Interest Balancing Model of Separate Consent to Personal Information
2022-10-17HuangLi
Huang Li
(a.Shanghai Jiao Tong University Koguan School of Law;b.Shanghai Key Laboratory of Integrated Administration Technologies for Information Security,Shanghai 200030,China)
Abstract:The separate consent system for personal information is original to China's legislation.There are contradictions and conflicts in understanding and application in many scenarios of separate consent.Therefore,the interpretative theory shall be developed to stabilize the construction foundation of the system.There is a dilemma in the application of separate consent due to the fact that different legally applicable persons have different value choices in terms of the relevant interests,and thus the balancing of those interests differs.Legislators balanced the values of personal dignity and freedom,production and living efficiency,public interests,etc.,to develop the personal information consent system,which consists of general consent,separate consent,and exempted consent.The results of the study are synthesized into a four-quadrant diagram illustrating the interest choices associated with a separate consent system for personal information.To counteract judicial arbitrariness of different judgments in the same case,it is also necessary to stratify the interests in the interest balancing according to the fourquadrant diagram.In order to address the conflicts in understanding and application of separate consent,an interest-balancing model of a separate consent will be developed through the interest hierarchy.
Keywords:separate consent;interest balancing;public interests;institutional interests;personal information
The understanding and application of separate consent to personal information have attracted high attention and demand in the industry.The separate consent involves the enterprise's considerations of multi-party cost and the core user experience.Therefore,as China's(PIPL)takes effect,conflicting questions arise.originated from the concept of a separate consent,which had not been incorporated into previous laws,and there is no comparable law in other countries.The enrichment and development of interpretative theory are therefore necessary to stabilize the design value and construction foundation of the system.Separate consent studies in China have produced few results at the present time.It is necessary to conduct theoretical research and application analysis on the separate consent system in academic and practical circles and introduce the legislative experience of China's personal information protection to the world.
1 Debate between Consent and Separate Consent in Relationships
Separate consent to personal information processing means that the information processor shall obtain the " explicit and voluntary consent " of the information subject prior to performing the specific act of processing personal information.Separate consent requires a higher degree of specificity of the consent content,and it is also referred to as " independent and explicit special consent " as opposed to general and package consent.Furthermore,each separate consent should be conducted through a pop-up window,a separate agreement,a separate page,etc.On one hand,this increases the cost of product design and compliance for enterprises.On the other hand,it makes different effects on users.Separate consent is respect for conservative users'rights and interests.Continually separate consent is inefficient and wasteful for extroverted and efficient users.It is important to note that personal information has dual attributes of private law and public law.Consequently,it is essential to take both the protection of personal rights and interests as well as the value of the circulation and utilization of information into consideration.PIPL is characterized by these two fundamental values,which are particularly evident in the separate consent system.
The purpose of this paper is to elicit the application question of separate consent through a case.It is necessary for multinational companies to transmit employees'personal information abroad in order to manage their human resources.Is it necessary to obtain separate consent from employees?Many multinational companies face this problem.Employees are subjected to background checks as part of the information transmission process.Background checks may not be agreed to by employees,which adversely affects the normal operation of the organization.In accordance with Article 13 of the PIPL," the individual's consent is not required for the conclusion or performance of a contract to which the individual is a contracting party or for conducting human resource management under the labor rules and regulations developed in accordance with the law and a collective contract signed in accordance with the law;"Additionally,Article 39 of the PIPL stipulates that,if personal information processors disclose personnel information outside of the People's Republic of China,individuals shall be informed of the overseas recipient's name,organization name,contact information,processing purposes,processing methods,categories of personal information,and a description of the methods and procedures by which individuals exercise the rights provided for in this law over overseas recipients,etc.,and obtain the consent of each individual separately.As a result,the application of PIPL Article(30)to this case is exempt from the requirement of separate consent.However,the provisions of Article 39 require separate consent.Separate consent has been applied in a manner that is contradictory and conflicting.
