Cu(ClO4)2诱导的N-苯基二吡啶甲基胺的邻位苯甲基化及其溴桥联铜配合物的形成
2011-11-10马正平陈秋云
马正平 叶 亚 陈秋云
(江苏大学化学化工学院,镇江 212013)
Cu(ClO4)2诱导的N-苯基二吡啶甲基胺的邻位苯甲基化及其溴桥联铜配合物的形成
马正平 叶 亚 陈秋云*
(江苏大学化学化工学院,镇江 212013)
N-苯基二吡啶甲基胺和苯甲基溴在Cu(ClO4)2存在的条件下反应导致N-苯基二吡啶甲基胺的邻位苯甲基化和一个新的溴桥联的双核铜配合物的形成。实验结果显示阴离子显著影响反应的选择性,CuCl2和Cu(NO3)2不能提高N-苯基二吡啶甲基胺邻位苯甲基化的选择性。NMR和元素分析数据证实N-苯基二吡啶甲基胺邻位苯甲基化产物的形成。X-射线晶体结构数据表明溴桥联的双核铜配合物中铜原子被3个N原子,1个配位溴离子和1个μ2-桥联的溴结合形成扭曲的三角双锥的构型。研究结果表明Cu(ClO4)2可作为N-苯基二吡啶甲基胺邻位烷基化反应的催化剂。研究结果有助于设计新的选择性苯甲基化催化剂。
苯甲基化;铜配合物;N-苯基二吡啶甲基胺;晶体结构
Di(picolyl)amine(dpa)and its derivatives are used as neutral,deprotonated chelating ligands to complex copper(Ⅱ)atoms to mimic non-heme dioxygenase[1-2].The reaction of dpa with Cu(ClO4)2or CuCl2leads to hexacoordinated[Cu(dpa)2](ClO4)2[3]or the mononuclear complex[Cu(dpa)Cl2][4],respectively,in which the geometry of reported Copper(Ⅱ)-dpa complexes is a distorted square pyramidal or trigonal bipyramidal.Theutility of these ligands is enhanced by the ease with which substituents may be introduced on the imino nitrogen atom,thus resulting the different antitumor activities and catalyzing activities of manganese(Ⅱ)complexes of dpa and its derivatives[5].So the synthesis of N-substituted dpa derivatives is meaningful to design functionalcomplexes[6].Although the intramolecular hydroxylation reaction and the antitumor activities for complexes of N-substituted di(picolyl)amine were extensively studied,there is no reporton its intramolecular benzylation[7-9].
Friedel-Crafts reaction of aromatic compounds is one of the important reactions for forming carboncarbon bonds,as the products serve as useful starting materials for synthesis of pharmaceuticals and materials[10].They are formed due to replacement of a hydrogen atom of an aromatic compound by a benzyl group derived from benzylating agent in the presence of Lewis acid (e.g.AlCl3,BF3,FeCl3,ZnCl2,etc.)or protonic acids.The copper(Ⅱ) complexes of(2-pyridyl)alkylamine were reported to activate C-X bond giving C-C bond formation[11].Copper-containing mesoporous silicas(Cu-HMS-n)and CuCl2were also widely used as mild,heterogeneous FriedelCrafts benzylation catalysts[12-13].Treatment of[Cu(NCMe)4][PF6]with chelating ligands gave[CuL(NCMe)][PF6](L=9,9-dimethyl-4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-xanthene),which could catalyze the alkylation of diphenylphosphine (PPh2)with PhCH2Br in the presence of the base NaOSiMe3to yield intramolecular benzylation products (PPh2CH2Ph)[14].Here we report a intramolecular ortho-benzylation of N-benzyl di(pyridylmethyl)amine with benzyl bromide and the formation of μ2-Br-bridged copper(Ⅱ) complexes.
1 Experimental
1.1 Chemical reagents,analysis and physical measurements
All reagents are of commercial grade and used as received.Bis(2-pyridylmethyl)-benzylamine (phdpa)was synthesized as reported[15].IR spectra were recorded on a Nicolet210 spectrometerin KBrpellets.Elemental analyses were performed by the Perkin-Elemer 240.1H NMR and13C NMR spectra were measured on a Bruker 400 MHz spectrometer.The electronic absorption spectra were recorded in the 900~190 nm region using the UV-2450 spectrophotometer.
