发酵型饮料酒中生物胺研究进展
2013-07-22李志军栾同青钟其顶孟镇熊正河
李志军,栾同青,钟其顶,孟镇,熊正河
(1.中国食品发酵工业研究院,北京 100027;2.全国食品发酵标准化中心,北京 100027)
生物胺是一类含氮低分子量碱性有机化合物,存在于多种食物中,尤其是发酵香肠、葡萄酒、啤酒和黄酒等发酵加工食品[1]。生物胺是生成荷尔蒙、核酸、蛋白质等重要生命成分的前体物质,其中腐胺、精胺、亚精胺和尸胺等是生物活性细胞必不可少的组成部分,在调节核酸与蛋白质的合成及生物膜稳定性方面起着重要作用[2];同时,腐胺和尸胺是生成致癌物质和亚硝基化合物的前体物质[3-4],组胺、酪胺等会引起头痛和消化问题,当人体摄入过量的生物胺时,就会引起诸如头痛、恶心、心悸、血压变化、呼吸紊乱等过敏反应,严重的还会危及生命。
生物胺中以组胺对人体健康危害最大[5]。人体内存在单胺氧化酶,可分解体内生物胺,而酒精会抑制单胺氧化酶的活性[6],从而提高人体对生物胺的敏感性,降低了组胺产生危害作用的剂量,因此,发酵型饮料酒中生物胺安全性尤其是组胺限量问题受到高度重视。部分国家已制定了严格的葡萄酒中组胺限量:如澳大利亚、匈牙利和瑞士不得高于10 mg/L,法国不得高于8 mg/L,比利时不得高于5 mg/L~6 mg/L,荷兰不高于3 mg/L,德国不得高于2 mg/L[7-8]。
1 发酵型饮料酒中生物胺研究
1.1 葡萄酒中生物胺研究进展
Bauza 等[9]研究表明,酿酒葡萄的果皮和果肉中存在腐胺等生物胺,当将葡萄果皮、果肉同时压榨发酵葡萄酒时,葡萄中存在的腐胺等生物胺会部分地进入葡萄酒中。酒精发酵结束之后,几乎所有红葡萄酒和部分白葡萄酒都需要进行苹果酸-乳酸发酵(MLF)。在MLF 中,如果含有携带氨基酸脱羧酶基因的乳酸菌,那么这种乳酸菌不仅能够分解苹果酸,而且还可以作用于酒中的氨基酸使其脱羧形成生物胺[10-14]。若葡萄酒在酒精发酵结束后与酵母酒脚一起贮存,酵母自溶释放的游离氨基酸能够被具有氨基酸脱羧酶基因的微生物水解和脱羧,因此带酒脚贮存的葡萄酒中生物胺的含量通常会较高[13,15]。可见,葡萄酒中的生物胺主要来自原料、酿造过程和贮存过程。
研究[2,16-19]表明,葡萄酒中含有苯乙胺、腐胺、尸胺、组胺、酪胺、精胺和亚精胺等生物胺,其中组胺、酪胺和腐胺为葡萄酒中主要的生物胺,在经过MLF 后,这三种生物胺比其他生物胺的含量明显要高。其他生物胺,如苯乙胺和尸胺,在酿酒过程中有所降解[1]。表1为部分国家葡萄酒中生物胺的种类及含量水平。
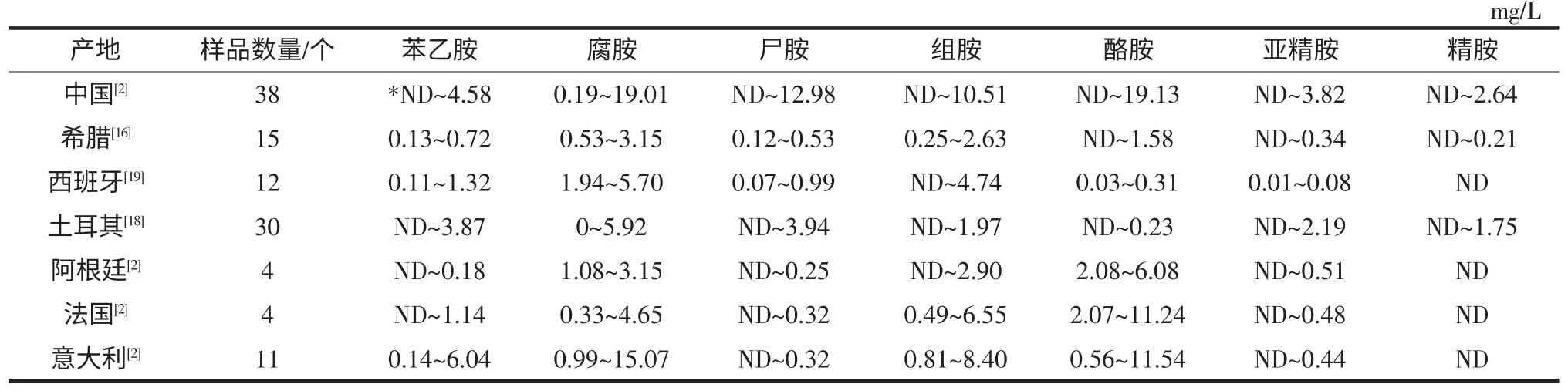
表1 部分国家葡萄酒中生物胺种类及含量水平Table 1 The content of biogenic amines in wine in some countries
目前,针对葡萄酒中生物胺,主要通过接种无氨基酸脱羧酶活性的菌株进行MLF[13-20]和及时终止MLF等措施降低葡萄酒中的生物胺[15]。
1.2 啤酒中生物胺的研究进展
根据啤酒中生物胺的来源,可将它们分为3 类:第一类来自原料,如麦芽中含有鲱精胺、腐胺、精胺和亚精胺等,酒花中含有酪胺、2-苯乙胺和多元胺等生物胺;第二类产生于糖化过程,如酪胺、鲱精胺和尸胺等;第三类在发酵过程中产生,如酪胺和色胺等。研究表明[21-23],啤酒中的生物胺与原料质量、酿造工艺等密切相关。
