大气探测与雷电防护研究进展
2010-07-07
大气探测与雷电防护
大气探测与雷电防护研究进展
2010年,大气探测所紧跟雷电监测、预警、防护以及地基云观测的国际研究前沿,不断开拓创新,在一些关键技术和关键科学问题方面取得显著的进步,主要成果如下。
1. 在触发闪电回击电流以及自动气象站雷电防护研究方面获得突破
闪电回击过程是雷电防护的主要对象,回击电流参数对雷电防护理论和标准研究以及防护产品检测具有重要参考价值。大气探测所多年来在广东开展了人工触发闪电试验,并不断提高电流测量技术。以多年电流采集数据为基础,统计分析了闪电放电过程的回击电流特征。结果显示,电流峰值的几何平均值为16.59 kA,半峰宽度的几何平均值是21.91 µs,10%~90%平均陡度的几何平均值为29.61 kA·µs-1,最大陡度的几何平均值是55.89 kA·µs-1,回击之后1 ms内的电荷转移为1.61 C,回击之后1 ms的比能量为6.60×103A2·s。广东触发闪电试验中的回击电流平均而言比其他研究中报道的回击过程要强。研究发现,峰值电流与10%~90%的平均陡度有一定的线性相关关系(R2=0.64),与最大陡度有较好的线性相关关系(R2=0.74),与回击后1 ms内的电荷转移有强的幂函数关系(R2=0.89),与回击之后1 ms内的比能量有显著的对数函数关系(R2=0.92)。此外,还观测到一次高度触发闪电的初始回击过程电流(以前的报道中只有4次这样的电流被测量,但只有2次在该阶段的电流数据质量较高而被分析),它具有较小的半峰宽度(2.12 µs),电荷传输(36.37 mC)和比能量(181.56 A2·s),但是其他的参数与前面统计的回击过程接近。
基于触发闪电,大气探测所还开展了真实雷电环境中自动气象站架空电源线和垂直信号线感应电压和电流的特征研究。结果发现,架空电源线中与回击(电流范围-6.67~-26.47 kA)对应的感应电压脉冲峰值电流显示出双极性的特征。次峰和主峰的感应电压范围分别为0.99~4.47 kV和-4.98~-1031 kV。脉冲持续时间111.00~155.40 µs。依据主峰之后波形恢复的形状,脉冲可以分为慢恢复和震荡恢复两种类型。在风速垂直信号上对应回击过程的感应电压波形也表现出两种类型,一种在主峰后有次峰,一种在主峰后无次峰,所有的主峰都呈现“V”形结构。垂直信号线上感应电压脉冲的半峰宽度、10%~90%上升时间、10%~90%平均陡度和脉冲峰值(主峰:-0.41~-3.10 kV;次峰:46.59 ~1861.17 V)要比架空电源线上的感应电压脉冲小很多。感应电压的幅度与回击电流的幅度没有明显的比例关系。通过连接电源线的电涌保护器的感应电流范围在-0.22~-1.64 kA,在电流脉冲之后的残压持续时间比在高电压试验中模拟记录的残压时间长很多。通过这个研究,对自动气象站遭雷击损坏的机理有了更清楚的认识,也为自动气象站的雷电防护提供了基础参数。

高度触发闪电(T201005)的光学照片(通道闪击到连接电流测量设备的引雷针上)Image shot by digital camera of the lower part of the altitude triggered lightning T201005 (the channel struck to the lightning rod connected with the current measuring equipment in series).