1.2 Synthesis of[(phdpa)2Cu2(Br2)(μ2-Br](ClO4)(H2O)0.5(1)and[phCH2phdpa+2H+](ClO4)2(2)
A solution of Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O(471 mg,1 mmol)in methanol(2 mL)was added dropwise to the methanol solution (10 ml)of bis-(2-pyridylmethyl)-benzylamine(phdpa)(290 mg,1 mmol).After stirred for 30 min at room temperature,benzyl bromide(12.7 mg,1 mmol)in methanol(20 mL)was added and stirred at 80℃for 2 h,then cooled to room temperature.The purple crystals of 1 were obtained after evaporation of the methanol solution for 24 h.Yield 0.31 g(40%).Anal.Calcd.for C38H38Br3ClCu2N6O4.5(%):C 43.26,H,3.70,N,7.96,Cu,11.97;Found(%):C 43.13,H,3.73,N,7.84,Cu,11.84.IR(KBr,cm-1):ν(O-H)3373s,ν(=CH)3081m,ν(-CH2-)2 828 m, ν(C=N)1 612, ν(C=C),1 574 m,1 473 m,δ(CH,pyridine)773 s,ν(ClO4)1100 s,623 m.UV-Vis(CH3OH,nm (ε×10-4,L·mol-1·cm-1)):205 (2.73),259(1.59),296(0.40),682(0.01).
The white powders[phCH2phdpa+2H+](ClO4)2(2)were obtained by further evaporation of above filtrate.Yield 0.14 g(20%).Anal.Calcd.for C26H27Cl2N3O8(%):C 50.83,H,4.69 N,7.24;Found(%):C 50.92,H,4.60,N,7.27.1H NMR (400 MHz,DMSO-d6):δ:3.7(s,2H,CH2Ar);4.0(s,2H,CH2Ar);4.1(s,2H,CH2Py);5.89(s,2H,CH2Py);7.0~7.5(m,9H,Ar-);7,7~8.8(m,8H,Py);9.1(s,2H,H+).13C NMR(400 MHz,DMSO-d6):δ:54.6~60.0(CH2);120~160(Py or Ar).IR(KBr)ν/cm-1:ν(NH)3265m,ν(=CH)3060 m,ν(-CH2-)2925 m,ν(C=N)1663,ν(C=C)1589 s,1569 m,1473 m,1433 m, δ(CH,pyridine)760 s,699 s.UV-Vis(CHCl3,nm (ε×10-4,L·mol-1·cm-1)):203(4.12),260(1.75).
1.3 Ortho-benzylation reaction
The intramolecular ortho-benzylation of phdpa by benzyl bromide was used as a model reaction for Cu(Ⅱ)catalytic properties.A solution of CuX2(1 mmol)(X=Cl-,NO3-,ClO4-)was added to the methanol solution(10 mL)of bis-(2-pyridylmethyl)-benzylamine(phdpa)(290 mg,1 mmol).After stirred for 30 min at room temperature,benzyl bromide (12.7 mg,1 mmol)in methanol(20 mL)was added and the reaction was carried out with stirring at room temperature for 2 h.The conversion of phdpa was evaluated by analyzing samples of the reaction mixture collected by HPLC.The selectivity is expressed by the molar ratio of formed ortho-benzylaton products to converted phdpa.
1.4 X-ray crystal structure determinations
Crystallographic data for[(phdpa)2Cu2(Br2)(μ2-Br](ClO4)(H2O)0.5(1)are listed in Table 1.The blue prism crystals of the complex were selected for lattice parameter determination and collection of intensity data at 293 K on a Rigaku Mercury2 CCD Area Detector with monochromatized Mo Kα radiation (λ=0.071 073 nm).The data were corrected for Lorenz and polarization effects during data reduction.A semi-empirical absorption correction from equivalents based on multiscans was applied.The structure was solved by direct methods and refined on F2by full-matrix least-squares methods using SHELXTL program[16].All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.Hydrogen atoms were introduced in their calculated positions.All computations were carried out using the SHELXTL-PC program package.
CCDC:759823.