Opinion 1:Separate consent is not required.In terms of semantic interpretation," consent " is the superior concept to " separate consent ".Why is separate consent required if no consent is required?When the cross-border purpose of personal information is included in the processing purpose for obtaining individual consent,Zhang Linghan argues that separate consent is not required.For instance,when multinational corporations collect personal information for the legitimate purpose of human resource management,the cross-border processing of personal information of employees is consistent with the legitimate purpose and no additional consent is required.Long Weiqiu believes that the " separate consent " model is also one of the informed consent rules.Therefore,this article employs Article 13(2)naturally and does not require separate emphasis.As Cheng Xiao argues,whether the personal information processors process the personal information with the individual's consent or in compliance with laws and administrative regulations,as well as providing the personal information to other personal information processors,they must inform the parties concerned and obtain their separate consents.unless otherwise required by laws and administrative regulations(the situations in PIPL Article 13(2)-(7).
Opinion 2:Separate consent is required.From the perspective of system interpretation,Article 39 of the PIPL is a special provision for cross-border data,which shall take precedence over the application of the general provisions of Article 13.Article 14 of the PIPL provides that "Where personal information is handled based on individual consent,said consent shall be given by individuals under the precondition of full knowledge,and in a voluntary and explicit statement.Where laws or administrative regulations provide that separate consent or written consent shall be obtained to handle personal information,those provisions are to be followed."Separate consent,according to Shi Yuhang,is not merely a subset of " consent " but a higher standard of consent.Regardless of the legal basis for processing personal data," separate consent " is required under the applicable circumstances.In the PIPL publicity meeting,Yang Heqing from the Legislative Affairs Committee of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress,stated:"The situations required for human resource management should be evaluated in light of particular scenarios.If sensitive personal information is involved,greater care should be taken."Hua Qing from the Cyberspace Administration of China stated,"Whether the enterprise is for human resource management or other purposes,it shall adhere to the Personal Information Protection Law's principles of legitimacy,rationality,and minimization."
The relationship between consent and separate consent is the central issue in the construction of the separate consent system,and we shall clarify the construction's focal point in light of the transmission of personal information by multinational companies.First,is the position of separate consent in the system.Since the logical relationship between the concepts of consent and separate consent under PIPL is unclear,it is necessary to systematically sort out the system of separate consent and investigate its rationale,given that contextual interpretation cannot resolve the application conflict.Second,is the value of separate consent choice.When contextual and systemic interpretations fail to resolve the issue,additional methods,such as theoretical and sociological interpretations,may be employed.Legislation is the process of recognizing and expressing interests,and recognizing and expressing interests varies according to the applicant of the law.Prior to adjusting the various interests,it is necessary to comprehend and recognize them.Therefore,it is necessary to conduct additional research on the hierarchy of individual interests and value choices.
2 The Systematic Approach to Separate Consent
Although Roman jurists had previously asserted systematic interpretation,it was Savigny who established the influential doctrine.Larenz generalized the locutionary approach to systemic interpretation from Savigny's doctrine that,when determining the meaning of a concept,we should take into account the structural characteristics of the law in which it is located.The rigorously deduced Pandekt jurisprudence and nineteenth-century conceptual jurisprudence viewed jurisprudence as a logical system in which " there is a meaningful sequential arrangement between legal norms "utilizing " the location of the legal provisions "as the abstract concept evaluative interpretation.According to the orientation-based systemic interpretation method,separate consent's systemic structure,including the relevant concepts of superordination,congruence,and subordination,shall be sorted out first.
2.1 General Consent
2.2 Exempted Consent
The exempted consent provisions in paragraphs 2-7 of the PIPL are reflected in Article 13 of the PIPL.Samples are used to stipulate this.In view of China's economic level and institutional development,these scenarios represent the benefits that should be considered.Scholars have also argued that the rational limitations of information subjects as natural persons and the intellectual gap when confronting information controllers are conducive to creating problems such as the " decision dilemma ".As consent has limitations,consent is not required for the legitimate processing of personal information.
