线粒体靶向抗氧化剂研究进展
2015-12-28樊鹏程,葛越,蒋炜等
·综述·
线粒体靶向抗氧化剂研究进展
樊鹏程1,2,葛越3,蒋炜1,2,景临林1,2,马慧萍1,2,贾正平1,2(1.兰州军区兰州总医院药剂科,甘肃 兰州 730050;2.全军高原环境损伤防治研究重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730050;3.延安市宝塔区妇幼保健院,陕西 延安 716000)
[摘要]线粒体是细胞呼吸的主要场所,在细胞的生命周期中扮演重要角色,三羧酸循环和氧化磷酸化都是在线粒体中进行。线粒体功能障碍可导致一系列疾病,如缺血-再灌注损伤、败血症和糖尿病等。线粒体是神经退行性病变的治疗靶点,也是药物转运策略研究的引人注目的靶位。虽然线粒体所介导的疾病进程的分子机制尚未完全阐明,但氧化应激是关键的环节。开发线粒体靶向的抗氧化应激保护药物具有诱人的前景。线粒体靶向抗氧化剂是指以线粒体为作用靶位的具有抗氧化作用的药物。该文介绍了现有的线粒体靶向抗氧化剂的概念、分类及其疾病治疗研究进展。
[关键词]线粒体靶向;抗氧化剂;活性氧;氧化应激
[基金项目]国家自然科学基金资助项目(81202458);全军医药卫生科研项目(CLZ12JB06)
[作者简介]樊鹏程,博士.Tel:(0931)8994671;E-mail:fpch2001@yeah.net
[通讯作者]贾正平.E-mail:pharmapaper@hotmail.com
[中图分类号]R329.28[文献标志码]A
DOI[]10.3969/j.issn.1006-0111.2015.01.001
[收稿日期]2013-11-28[修回日期]2014-03-26
Research progress in mitochondria-targeted antioxidants
FAN Pengcheng1,2,GE Yue3,Jiang Wei1,2,JING Linlin1,2,MA Huiping1,2,JIA Zhengping1,2(1.Department of Pharmacy,Lanzhou General Hospital of Lanzhou Region,Lanzhou 730050,China;2.Key Laboratory of Entire Army Plateau Environment Injury Prevention Research,Lanzhou 730050,China;3.Meternal and Child Health Care of Baota District,Yan′an 716000,China)
Abstract[]Mitochondria are the main places of cellular respiration as well as the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.It plays an important role in controlling the life and death of cells.Mitochondrial dysfunction leads to a series of human diseases such as ischemia-reperfusion injury,sepsis and diabetes.Mitochondrial become an attractive target for drug transporters strategy and therapeutic targets for neurodegeneration.Although the molecular mechanisms responsible for mitochondria mediated disease processes are not fully elucidated yet,the oxidative stress appears to be critical.Accordingly,strategies are being developed for the targeted delivery of antioxidants to mitochondria.The prospect of development of mitochondrial targeted drugs with anti-oxidative stress protection is tempting.Mitochondrial targeting antioxidants were the antioxidant drugs which took mitochondria as the target site.In this review,weintroduced the conception and classification of mitochondrial targeted antioxidants and the research progress of disease treatment by mitochondrial targeted antioxidants.
