构图Fig.8 Structure of fertilizer delivery tube
3.2.4风机选型
根据流量及气速要求,本设备选用工作电压为12 V、功率为72 W的可调速离心风机,机芯由德国ebmpapst公司生产,额定转速为3 200 r/min,型号为R1G190-AC11-52。
4 施肥控制系统设计
4.1风送式水田侧深施肥控制系统总体设计
风送式水田侧深施肥控制系统是基于实时车速的精准施肥作业控制[29-30],系统包括具有GPS接收模块的车载控制终端,施肥控制器、作业状态传感器、排肥驱动电机、鼓风机等,系统结构如图9a所示。
施肥控制系统使用排肥轴目标转速讯息、实际排肥轴转速讯息和车速讯息等将车载控制终端和施肥控制器联系起来[30-31]。排肥轴目标转速讯息是车载控制终端发送给施肥控制器的目标转速讯息;实际排肥轴转速讯息是施肥控制器反馈给车载控制终端的当前施肥量表征值;车速讯息是车载控制终端通过GPS接收器接收到的数据计算所得的当前车速,车速讯息通过总线发送给施肥控制器。车载控制终端与施肥控制器通过RS485总线通信,按照串行链路上MODBUS协议的定义,采用RTU传输模式。作业过程中,车载控制终端通过解析GPS数据计算车体行驶速度,计算排肥驱动电机目标转速,实现电机转速的实时控制。施肥作业控制流程如图9b所示。
4.2车载控制终端
车载控制终端是Windows XP操作系统,针对水田侧深精准施肥作业需求,利用eMbeddedVisualC++集成开发环境,在该终端的操作系统上设计了施肥控制软件,车载控制终端与施肥控制器采用RS485串行总线通讯模式。该软件通过调用终端中集成的高精度GPS模块,解析接收到的GPS数据,通过计算,获取车体行驶速度。软件界面能实时显示电机转速、作业状态传感器状态值信息,同时该软件允许用户根据实际作业需求设定工作参数。软件界面如图9c所示。

图9 施肥控制系统框图Fig.9 Control system block diagram
4.3施肥控制器
施肥控制器主要任务是采集当前排肥驱动电机转速并将数据上报给车载控制终端,接收车载控制终端发送的电机目标转速,并驱动电机达到目标转速。施肥控制器采用型号为AQMD2410NS的直流有刷电机驱动器,设置为自测速闭环控制,电机转速用驱动器内部集成的PID调节方式实现稳速,其中比例系数Kp值为0.2,积分时间常数Ti值为0.15,微分时间常数Td值为0.15,采样节拍周期Td为1 ms。
本施肥装置共6行,插秧机幅宽为1.8 m,肥盒每转排肥量为20 g,目标施肥量、机具行驶速度、排肥驱动电机转速之间具有如下关系

式中n1为排肥驱动电机转速,r/min;t为时间,s;S为作业面积,hm2;l为机具行驶路程,m;v为行驶速度,m/s;G为目标施肥量,kg/hm2。
5 机具性能试验与分析
参照GB/T 20346.1-2006《施肥机械试验方法》第1部分全幅宽施肥机及NY/T 1003-2006《施肥机械质量评价技术规范》对风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置进行了台架及田间试验。
5.1台架试验
在北京市昌平区小汤山国家精准农业示范基地对电机在不同转速下对各行排肥量一致性进行测定。试验时,肥料容积超过肥箱容积的二分之一,测定行数为6行,由于水田侧深施肥量小,寒地水稻侧深施肥量在300 kg/hm2左右[2-3],正常稳定施肥作业时,排肥驱动电机转速为20~30 r/min,本试验所设置排肥驱动电机转速分别为10、20、30、40 r/min,测定时间为5 min,每个排肥器在每个转速下重复试验5次,试验完成后,将6个排肥口的肥料分别收集编号,用精度为0.001 g的电子天平进行称量并记录。将20组试验结果进行汇总统计,统计结果如表2所示,并按式(5)计算各行排量一致性的标准差和变异系数。
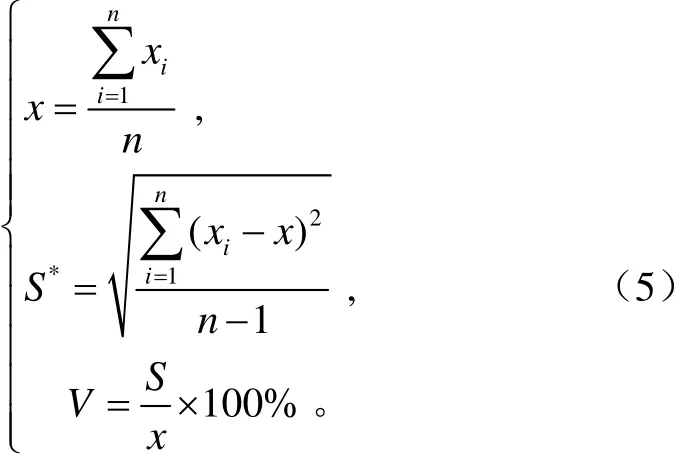
式中xi为每行各次平均排肥量,g;x为每行各次平均排量的平均值,g;S*为各行排量一致性的标准差,g;V为各行排量一致性的变异系数,%;n为测定行数(排肥口个数)。在式(5)中,当n<30时,分母取(n-1),当n≥30时,分母取n。
从表2中可以看出,相同转速下,各行之间排肥量变异系数小,一致性好,排肥量比较恒定,随着转速的提高平均排肥量基本呈线性增加,不同转速下,肥盒每转排肥量比较稳定,随转速的提高,每转排肥量有减小的趋势。

表2 各行排肥量一致性测定统计结果Table 2 Statistical results of each row fertilizer quantity consistency determination
5.2田间试验
5.2.1试验设计
为检验设备的实际作业性能,2015年5月中旬在黑龙江七星农场建三江北大荒精准农业农机中心试验田进行试验,并对施肥装置进行了施肥均匀性试验,施肥总面积为6 666.7 m2,试验所用肥料为云南天化国际化工有限公司生产的复合肥料,所用车载平台为洋马VP6乘坐式水稻插秧机。田间试验如图10所示。

图10 插秧机与施肥装置配合使用进行田间试验Fig.10 Field experiment of using rice transplanter and fertilizing device
试验时将施肥区域分为10个46.3 m×14.4 m的小施肥区,在长度方向上每隔14.4 m(8倍幅宽)树立一个标记杆,每个小施肥区可进行4次往复施肥作业。
5.2.2施肥均匀性测定
施肥试验时,插秧机稳定行驶速度为1 m/s,预置施肥量为300 kg/hm2,插秧机在施肥小区域往复施肥4次进行1次肥料称质量并计算当前施肥区施肥量,统计结果如表3所示,并按式(6)进行施肥量偏差计算。

式中γs为施肥量偏差,%;Wq为试验前肥箱内化肥质量,kg;Wh为试验后肥箱内剩余的化肥质量,kg;S为施肥作业面积,m2;F为预置施肥量,kg/hm2。
从表3可以看到,施肥装置施肥量总体比较稳定,当预置施肥量为300 kg/hm2时,车辆行驶速度为1 m/s时,施肥量偏差控制在5.82%以内。
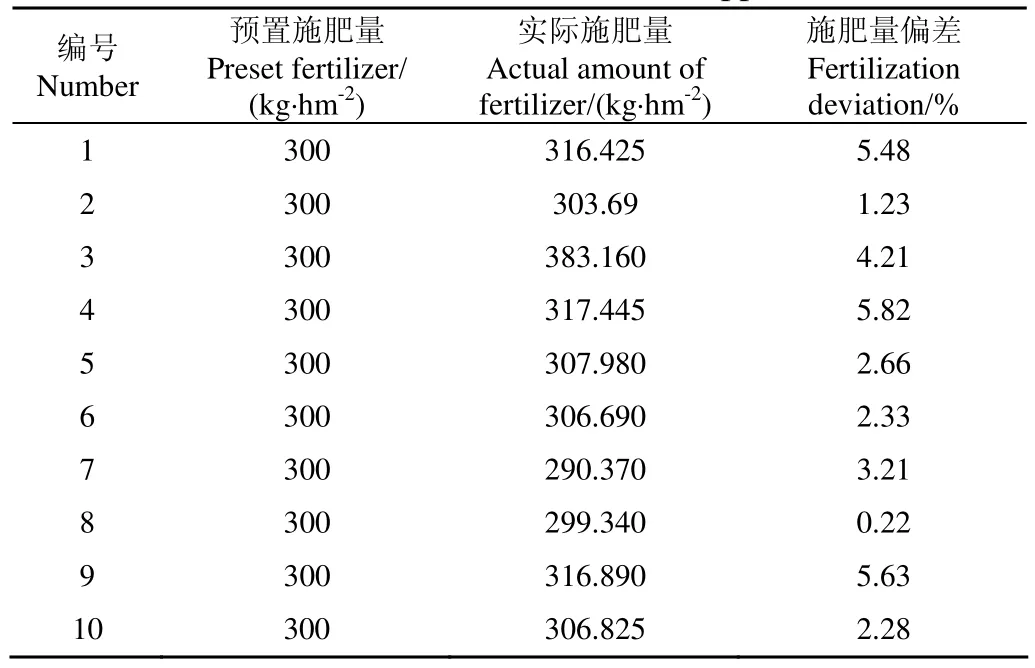
表3 田间施肥统计结果Table 3 Statistical results of field application
6 结 论
1)针对寒地水稻侧深施肥生产需要,设计了风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置,并开发了一套适合该装置的精准施肥作业控制系统。该装置与插秧机配套使用时,在设定目标施肥量的情况下,能够根据插秧机行驶速度实时调整施肥量,能实现连续带状侧深精准施肥作业,提高施肥均匀性和肥料利用率。
2)田间作业试验表明,施肥装置能稳定完成施肥作业,当车体行进速度为1 m/s,预置施肥量为300 kg/hm2时,目标施肥量与实际施肥量相对误差控制在5.82%以内,施肥作业精度达到了设计目标。下一步需要进行更多的田间试验,进一步测试系统的稳定性和可靠性。
[参考文献]
