纳米制冷剂对换热和压缩机性能影响研究进展
2015-12-28陈梦寻张华娄江峰
陈梦寻,张华,娄江峰
(1上海理工大学能源与动力工程学院,上海 200093;2浙江盾安人工环境设备股份有限公司,浙江 诸暨 311835)
纳米制冷剂对换热和压缩机性能影响研究进展
陈梦寻1,张华1,娄江峰2
(1上海理工大学能源与动力工程学院,上海 200093;2浙江盾安人工环境设备股份有限公司,浙江 诸暨 311835)
纳米技术在制冷设备中的应用是目前制冷领域的创新性研究之一。本文综述了纳米技术在制冷领域的最新研究成果,在节能环保的背景下总结了纳米材料应用于制冷系统中的优势,简单介绍了近几年常用的制备方法,列举了不同的纳米制冷剂对换热效果的影响,阐述了纳米颗粒在减小压缩机摩擦、提高压缩机性能方面的作用。提出如何制备具有长期稳定性的纳米制冷剂、建立纳米制冷剂流动沸腾换热和压降特性模型、确保纳米粒子可以在制冷系统各部件中运行稳定无沉淀是未来纳米技术在制冷领域研究的关键问题。
纳米制冷剂;热导率;沸腾换热;压缩机
中国制冷空调行业 2013年累计实现工业总产值超过5600亿元[1],制冷设备投入使用产生了巨大的能耗,节能环保的呼声迫使研究者们积极探索制冷及相关领域的节能方法。目前,提高制冷设备能效的主要途径集中在提高压缩机的运行效率和减小换热器的传热温差两个方面。自Choi[2]首次提出纳米流体以来,研究者们对纳米流体在不同基液中的制备、物性特征和应用展开研究,实验结果显示,将金属氧化物、碳纳米管或纯金属等纳米颗粒(如Ag、ZnO、AlN、CNT等)放入基液中,流体的热导率和传热系数明显提高[3-6]。在这样的背景下,纳米制冷剂的概念被提出。纳米制冷剂是指将纳米颗粒添加到制冷剂中得到的稳定悬浮液,可应用于制冷、空调和热泵系统中,其作用的效果主要体现在换热与摩擦两个方面。研究表明,在制冷剂中加入纳米颗粒可增强换热性能、加强压缩机润滑效果、提高制冷系统的COP、降低能源消耗[7]。Saidur等[8]将质量分数0.1%TiO2/矿物油与R134a混合,系统能耗降低26.1%。Venkataramana等[9]将0.1g/L TiO2/矿物油分别与制冷剂R134a、R436a、R436b混合,发现在蒸气压缩制冷系统中可以平稳运行,且降低了系统的不可逆性。相较于改变制冷设备基本部件和工质,通过添加一定量纳米材料实现制冷系统能效和可靠性的提高,是更为节能高效的创新思路,目前该研究处于起步阶段,有待进一步探索。
1 纳米制冷剂的制备
制备出稳定的纳米流体是纳米流体研究和应用的前提。纳米粒子在液相介质中受到的作用力主要是范德华力和静电力,纳米粒子分散相的高表面能和布朗运动使纳米流体的主要不稳定性表现为团聚和沉淀[10]。为提高纳米粒子的分散稳定性,研究者们多用超声振荡和添加分散剂的方法制备纳米制冷剂/纳米冷冻机油。分散剂与纳米粒子表面发生反应形成络合物,从而有效改善纳米粒子的界面性质,使其具有亲油性或者亲水性。表1列出了一些研究人员在制备油基纳米流体使所用到的分散剂。由表1可知,使纳米粒子在油基溶液中分散稳定性良好的分散剂主要有油酸、失水山梨醇的脂肪酸酯(Span和Tween)、硅烷偶联剂(KH570)和辛基硅烷等。