[Key words]mitochondria-targeted;antioxidant;reactive oxygen species;oxidative stress
线粒体在细胞的生命周期中扮演重要角色,是连接细胞应激信号通路和神经细胞凋亡的重要桥梁[1],它参与了缺氧致神经细胞凋亡的过程[2,3]。线粒体是细胞呼吸的主要场所,三羧酸循环和氧化磷酸化都是在线粒体中进行。线粒体除了通过位于其内膜的呼吸链发挥细胞呼吸的功能外,在维持细胞正常物质代谢及离子转运中都具有重要作用。研究表明,线粒体损伤可能是神经细胞缺氧损伤的中心环节,缺氧会导致神经元细胞线粒体膜去极化,线粒体膜电位降低[4,5],呼吸链电子传递受阻,能量代谢障碍,以及各种生理学指标改变,从而导致线粒体功能异常。缺氧对线粒体的影响还表现为细胞色素C释放[6],活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)生成增加[6],线粒体通透转运孔开放等。在一些神经退行性病变中亦发现线粒体功能异常,如阿尔茨海默症、帕金森症、亨廷顿舞蹈症及肌萎缩侧索硬化症[7]。
1线粒体靶向抗氧化剂概念
近年来新型体内抗氧化药物的开发越来越为研究者所关注[8-10]。线粒体因其在细胞能量代谢、细胞凋亡、钙离子内稳态、细胞信号通路中的重要地位而成为药物转运策略的诱人靶点[7-11]。同时线粒体也是神经退行性病变的治疗靶点,开发线粒体靶向的神经保护药物的研发具有诱人的前景[7-12]。线粒体靶向抗氧化剂是指以线粒体为作用靶位的具有抗氧化作用的药物。线粒体靶向抗氧化剂包括:以三苯基膦为载体的线粒体靶向抗氧化剂;基于氨基酸和多肽的线粒体靶向抗氧化剂;谷胱甘肽胆碱酯和N-乙酰基-L-半胱氨酸。其中MitoQ和SkQR1对缺血再灌注及缺氧致氧化应激引起的大鼠神经损伤具有保护作用[13]。
2线粒体靶向抗氧化剂分类
有关药物选择性靶向线粒体研究有许多途径,包括基于线粒体生物物理学的靶向方法:基于线粒体内膜高负电位的线粒体靶向药物;基于线粒体内特定酶催化前药释放药物;基于转运载体传递的前药。目前已有的线粒体靶向抗氧化剂大致分为三类:①基于三苯基膦作为线粒体载体的化合物;②基于氨基酸和多肽的线粒体靶向化合物;③体内抗氧化分子为母核的线粒体靶向化合物。
2.1 以三苯基膦为载体的线粒体靶向抗氧化剂
三苯基膦类线粒体靶向抗氧化剂主要是利用线粒体外膜与间隙、内膜与基质之间膜电位负电势的差异,以脂溶性和正电性均较高的三苯基膦分子作为载体,将具有抗氧化作用的母核分子在线粒体中跨膜转运至线粒体基质以起到清除过多ROS的作用[7,11,14-17]。MitoVit E是最早出现的该类线粒体靶向抗氧化剂,由新西兰达尼丁Otago大学化学与生化部的Smith等最早合成[18]。研究发现以线粒体膜电位作为药物分子向线粒体迁移的动力,MitoVit E在线粒体和胞浆中的浓度差异达5 000~6 000倍,并由此证明了一个新的概念,即将抗氧化剂定向转运进入线粒体能够选择性地阻止线粒体氧化损伤[18]。