2.3 Separate Consent
Some data processing behaviors are subject to separate consent,which is intended to alert individuals in a more prominent and distinctive manner than general consent,for example,a separate pop-up window,a separate consent agreement,a separate description of the processing purposes,methods,deadlines,and objects.It is not possible to grant general authorization through the adoption of package agreements or the licensing of multiple entities.PIPL reflects five main situations:(1)external provision(Article 23);(2)public provision(Article 25);(3)use of images and identification information collected by image acquisition and personal identification equipment installed in public places for purposes other than maintaining public security(Article 26);(4)processing sensitive personal information(Article 29);(5)overseas provision(Article 39).
2.4 Written Consent
As stated in Article 14 of PIPL:"Whenever personal information is processed with individual consent,that consent shall be given voluntarily and explicitly,subject to full disclosure.For processing personal information,any law or administrative regulation that requires separate consent from an individual or a written consent shall prevail."Article 1008 of China's Civil Code states,"As part of the development of new drugs and medical devices or the development of new prevention and treatment methods,clinical experiments need to be approved by the competent department and approved by the ethics committee upon examination.According to the law,subjects or their guardians shall be informed of the purpose,use,potential risks,and other details,and their written consent shall be obtained."Essentially,written consent is a method for protecting the right to life and health,and it remains a separate consent with specific and unique formal requirements.
Comparatively,the consent regime in China's PIPL is heavily influenced by the EU GDPR,and the conditions for lawful processing under Article 6 of the GDPR are exempt from consent except for(a)obtaining the consent of the information subject,and(b)-(f).According to Article 7 of the GDPR Conditions for Consent,written consent is a requirement,similar to the separate consent requirement in China's PIPL.The information shall be presented in a clear and distinct manner from the other matters,in an intelligible and easily accessible form,using clear and straightforward language.The consent regime is the basis for the protection of personal information and therefore needs to be continually refined to accommodate different scenarios of application.In China,to reflect the fine granularity of the protection of personal information,a separate consent system is based on the refinement of the existing consent system.
In various articles about the PIPL,there are provisions for general consent,exempted consent,and separate consent.We may fall into the trap of creating a static two-dimensional logic tree if we analyze the external system only from the context,assuming that consent and exempted consent are superior concepts,and that separate consent and general consent are inferior concepts,resulting in a conclusion that separate consent is naturally not required in cases of exempted consent.However,the three consent cases are not classified under the same criteria,nor under the same dimensions,and therefore cannot be analyzed by either/or logic.In order to move toward a substantivist paradigm of value analysis,we need to abandon the formalist paradigm of conceptual analysis.
3 The Value Choice of Separate Consent
By using conceptual jurisprudence,the adjudication process is able to withstand scrutiny due to its formal rationality,which facilitates the unification of the application and understanding of the law,and the recognition of the legitimacy of legal decisions.Lawmaking is open,legal norms are abstract,and legislators make legal omissions,so it is difficult for existing legal norms to fully cover the facts and to meet the legal judgment needs in accordance with the so-called logical self-contained system of conceptual jurisprudence.Currently,substantive analysis is necessary in order to interpret the facts,legal norms,and the interaction between facts and the law using the principles and methods of substantive analysis.The most widely used method involves value analysis,in which the value level and value choices behind the legislation are explored,and the legal implications between concepts and reality are clarified.
3.1 The Hierarchy of Values
Individuals'personal information should be protected because it contains information about them,and the rights or interests of those individuals need to be protected.The concept of subject rights implies that people as subjects should be respected,independent,and treated equally(within the scope of citizens'basic rights).It should be the personality interests at the level of private law.Its legitimacy is derived from the self-determination of personal affairs,which are derived from the constitution's subject status,freedom,and dignity.In reality,a person's right to self-determination of personal information is a fundamental right that protects his or her dignity and freedom.