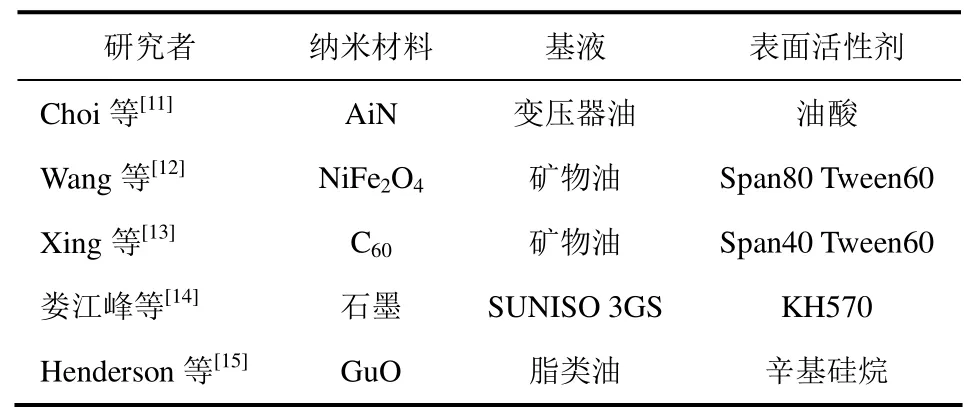
表1 纳米流体研究中常用表面活性剂汇总
Xing等[13]在研究富勒烯C60纳米油对冰箱压缩机性能的影响实验中,先制备C60纳米油,用分散剂span-40和tween-60对C60纳米颗粒表面改性,添加到矿物油SUNISO 3GS中超声60min,表征稳定后再添加到R114制冷系统中测试。娄江峰等[16]在探究纳米石墨冷冻油对R600a冰箱性能影响的实验中,制备纳米石墨冷冻机油是先用硅烷偶联剂KH570在无水乙醇中修饰纳米石墨,再加入冷冻机油SUNISO 3GS中,超声分散2h,并在100MPa下高压均质,由此制得的纳米石墨冷冻机油静置 30天无明显沉淀,表征稳定后再注入制冷系统中与制冷剂R600a混合。
尽管在纳米流体里加入分散剂能提高纳米流体的分散稳定性,但Liu等[17]、Heris等[18]、Trisaksri等[19]在研究中均没有用到分散剂。Peng等[20]认为分散剂在沸腾换热过程中可能会导致吸附和凝聚,影响传热特性。Peng等[20]制备了R113纳米制冷剂,先按质量比例将Cu纳米粒子与VG68混合,直接加入制冷剂R113中,超声分散1h后观察发现,由此制备的纳米制冷剂在12h内无凝聚沉降,而实验过程不到4h,可以保证实验过程中纳米制冷剂的一致性。
研究已制备的纳米材料/制冷剂配对有 TiO2/ R141b[19]、CNTS/R113[21]、Cu/R113[22-23]、TiO2/ R600a[24]、Al2O3/R141b[25]等。制备纳米制冷剂,超声分散是必不可少的环节,超声时间大多为1~2h,但研究者们在是否应适当添加分散剂上观点不统一,仍需进一步探究;已有的研究成果在纳米制冷剂制备方面涉及的制冷剂种类较少,有待完善。
2 纳米制冷剂的换热性能
2.1 热导率
在制冷和空调领域的应用中,纳米流体的热导率是影响换热效果非常重要的因素。当制冷系统运行时,纳米冷冻机油会随着制冷剂一起循环并一直处于液相,热导率是分析对制冷系统各部件传热性能影响的基础参数,因此有必要开展纳米冷冻机油的热导率研究。
Mahbubul等[26-27]研究Al2O3/R141b和Al2O3/R-134a纳米制冷剂热导率,发现纳米制冷剂的热导率随温度的升高而增大,随纳米颗粒体积分数的增加而增大,随纳米颗粒粒径的增大而减小。其中,纳米颗粒体积分数对热导率的影响更大。Corcione[28]为验证纳米制冷剂的热导率,开发了经验关联式。Sitprasert等[29]根据纳米颗粒体积分数、纳米颗粒大小和随温度而变化的边界层的影响提出热导率模型,确定纳米制冷剂Al2O3/R-134a的热导率。
Jiang等[30]在深入探究CNT纳米制冷剂热导率的影响因素时发现,CNT纳米制冷剂热导率随CNT体积分数的增大而增大,且在同一浓度下,CNT纳米颗粒的直径越小、长宽比越大,热导率越大。实验结果如图1所示。