研究者发现MitoVit E能够减少由H2O2诱导的Jurkat细胞中半胱氨酸蛋白酶-3(caspase-3)的活化[19],从而减少因氧化应激引起的细胞凋亡。MitoQ几乎是和MitoVit E同时出现[20],是最早研究的三苯基膦类线粒体靶向药物之一,也是目前研究最为热门的线粒体靶向抗氧化剂[21]。MitoQ的设计思想来源于癸基泛醇的抗氧化及对线粒体的保护作用[13],并通过三苯基膦载体将癸基泛定向运输入线粒体基质,其在线粒体中的含量和胞质中相差500~600倍[20,22]。Rodriguez等对MitoQ安全性进行了评价,认为其治疗剂量下长期口服对小鼠是安全的[23]。目前国外已经进入Ⅲ期临床研究,有可能成为第一个上市的线粒体靶向药物[7-11]。MitoQ具有多种活性,包括:对缺血再灌注肝脏的保护作用[12,20],对脂肪性肝炎和CCl4引起的中毒性肝炎具有保护作用[24];对脂多糖肽聚糖诱发败血症模型大鼠的保护作用[25];对Parkinson模型小鼠的治疗作用[26];对可卡因导致心肌线粒体损伤的保护作用[27];对有机磷所致大鼠氧化应激和脑损伤的保护作用[28];对化疗药物顺铂引起的肾功能损伤具有保护作用[12]。可以看出MitoQ的保护作用主要集中在因氧化应激所导致的自由基释放增加而引起的组织损伤。
三苯基膦类线粒体靶向抗氧化剂除MitoVit E和MitoQ外,还有MitoPBN、MitoPeroxidase,其结构见图1。

图1 三苯基膦类线粒体靶向抗氧化剂结构图
2.2 基于氨基酸和多肽的线粒体靶向抗氧化剂
SS四肽(SS tetrapeptides)类线粒体靶向抗氧化剂为一类芳香族阳离子多肽,其结构基序为交替的芳香环、氨基酸残基以及2′,6′-二甲基酪氨酸残基(Dmt)[29],见图2。这类四肽化合物的抗氧化活性来源于其结构中的Dmt,因其相关化合物3,5-二甲基苯酚为一类已知的酚类抗氧化剂[30]。其最初的研究目的是为了开发一类具有中枢活性的阿片类镇痛药[31,32]。该类化合物包括Dmt-D-Arg-Phe-Lys-NH2(SS-02),Phe-D-Arg-Phe-Lys-NH2(SS-20) (不含Dmt),以及D-Arg-Dmt-Lys-Phe-NH2(SS-31),Dmt-D-Arg-Phe-Atn-Dap-NH2(SS-19)。SS-02可以清除H2O2并抑制亚油酸和低密度脂蛋白引起的脂质过氧化,由此证明了该类四肽的抗氧化剂特性[29]。同SS-02含有相同氨基酸残基但是序列不同的SS-31有着相似的抗氧化作用,不含有Dmt的SS-20则无抗氧化剂活性。由此提示该类四肽的抗氧化活性来源于Dmt。SS-02 和SS-31可以防止缺氧30 min的离体缺血再灌注豚鼠心肌收缩力下降,SS-20则无此效果。这些研究结果提示,这类细胞渗透性四肽是有效的抗氧化剂。同时该类化合物不需要增加阳离子分子作为线粒体转运分子,故可能对去极化的线粒体也有效果。