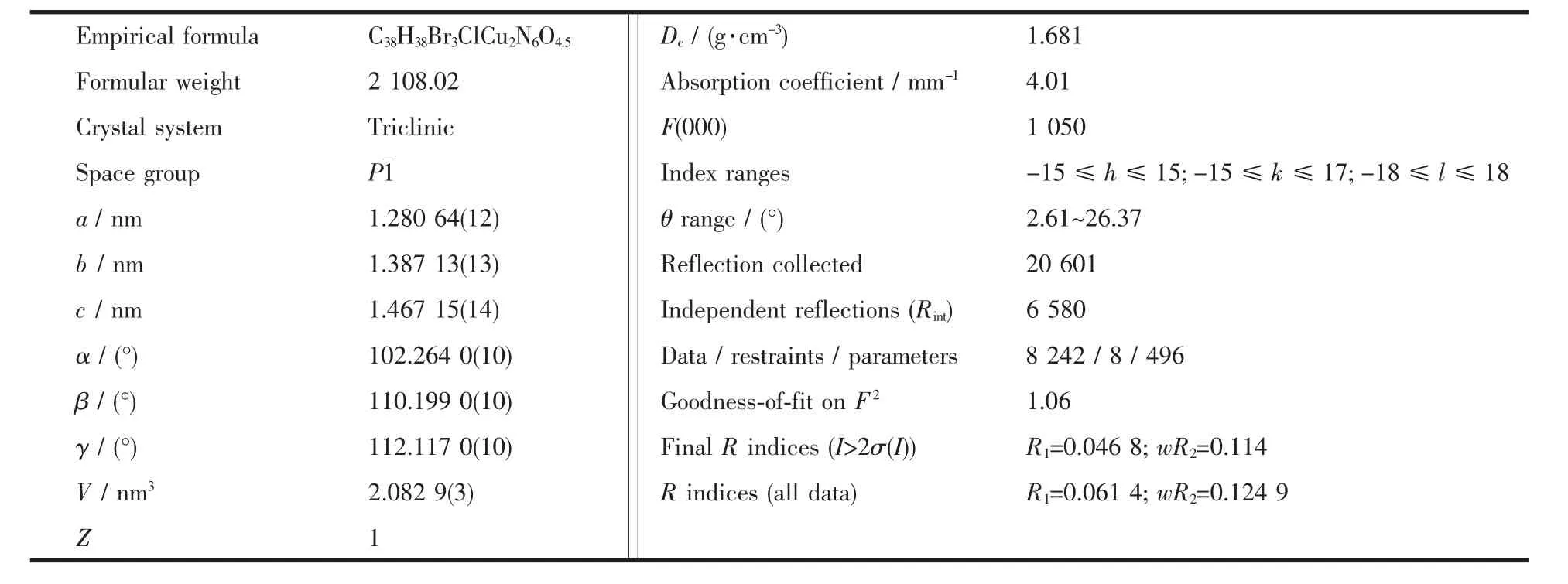
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement details for the complex 1
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Reaction of phdpa and Cu(ClO4)2with benzyl bromide
The spectroscopic titration for the solution of phdpa and Cu(ClO4)2and its interaction with benzyl bromide in methanol solution is shown in Fig.1.The solution of phdpa and Cu(ClO4)2show a d-d transition band at 641 nm indicating the formation of complex phdpa-Cu(ClO4)2(Fig.1 line a).A strong increase of the absorbance of d-d transition with red shift about 40 nm was observed when the benzyl bromide was added in 30 min.The results indicate the possible coordination of bromide anion to the complex phdpa-Cu(ClO4)2in methanol solution,which was confirmed by X-ray structure(Fig.2 and Scheme 1,(0)).However,there is no change for the absorption of d-d transition when the benzyl bromide was added to the solution of Cu(ClO4)4-phdpa system in MeCN,which are possible due to that the coordinated MeCN cannot be replaced by bromine atoms.Thisissimilarto the reported complex[Cu(phdpa)(CH3CN)2](ClO4)2(2).