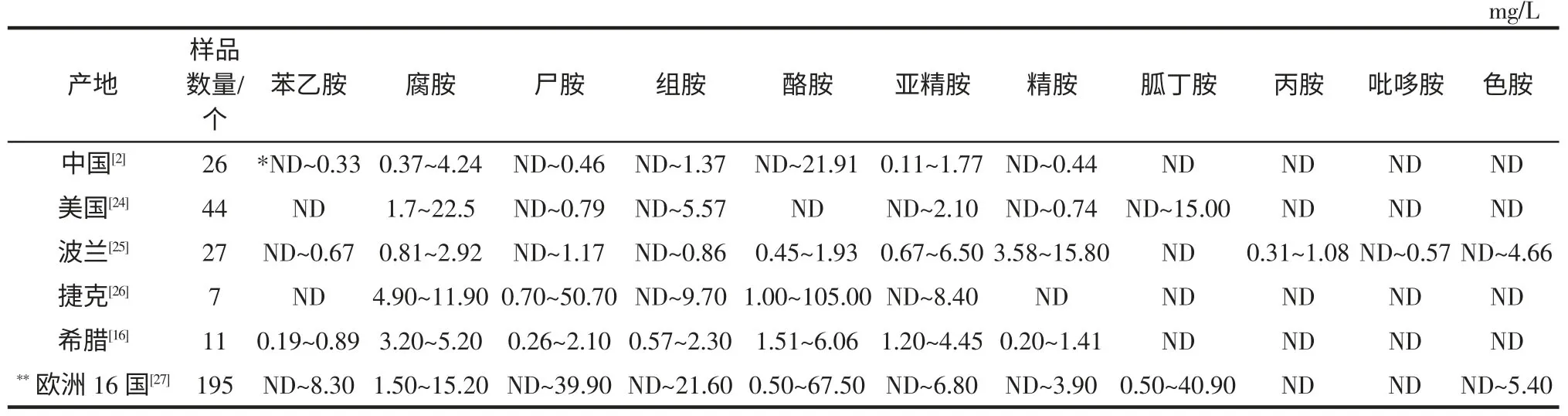
表2 部分国家啤酒中生物胺种类及含量水平Table 2 The content of biogenic amines in beer in some countries
研究[2,16,22-27]显示,啤酒中存在苯乙胺、腐胺、尸胺、组胺、酪胺、亚精胺、胍丁胺、丙胺、吡哆胺和色胺等多种生物胺,其中酪胺和尸胺的含量较高。表2 为部分国家啤酒中的生物胺种类及含量水平。
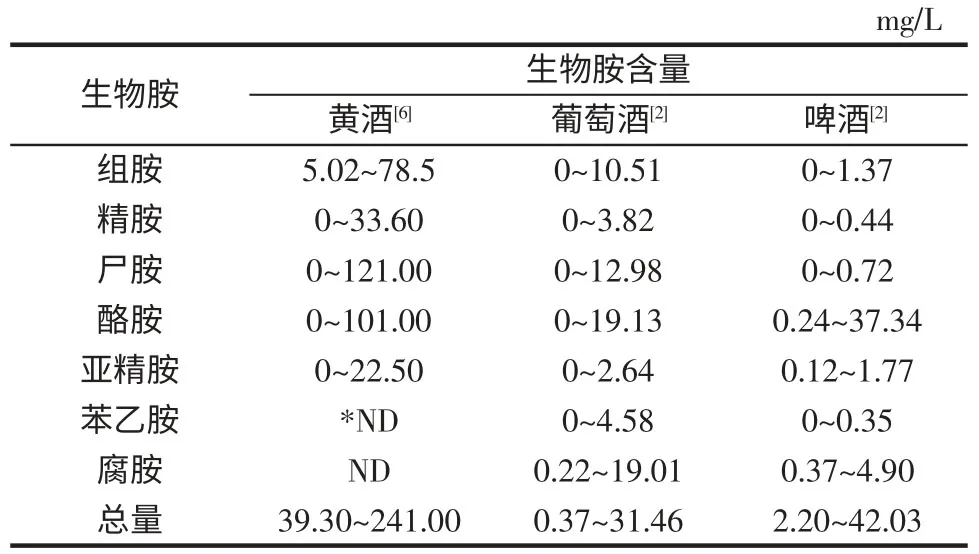
表3 三种酿造酒中生物胺的种类及含量水平Table 3 The content of biogenic amines in three fermented alcohoblic beverages
研究表明,加强卫生管理和在发酵过程中添加适量的抑制剂等措施也可以达到降低啤酒中生物胺含量的目的[20-29]。也有研究者[28]提出对麦汁中的氨基酸进行限量可以降低啤酒中生物胺的含量。
1.3 黄酒中生物胺研究进展
由于黄酒的酿造地区和发酵方法存在差异,所以不同黄酒中生物胺的种类有很大不同,黄酒中发现的生物胺主要有尸胺、腐胺、组胺、酪胺、精胺、亚精胺、苯乙胺、羟苯乙醇胺和色胺等[6、30-31]。陆永梅等[6]对中国4个黄酒产区的14 种黄酒进行了检测。结果显示黄酒中含有组胺、尸胺、酪胺、精胺和亚精胺等5 种生物胺,其含量比其他酿造酒(啤酒和葡萄酒)明显偏高。葡萄酒、啤酒和黄酒中的生物胺种类及含量水平见表3。
黄酒中生物胺含量明显高于啤酒和葡萄酒的原因可能主要是黄酒中的氨基酸含量明显高于其他酿造酒,这为生物胺的形成提供了大量的前体物质。黄酒中含有丰富的氨基酸,它与黄酒质量和风味密切相关。黄酒中的氨基酸,一是来自原料(包括米浆水)、糖化发酵剂等配料中的蛋白质分解;二是来自酵母、霉菌等微生物自溶等。据研究者对黄酒中氨基酸的分析测定表明:黄酒中含有21 种氨基酸,其中4 种是未知氨基酸,8 种是人体必需的氨基酸[32]。表4 比较了三种酿造酒中氨基酸的含量水平。相关报道。
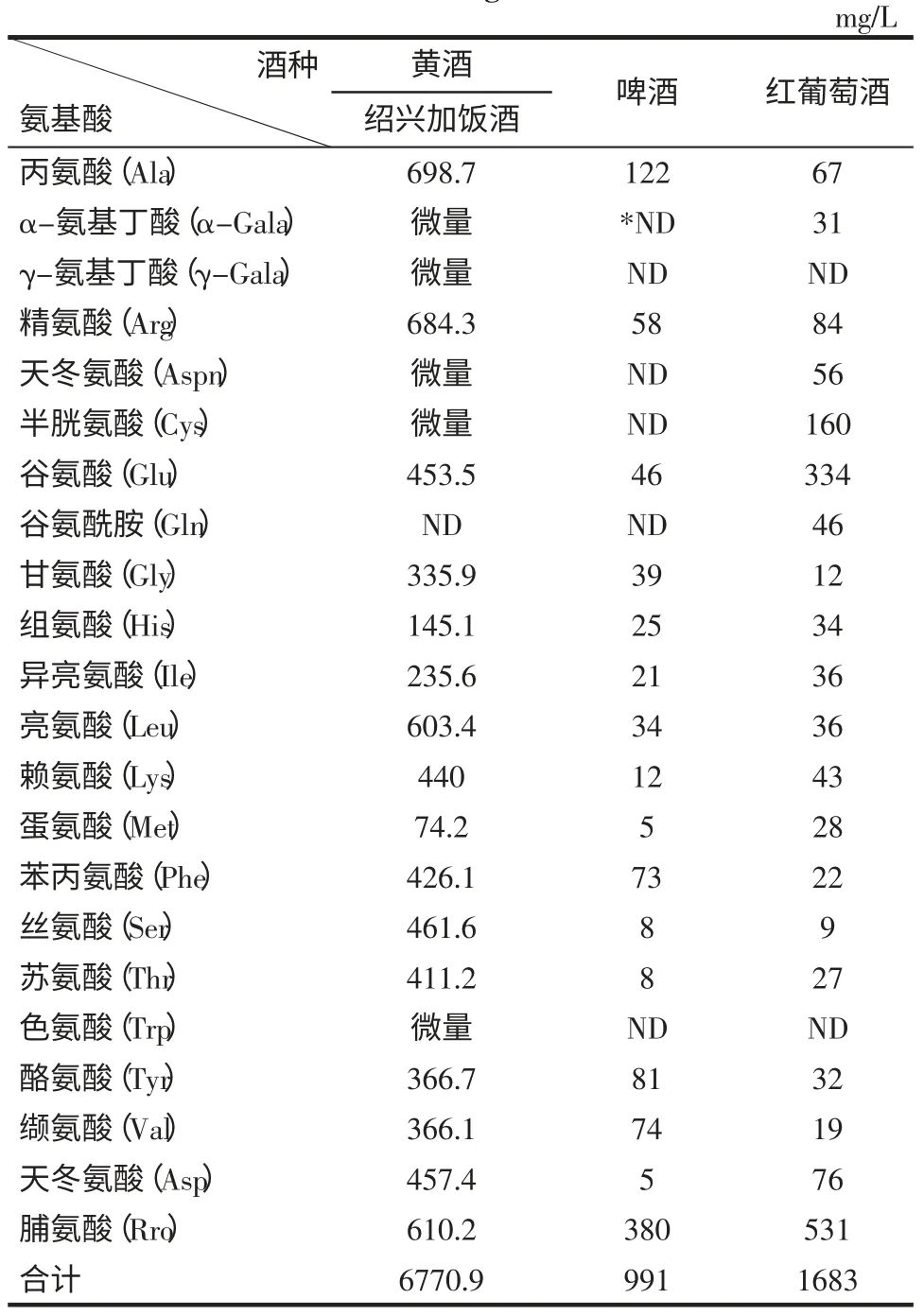
表4 酿造酒中氨基酸的含量水平Table 4 The content of amion acids in fermented alcohoblic beverages
黄酒酿造是一个开放式的过程,容易感染杂菌,特别是在制作的酒曲里微生物种类繁杂,易感染具有氨基酸脱羧酶活性的微生物,其次,在煎酒过程中若没有做到完全灭菌,可能会在贮存期间形成生物胺,降低黄酒品质,可能会对消费者健康带来潜在危害。目前尚无对黄酒中生物胺控制措施研究的
2 发酵型饮料酒中生物胺检测方法的研究
目前,生物胺的检测方法主要有反相高效液相色谱(RP-HPLC)法[6-7,19,25,30,33-41],毛细管电泳(CE)[42]法,离子色谱(IC)法[43],薄层色谱(TLC)法[44],高效液相色谱串联质谱(HPLC-MS/MS)法[45],生物传感器(Biosensor)法[46]和气质联用色谱(GC-MS)法[47-48]等,其中,以RPHPLC 法最为常用。
