The Efficacy of Banxia Baizhu Tianma Decoction (半夏白术天麻汤) Combined with Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction (血府逐瘀汤) for Essential Hypertension and the Effects on Endothelial Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
2020-12-31LIUYinan刘逸南LEIYanTAOLili陶丽丽YANGJingXIUChengkui修成奎WANGXueLIUYiqing刘奕清WUDanWUYeHUYanhong胡艳红WANGJiali王佳丽YUBowen于博文
LIU Yi-nan (刘逸南), LEI Yan (雷 燕), TAO Li-li (陶丽丽), YANG Jing (杨 静), XIU Cheng-kui (修成奎),WANG Xue (王 雪), LIU Yi-qing (刘奕清), WU Dan (吴 丹), WU Ye (吴 烨),HU Yan-hong (胡艳红), WANG Jia-li (王佳丽), YU Bo-wen (于博文)
1 Experimental Research Center, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700,China
2 Department of Internal Medicine, Eye Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100040, China Correspondence to: Prof.LEI Yan, Tel: 13651217893,Email: 13651217893@163.com
ABSTRACT Objective:Banxia Baizhu Tianma Decoction (半夏白术天麻汤, BBTD) combined with Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction (血府逐瘀汤, XFZYD) is widely used to treat essential hypertension in China, but its efficacy remains largely unexplored.We systemically summarized relevant evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to assess the therapeutic efficacy of BBTD+XFZYD.Methods:This review retrieved 6 databases like Pubmed, Cochrane Library, Embase, CNKI, et al.RCTs of BBTD+XFZYD plus conventional Western drugs (experimental group) and conventional Western drugs alone (control group) for hypertension was collected from the database establishment to August 5, 2020.And the outcomes included clinical total effective rate, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), nitric oxide (NO)and endothelin-1 (ET-1).All studies' risk of bias were assessed by the Cochrane Collaboration tool 5.1.0.The data was statistically analyzed by RevMan5.3 Software.Results:Six studies with 608 participants were identified.About duration of treatment, 4 studies were 1 month, 2 studies were 2 months.The quality presented a high risk of bias.The experimental group showed that clinical total effective rate of the 1-month and 2-month was higher (P<0.00001), the systolic pressure was significantly lower (P<0.05), the NO increased (P<0.00001), and the ET-1 decreased (P<0.00001) compared with the conventional Western drugs used alone.However, DBP was significantly lower (P<0.05) at 2 months of treatment.Conclusion:BBTD+XFZYD plus conventional Western drugs might reduce blood pressure, improve clinical efficacy,repair endothelial function, but still need high-quality RCTs to better assess the outcomes.
KEYWORDS Banxia Baizhu Tianma Decoction; Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction; Essential hypertension;Endothelial function; Systematic review; Meta-analysis
INTRODUCTION
Essential hypertension is a complex syndrome affected by a variety of genetic and environmental factors, affecting the health of more than 1.3 billion people[1-3].Between 2000 and 2010, the global age-standardized prevalence of hypertension in adults aged over 20 years increased by 5.2%[3].In China, at least 23.2% of adults suffer from hypertension[4].Hypertension as the primary risk factor for cardiovascular disease, renal failure and premature death[5,6]imposes a great burden on public health.
The endothelium forms an essential component of the vasculature and is crucial for cardiovascular disease (CVD) because of its structural barrier function and its biological activities.[7]Endothelial layer can regulate vascular tone and growth by producing several vasoactive substances such as nitric oxide (NO), endothelin (ET) and angiotensin II[8].Studies[9-12]in recent years have shown that the occurrence of hypertension is related to NO deficiency and ET-1 increases.Endothelial function plays an important role in the occurrence and development of hypertension.It already exists in the pre-hypertension stage, which can cause changes in the function of microvessels and participate in the link of target organ damage[13].Therefore, it is necessary to explore anti-hypertensive therapy from the perspective of improving endothelial function.Some anti-hypertensive drugs have been shown to improve endothelial function, such as nebivolol and carvedilol[14], but the conventional treatment has some problems, such as poor compliance and adverse reactions[15].Despite continuous progress in the development of antihypertensive drugs, prevalence of hypertension worldwide pinpoints necessity for identification of novel and vigorous anti-hypertensive therapy[16].