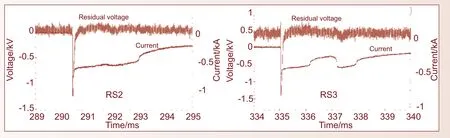
触发闪电(T200804)在采集器前端产生的通过SPD的残压和感应电流Waveforms of residual voltage and induced current produced by return strokes of T200804 through the SPD at the front of the acquisition device
2. 基于触发闪电对地闪定位系统的探测效能进行了初步评估
闪电定位系统(LLS)是目前最主要的雷电监测手段,在雷电预警以及雷电防护等工作中起着重要的作用,但其性能指标大多基于理论分析,客观检验工作一直比较缺乏。人工触发闪电由于时间地点确定,电流可测,在闪电定位系统的效能客观评估方面具有自身的独特优势。大气探测所利用广东从化人工触发闪电近距离光电观测的部分数据,分析了广东电网闪电定位系统对人工触发闪电事件及其回击过程的探测效率和探测精度。结果表明,对于14次包含有回击过程的人工触发闪电事件,闪电定位系统共探测到13次,探测效率约为93%(即13/14);对于能够利用观测资料确认的62次回击过程,闪电定位系统共探测到26次,探测效率约为42%;参与定位的站数≥3个的回击记录有24次,其中有21次回击过程属于接地点已知的地面触发闪电事件,闪电定位系统对这些回击过程接地点位置的平均定位误差约为760 m;对于其中9次有雷电流直接测量结果的回击过程,闪电定位系统雷电流峰值反演结果的相对误差约为14%。
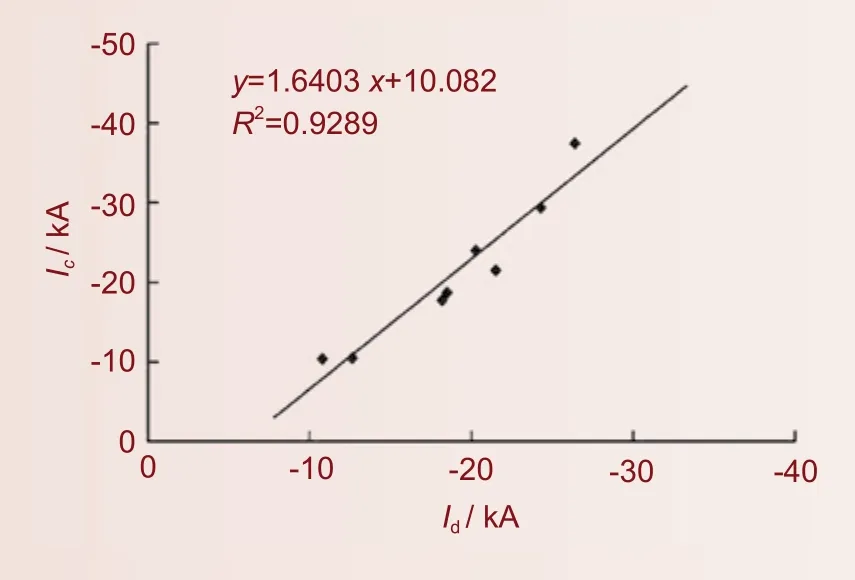
3. 深入认识了雷暴活动中的特殊放电——袖珍云闪的特征,并在台风闪电活动特征研究方面取得初步进展
袖珍云闪(CID)是近年来大气电学研究的一个热点,大气探测所利用位于广州从化和重庆两地的VLF/LF多站闪电探测系统观测到的CID,全面分析了CID不同于常规地闪和云闪的多方面的性质,并重点比较了正CID和负CID两者之间的差异。主要得到了以下几方面结论:CID能够产生非常大的电场变化,总体上比地闪回击产生的电场变化更大;负CID产生的电场变化总体上又比正CID大;CID的发生具有一定的孤立性,这种孤立性主要指在CID发生之前有其他放电事件的概率非常小。而正CID与负CID相比,前者更有可能引发其他的放电事件。CID产生的低频辐射在地面与电离层之间会发生反射,反射信号被测站记录到就形成电离层反射脉冲,利用反射脉冲和原脉冲之间的时间差关系,发展了一种对CID实现三维定位的新方法,该方法能够对较大范围内的CID实现较为准确的三维定位,利用这一点计算了大量正、负CID的放电高度,发现正CID主要发生于7~15 km,而负CID主要发生于15~18 km。CID与雷暴强度之间存在着一定的联系,总的来看,CID频数随着雷暴的增强有一定的增多趋势。通常情况下雷暴过程主要产生正CID,但随着雷暴的增强,负CID的比例也有增大的趋势。综合以上正CID与负CID之间的差异,可以认为负CID是一种更为特殊的放电事件。
随着闪电探测技术的发展,越来越多的试验和研究开始关注热带气旋中的闪电活动。利用全国闪电监测网获取的地闪定位资料,大气探测所初步分析了1999—2010年登陆我国广东地区的33个热带气旋的闪电活动时空分布特征。研究发现,不同强度热带气旋闪电活动存在差异,成熟台风闪电活动存在明显径向分布特征:闪电主要发生在200~500 km的外雨带区域,60~200 km的内雨带区域闪电活动较少,台风中心至60 km的眼壁区域则又呈现出闪电活动的密集区。内雨带具有层状云结构特性,具有较高的正地闪比例。眼壁闪电对台风强度及其变化具有一定指示作用,台风中心风速快速增大时,眼壁闪电爆发,闪电爆发几小时后中心风速达到极大值、中心气压最低。台风眼壁闪电的爆发,预示着台风将快速增强,对台风对流结构及其变化具有重要指示作用。利用多普勒雷达和TRMM卫星观测资料,研究了台风Molave(0906)闪电活动的时空变化与台风对流结构的演变关系,对台风不同区域的对流结构和水凝物粒子分布进行了对比。结果表明,外雨带比内雨带具有更强烈的反射率因子和上升气流,相同反射率值达到的高度,外雨带高于内雨带。云水、可降水、云冰和可降冰4种水凝物粒子的密度值和高度分布,外雨带明显大于内雨带。