RP-HPLC 具有分析速度快、检测灵敏度高、定量分析准确的特点,是目前发酵型饮料酒中生物胺含量分析测定的主要手段。由于生物胺分子中缺乏发色基团,在采用RP-HPLC 方法测定时,为了提高检测的灵敏度,需要采用柱前或柱后衍生技术,以单检测器进行检测。由于柱后衍生所需的仪器设备昂贵,投资大,所以研究者多选择柱前衍生法。目前,食品中生物胺的衍生试剂主要有丹磺酰氯(Dns-Cl)、邻苯二甲醛(OPA)、苯甲酰氯(Benzoyl Chloride)[49]、咔唑乙酰氯(AQC)、二硝基苯甲酰氯(Dabs-Cl)、3,5-二硝基-4-氯-三氟甲基苯(CNBF)、9-芴基甲基-氯甲酸酯(FMOC-Cl)[50]和苯基异硫氰酸盐(PITC)[51]等。使用衍生剂可以提高检测灵敏度,但其也具有一定的局限性,例如Benzoyl Chloride 和PITC 衍生物不产生荧光,只能用灵敏度较低的紫外检测器;FMOC-Cl 会产生从单胺到多胺的多重产物,对测定复杂基质的样品会产生严重的干扰;Dns-Cl 不仅可以与生物胺反应,还可以与酚、氨基酸和一些糖类反应,且衍生反应时间较长;OPA 的衍生时间短,但是衍生产物不稳定。衍生试剂的选择以衍生产物稳定性好、杂质少、衍生过程简单为原则。发酵型饮料酒成分复杂,可能含有氨基酸、多酚类及非极性物质等,这些物质会对生物胺的分离和定量产生干扰,并可能堵塞色谱柱,因此,在样品进入仪器分析前,往往需要采用固相萃取(SPE)法或液-液萃取(LLE)法对其进行前处理,以改善分离和分析效果。目前,对于发酵型饮料酒中生物胺检测的RPHPLC 方法中,研究者最常用的衍生试剂是Dns-Cl 和OPA,前处理至少采用0.45 μm 滤膜过滤,检测器一般采用荧光检测器或紫外检测器,色谱柱一般采用C18柱。详见表5。

表5 发酵型饮料酒中常见的RP-HPLC 测定生物胺方法Table 5 Methods for determination biogenic amines in fermentsd alcohoblic beverages by RP-HPLC
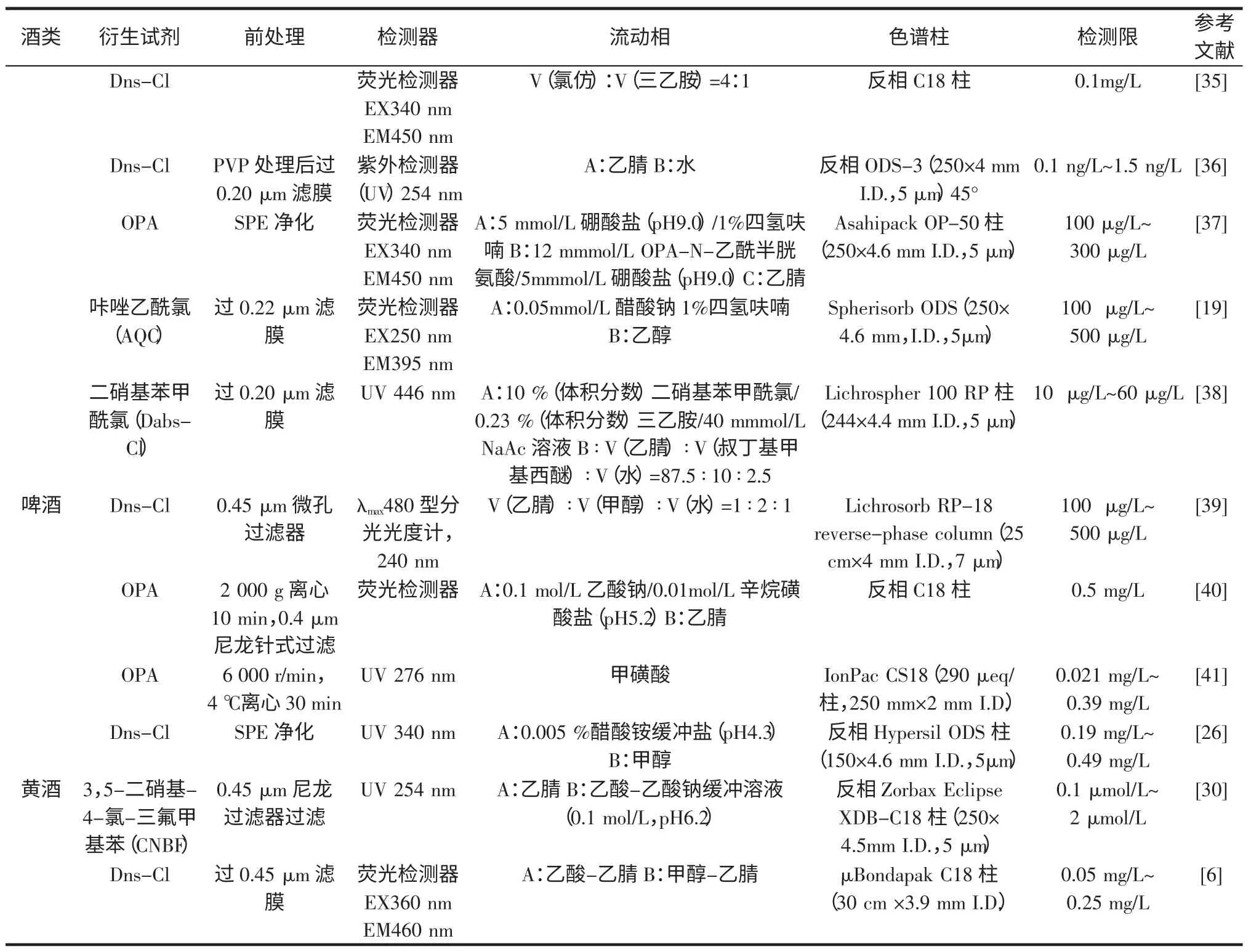
续表5 发酵型饮料酒中常见的RP-HPLC 测定生物胺方法Continue table 5 Methods for determination biogenic amines in fermentsd alcohoblic beverages by RP-HPLC
3 结论
发酵型饮料酒中的生物胺主要来自原料和发酵酿造过程。尸胺、组胺、酪胺、亚精胺和精胺等是葡萄酒、啤酒和黄酒等发酵型饮料酒中的主要生物胺,其中,黄酒中生物胺的检出含量最高。在生物胺检测方法中,RP-HPLC 法仍是目前最为简便、稳定、成熟可靠的测定方法。生物胺相关技术标准和控制技术措施的研究与制定,是有效控制发酵型饮料酒中生物胺,达到提高发酵型饮料酒质量安全的目的有效手段。
[1]张剑,钟其顶,熊正河,等.葡萄酒中生物胺的研究进展[J].酿酒科技,2010(7):80-85
[2]李志军.食品中生物胺及其产生菌株检测方法研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学,2007:10-11
[3]Bardocz S,Grant G,Brown D S,et al.Polyamines in food-implications for growth and health[J].The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,1993,4(2):66-71