[1] 曾希柏,李菊梅. 中国不同地区化肥施用及其对粮食生产的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2004,37(3):387-392. Zeng Xibai, Li Jumei. Fertilizer application and its effect on grain production in different counties of China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2004, 37(3): 387-392. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 夏艳涛,吴亚晶. 寒地水稻侧深施肥技术研究[J]. 北方水稻,2014(1):30-32. Xia Yantao, Wu Yajing. Study on side deep fertilizing of rice in cold area[J]. North Rice, 2014(1): 30-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 白雪,郑桂萍,王宏宇,等. 寒地水稻侧深施肥效果的研究[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2014(6):40-43. Bai Xue, Zheng Guiping, Wang Hongyu, et al. Research on the effect of side and deep fertilizing for rice in cold reign[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2014(6): 40-43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] Miyoko W,Tomoko Y,Kazuyoshi S, et al. Distribution of anammox bacteria in a free-water-surface constructed wetland with wild rice (Zizania latifolia)[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 81: 165-172.
[5] Sheng Z,Sho S,Shohei R, et al. Effect of infiltration rate on nitrogen dynamics in paddy soil after high-load nitrogen application containing 15N tracer[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2011, 37(5): 685-692.
[6] Kaoru A,Yasuo O. Wastewater treatment by using kenaf in paddy soil and effect of dissolved oxygen concentration on efficiency[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2007, 29(2): 125-132.
[7] 中村奈,中川善清,清水孝式. 施肥机[P]. 中国专利:103583126, 2014-02-19.
[8] 大前健介,椿本彰史. 施肥装置[P]. 中国专利:103858576,2014-06-18.
[9] 位国建,荐世春,姜伟,等. 1GF-200旋耕施肥机的设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2014(9):190-192. Wei Guojian, Jian Shichun, Jiang Wei, et al. Design and experiment of 1GF-200 rotary tiller with fertilizing[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014(9): 190-192. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 位国建,荐世春,付乾坤,等. 水稻插秧施肥联合作业机的设计[J]. 农机化研究,2015(11):104-107,112. Wei Guojian, Jian Shichun, Fu Qiankun, et al. The design of rotary transplanting with fertilizing combine machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015(11): 104-107, 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 朱松,张瑞宏,张剑峰,等. 水田旋耕施肥复式作业机设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2015(7):147-150. Zhu Song, Zhang Ruihong, Zhang Jianfeng, et al. Design and test of teamwork machine rototilling and fertilizing in paddy field[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015(7): 147-150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 陈长海,许春林,毕春辉,等. 水稻插秧机侧深施肥技术及装置的研究[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报,2012,24(6):10-12,25. Chen Changhai, Xu Chunlin, Bi Chunhui, et al. Researching of rice transplanter deep side fertilizing technology and device[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2012, 24(6): 10-12, 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 陈雄飞,罗锡文,王在满,等. 水稻穴播同步侧位深施肥技术试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(16):1-7. Chen Xiongfei, Luo Xiwen, Wang Zaiman, et al. Experiment of synchronous side deep fertilizing technique with rice hill-drop drilling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(16): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 曾山,汤海涛,罗锡文,等. 同步开沟起垄施肥水稻精量旱穴直播机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(20):12-19. Zeng Shan, Tang Haitao, Luo Xiwen, et al. Design and experiment of precision rice hill-drop drilling machine for dry land with synchronous fertilizing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(20): 12-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 赵军,于洁,王熙,等. 