Efficiency refers to the ability of human beings to obtain the means of life from nature,which reflects the relationship between man and nature.As we move into the era of "Time is Life ",efficiency represents not only the property value but also the value of a person.A situation in which the efficiency of individuals and organizations is reduced and costs increase is likely to result in a reduction in society's efficiency,as well as a violation of individuals'basic survival rights and interests.According to PIPL Article 13(ii),the value of production and living efficiency is the reason for exempted consent.The first requirement is the conclusion or performance of a contract in which an individual is a party,which is the most common scenario in the business world.An agreement should be based on the consent of all parties,i.e.the consent of both parties.The priority of efficiency in performing the contract,therefore,does not require separate consent.Second,enterprises shall also deal with personal information based on human resource management,which is also common in enterprise business activities.The management of human resources involves the handling of personal information.Individual consent will impose a greater burden on the enterprise in terms of management.Overall,the exempted consent matters outlined in PIPL Article 13 correspond to the most common situations in which personal information is processed.The principle of " efficiency value first " shall be implemented in accordance with applicable laws and regulations(contract law system and labor law system).In PIPL Article 13(6),it is stated that the principle of efficiency is applied to the legitimate dissemination of public information.Without the need for secondary consent,the default information subject has consented to the legitimate public use of the information.
There is a need to ensure a balance between the rights of individuals regarding their personal information,the rights and freedoms of others,and the public interests.PIPL reflects the following public interests:a.It is necessary for the performance of statutory duties or obligations.This is the processing behavior of the administrative organ based on " enforceability " and " publicity ",representing the will of the state.Thus,the legal basis for its processing of personal information is and can only be legal provisions,not " consent ".b.As part of the response to public health emergencies,the public interests are also taken into account.During the period of epidemic prevention and control,both Europe and the United States have defended the right to privacy,but neither balances the relationship between personal informed consent and the need to control the spread of the disease.As a result of the complete reliance on the voluntary uploading of information by citizens,epidemic prevention and control have been delayed.The social system of my country should also fully reflect the value prioritization of social and public interests,and epidemic control should take precedence over personal information control.c.Use personal information within a reasonable range for the purpose of reporting news,monitoring public opinion,etc.These actions are all aimed at protecting the interests of the public.
3.2 Diagram of Value Choice Four Quadrants
In addition to personal dignity and freedom interests,the value of production and living efficiency and public interests are also included in the interests of personal information.It was built keeping these three interests in mind when the consent system was implemented in the field of personal information protection.According to PIPL,the basic consent system consists of three components:general consent,exempted consent,and separate consent.However,it continues the principle of European personal data protection,in which the legitimate basis for processing personal data is taken as the legal basis.Consent is not the only factor.As stated by GDPR,the protection of personal data is not an absolute right,but shall be balanced between different interests in accordance with the principle of proportionality.Generally,in the U.S.,only laws at the federal level set the threshold for " prior consent " for specific situations and a particular scope of personal information,while in general,the subject of the use of personal information may choose to " opt-in ",and " default consent " and " opt-out " are also considered to be respecting the subject's rights.The essence of the consent system is not the absolute protection of interest,but rather a dynamic balance of value choices.In spite of the fact that this balance is not static and solidified,it changes according to situational characteristics,cultural background,common sense habits,and other legal regulations.
By exempting consent,the value of production and living efficiency is strengthened,as well as the value of the public interests.In a particular scenario,the two values mentioned above are prioritized.It is a system of interests balancing in which personal dignity and freedom are prioritized in situations that have a serious impact on an individual's rights and interests.There are three values that shall be taken into account when developing the general consent system:the value of personal dignity and freedom,the value of public interests,and the value of production and quality of life.The author draws a four-quadrant diagram of value choice for the consent system in order to illustrate the relationship between value choice and the three systems.