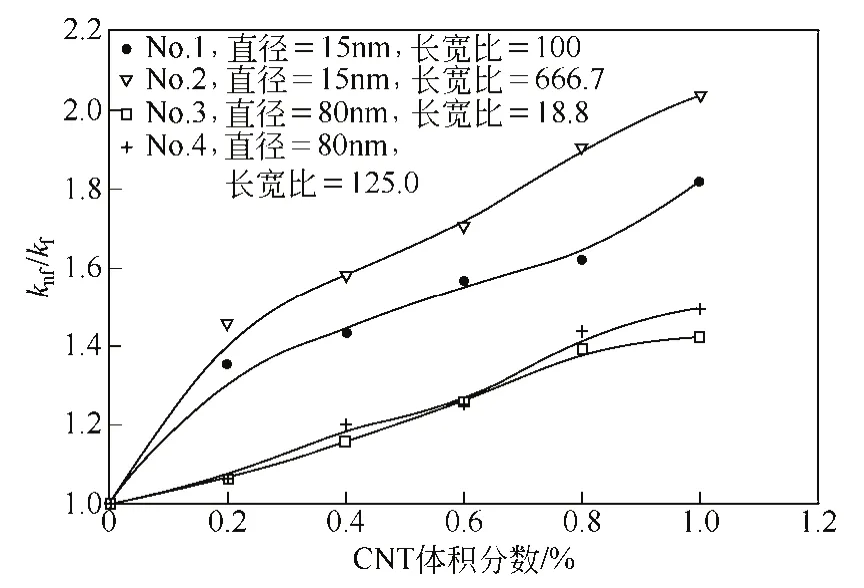
图1 4种CNT在不同体积分数下CNT-R113的热导率[30]
目前关于纳米冷冻机油热导率的研究成果只局限于几种纳米材料,未来应拓展研究可用于制冷领域的多种纳米材料,发现在确保定性的基础上可制备出具有最佳粒径、最佳浓度的纳米制冷剂/纳米冷冻机油。
2.2 沸腾换热
纳米流体作为一种新型的换热介质,其沸腾换热特性一直是纳米流体研究的热点。在制冷领域,国内外学者已经展开了关于纳米粒子对制冷剂及含油制冷剂沸腾换热性能影响的实验研究,主要集中在对高温纳米制冷剂(R113、R123、R141b、R134a)及其含油混合物的池沸腾换热和流动沸腾换热特性方面,如表2、表3所示。
由于目前的研究成果有限,不同的研究者以不同的制冷剂为基液,对混合流体的沸腾换热研究成果尚有矛盾的地方。大部分研究者发现,纳米粒子的添加有利于强化制冷剂/含油制冷剂的沸腾换热特性,同时也有少量实验结果表明,特定的纳米粒子会恶化池沸腾换热。
由表2、表3可知,目前关于纳米制冷剂的研究大多集中在非常用制冷剂上,而将纳米粒子添加到常用制冷剂R410A、R32(空调)与R600a(冰箱),或者含油制冷剂中的研究则还处于初步阶段,更未见定量的预测模型报道,需要进行深入、系统的实验研究。有关含纳米冷冻机油/制冷剂管内流动沸腾换热特性的关联式也未见报道。物性(密度、黏度、表面张力、比热容)对沸腾换热的特性有重要的影响,而目前对物性方面准确的研究成果比较缺乏,限制了该领域的研究。
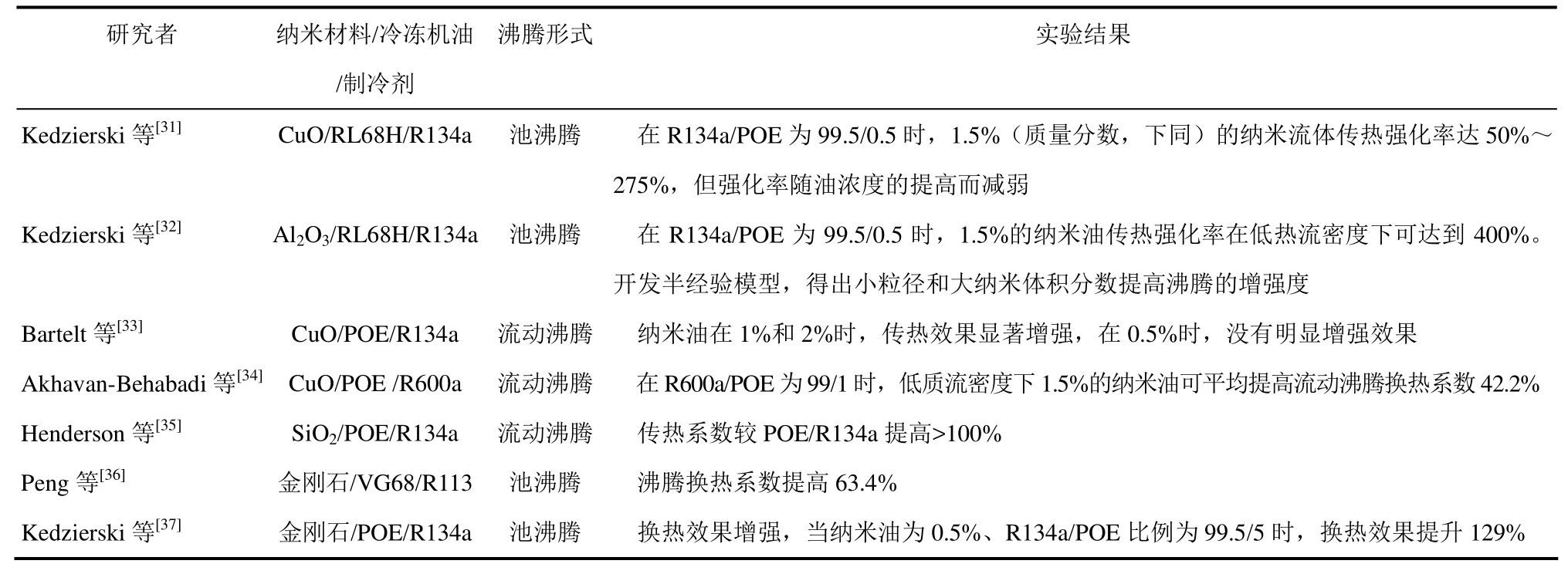
表2 纳米粒子/冷冻机油/制冷剂混合物沸腾换热的研究现状
3 纳米制冷剂对压缩机的性能改善
一般来说,润滑剂的黏度降低,摩擦系数降低,但由于润滑剂的承载力下降,磨损率随之增加。研究结果表明,添加了纳米粒子的润滑油可有效降低摩擦系数和磨损率,提升压缩机的运行效率和可靠性。
Lee等[47-48]、Xing等[13]在探究纳米冷冻机油对压缩机性能的影响时都选用富勒烯C60纳米材料。Lee等[47]探究添加了富勒烯纳米油的制冷剂在滑动推力轴承的滚动压缩机中的耐磨特性。在滑动推力轴承中,当轨道板速度在300r/min和3000r/min之间时,纳米油的摩擦系数比纯油小。推测可能是因为富勒烯纳米颗粒嵌入摩擦表面之间改善了润滑性能,同时也能防止转子间金属表面直接接触引起的磨损。Lee等[48]发现将富勒烯纳米粒子与矿物油混合,可以在冰箱压缩机中稳定运行,且当纳米粒子浓度为0.1%(体积分数)时,润滑效果最好,摩擦系数降低90%。Xing等[13]将富勒烯纳米粒子添加到矿物油SUNISO 3GS中,与制冷剂R600a混合,研究对冰箱压缩机性能的影响,发现随着纳米颗粒浓度的增加明显下降,纳米油的摩擦系数下降,且在低负载时下降更明显,压缩机机壳表面温度也随之降低,润滑效果很好,提高了冰箱压缩机的性能。