2.2 Formation of N-[(2-benzyl)benzyl]-di(picolyl)amine perchlorate(2)
The formation of ortho-benzylation product N-[(2-benzyl)benzyl]-di(picolyl)amine perchlorate(2)was confirmed by1HNMR data.1H NMR spectra of N-[(2-benzyl)benzyl]-di(picolyl)amine showed the signals of the respective protons of the synthesized compounds(2),which were verified on the basis of their chemicals shifts,multiplicities.These spectra showed characteristic signals about CH2protons at 3.7~4.1 ppm and 5.89 ppm,which are assigned to CH2(benzylmethyl group,phCH2;pyridylmethyl group,pyCH2)protons.The relative high chemical shifs indicate the existence of protonated N-[(2-benzyl)benzyl]-di (picolyl)amine perchlorate (2).The ortho-benzylation may be due to the coordination of bromine in benzyl bromine to the copper atom(Scheme 1,intermediate(0)).
2.3 Spectroscopic characteristics of the complex 1
The IR spectrum of the complex[(phdpa)2Cu2(Br2)(μ2-Br](ClO4)(H2O)0.5(1)shows a broad band at 3 373 cm-1assigned to ν(OH)of the uncoordinated water which are confirmed by elemental analysis and X-ray structure.The bands between 2 828 and 3 081 cm-1for complex(1)can be assigned to the stretching vibration of saturated hydrocarbon and arene C-H in the IR spectra.The pyridyl ring vibration bands and δ (CH)vibration of pyridyl ring in complexes are all shifted.The pyridyl ring vibrations bands were approximately 1 612 and 1 574 cm-1for complex (1).The δ(CH)vibration bands of pyridyl ring for the complex(1)were found at approximately 773 cm-1.These shifts can be explained by the fact that the nitrogen atoms of pyridyl ring of the ligands donate a pair of electrons each to the central metal forming coordinate covalent bond.The absorption bands occurring in the IR spectra of the complex 1 at 1 100 and 623 cm-1corresponds to the asymmetric Cl-O stretching mode and the asymmetric Cl-O bending mode respectively.The electronic spectrum of the complex 1 exhibits four bands at 205,359,296 and 682 nm and these are assigned due to π→π*,C-T,n→π*and d-d transitions,respectively,thevisiblespectraexhibitsaband682nmcorresponding to five-coordinated square pyramidal Cu(Ⅱ) complex.
2.4 Crystal structure of[(phdpa)2Cu2(Br2)(μ2-Br](ClO4)(H2O)0.5
The molecular structure of[(phdpa)2Cu2(Br2)(μ2-Br](ClO4)(H2O)0.5with the atomic labeling scheme is shown in Fig.2 and selected bond lengths and angles are listed in Table 2.The ligand (phdpa)acts as a tridentate ligand toward the Cu(Ⅱ) atom.The Cu(Ⅱ) atoms are coordinated by three N atoms(N1,N2,N3 for Cu1,N4,N5,N6 for Cu2),one coordinated bromine atoms(Br1 for Cu1 or Br2 for Cu2)and a bridged bromine atom Br3 resulting in dinuclear Cu(Ⅱ)complex[(phdpa)2Cu2(Br2)(μ2-Br)](ClO4)(H2O)0.5.The Cu1 and Cu2 thus show distorted trigonal bipyramidal geometry.Atoms N1,N2,N3 and Cu1 form the equatorial trigonal plane(mean deviation 0.004 1)while Br3 and Br1 occupy the apical positions.The Cu1 atom locates in the center of this plane with N1-Cu1-N3 of 163.63(15)°and N2-Cu1-Br1 of 164.731(10)°.Atoms N4,N5,N6 and Cu2 also form a equatorial trigonal plane(mean deviation 0.045 4).Cu2 was shifted about 0.007 93 nm to this plane and the bond angles of N4-Cu2-N6 and N5-Cu2-Br2 was 164.24°and 151.37°,respectively.The angle of two trigonal plane is 130.7°.The Cu-N bond distances are in the range of 0.199 5(4)~0.205 5(3)nm and the Cu1-Br3 and Cu2-Br3 bond distances are 0.280 96(7)and 0.274 70(7)nm,which are longer than those of Cu1-Br1 and Cu2-Br2 bond distances (0.237 91(7)and 0.23939(7)nm).Cu1-Br3-Cu2 angle is 134.88(2)°.