[4]Halasz A,Barath A,Simon-Sarkadi L,et al.Biogenic amines and their production by microorganisms in food[J].Trends in Food Sci-ence and Technology,1994,5(2):42-49
[5]Bodmer S,Imark C,Kneubühl M.Biogenic amines in foods:Histamine and food processing[J].Inflammation Research,1999,48(6):296-300
[6]Lu Yongmei,Lu Xin,Chen Xiaohong,et al.A survey of biogenic amines in Chinese rice wines[J].Food Chemistry,2007,100(4):1424-1428
[7]M H Silla Santos Biogenic amines:their importance in foods,International Journal of Food Microbiology,1996,29(2/3):213-231
[8]Lehtonen P,Determination of amines and amino acids in wine-A Review[J].A merican journal for Enology and Viticulture,1996,47(2):127-133
[9]Bauza T,Kelly M T,Blaise A.Study of polyamines and their precursor amino acids in Grenache noir and Syrah grapes and wine of the Rhone Valley[J].Food Chem,2007,105(1):405-413
[10]Arena M E,Manca de Nadra M C.Biogenic amine production by Lactobacillus[J].Journal of Applied Microbiology,2001,90(2):158-162
[11]Bover-Cid S,Iquierdo-Pulido M,Marine-Font A,et al Biogenic mono-,di-and polyamine contents in Spanish wines and influence of a limited irrigation[J].Food Chemistry,2006,96(1):43-47
[12]沈念原,王秀芹.高效液相色谱法测定葡萄酒中生物胺的含量[J].食品工业科技,2011,32(4):394-396
[13]孔维府,范春艳,张翛翰,等.论葡萄酒中生物胺生成的影响因素及其检测方法[J].中国酿造,2010(6):13-16
[14]Halase A,Baratha,Simon-Sarkadi L,et al.Biogenic amines and their production by microorganisms in food[J].Trends Food Sci Tech,1994,5(2):42-49