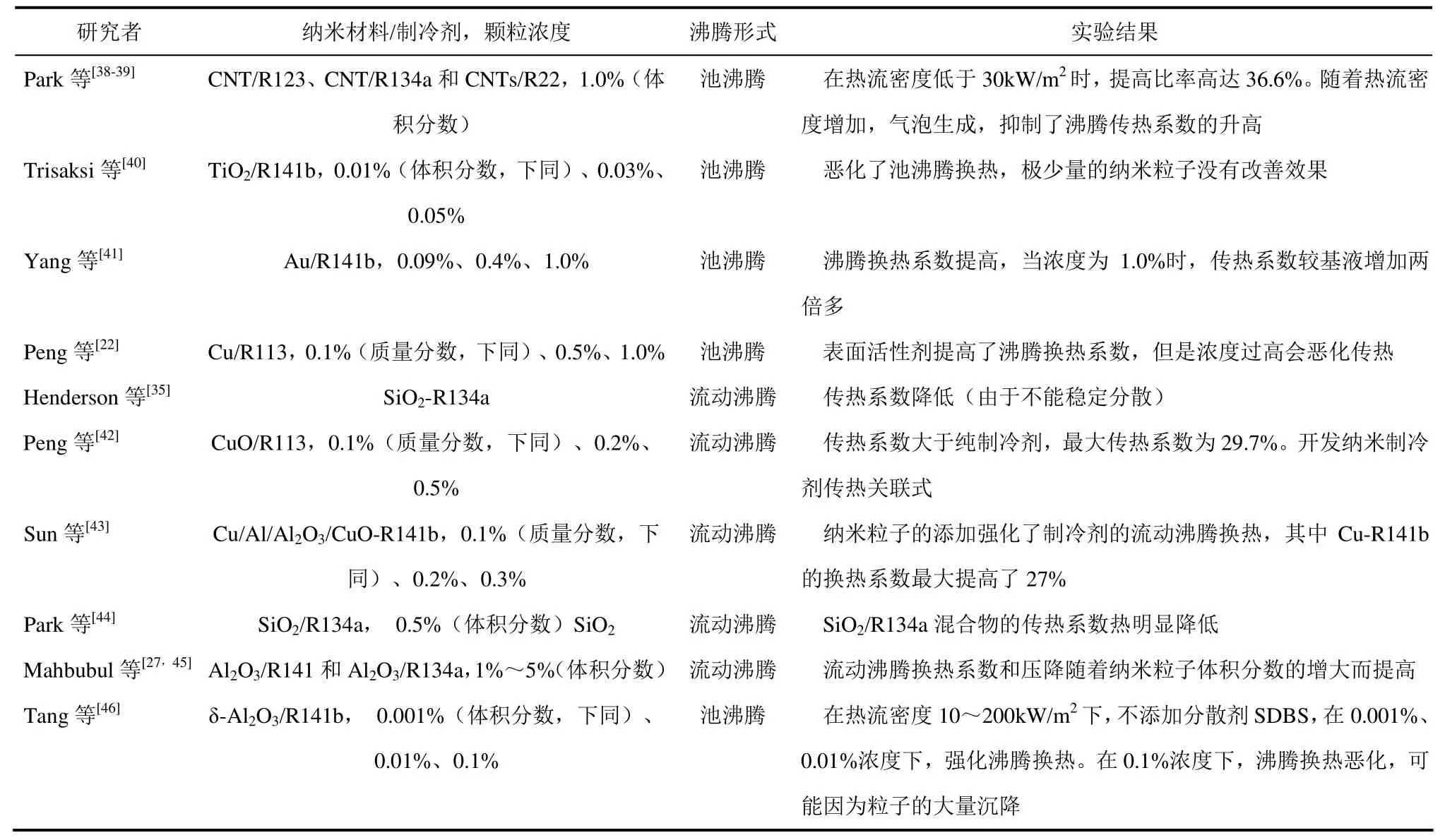
表3 纳米粒子/制冷剂混合物沸腾换热的研究现状
此外,Fe3O4[49]、TiO2[50]、石墨[16]等纳米材料制备的纳米冷冻机油对压缩机性能的改善效果也值得关注。Fu等[49]将Fe3O4纳米粒子添加到矿物油中,以HFC134a/HC600a为制冷剂,测试冰箱的性能,实验数据显示,压缩机机壳的温度每升高2.2℃,吸气温度略有改变,排气温度下降3.5℃,蒸发器平均温度下降0.3℃,冷却时间减少了148s。Bi等[50]发现HFC134a/矿物油/TiO2纳米流体在家用冰箱的工作中可平稳有效运行。当TiO2质量分数为0.1%时,能量消耗较HFC134a/POE节省26.1%。纳米颗粒提高了矿物油在HFC134a中的溶解度,增大了压缩机的回油率。娄江峰等[16]在探究纳米石墨冷冻油对冰箱性能影响的实验中发现,采用0.1%纳米石墨冷冻油时平均耗电量降低4.55%,压缩机的排气和吸气压力均随着纳米冷冻油浓度的提高而降低,且排气压力的降低幅度更大。
已有研究成果表明,纳米粒子的添加可以改善矿物油的性能,加强压缩机的冷却效果,降低压缩机的进、排气压力,降低摩擦系数和制冷系统(冰箱)的能量消耗。纳米制冷剂具有提高压缩机运行可靠性以及减小运行能耗的潜力。
4 结 语
目前,纳米技术在制冷领域的应用研究已经有了具备指导性意义的成果:纳米颗粒的添加有利于强化制冷剂/含油制冷剂的沸腾换热特性,将纳米冷冻机油应用于制冷系统可有效降低摩擦系数和磨损率,提升压缩机的性能,提高整个制冷系统的COP,但该研究仍处于起步阶段,未来还应在以下几方面探索。
(1)纳米制冷剂的制备通常只是保证了纳米制冷剂在实验过程中若干小时的稳定性,若投入商业使用,稳定性是需要长期保证的。如何制备长期稳定的纳米制冷剂,同时探索其他性能优异的纳米材料(如石墨烯和金属纳米线等)和其他类矿物油、POE油和PAG油等,是纳米技术在制冷领域应用中需要解决的研究难点。
(2)纳米冷冻机油和制冷剂混合物的相变过程非常复杂,需要拓宽实验工况范围,如纳米粒子的浓度、纳米冷冻机油的含量、质量流量、热流密度和实验管径等,在积累更多高精度的实验数据的基础上,结合混合物的管内流型和气泡的生长规律,建立可准确预测含纳米油制冷剂流动沸腾换热和压降特性参数的模型,为采用纳米冷冻机油的制冷系统开发设计提供必要的理论基础。
(3)为保证采用纳米冷冻机油的制冷设备长期稳定运行,需要考察纳米冷冻机油在压缩机内摩擦以及随制冷剂循环流动时的稳定性,测试纳米粒子在制冷系统各部件中的残留情况,研究纳米粒子随冷冻机油的输运特性,进而优化制冷设备的设计,以确保纳米粒子不会沉积在毛细管或其他部件中。
[1]张朝晖,陈敬良,刘晓红,等.中国制冷空调工业协会再谈中国制冷空调行业的转型升级发展[J].制冷与空调,2014,14(1):1-5.