正、负袖珍云闪CID的高度分布(正CID主要出现在7~15 km高度,负CID主要出现在15~18 km高度)Height distribution of the CIDs, (Positive CIDs mainly occur at the height of 7-15 km while negative CIDs mainly occur at the height of 15-18 km)

台风“莫拉菲”(0906)闪电活动和雷达回波叠加图Overlay of lightning activities and radar reflectivity of Typhoon Molave
4. 雷电监测预警系统平台获得进一步完善和推广,并服务于上海世博会的气象保障
2010年,大气探测所进一步完善了雷电监测和临近预警系统平台,针对雷电业务的需求,改进雷电临近预警算法,并更新了平台下雷电实时监测系统、雷电监测分析系统、雷电临近预警系统以及雷电预警产品评估系统的功能。新平台在2010年汛期的雷电预警业务中发挥了重要作用,全天候向中国天气网提供雷电监测预警公共服务产品。更新后的雷电临近预警系统在北京、湖北、湖南、青海等地开展了运行试验,大气探测所同步提供技术支持。以此为基础,2010年10月16—17日在成都开展了第4期的雷电临近预警技术交流会,对各地典型雷暴天气过程的预警预报进行分析和交流,有效提高了雷电预警的服务能力。同时还对改进后的雷电临近预警系统进行了应用推广培训,对升级情况和操作进行了详细的介绍。
针对上海世博会对雷电预警的要求,大气探测所先期对雷电临近预警系统进行了必要的算法升级,升级后的雷电临近预警系统CAMS_LNWS运行稳定、界面友好,能够快速生成0~1 h雷电发生概率、重点区域雷电发生概率以及雷电活动区域移动趋势等产品,为上海市气象局雷电预警信号的发布提供重要参考。在雷电临近预警系统参与上海世博会服务期间,大气探测所研究人员全程跟踪,提供不间断的技术支持,为世博会气象保障做出了自己的贡献。
5. 统计多年雷电灾害数据,对我国雷灾特点有进一步认识
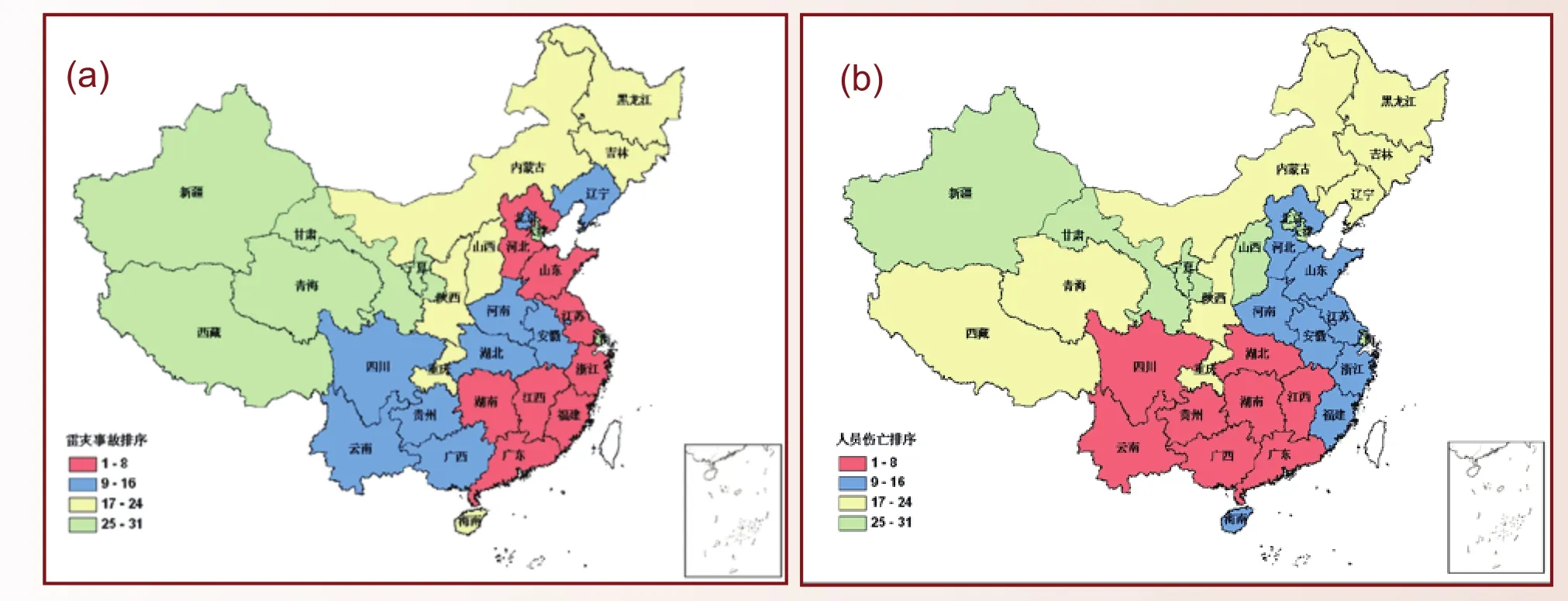
全国雷电灾害发生事故排序图(a)和全国雷电灾害人员伤亡排序图(b)The rank of each province in the number of lightning-related damages (a) and the rank of each province in the number of lightningrelated casualties (b) in China
利用1997—2010年全国雷电灾害数据库资料,分析研究了我国雷电灾情的时空分布等特征。我国雷电灾害多发生在南部地区和东部沿海地区,7—9月是雷灾多发季节。从年际变化上,1997—2007年雷电灾害呈上升趋势,2008年后有所下降。每百万人每年雷击死亡率和受伤率分别为0.31和0.28,且伤亡人数以农村居多。为了揭示我国不同区域雷击致人伤亡的易损度,采用闪电密度、人员伤亡频数、人口数和区域面积4个指标进行聚类分析,给出我国雷击致人伤亡的6类风险区划结果。结果表明,广东、上海和海南为1类地区,雷击致人伤亡易损度特征值高达每万平方公里6.89人;内蒙古、新疆和西藏为易损度最低的6类地区,每万平方公里人员伤亡0.14人,分类结果较好地反映了雷击致人伤亡事件的区域易损度特征。
6. 雷电光、电、磁探测设备研制和应用实现较大突破