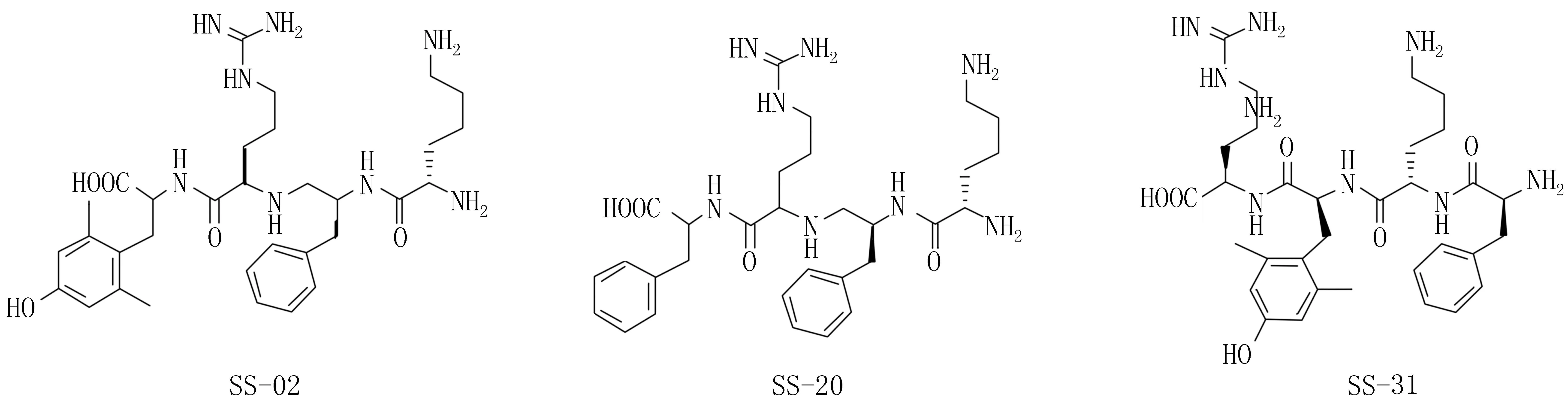
图2 基于氨基酸和多肽的线粒体靶向抗氧化剂结构图
2.3 谷胱甘肽胆碱酯和N-乙酰基- L-半胱氨酸
谷胱甘肽在抗氧化防御及生物体亲电子物质解毒机制中扮演关键角色。有研究表明,二羧酸和2-酮戊二酸载体负责将谷胱甘肽转运至线粒体中[33]。虽然线粒体谷胱甘肽池中谷胱甘肽的数量约仅占15%,但是线粒体谷胱甘肽池在细胞防护中起着关键作用。开发增加线粒体中谷胱甘肽浓度的药物及其他硫醇抗氧化剂可防止细胞免受氧化损伤,起到线粒体保护作用[16]。MitoGSH和相关化合物MitoNAC(图3)可减轻叔丁基氢过氧化物诱导的大鼠心肌线粒体去极化,延迟H2O2诱导的新生大鼠心室肌细胞和纹状体神经元线粒体去极化过程,减少N-methyl-d-aspartate诱导的纹状体神经元ROS生成。因此,开发谷胱甘肽及其相关的硫醇线粒体靶向抗氧化剂是一种预防氧化应激相关线粒体功能异常的有效途径。其在氧化应激相关急慢性疾病的治疗领域存在广泛的应用前景。
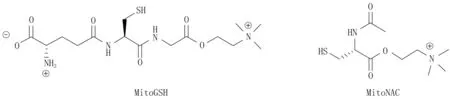
图3 MtioGSH和MitoNAC线粒体靶向抗氧化剂结构图
3小结
线粒体在细胞的生命周期中发挥重要作用,线粒体内ROS爆发导致线粒体损伤,进而引起细胞凋亡是致缺氧、缺血再灌注损伤、神经退行性病变、衰老等病理过程的关键环节。上述病理过程早期,细胞线粒体中产生大量自由基,使细胞处于ROS等氧化物过量聚集的氧化状态,氧化应激失衡导致线粒体膜和细胞膜脂质过氧化,线粒体能量代谢障碍及凋亡信号通路激活等损伤出现。线粒体损伤和机体自由基释放增加密切相关,保护或维持线粒体功能可达到预防或治疗氧化应激所致机体损伤的作用。开发以线粒体为特定作用部位的靶向制剂能够对线粒体提供特异性保护作用,使得线粒体免受氧化应激损伤。亲脂性阳离子基团在线粒体靶向抗氧化剂运载方面显示了巨大的潜力。但其仍存在如下不足:①传递能力(只有电中性及小分子量的分子可以被转运);②其亚定位(这类化合物倾向定位于线粒体基质及连接基质的内膜内表面,而无法定位于发生许多重要代谢过程的线粒体内膜外表面、外膜、膜间隙);③其毒性(在高浓度时他们可以使线粒体膜电位去极化而危及细胞生存)。
研究新的具有抗氧化作用且毒性小的线粒体靶向药物,是治疗缺血再灌注损伤、神经退行性病变、缺氧等疾病的靶向药物研究领域的一条新途径。
【参考文献】
[1]Jordan J,de Groot PW,Galindo MF.Mitochondria:the headquarters in ischemia-induced neuronal death[J].Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem,2011,11:98-106.