[2]Choi S U S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles,developments and applications of non newton flows[J]. Applied A:Materials Science&Processing,1995,66:99-105.
[3]Pankaj Sharma,Il-Hyun Baek,Taehyun Cho,et al. Enhancement of thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol based silver nanofluids[J]. Powder Technology,2011,208(1):7-19.
[4]Yu Wei,Xie Huaqing,Chen Lifei,et al. Investigation of thermal conductivity and viscosity of ethylene glycol based ZnO nanofluid[J]. Thermochimica Acta,2009,491(1-2):92-96.
[5]Yu Wei,Xie Huaqing,Li Yang,et al. Experimental investigation on thermal conductivity and viscosity of aluminum nitride nanofluid[J]. Particuology,2011,9:187-191.
[6]Meng Zhaoguo,Wu Daxiong,Wang Liangang,et al. Carbon nanotube glycol nanofluids:Photo-thermal properties,thermal conductivities and rheological behavior[J]. Particuology,2012,10:614-618.
[7]Ali Celen,Alican Çebi,Melih Aktas,et al. A review of nanorefrigerants: Flow characteristics and applications[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration,2014,44:125-140.
[8]Saidur R,Kazi S N,Hossain M S,et al. A review on the performance of nanoparticles suspended with refrigerants and lubricating oils in refrigeration systems[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2011,15(1):310-323.