光、电、磁信号是雷电发生过程中所产生的最基本特征参量,其有效探测已经成为雷电物理以及防护研究的必备手段。大气探测所紧跟雷电光、电、磁探测技术的前沿动态,总结了以往探测中存在的问题,针对光电磁探测设备的集成化及自动化,在探测平台集成及应用方面进行了研究和开发,其主要成果集中在以下几个方面:(1)研制开发了雷电光辐射探测装置和光触发装置,成功获得了闪电绝对光强和相对光强参量,实现了基于闪电光辐射信号特征的设备同步触发。(2)研制开发了雷电电场变化和三维磁场探测装置,获得了电场变化和三维磁场数据,实现了电场变化设备的标定。(3)研制开发了雷电集成化电磁场探测平台,并进一步集成了光辐射场的探测功能,成功获得了闪电光电磁信号的同步观测信息,实现了光、电、磁信号的自动同步测量,提高了获取数据的一致性。(4)基于雷电的电、磁集成化探测,研制开发了多功能单站闪电探测定位系统,成功获取了闪电电磁信号波形和闪电定位结果,实现了波形获取和定位输出一体化,能够同时满足科研和业务的双重需求。


多功能单站探测定位系统及其显示界面Multifunctional single-station lightning detection system and the display interface
7. 地基云自动化观测技术和系统开发取得显著进展
“地基云自动化观测关键技术研究和系统研制”是中国气象科学研究院基本科研业务费重点项目,其目标是研制具有我国自主知识产权的地基云自动化观测系统,建立综合应用可见光数字云图和云底高度测量结果的地基云自动化观测技术和方法,开发稳定可靠的软硬件系统,为实现地基云的全面自动观测奠定坚实的基础。项目通过3年的实施,截止2010年已取得如下成果:(1) 解决了地基全天空云观测软硬件系统的关键技术问题,包括摄像单元两种遮光结构的设计与实现以及地基全天空云图自动曝光控制的实现。研发出的样机经历了野外试验的检验,能够长期稳定可靠地运行,自动获取全天空可见光云图并计算得到总云量。(2) 建立了基于自适应阈值、局部阈值插值以及混合阈值等的云检测算法,提升了云检测的准确度;建立了一个初步的标准云图数据库和多种云图特征提取算法,并开发了基于内容的数字云图检索系统,为下一步开展云状识别方法研究奠定了基础。(3) 开发了多套专用软件,如鱼眼图像校正软件、云状人工识别分类软件、数字云图检索软件等,为顺利开展地基全天空云观测试验、建立云图数据库以及进行云检测和云状识别方法研究等提供了条件。
项目组开发的地基全天空云观测系统在北京市观象台、广东省从化市气象局、广东省阳江市气象局和中国气象科学研究院开展了较长时间的观测试验,积累了丰富的地基云图资料。在2010年WMO第8届国际探空仪系统对比试验中,地基全天空云观测系统提供了相应的产品,得到了较好的应用。
架设在北京市观象台的地基全天空云观测系统设备和部分结果示例The TCI device installed in the Beijing Meteorological Observatory and some sample results
Atmospheric Detection and Lightning Protection
Advances in Atmospheric Sounding and Lightning Protection Researches
In 2010, the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding kept close in step with the international research front of the lightning monitoring, warning and protection and ground-based automatic cloud observation, kept on exploring and innovating, and made great progress in some key technologies and scientif c points, which is summarized as follows.
1. Obtain a major breakthrough in the research of return stroke currents of triggered lightning and the lightning protection of the automatic weather station