[2]Finkel T.Radical medicine:treating ageing to cure disease[J].Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2005,6:971-976.
[3]Fantinelli JC,Perez Nunez IA,Gonzalez Arbelaez LF,etal.Participation of mitochondrial permeability transition pore in the effects of ischemic preconditioning in hypertrophied hearts:role of NO and mitoK(ATP)[J].Int J Cardiol,2011,166:173-180.
[4]Larsen GA,Skjellegrind HK,Berg-Johnsen J,etal.Depolarization of mitochondria in isolated CA1 neurons during hypoxia,glucose deprivation and glutamate excitotoxicity[J].Brain Res,2006,1077:153-160.
[5]Lee DR,Helps SC,Macardle PJ,etal.Alterations in membrane potential in mitochondria isolated from brain subregions during focal cerebral ischemia and early reperfusion:evaluation using flow cytometry[J].Neurochem Res,2009,34:1857-1866.
[6]Dave KR,Bhattacharya SK,Saul I,etal.Activation of protein kinase C delta following cerebral ischemia leads to release of cytochrome C from the mitochondria via bad pathway[J].PLoS One,2011,6(7):e22057.
[7]Moreira PI,Zhu X,Wang X,etal.Mitochondria:a therapeutic target in neurodegeneration[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2010,1802:212-220.
[8]Diogo CV,Grattagliano I,Oliveira PJ,etal.Re-wiring the circuit:mitochondria as a pharmacological target in liver disease[J].Curr Med Chem,2011,18:5448-5465.
[9]Walters AM,Porter GAJ,Brookes PS.Mitochondria as a drug target in ischemic heart disease and cardiomyopathy[J].Circ Res,2012,111:1222-1236.
[10]Reale M,Pesce M,Priyadarshini M,etal.Mitochondria as an easy target to oxidative stress events in Parkinson′s disease[J].CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets,2012,11:430-438.
[11]Gruber J,Fong S,Chen CB,etal.Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants and metabolic modulators as pharmacological interventions to slow ageing[J].Biotechnol Adv,2012,31:563-592.
[12]Mukhopadhyay P,Horvath B,Zsengeller Z,etal.Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation triggers inflammatory response and tissue injury associated with hepatic ischemia-reperfusion:therapeutic potential of mitochondrially targeted antioxidants[J].Free Radic Biol Med,2012,53:1123-1138.
[13]Telford JE,Kilbride SM,Davey GP.Decylubiquinone increases mitochondrial function in synaptosomes[J].J Biol Chem,2010,285:8639-8645.
[14]Coulter CV,Kelso GF,Lin TK,etal.Mitochondrially targeted antioxidants and thiol reagents[J].Free Radic Biol Med,2000,28:1547-1554.
[15]Modica-Napolitano JS,Aprille JR.Delocalized lipophilic cations selectively target the mitochondria of carcinoma cells[J].Adv Drug Deliv Rev,2001,49:63-70.
[16]Sheu SS,Nauduri D,Anders MW.Targeting antioxidants to mitochondria:a new therapeutic direction[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2006,1762:256-265.
[17]Skulachev VP.Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants as promising drugs for treatment of age-related brain diseases[J].J Alzheimers Dis,2012,28:283-289.
[18]Smith RA,Porteous CM,Coulter CV,etal.Selective targeting of an antioxidant to mitochondria[J].Eur J Biochem,1999,263:709-716.
[19]Hughes G,Murphy MP,Ledgerwood EC.Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate the temporal activation of nuclear factor kappaB to modulate tumour necrosis factor-induced apoptosis:evidence from mitochondria-targeted antioxidants[J].Biochem J,2005,389:83-89.
[20]Kelso GF,Porteous CM,Coulter CV,etal.Selective targeting of a redox-active ubiquinone to mitochondria within cells:antioxidant and antiapoptotic properties[J].J Biol Chem,2001,276:4588-4596.