As shown in Figure 1,the abscissa indicates the progressive increase in the importance of personal dignity and freedom from left to right,whereas the ordinate indicates the progressive rise in the importance of production and living efficiency,and public interests.As a result of the intersection of these two coordinates,three of the four quadrants correspond to the value ranges of general consent,separate consent,and exempted consent,respectively.
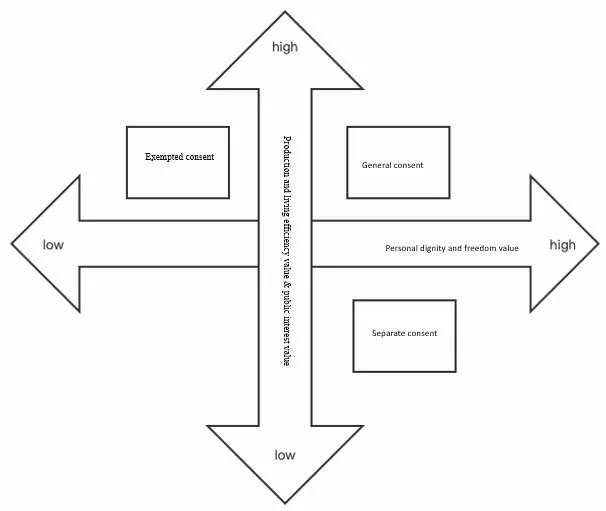
Figure 1 Four-Quadrant Diagram of Value Choice
Accordingly,separate consent does not constitute a subset of general consent,nor does it constitute a subordinate concept of general consent.There are two values located in different quadrants of the value coordinate.In response to the sliding of the value on the axis,the three forms of consent will be merged and transformed.As a whole,general consent,separate consent,and exempted consent provide the legitimacy basis for processing personal information.As a result of exempted consent,it is necessary to illustrate that it does not imply that it is possible to achieve production,living efficiency,or public good by infringing upon personal dignity and freedom.There should be no subjective fault associated with the infringement,at least.The exempted consent cannot be viewed as an infringement of affirmative subject matter because consent is not the same as authorization.Therefore,the exempted consent cannot be regarded as an infringement of affirmative subject matter.An individual's right to selfdetermination of information is not infinitely amplified by the personal consent system,but rather is the result of forfeiting time efficiency in order to achieve procedural justice.
4 Interest Balancing Model of Separate Consent
4.1 An Introduction to the Theory of Interest Balancing
Since the interest balancing theory was developed by Japanese scholars Isoichiro Kato and Yingichi Hino in the 1960s,it has dominated the field of Japanese civil law interpretation for decades and contributed to the development of civil law interpretive theory and civil trial practice as well.Interest balancing theory has been widely applied in the field of civil justice trials in China since its introduction.Corporate legal affairs have been elevated to an unprecedented level of prominence with the rapid development of Internet technology and business models,and have become the first line of legal understanding and application.The compliance action of corporate legal affairs is a process of interaction and balance of various interests,and interest balancing runs through the work of legal affairs all the time.The implementation of " individual consent " is subject to the checks and balances of technical costs,user product experience,user informed consent rights and interests,regulatory requirements,and other interests.Accordingly,one of the important methods of interpretive theory is the interest balancing theory for understanding and applying the law.
4.2 Interest Balancing Model of Separate Consent
As a result of the interest hierarchy structure,the author derived a model for balancing interest if separate consent was obtained.Based on the case scenarios,the interests were divided into the specific interests of the parties,group interests,institutional interests,and public interests.Different separate consent schemes were proposed and graded according to their level of interest protection.The four interests have a hierarchical relationship.Priority will be given to the more abstract interests.First,the public interests shall be taken into consideration.Second,it is concerned with the implementation of institutional interests,group interests,and specific interests of the parties involved.
Returning to the opening case,for the purpose of human resource management,a multinational company needs to transmit the personal information of its employees abroad.Does it need the individual consent of the employees?