The return stroke process of lightning discharge is the primary object of lightning protection. The parameters about the return stroke currents of lightning are of great value for the research on the theory and standard of lightning protection and the testing of the lightning protection products. The Institute of Atmospheric Sounding has conducted the Artif cially Triggering Lightning Experiment in Guangdong for many years and constantly advanced the current measurement technology. Based on the current data, the characteristics of the return stroke currents were investigated. The geometric mean (GM) value of the peak value current (IPeak) was 16.59 kA, the half-peak width (tHPW) was 21.91 µs, the 10%~90% risetime (t10%~90%) was 0.45 µs, the 10%~90% average gradient (G10%~90%) was 29.61 kA µs-1, the maximum gradient (GMax) was 55.89 kA µs-1, the charge transfer in 1 ms after the beginning ofthe return strokes (Q1ms) was 1.61 C, and the action integral in 1 ms after the beginning of the return strokes (AI1ms) was 6.60×103A2s. The RSs in GCOELD were, on average, stronger than those reported by other authors referenced in this study. The peak value current had a general good linear relation with G10%~90%(determination coefficient (R2=0.64), a good linear relation with GMax(R2=0.74), a strong power function relation with Q1ms(R2=0.89), and an excellent logarithmic function relation with AI1 ms (R2=0.92). Additionally, the current of the initial-stage return stroke (ISRS) of an altitude TLF was analyzed (as we know, only four ISRSs were reported in previous studies, of which, only two were investigated with their high-quality current waveforms) and found to have small tHPW(2.12 µs), charge transfer (36.37 mC) and action integral (181.56 A2s), but was similar to other RSs for all other parameters.