[15]张春晖,夏双梅.葡萄酒中的生物胺的生产与工艺控制[J].食品科学,2002,23(10):128-130
[16]Loukou Z and Zotou A.Determination of biogenic amines as dansyl derivatives in alcoholic beverages by high -performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection and characterization of the dansylated amines by liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry.J Chromatography A,2003,996(1):103-113
[17]Fernandes J,Ferreira MA.Combines ion-pair extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of diamines,polyamines and aromatic amines in Port wine and grape juice[J].J Chromatogr A,2000,886(1):183-195
[18]Anli RE,Vural N,Yilmaz S.The determination of biogenic amines in Turkishredwines[J].FoodCompositionandAnalysis,2004,17(1):53-62
[19]Busto O,Guasch J,Borrull F.Determination of biogenic amines in wine after precolumn derivatization with 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate[J].Journal of Chromatography A,1996(737):205-213
[20]Lonvand-Funel A.Biogenic amines in wines:role of lactic acid bactria[J].FEMS Microbiol Lett,2001,199(2):1-l3
[21]徐岩.啤酒酿造中腐败细菌的研究[J].酿酒,2000(6):68-72
[22]吴延东.生物胺对啤酒质量的影响[J].酿酒科技,2004(1):59-60
[23]朱玉强.啤酒酿造过程中生物胺的产生与控制研究[J].酿酒科技,2006(7):26-27
[24]Brian M.De Borba,Jeff S.Rohrer.Determination of biogenic amines in alcoholic beverages by ion chromatography with suppressed conductivity detection and integrated pulsed amperometric detection[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2007(1155):22-30