[9]Venkataramana Murthy,Padmanabhan V,Senthilkumar Palanisamy. The use of TiO2nanoparticles to reduce refrigerator irreversibility[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2012,59:122-132.
[10]Zoubida Haddad,Cherifa Abid,Hankan F Oztop,et al. A review on how the researchers prepare their nanofluids[J]. International Journal of Thermo Science,2014,76(1):168-189.
[11]Choi C,Yoo H S,Oh J M. Preparation and heat transfer properties of nanoparticle-in-transformer oil dispersions as advanced energy-efficient coolants[J]. Current Applied Physics,2008,8(6):710-712.
[12]Wang Ruixiang,Wu Qingping,Wu Yezheng. Use of nanoparticles to make mineral oil lubricants feasible for use in a residential air conditioner employing hydro-fluorocarbons refrigerants[J]. Energy and Buildings,2010,42(11):2111-2117.
[13]Xing Meibo,Wang Ruixiang,Yu Jianlin. Application of fullerene C60 nano-oil for performance enhancement of domestic refrigerator compressors[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration,2014,40:398-403.
[14]娄江峰,张华,王瑞祥,等.颗粒形态和浓度对纳米石墨冷冻机油密度和黏度的影响[J].化工学报,2014,65(10):3846-3851.
[15]Henderson Kristen,Young-Gil Park,Liu Liping,et al. Flow-boiling heat transfer of R134a-based nanofluids in a horizontal tube[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2010,53(5-6):944-951.