[21]Solesio ME,Prime TA,Logan A,etal.The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant MitoQ reduces aspects of mitochondrial fission in the 6-OHDA cell model of Parkinson′s disease[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2013,1832:174-182.
[22]Asin-Cayuela J,Manas AR,James AM,etal.Fine-tuning the hydrophobicity of a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant[J].FEBS Lett,2004,571:9-16.
[23]Rodriguez-Cuenca S,Cocheme HM,Logan A,etal.Consequences of long-term oral administration of the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ to wild-type mice[J].Free Radic Biol Med,2010,48:161-172.
[24]Zelber-Sagi S,Lurie Y,Nitzan-Kaluski D,etal.Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants prevent liver injury in animal models of steatohepatitis and CCl4intoxication[J].Alcoholic Liver Dis,2006,S267.
[25]Lowes DA,Thottakam BM,Webster NR,etal.The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ protects against organ damage in a lipopolysaccharide-peptidoglycan model of sepsis[J].Free Radic Biol Med,2008,45:1559-1565.
[26]Ghosh A,Chandran K,Kalivendi SV,etal.Neuroprotection by a mitochondria-targeted drug in a Parkinson′s disease model[J].Free Radic Biol Med,2010,49:1674-1684.
[27]Vergeade A,Mulder P,Vendeville-Dehaudt C,etal.Mitochondrial impairment contributes to cocaine-induced cardiac dysfunction:prevention by the targeted antioxidant MitoQ[J].Free Radic Biol Med,2010,49:748-756.
[28]Wani WY,Gudup S,Sunkaria A,etal.Protective efficacy of mitochondrial targeted antioxidant MitoQ against dichlorvos induced oxidative stress and cell death in rat brain[J].Neuropharmacology,2011,61:1193-1201.
[29]Zhao K,Zhao GM,Wu D,etal.Cell-permeable peptide antioxidants targeted to inner mitochondrial membrane inhibit mitochondrial swelling,oxidative cell death,and reperfusion injury[J].J Biol Chem,2004,279:34682-34690. J,de Groot PW,Galindo MF.Mitochondria:the headquarters in ischemia-induced neuronal death[J].Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem,2011,11:98-106.
[30]Wright JS,Carpenter DJ,McKay DJ,etal.Theoretical calculation of substituent effects on the O-H bond strength of phenolic antioxidants related to vitamin E[J].J Am Chem Soc,1997,119:4245-4252.
[31]Schiller PW,Nguyen TM,Berezowska I,etal.Synthesis and in vitro opioid activity profiles of DALDA analogues[J].Eur J Med Chem,2000,35:895-901.
[32]赵善民,何显教,晋玲,等.急性低氧对家兔血压心率微血管反应性及自由基的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2003,19:341-344.
[33]Chen Z,Putt DA,Lash LH.Enrichment and functional reconstitution of glutathione transport activity from rabbit kidney mitochondria:further evidence for the role of the dicarboxylate and 2-oxoglutarate carriers in mitochondrial glutathione transport [J].Arch Biochem Biophys,2000,373:193-202. JS,Carpenter DJ,McKay DJ,etal.Theoretical calculation of substituent effects on the O-H bond strength of phenolic antioxidants related to vitamin E[J].J Am Chem Soc,1997,119:4245-4252.
[31]Schiller PW,Nguyen TM,Berezowska I,etal.Synthesis and in vitro opioid activity profiles of DALDA analogues[J].Eur J Med Chem,2000,35:895-901.
[32]赵善民,何显教,晋玲,等.急性低氧对家兔血压心率微血管反应性及自由基的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2003,19:341-344.
[33]Chen Z,Putt DA,Lash LH.Enrichment and functional reconstitution of glutathione transport activity from rabbit kidney mitochondria:further evidence for the role of the dicarboxylate and 2-oxoglutarate carriers in mitochondrial glutathione transport [J].Arch Biochem Biophys,2000,373:193-202.
[本文编辑]陈静