[25]Anna Slomkowska·Wojciech Ambroziak.Biogenic amine profile of the most popular Polish beers[J].Eur Food Res Technol,2002(215):380-383
[26]Pavel Kalac,Jan Savelb,Martin Krzeka,et al.Biogenic amine formation in bottled beer[J].Food Chemistry,2002(79):431-434
[27]S.Tombelli,M.Mascini.Electrochemical biosensors for biogenic amines:a comparison between different approaches[J].Analytica Chimica Acta,1998(358):277-284
[28]管敦仪.啤酒工业手册:上册[M].北京:轻工业出版社,1982:156
[29]顾国贤,涂俊铭,李永仙,等.啤酒无菌酿造[J].酿酒,2000(3):49-53
[30]Jae Young Kim,Donghee Kim,Pojeong Park,et al.Effects of storage temperature and time on the biogenic amine content and microflora in Korean turbid rice wine,Makgeolli[J].Food Chemistry,2011,128(4):87-92
[31]谢铭.黄酒中生物胺的分析研究[J].广州化工,2010,38(4):139-141
[32]傅金泉.黄酒生产技术[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2005:284
[33]A Marcobal,M C Polo,P J Martin-Alvarez,et al.Biogenic amine content of red Spanish wines:comparison of a direct ELISA and an HPLC method for the determination of histamine in wines[J].FoodResearch International,2005(38):387-394
[34]Charalampos Proestos,Paul Loukatos,Michael Komaitis.Determination of biogenic amines in wines by HPLC with precolumn dansylation and fluorimetric detection[J].Food Chemistry,2008(106):1218-1224
[35]Antonella Costantini,Francesca Doria,Enrico Vaudano,et al.Chemical and molecular methods for the control of biogenicamineproductionbymicroorganisms[J].AnnMicrobiol,2011,61:173-178