2.5 Cu(Ⅱ)catalyzed ortho-benzylation of phdpa
The intramolecular ortho-benzylation of phdpa catalyzed by copper(Ⅱ) salt were summarized in Table 3.Allreactionsproceeded smoothly,and 32%~62%conversion of phdpa was reached in 2 h.In practice,when the benzylation was over,a purple deposit derived from reaction medium appeared gradually after magnetic stirring wasdiscontinued.The selectivity ofN-alkylation catalyzed by Cu(Ⅱ) salt depended on anions.Among these copper salt catalysts,only Cu(ClO4)2shows high ortho-benzylation activity.CuCl2and Cu(NO3)2has no obvious effect on the selectivity of ortho-benzylationof phdpa,but they increased total conversion of phdpa.The enhanced conversion in Cu(Ⅱ)complex reaction system may be due to the activation of C-Br bond by Cu(Ⅱ)complexes.The high selectivity(90%)for the intramolecular ortho-benzylation of phdpa-Cu(ClO4)2system was possibly due to the coordination of bromine atom in benzyl bromide to the copper(Ⅱ)atom in complex phdpa-Cu(ClO4)2(Scheme 1,intermediate(0)).The only 51%conversion of phdpa(in 1∶1 molar ratio of Cu(Ⅱ)salt and benzyl bromide)was due to the formation of Br bridged complexes,which is not a good catalyst to the ortho-benzylation.Experimental results indicate that Cu(ClO4)2was a good catalyst for the intramolecular ortho-benzylation of phdpa.
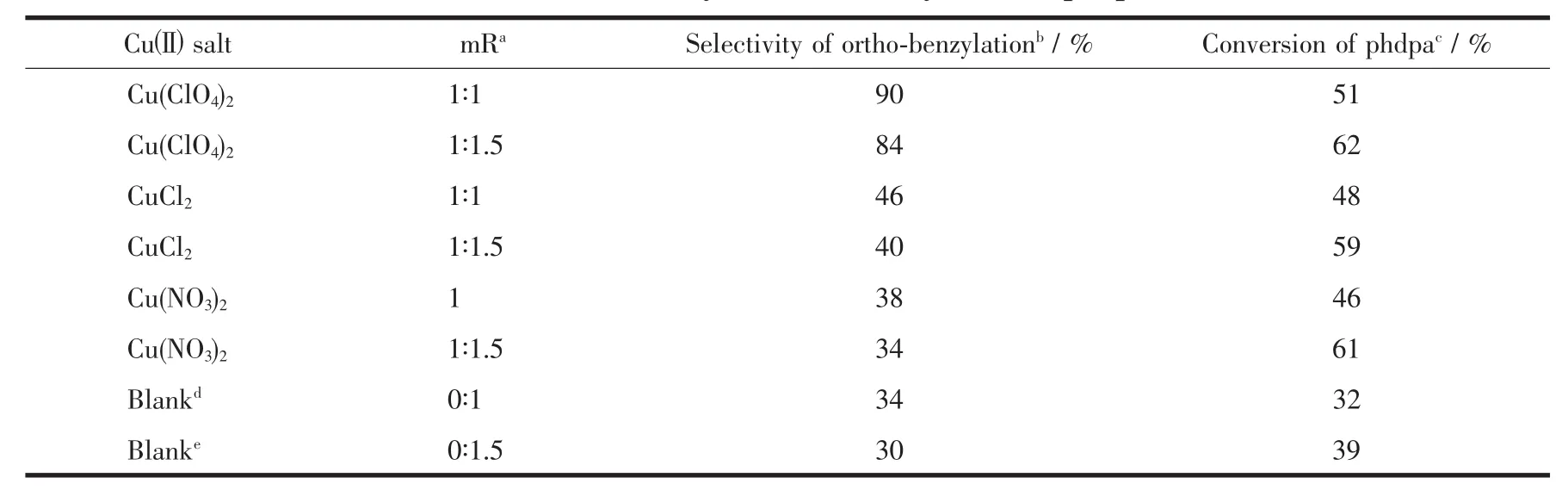
Table 3 Cu(Ⅱ)catalyzed ortho-benzylation of phdpa
3 Conclusions
The reaction ofN-benzyl di(pyridylmethyl)amine(phdpa)and Cu(ClO4)2with benzyl bromide in methanol leads to the ortho-benzylation of phdpa with the formation of μ2-Br-bridged copper(Ⅱ) complexes due to the coordination of bromine atoms to the center copper atom in phdpa-Cu(ClO4)2.Experimental results indicate that Cu(ClO4)2was a good catalyst for the intamolecular ortho-benzylation of phdpa.This experimental result is meaningful to find selective benzylation catalysts.