Using the triggered lightning as a tool, the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding also do a piece of research on the characteristics of the induced voltage and current generated by triggered lightning on an overhead power line and on the vertical signal line of an automatic weather station (AWS). Pulses of induced voltage on the overhead power line corresponding to the return strokes with the peak currents ranging from -6.67 to -26.47 kA showed bipolar features. Sub-peaks and main peaks ranged from 0.99 to 4.47 kV and from –4.98 to –10.31 kV, respectively, and pulse durations ranged from 111.00 to 155.40 µs. The pulses were classified into two types according to the shape of the recovering waveform following the main peaks: slow-recovery type and oscillating-recovery type. The induced voltage waveforms corresponding to the return strokes on the vertical signal line of wind speed were also of two types: with and without a sub-peak after the main peak. All the main peaks were “V” shaped. Values of halfpeak widths, 10%–90% risetimes, 10%–90% average gradients, and peaks of pulses (main peaks, –0.41 to –3.10 kV; sub-peaks, 46.59 to 1861.17 V) on the vertical signal line were much smaller than those of pulses on the overhead power line. The amplitudes of the induced voltage were out of proportion with the amplitudes of the return stroke currents. The peaks of induced currents through the surge protection device (SPD) embedded on the power line ranged from –0.22 to –1.64 kA. The duration of residual voltage after the end of the current pulses was longer than that recorded in high-voltage experiments. Through this study, we got a better understanding on the mechanism of the AWS being destroyed by lightning. The results provided basic parameters for the research of the AWS’s protection from lightning.
2. Estimate the performance of the cloud-to-ground lightning location system by using the triggered lightning as the real source
Lightning location system (LLS), as the main tool for lightning monitoring, plays an important role in lightning warning and lightning protection. However, the performance index of LLS is always determined by theoretical analysis, there being less testing based on an objective method. Artificial triggered lightning, with its clear triggering time and location and measurable current, is of unique advantages in objectively estimating the performance efficiency of the LLS. Utilizing the near-distance optical and electrical observation of the triggered lightning, the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding tested the detection efficiency and detection accuracy of the LLS operated by the electricity department of Guangdong. The results show that the LLS detected 13 of 14 triggered lightning f ashes, the detection eff ciency of the LLS on lightning f ash being calculated to be about 93%. For the 62 return stroke processes determined by the observation data, only 26 of them were detected by the LLS, the detection efficiency on the return stroke being about 42%. A total of 24 of 62 return stroke processes were detected by 3 or more sensors of the LLS. By comparing the detection data of the LLS with the real location of a total of 21 return stoke processes, the average location error of the LLS was found to be about 760 m. The LLS showed a relative error of 14% in the inversion of the current peak value, by comparing with the current data measured in the base of 9 return stroke channels.
3. Get a deep understanding on the characteristics of a kind of special discharge in the thunderstorms —compact intracloud discharges, and make some progress in the study on the lightning activities in typhoons
Compact intracloud discharge (CID) is a hot research topic of atmospheric electricity in recent years. On thebasis of a large amount of CIDs recorded by VLF/LF lightning location networks in Guangzhou and Chongqing, the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding analyzed the multiple characteristics of CIDs that are different from regular intracloud and cloud-to-ground lightning. Differences between +CIDs and –CIDs were specially investigated. There were conclusions in following respects: CIDs produce very large electric field changes, which are generally larger than that produced by return strokes. Compared with +CIDs, –CIDs generally produce larger electric f eld changes. CIDs are usually isolated with other discharge processes, which means that CIDs rarely follow other discharge processes. Compared with –CIDs, +CIDs have much higher possibility to be the initiation processes of regular discharge processes. Low frequency radiation signals produced by CIDs can be ref ected between the ground and the ionosphere and can produce ionospheric reflection pairs. Using the time differences between the reflection signals and the original signals of CIDs, a new method for determining 3D locations of CIDs are developed. This method can accurately determine 3D locations of CIDs in a large area. With this method, discharge heights of large amounts of both polarities of CIDs are computed, and it is found that +CIDs mainly occur at a height of 7~15 km while –CIDs mainly occur at a height of 15~18 km. There are certain relationships between CIDs and convective strength. CID rate generally increases with convective strength. Thunderstorms usually produce much more +CIDs than –CIDs, but the percentage of –CIDs increases as the convective strength increases. The above differences between +CIDs and –CIDs are comprehensively analyzed, and –CID is considered to be a more special type of discharge.