[36]Zotou A,Loukou Z,Soufleros E,et al.Determination of Biogenic Amines in Wines and Beers by High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Pre-column Dansylation and Ultraviolet Detection[J].Chromatographia 2003,57(7/8):429-439
[37]Busto O,Miracle M,Guasch J,et al.Determination of biogenic amines in wines by high-performance liquid chromatography with on-column fluorescence derivatization[J].Journal of Chromatography A,1997(757):311-318
[38]Roberto R,Mercedes S V,Domingo G,et al Characterization of selected Spanish table wine samples according to their biogenic amine content from liquid chromatographic determination[J].J Agric Food Chem,2002,50(16):4713-4717
[39]O O Lasekan,W O Lasekan.Biogenic amines in traditional alcoholic beverages produced in Nigeria[J].Food Chemistry,2000(69):267-271
[40]Loret S,Deloyer P,Dandrifosse G.Levels of biogenic amines as a measure of the quality of thebeer fermentation process:Data from Belgian samples[J].Food Chemistry,2005(89):519-525
[41]Brian M De Borba,Jeff S Rohrer.Determination of biogenic amines in alcoholic beverages by ion chromatography with suppressed conductivity detection and integrated pulsed amperometric detection[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2007(1155):22-30
[42]Lin WC,Lin CE,Lin E C.Capillary zone electrophoretic separation of biogenicamines:influenceof organic modifier[J].J Chromatogr A,1996,755(1):142-146