Complementary and alternative medicines (CAM)are becoming more popular and frequently used in patients with CVD.Studies conducted in western countries report as much as 65 % of the study population using some form of CAM[17,18].Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), an important part of CAM,is widely accepted and used in clinical practice.TCM is a potential therapy for due to its advantages of small adverse reactions, syndrome differentiation for treatment, stable curative effect, long duration, overall regulation, and no obvious drug dependence[19].Banxia Baizhu Tianma Decoction (半夏白术天麻汤, BBTD) and Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction (血府逐瘀汤, XFZYD) are famous TCM formulas, which are included in Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China[20].They contain 18 crude drugs, including Pinellia ternata (半夏), Atractylodes macrocephala(白术), Gastrodia elata (天麻), tangerine peel (陈皮), Poria cocos (茯苓), Glycyrrhiza (甘草), Ginger(生姜), Red jujube (红枣), Angelica sinensis (当归),Rehmannia glutinosa (地黄), Prunus persica (桃仁),Flos Carthami (红花), Fructus Aurantii (枳壳), Radix Paeoniae Rubra (赤芍), Bupleurum chinense (柴胡),Ligusticum wallichii (川芎), Platycodon grandiflorum(桔梗), Achyranthes bidentata Blume (牛膝).They have been widely used to treat essential hypertension in clinical practice for centuries in China[21-23].Furthermore, both BBTD and XFZYD can improve endothelial function by increasing NO synthesis and decreasing ET-1 content[24-27].
Currently, BBTD+XFZYD combined with antihypertensive drugs has been widely used as an effective method for the treatment of essential hypertension and improve endothelial function in China.And a number of clinical studies of BBTD+XFZYD reported the clinical effect ranging from case reports and randomized clinical trials.However, there is no critically appraised evidence such as systematic reviews or meta-analys is on efficacy of BBTD+XFZYD for essential hypertension and endothelial function to justify their clinical use and their recommendation.Therefore, this study followed the principle of evidence based medicine "PICOS".It performed a randomized controlled trial (RCTS) for BBTD+XFZYD combined with conventional western medicine for hypertension, and performed a metaanalysis for it to assess the current clinical evidence of BBTD+XFZYD for essential hypertension and the effects on endothelial function.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have followed a previously published systematic review protocol[28].This study has also been registered in INPLASY (registration number:INPLASY202080013, DOI number: 10.37766/inplasy2020.8.0013).
Inclusion Criteria for Study Selection
Types of studies.
All randomized controlled clinical trials(RCTs)of BBTD+XFZYD for the management of patients with essential hypertension, whether blinded or not, was included.There were no restrictions on methodological quality of eligible RCTs, language,or time.Animal studies and reviews were not considered.
Types of patients
We included adult patients (18 years of age and older) with essential hypertension.It was no limit to sex, ethnicity or disease severity.Essential hypertension was confirmed according to the standard diagnostic criteria "2018 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension"[29]:systolic blood pressure (SBP)140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP)90 mmHg.
Types of interventions
The control group was treated with conventional western treatment and combined treatment of BBTD+XFZYD and conventional treatment was used in the experimental group.And the experimental group was treated with BBTD+XFZYD (monotherapy or with conventional treatment.The same conventional pharmacotherapy must be used in the control group).There was no limit to forms of BBTD+XFZYD, including decoction,tablets, capsules, pills, powders, and extracts.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes.
The primary outcome indicators are determined according to Guidelines for the Clinical Research of Chinese Medicine New Drugs[30]: (1)markedly effective: DBP reached the normal range and decreased >10mmHg or DBP did not fall to normal,but it had decreased20mmHg.(2)effective: DBP reached the normal range and decreased <10mmHg or DBP decreased by 10-19mmHg, but did not reach the normal range or SBP decreased >30mmHg.(3) invalid: did not meet the above criteria.Clinical total effective rate=[(markedly effective+effective)/total number of patients]*100%.
Secondary outcomes.