[16]娄江峰 ,张华 ,王瑞祥.纳米石墨冷冻油对 R600a冰箱的性能影响[J].化工学报,2014,65(2):516-521.
[17]Liu Z H,Xiong J G,Bao R. Boiling heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids in a flat heat pipe evaporator with micro-grooved heating surface[J]. Int. J. Multiphase Flow,2007,33:1284-1295.
[18]Heris S Zeinali,Esfahany M Nasr,Etemad S G. Experimental investigation of convective heat transfer of Al2O3/water nanofluid in circular tube[J]. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow,2007,28(2):203-210.
[19]Trisaksri Visinee,Wongwises Somchai. Nucleate pool boiling heat transfer of TiO2-R141b nanofluids[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2009,52(5-6):1582-1588.
[20]Peng Hao,Ding Guoliang,Jiang Weiting,et al. Heat transfer characteristics of refrigerant-based nanofluid flow boiling inside a horizontal smooth tube[J]. Int. J. Refrig.,2009,32(6):1259-1270.
[21]Peng H,Ding G.,Hu H,et al. Influence of carbon nanotubes on nucleate pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of refrigerant-oil mixture[J]. Int. J. Thermal Sci.,2010,49:2428-2438.
[22]Peng Hao,Ding Guoliang,Hu Haitao,et al. Effect of nanoparticle size on nucleate pool boiling heat transfer of refrigerant/oil mixture with nanoparticles[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2009,54(6):1839-1850.
[23]Peng H,Ding G.,Hu H. Effect of surfactant additives on nucleate pool boiling heat transfer of refrigerant-based nanofluid[J]. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci.,2011,35:960-970.
[24]Bi Shengshan,Guo Kai,Liu Zhigang,et al. Performance of a domestic refrigerator using TiO2-R600a nano-refrigerant as working fluid[J]. Energy Convers. Manage,2011,52(1):733-737.
[25]Mahbubul I M,Saidur R,Amalina M A. Thermal conductivity,viscosity and density of R141b refrigerant based nanofluid[J]. Proc. Eng.,2013,56:310-315.
[26]Mahbubul I M,Saidur R,Amalina M A. Influence of particle concentration and temperature on thermal conductivity and viscosity of Al2O3/R141b nanorefrigerant[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer,2013,43:100-104.
[27]Mahbubul I M,Fadhilah S A,Saidur R,et al. Thermophysical properties and heat transfer performance of Al2O3/R134a nanorefrigerants[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2013,57(1):100-108.
[28]Corcione M. Empirical correlating equations for predicting the effective thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of nanofluids[J]. Energy Convers. Manage,2011,52(1):789-793.
[29]Sitprasert C,Dechaumphai P,Juntasaro V. A thermal conductivitymodel for nanofluids including effect of the temperature-dependent interfacial layer[J]. J. Nanopart. Res.,2009,11(6):1465-1476.
[30]Jiang W,Ding G,Peng H. Measurement and model on thermal conductivities of carbon nanotube nanorefrigerants[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences,2009,48:1108-1115.
[31]Kedzierski M A,Gong M. Effect of CuO nanolubricant on R134a pool boiling heat transfer[J]. Int. J. Refrigeration,2009,32:791-799.
[32]Kedzierski M A. Effect of Al2O3nanolubricant on R134a pool boiling heat transfer[J]. Int. J. Refrigeration,2011,34:498-508.
[33]Bartelt K,Park Y,Liu L,et al. Flow boiling of R134a/POE/CuO nanofluids in a horizontal tube[C]//International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference,Purdue,2008. West Lafayette,Indiana,USA.
[34]Akhavan-Behabadi M A,Nasr M,Baqeri S. Experimental investigation of flow boiling heat transfer of R600a/oil/CuO in a plain horizontal tube[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,2014,58:105-111.
[35]Henderson K,Park Y G,Liu L,et al. Flow boiling heat transfer of R134a-based nanofluids in a horizontal tube[J]. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transfer,2010,53:944-951.
[36]Peng Hao,Ding Guoliang,Hu Haitao,et al. Nucleate pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of refrigerant/oil mixture with diamond nanoparticles[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration,2010,33(2):347-358.
[37]Kedzierski M A. Effect of diamond nanolubricate on R134a pool boiling heat transfer[C]//Nanoscale Heat and Mass Transfer International Conference,Shanghai,China. 2009:389-398.