[43]Jean DC,Caterina C,Fabiano T,et al.Production of biogenic amines in“salamini italiani alla cacciatore PDO”[J].Meat Sci,2004,67:343
[44]Shalaby AR.Multidetection,semiquantitative method for determining biogenic amines in foods[J].Food Chem,1995,52:367-372
[45]程小燕,杨秋红,雷鄂蓉,等.高效液相色谱串联质谱检测地表水中五种生物胺[J].环境监测,2011,30(1):35-39
[46]TombelliS,MasciniM.Eiectrochemicalbiosensorsforbiogenicamines:acomparisonbetweendifferentapproaches[J].AnalyticaChimica Acta,1998,358(3):277-284
[47]Richard tham,bo holmstedt.Gas chromatographic analysis of histamine metabolites in human urine[J].J Chvomatog,1965(19):286-295
[48]Haruhisa Mita,Hiroshi Yasurda,Takao Srida.Simultaneous determination of histamine and n-methylhistamine in human plasma and urine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatogmphy,1980(221):1-7
[49]Hwang D F,Chang S H,Shiua C Y,et al High-performance liquid chromatography determination of biogenic amines in fish implicated in food poisoning[J].J Chromatogr A,1997,693:23-30
[50]Bauza T,Blaise A,Daumas F,et al.Determination of biogenic amines and their precursor amino acids in wine of the Vallee du Rhone by high-performance liquid chromatography with precolumn derivatization and fluorimetric detection[J].J Chromatogr A,1995,707(2):373-379
[51]Rodriguez I,Lee H K,Li S F Y.Separation of biogenic amines by micellar electrokinetic chromatography[J].J Chromatogr A,1996,745(1):255-262