With the development of lightning detection technology, more and more f eld experiment and research began to focus on lightning activities in tropical cyclones. Using cloud-to-ground lightning data from the national lightning detection network, the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding analyzed the temporal and spatial lightning activities in thirty-three tropical cyclones making landfall in Guangdong, China. The results show that characteristics of lightning activities varied in tropical cyclones with different intensity. A distinct radial variation in flash density was observed , with a maximum in the outer rainbands (200 to 500 km from the center), a light flash density in the inner rainbands (60 to 200 km from the center) and weak maximum in the eyewall (60 km from the center). The precipitation structure of inner rainband is similar with stratiform cloud and the ratio of positive flashes is the highest in the three regions. The inner core lightning is predictive to the typhoon’s intensity and its change. When the central wind speed increases, the eyewall lightning bursts. After several hours of the outbreaks of eyewall lightning, the central wind speed reaches the maxima. Therefore, an outbreak of lightning in the core region might indicate the imminent intensification of tyhoon, and has precisive value of typhoon’s convective structure and its change. With Weather Surveillance Radar and TRMM satellite data, the relationship between lightning activities and precipitation structure was examined for Typhoon Molave (0906) and an important piece of evidence for the convective structure in the inner and outer rainbands was provided. Results showed that the outer rainbands had higher radar reflectivity and updraft than the inner rianbands. The region of the same reflectivity in the outer rainbands reached a higher altitude. Vertical hydrometeor profiles in both rainbands were calculated and showed a higher cloud and precipitation ice density and located height in the outer rainbands, which indicated a higher ice particle content in the melting region. The knowledge of lightning activities in landfalling typhoons will be quite useful to landfalling typhoon forecasters.
4. The system platform of lightning monitoring and warning is further improved and serve for the weather service at Shanghai World Expo
In 2010, the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding further perfected the construct of the lightning monitoring and lightning nowcasting and warning system platform, advancing the algorithm and updating the function of the lightning real-time monitoring system, lightning detection and analysis system, lightning nowcasting and warning system (CAMS_LNWS) and evaluation system of lightning warning products, which commonly comprised the platform. The new platform had played an important role in the operation of lightning warning in the flood season in 2010, providing the public product of lightning monitoring and warning to the “Weather China” website withoutany break. Under the technical assistance coming from the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding, the updated CAMS_ LNWS was tested in Beijing, Hubei, Hunan, Qinghai and many other provinces. Based on the testing, the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding conducted the phase 4 seminar sessions on lightning nowcasting and warning technology in Chengdu from 16 to 17 October 2010. The participants at the seminar sessions analyzed and exchanged their knowledge on the warning and prediction of the lightning activities and thunderstorms in their working places. After that, the researchers of the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding detailedly introduced the improvement and testing of the new-version CAMS_LNWS and trained the participants to master the operation of the CAMS_LNWS. The newversion CAMS_LNWS was f nally distributed to the participants for the further application in other meteorological bureaus and other departments who were concerned about the lightning activities.
In order to meet the requirements of the Shanghai World Expo for lightning warning, the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding updated the algorithm of the CAMS_LNWS in advance. The updated CAMS_LNWS, with stable running, friendly interface and fast computing capabilities for the products of 0~1 hour lightning probability, lightning probabilities in key locations and the moving trend of the lightning activities, contributory to that, Shanghai Meteorological Bureau released the lightning warning sign for the World Expo. During this process, the researcher of the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding devoted themselves to the weather service at Shanghai World Expo by being fully involved to provide sustaining technical assistance.