There are two main parties involved in this case:the employee and the multinational company.In particular,employees have a right to self-determination over their personal information,and they possess absolute control over how the information is circulated.In order to reduce corporate operating costs,multinational companies wish to manage employees'personal information transmission abroad and reduce the need for separate consent for these cumbersome processes.The interests of employees and employers are clearly in conflict when employees do not want their personal information to be transferred abroad.Employees'right to self-determination of their personal information is protected by separate consent,but multinational companies'interests are compromised by exempt consent.
There are two types of groups involved in this case:the workers and the processors of personal information.In addition to the specific interests of the parties involved,group interests are important considerations since the guiding effect of the decision will have an impact on the behavior of the relevant groups.It is the obligation of the labor law to adjust and protect the basic rights and interests of worker groups.In addition,the rights and interests of workers'personal information shall be protected in accordance with the concept and framework of social law.Social law characteristics and legal significance of personal information protection law.Since multinational companies are considered to be personal information processors under the PIPL,the outcome of this adjudication affects the decisions of the whole group of processors.Although separate consent strengthens workers'rights to control their personal information,it also affects their productivity and creates even more opportunities,so it is difficult to determine whether the program is positive or negative,with the tendency to have no effect.Separate consent,however,increases the obligations of personal information processors and therefore is detrimental to the privacy of individuals.This group of workers is also relatively adversely affected by the exemption consent program.In spite of this,it reduces the burden on personal information processors,which has a positive effect.
Institutional interests connect the interests of the group with the public interests of society and are an abstraction of the general rules of society.A consent system and a management system cross-border in the field of personal information protection are the main legal systems at play in this case.The consent regime contains both individual consent and exempted consent provisions.Therefore,either option is beneficial to the consent regime in general.China's,as well as relevant standard rules,is incorporated into the personal information exit management system.The main purpose of the personal information exit system is to protect the ability of individuals and the government to control relevant information.Currently,this does not include the circulation and use of personal information.Thus,if a multinational company sends personal information across borders without the consent of individuals,this will be detrimental to cross-border information transmission.
There are several issues of public interest involved in this case,most notably national security,group data security,and macroeconomics.The impact on social public interest is not significant if the personal information of employees that is not in large quantities,sensitive,and related to national security is transmitted across the border.
For human resource management purposes,multinational companies transfer employee information abroad.Considering that the information transferred is background check information,employees will either disagree with the transfer or be wary of the company when they learn about it,so it will affect the operation of the organization.Background check information is used within a reasonable range without affecting the employee's interests.If the PIPL Article 39 separate consent program is adopted,multinational companies as well as personal information processors with similar needs will be adversely affected.In one sense,this will increase the cost of managing the business.Conversely,it also hampers the right of the company's management to exercise its autonomy.Even if the PIPL Article 13 exemption consent option is adopted,employees'interests will not be affected and multinational companies'interests will be protected.It is evident from the total number of benefits with positive effects in the model that the waiver of consent is a relatively better option.
It will be necessary to provide more details in reality,such as when the quantity of cross-border information and the sensitivity level of its content reaches a certain level,which may involve the management system of crossborder personal information and the public interests of the society,then a separate consent or security assessment may be needed.
Epilogue
There will undoubtedly be some contradictions and conflicts in the understanding and application of the separate consent system,which was developed from the personal information protection legislation of China.In order to resolve these conflicts,it is necessary to recall the legislative value choice of the consent system.It is the result of legislators'balanced choices between the values of personal dignity and freedom,the value of production and living efficiency,and the value of the public interests.PIPL's consent systems include general consent,separate consent,and exempted consent.The interest balancing theory also applies to this scenario.To avoid subjective arbitrariness,the conflict problem of separate consent shall be resolved by using a model based on the hierarchical structure of specific interests,group interests,institutional interests,and public interests.An examination of how institutional interests and public interests are combined with personal information protection scenarios should be conducted in practical application.