机械驱动式精密变量施肥播种机的研制[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报,2006,18(2):49-52. Zhao Jun, Yu Jie, Wang Xi, et al. Research on a combined seed and fertilizer drill of precision variable rate control drived by engine[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang August First Land Reclamation University, 2006, 18(2): 49-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 张书慧,马成林,杜巧玲,等. 精确农业自动变量施肥机控制系统设计与实现[J]. 农业工程学报,2004,20(1):113-116. Zhang Shuhui, Ma Chenglin, Du Qiaoling, et al. Design of control system of variable rate f ertilizer applicator in precision agriculture[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2004, 20(1): 113-116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张书慧,马成林,吴才聪,等. 一种精确农业自动变量施肥技术及其实施[J]. 农业工程学报,2003,19(1):129-131. Zhang Shuhui, Ma Chenglin, Wu Caicong, et al. Development and application of a variable rate f ertilizer applicator for precision agriculture[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2003, 19(1): 129-131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 王秀,赵春江,孟志军,等. 精准变量施肥机的研制与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2004,20(5):114-117. Wang Xiu, Zhao Chunjiang, Meng Zhijun, et al. Design and experiment of variable rate fertilizer applicator[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2004, 20(5): 114-117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 耿向宇,李彦明,苗玉彬,等. 基于GPRS的变量施肥机系统研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2007,23(11):164-167. Geng Xiangyu, Li Yanming, Miao Yubin, et al. Development of variable rate fertilizer applicator based on GPRS[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2007, 23(11): 164-167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王太柱. 气流输送装置设计计算[J]. 农业机械,2008(22):64-65. Wang Taizhu. Design and calculation of air transport device[J]. Chinese Agricutural Mechanization, Agricultural Machinery, 2008(22): 64-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王太柱. 气流输送机构的参数确定[J]. 中国农机化,2008(4):74-78. Wang Taizhu. The confirming of the argument on air flow transportation mechanism[J]. Chinese Agricutural Mechanization, 2008(4): 74-78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李加念,洪添胜,冯瑞珏,等. 基于脉宽调制的文丘里变量施肥装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(8):105-110. Li Jianian, Hong Tiansheng, Feng Ruijue, et al. Design and experiment of venturi variable fertilizer apparatus based on pulse width modulation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(8): 105-110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王淼,黄兴法,李光永. 文丘里施肥器性能数值模拟研究[J].农业工程学报,2006,22(7):27-31. Wang Miao, Huang Xingfa, Li Guangyong. Numerical simulation of characteristics of venturi injector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2006, 22(7): 27-31. ( in Chinese with English abstract )
[24] 韩启彪,黄兴法,刘洪禄,等. 6种文丘里施肥器吸肥性能比较分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(4):113-117,136. Han Qibiao, Huang Xingfa, Liu Honglu, et al. Comparative analysis on fertilization performance of six venturi injectors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(4): 113-117, 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 马征,李耀明,徐立章. 农业工程领域颗粒运动研究综述[J].农业机械学报,2013,44(2):22-29. Ma Zheng, Li Yaoming, Xu Lizhang. Summarize of particle movements research in agricultural engineering realm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(2): 22-29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 胡克吉. 气力输送系统文丘里供料器的研究[D]. 