[38]Park K J,Jung D. Boiling heat transfer enhancement with carbon nanotubes for refrigerants used in building air conditioning[J]. Energy and Buildings,2007,39:1061-1064.
[39]Park K J,Jung D. Enhancement of nucleate boiling heat transfer using carbon nanotubes[J]. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transfer,2007,50:4499-4502.
[40]Trisaksri V,Wongwises S. Nucleate pool boiling heat transfer of TiO2/R141b nanofluids[J]. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transfer,2009,52:1582-1588.
[41]Yang C Y,Liu D W. Effect of nano-particles for pool boiling heat transfer of refrigerant 141B on horizontal tubes[J]. Int. J. Microscale Nanoscale Thermal Fluid Transport Phenomena,2010,1(3):233-243.
[42]Peng H,Ding D,Jiang W,et al. Heat transfer characteristics of refrigerant-based nanofluid flow boiling inside a horizontal smooth tube[J]. Int. J. Refrigeration,2009,32:1259-1270.
[43]Sun Bin,Di Yang. Flow boiling heat transfer characteristics of nano-refrigerants in a horizontal tube[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration,2014,38:206-214.
[44]Park Y,Sommers A,Liu L,et al. Nanoparticles to enhance evaporative heat transfer[C]//The 22nd Int. Congress of Refrigeration,Beijing,China,2007. Paper number:ICR07-B1-709.
[45]Mahbubul I M,Saidura R,Amalina M A. Heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of Al2O3-R141b nanorefrigerant in horizontal smooth circular tube[J]. Procedia Engineering,2013,56:323-329.
[46]Tang Xiao,Zhao Yaohua,Diao Yanhua. Experimental investigation of the nucleate pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of δ-Al2O3-R141b nanofluids on a horizontal plate[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,2014,52:88-96.
[47]Lee J,Cho S,Hwang Y,et al. Application of fullerene-added nano-oil for lubrication enhancement in friction surfaces[J]. Tribol. Int.,2009,42(3):440-447.
[48]Lee K,Wang Y H,Cheong S,et al. Performance evaluation of nano-lubricants of fullerene nanoparticles in refrigeration mineral oil[J]. Curr. Appl. Phys.,2009,9(2):128-131.
[49]Fu Liehu,Wang Ruixiang,Cong Wei,et al. Experiment study on performance of refrigerator using nano-particle additive[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2008,42:852-854.
[50]Bi Shengshan,Shi Lin,Zhang Lili. Application of nanoparticles in domestic refrigerators[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2008,28(14-15):1834-1843.
Research progress of influence on heat transfer and characteristics of compressor with nano-refrigerant
CHEN Mengxun1,ZHANG Hua1,LOU Jiangfeng2
(1School of Energy and Power Engineering,University of Shanghai for Science and Technology,Shanghai 200093,China;2Zhejiang DUN’AN Artificial Environmental Equipment Co.,Ltd.,Zhuji 311835,Zhejiang,China)
Application of nanotechnology in refrigeration equipment is one of the innovative researches in the field of refrigeration. Updated research achievements of nanotechnology in refrigeration field is reviewed,through summarizing the advantages of nanomaterials applied in refrigeration system under the background of energy conservation and environmental protection,introducing common preparation methods in recent years,enumerating the influence of different nano-refrigerants upon heat transfer,and explaining the effect of nano-particle in reducing friction and improving the performance of compressors. Several important questions have been raised:how to prepare long-term stable nano-refrigerant,how to build models of characteristics about flow boiling heat transfer and pressure drop of nano-refrigerant,as well as how to make sure that nano-particle will be stable in each part of the refrigeration system during running process. Researches should be focused on these problems in the future.
nano-refrigerant;thermal conductivity;boiling heat transfer;compressor
TB 61+2; TB 383
A
1000-6613(2015)12-4145-06
10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2015.12.003
2015-03-26;修改稿日期:2015-05-04。
国家自然科学基金(51176124)、上海市曙光计划(跟踪)(10GG21)及上海市研究生创新基金(JWCXSL1101)项目。
陈梦寻(1992—),女,硕士研究生,主要从事纳米制冷技术的研究。E-mail 1090357452@qq.com。联系人:张华,教授,博士生导师,主要从事制冷空调与新能源利用方向的研究。E-mail zhanghua3000@163.com。