5. Count the years of lightning disaster data and get a further understanding of the characteristics of lightning disasters in China
According to the data of National Lightning Hazards Database from 1997 to 2010, spatial and temple distribution of lightning disasters in China were analyzed. The southern and eastern costal areas have more frequent lightning disasters, and the disasters mainly occur in summer months from July to September. Lightning-related damages have increased in the period from 1997 to 2007 and then began to decrease since 2008. The national fatalities and injuries per million people per year are 0.31 and 0.28 respectively, and rural people suffer the most. In order to reveal the vulnerability of lightning stroke which leads to injuries and deaths in different regions, four indexes—lightning density, casualties frequency, population, and regional areas are used to evaluate the vulnerability by lightning stroke and provide six different kinds of risk zones which lead to injuries and deaths in China. Guangdong, Shanghai and Hainan pertain to vulnerability evaluation extreme high areas. In these areas, the vulnerability reaches up to 6.89 people for every ten thousand square kilometers. Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang and Tibet belong to vulnerability evaluation the lowest areas, there are only 0.14 people injured and dead for every ten thousand square kilometers. The result of classif cation is appropriate, and preferably ref ects regional vulnerability evaluation characteristics of the events in which the lightning stroke causes people’s casualties.
6. Development and application of the compositive detection device of lightning optical, electrical, and magnetic signals are achieving great progress
The signals of optical strength, electric field and magnetic field are the fundamental characteristic parameters of lightning process. The detection has become a necessary step for the research on lightning physics and protection. Following the frontier of optical, electrical and magnetic detection of lightning and summarizing the problem occurring in previous detection, the Institute of Atmospheric Sounding focused much on the integration of the detection platform and its application. The main research content and results are as follows: (1) The apparatus for the detection of optical radiation and the device using optical radiation to trigger the acquisition of other signals were developed. Based on this apparatus, the absolute and relative optical strength produced by lightning discharges was obtained, and multiple signals were synchronously collected with the optical radiation serving as the triggering source. (2) The data of the electric field changes and the 3D magnetic field associated with the lightning discharge, which were observed by the newly designed electric f eld change mill and 3D magnetic f eld sensor, were successfully obtained. Meanwhile, the electric field change mill was standardized for the real value but relativevalue. (3) The detection device of optical radiation was integrated into the platform of electromagnetic f eld to form a new comprehensive observation system, which made contributions to the synchronous collection of the multiple signals produced by lightning and the high degree of consistency among the different signals. (4) On the basis of the system integrating electric and magnetic devices, a new multifunctional single-station lightning detection system, by which the electromagnetic waveform was synchronously obtained and the location of the cloud-to-ground lightning was successfully completed. Furthermore, the results were output at the same time, which served for the requirements of both the research and operation.
7. Techniques and system development of ground-based automatic cloud observation have obtained striking progress
The project “Study on the key techniques of ground-based automatic cloud observation and development of system” was funded by the key project of basic research fund of Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences. Its goal is to manufacture an automated ground-based cloud observing system with independent intellectual property rights, establishing a ground-based cloud observation technique and method by integrating the visible light digital cloud image and cloud-base height, developing of stable and reliable hardware and software systems, and to lay a solid foundation for accomplishing a comprehensive automated observing of the ground-based cloud. Through three years of implementation, the project mainly achieved the following results by 2010: (1) Some key technical problems have been solved for ground-based cloud observing hardware and software systems, including the design and actualization of two kinds of light-shelter schemes for the camera unit, the accomplishment of automatic exposure control for achieving ground-based total-sky cloud images. The developed prototype has experienced some field tests, which can be long-term stable and has a reliable operation, automatically capturing the totalsky cloud images and calculating total cloudage. (2) Several cloud detection algorithms have been researched, including adaptive threshold, local threshold and hybrid threshold, which enhanced the accuracy of cloud detection. A preliminary standard cloud image database and several cloud feature extraction algorithms have been established and a content-based digital cloud images retrieval system has been developed, which will lay the foundation for future cloud type identification. (3) Several sets of special software have been developed, including fisheye image correction, cloud type identif cation and classif cation of artif cial, digital cloud image retrieval software, etc. These works provide convenient conditions for carrying out ground-based total-sky cloud observation experiments, establishing cloud image database, developing of cloud detection and cloud type identif cation methods.
The ground-based total-sky cloud imager (TCI), developed by the project team, has carried out a long-time observing experiments in the Beijing Meteorological Observatory, Conghua Meteorological Bureau, Yangjiang Meteorological Bureau and Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, and accumulated a wealth of groundbased cloud images.In the 8th WMO international radiosonde comparison experiments, TCI provided the corresponding product and got a preferable application.