青岛:青岛科技大学,2013. Hu Keji. The Research on Venturi Feeder in Pneumatic Conceying System[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science & Technology, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 佟飞虎. 文丘里管、文丘里喷嘴流量计的参数化设计[D].沈阳:东北大学,2007. Tong Feihu.The Parametric Design of Venturi Tube and Venturi Nozzle Flowmeter[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 刘剀,陆海峰,郭晓镭,等. 文丘里管结构对高浓度煤粉流动特征及压差特性的影响[J]. 化工学报,2015(5):1656-1666. Liu Kai, Lu Haifeng, Guo Xiaolei, et al. Influence of venturi structures on flow characteristic and pressure drop of gas-coal mixture[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2015(5): 1656-1666. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 于英杰,张书慧,齐江涛,等. 基于传感器的变量施肥机定位方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2009,40(10):165-168. Yu Yingjie, Zhang Shuhui, Qi Jiangtao, et al.Positioning method of variable rate fertilizer applicator based on sensors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2009, 40(10): 165-168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 孟志军,赵春江,刘卉,等. 基于处方图的变量施肥作业系统设计与实现[J]. 江苏大学学报:自然科学版,2009,30(4):338-342. Meng Zhijun, Zhao Chunjiang, Liu Hui, et al. Development and performance assessment of map-based variable rate granule application system[J].Journal of Jiangsu University: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 30(4): 338-342. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 陈立平,黄文倩,孟志军,等. 基于CAN总线的变量施肥控制器设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2008,39(8):101-104,185. Chen Liping, Huang Wenqian, Meng Zhijun, et al. Design of variable rate fertilization controller based on CAN bus[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2008, 29(8): 101-104, 185. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Design and experiment on air-blast rice side deep precision fertilization device
Zuo Xingjian1,2,3,4, Wu Guangwei2,3,4, Fu Weiqiang2,3,4, Li Liwei2,3,4, Wei Xueli2,3,4, Zhao Chunjiang1,3※
(1. College of Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Northwest A&F University, Yangling 712100, China; 2. National Research Center of Intelligent Equipment for Agriculture, Beijing 100097, China; 3. Key Laboratory of Agri-informatics, Ministry of Agriculture, Beijing 100097, China; 4. Beijing Key Laboratory of Intelligent Equipment Technology for Agriculture, Beijing 100097, China)
Abstract:Rice is the most important crop in China, which has the largest plant area, the highest per unit area yield and the most total output. Fertilization is an important process of rice production, which directly affects the yield of crops, and reasonable and effective use of chemical fertilizer can improve the yield of crops. At present, the mechanization level of rice fertilization is very low in China, and the artificial fertilization with a large amount of fertilizer causes the uneven distribution of fertilizer. The side deep fertilization for rice is an ideal way of fertilization. The fertilization device will apply fertilizer (basal and tiller fertilizer) quantitatively and with one-time positioning based on the agronomic requirements, and it can carry out a uniform fertilization to the rice’s side position with a certain depth, which can reduce nitrogen fertilizer amount of 20%-30% compared with the traditional fertilization operation. It is a cultivation technique with high output, stable yield and low cost. In view