[1]Wurtele C,Sander O,Lutz V,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2009,131:7544-7545
[2]Ciana C L,Phipps R J,Brandt J R,et al.Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl.,2011,50:478-482
[3]Puckett C A,Ernst R J,Barton J K,et al.Dalton Trans.,2010,39:1159-1170
[4]Choi K Y,Ryu H,Sung N D.J.Chem.Crystallogr.,2003,32:947-950
[5]Chen Q Y,Zhou D F,Huang J,et al.J.Inorg.Biochem.,2010,104:1141-1149
[6]DU Jun(杜 俊),WU Zi-Yi(吴 子 怡),JIA Mo(贾 默),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2008,24(10):1669-1674
[7]HUANG Juan(黄娟),CHEN Qiu-Yun(陈秋云),WANG Ling-Yun(王玲昀),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2009,25(6):1077-1089
[8]CHEN Qiu-Yun(陈秋云),HUANG Juan(黄娟),LI Jun-Feng(李军峰),et al.Chinese Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2008,24(11):1789-1793
[9]Kunishita A,Scanlon J D,Ishimaru H,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2008,47:8222-8232
[10]Duong H A,Gilligan R E,Cooke M L,et al.Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl.,2011,50:483-486
[11]Zhao J L,Liu L,Sui Y,et al.Org.Lett.,2006,8:6127-6130
[12]Lee H G,Won J E,Kim M J,et al.J.Org.Chem.,2009,74:5675-5678
[13]Bachari K,Cherifi O.Cat.Commun.,2006,7:926-930
[14]Cain M F,Hughes R P,Glueck D S,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2010,49:7650-7662
[15]Li J F,Chen Q Y.Spectrachim.Acta A,2009,72:25-28
[16]Sheldrick G M.SHELXTL-97,Program for Crystal Structure Solution and Refinement,University of Gottingen,Germany,1997.
Cu(ClO4)2Induced Ortho-Benzylation of N-Benzyl Di(pyridylmethyl)amine and the Formation of μ2-Br-Bridged Copper(Ⅱ) Complexes
MA Zhen-Ping YE Ya CHEN Qiu-Yun*
(School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineer,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang,Jiangsu 212013,China)
The reaction of N-benzyl di(pyridylmethyl)amine(phdpa)and benzyl bromide in the presence of Cu(ClO4)2,leads to the ortho-benzylation of phdpa with the formation of μ2-Br-bridged copper(Ⅱ)complexes due to the coordination of bromine atoms to the center copper atom in phdpa-Cu(ClO4)2.CuCl2and Cu(NO3)2could not increase the selectivity for intramolecular ortho-benzylation of phdpa indicating that anions have great effect on the reaction.The ortho-benzylation product N-[(2-benzyl)benzyl]-di(picolyl)amine perchlorate was confirmed by NMR data and elemental analysis.X-ray crystal structure of μ2-Br-bridged dinuclear copper(Ⅱ)complex shows that two copper(Ⅱ)ions are coordinated by three N atoms,one coordinated bromine atom and a bridged bromine atom resulting in a distorted trigonal bipyramidal geometry.This experimental result indicates that Cu(ClO4)2could induce selectively the intramolecular ortho-benzylation of phdpa.This experimental result is meaningful to find selective benzylation catalysts.CCDC:759823.
benzylation;copper(Ⅱ)complex;N-benzyl di(pyridylmethyl)amine;crystal structure
O614.121
A
1001-4861(2011)11-2251-06
2011-04-09。收修改稿日期:2011-08-11。
国家自然科学基金(No.20971059)和江苏大学高级人才基金(No.06JDG050)资助项目。
*通讯联系人。 E-mail:chenqy@ujs.edu.cn