of the low-level mechanization of rice fertilization in China, the large amount of fertilizer application and the low fertilizer utilization in the traditional manual fertilization, combined with the agronomic characteristics of side deep fertilization, we analyzed the fertilization method of wind delivering and developed the air-blast rice side deep precision fertilization device. This device adopted the modularization design and was combined with riding type rice transplanter for use. In the process of operation, the fertilizer granules fell into the deep trench with a certain amount under the effect of gravity and wind; the trench with 5 cm depth was dug by fertilizer exports at the position 3 cm away from seedling side, and the fertilizers would be covered in the mud by covering plate. The device used the rated voltage of 12 V and the power of 72 W; the blower was used to transport fertilizer based on the Venturi effect, and the inner diameter of fertilizer conveying pipe was 25 mm and the velocity was 21 m/s; the global position system (GPS) was used to measure transplanter speed. The speed of the vehicle was proportional to the speed of the motor by using the precision fertilization control method, which could match the vehicle speed and drive motor speed in real time. The speed measurement closed-loop control was used as the control system. Motor drive used the AQMD2410NS direct current motor drive, and motor hold a stable speed by using the internal drive integration of the proportion-integration-differentiation (PID). The vehicle control terminal was designed under the embedded Visual C++ integrated development environment in the XP Windows operating system, the interface could display the current operating data, and meanwhile, the user could set the working parameters according to the actual operating requirements. When presetting fertilization amount to 300 kg/hm2, the motor rotation speed was 10, 20, 30 and 40 r/min, respectively. The fertilizer difference test with 6 fertilizer discharging ports was carried out, and the coefficients of variation of fertilizer application amount were 2.3%, 2.1%, 2.2% and 1.8%, respectively. The experiments were conducted on Heilongjiang Seven-star Farm, and the result showed, planting and fertilization could be done completely and independently in one time when fertilization device and riding type rice transplanter operated. When the preset rate of fertilization was 300 kg/hm2and the vehicle speed was 1 m/s, the fertilization device could realize the precision fertilization, and the deviation of fertilization application amount was within 5.82%, which could meet the requirement of the actual production. The research provides reference for the development of the rice variable fertilization control technology and the research and development of the rice side deep fertilization device.
Keywords:agricultural machinery; design; crops; air-assisted; precision fertilization; side deep fertilization
通信作者:※赵春江,男(汉族),河北定州,研究员,博士,博士生导师,主要从事农业信息化、精准农业技术的研究.。杨凌 西北农林科技大学机械与电子工程学院,712100。Email:zhaocj@nercita.org.cn
作者简介:左兴健,男(汉族),四川绵阳,主要从事精准农业智能装备技术研究。杨凌 西北农林科技大学机械与电子工程学院,712100。
基金项目:863计划粮食作物规模化生产精准作业技术与装备(2012AA101901)
收稿日期:2015-08-15
修订日期:2015-12-12
中图分类号:S224.21
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1002-6819(2016)-03-0014-08
doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.03.003