The secondary outcome includes: Systolic Blood Pressure(SBP), Diastolic Blood Pressure(DBP),Nitric Oxide(NO), endothelin-1 (ET-1) and adverse reactions, etc.
Search strategy
Two researchers systematically searched the published reports on RCTs of BBTD+XFZYD treatments in patients with essential hypertension throughout six databases: Pubmed(1959-Augest 5,2020), Embase(1966-Augest 5,2020), Cochrane Library(1996-Augest 5,2020), China National Knowledge Infrastructure(1979-Augest 5,2020),Wan fang Database(1989-Augest 5,2020), and VIP Information(1989-Augest 5,2020).No restriction on publication language and status was preset.The following keywords were used: essential hypertension, hypertension, blood pressure, banxia baizhu tianma and xuefu zhuyu.Otherwise, two researchers also manually retrieved literature from the Chinese Clinical Trial Register, Baidu and Google to acquire other unpublished articles.
Study selection
Two researchers first searched all the literatures independently, filtering the titles and abstracts of the relevant studies to eliminate duplication.Two other researchers reviewed all extracted titles and abstracts and screened the full text to determine eligible studies based on previous inclusion/exclusion criteria.Discrepancies were resolved through discussion or consultation with a third researcher.
Data Extraction
Information of the eligible studies were extracted by two researchers independently using a standardized data extraction form.The extracted details included: (1) basic information of the studies: title, authors' name, and publication time; (2) basic characteristics of the patients: age,gender, sample size, diagnosis, blood pressure and endothelial function before the treatment; (3)basic characteristics of the studies: methodological quality, interventions in the treatment and control groups, compositions, dosage, duration of treatment,administration methods of BBTD+XFZYD; (4)primary and secondary outcome measures.The correspondence authors of the included studies were contacted by email and telephone number to obtain the missing data.
Quality Appraisal
Two researchers independently assess the risk of bias in the eligible studies through the risk assessment tool for bias in the Cochrane Handbook version 5.1.0[31].The evaluation was mainly made from seven aspects: (1) random sequence generation(selection bias); (2) allocation concealment (selection bias); (3) blinding of participants and personnel(performance bias);(4) blinding of outcome data(attrition bias); (5)incomplete outcome data (attrition bias); (6)selective reporting(reporting bias); (7) Other biases.And it evaluates the seven aspects according to "low risk", "Not clear" and "High risk".Two researchers independently completed the methodological quality evaluation of the eligible studies.If there was any disagreement in the assessment, we would discuss or consult with a third researcher.
Statistical Analysis
Meta-analysis was processed by Review Manager software(version 5.3).Dichotomous outcome was expressed by risk ratio(RR), continuous data as mean difference (MD), both with 95%confidence interval(CI).P<0.05 was considered to indicated a statistically significant result.The heterogeneity test was determined by combining the Q value test with the I2test.WhenP>0.1 and I2<50%,there was no heterogeneity, and the fixed-effect model was used for analysis.If I2was over 50%,there was moderate heterogeneity, and if I2was over 75% is considered as high heterogeneity[32], we would use random-effect model to pool the result.
RESULTS
Study Selection
We finally identified 223 articles according to the search strategy.33 studies were excluded because of duplicated publication.After screening the abstracts, 179 articles were excluded because of animal studies, review, with errors that affect the final analysis result, or the study objectives were different from that of this review,etc.Full texts of 11 articles were assessed for eligibility and 6 eligible studies[33-38]were ultimately identified in the review.The included RCTs were all conducted in China and published in Chinese.The flow diagram of study search and selection was summarized in Figure 1.

Figure 1.The Flow Chart of Study Search and Selection
Study Characteristics
There were 608 patients (304 patients in each groups) in the 6 studies.The average age of the participants ranged from 52 years to 61 years, and the proportion of male patients was about 60.7%.The studies included only interventions with BBTD+XFZYD plus conventional western treatment versus conventional western treatment alone.Conventional drugs referred to treatment according to the guidelines, including angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors(ACEI),angiotensin receptor blocker(ARB),beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, nitrates and platelet aggregation inhibitor.The treatment duration ranged from 1 month to 2 months.Only 1 study reported the adverse reactions.The characteristics of eligible studies were summarized in Table 1.
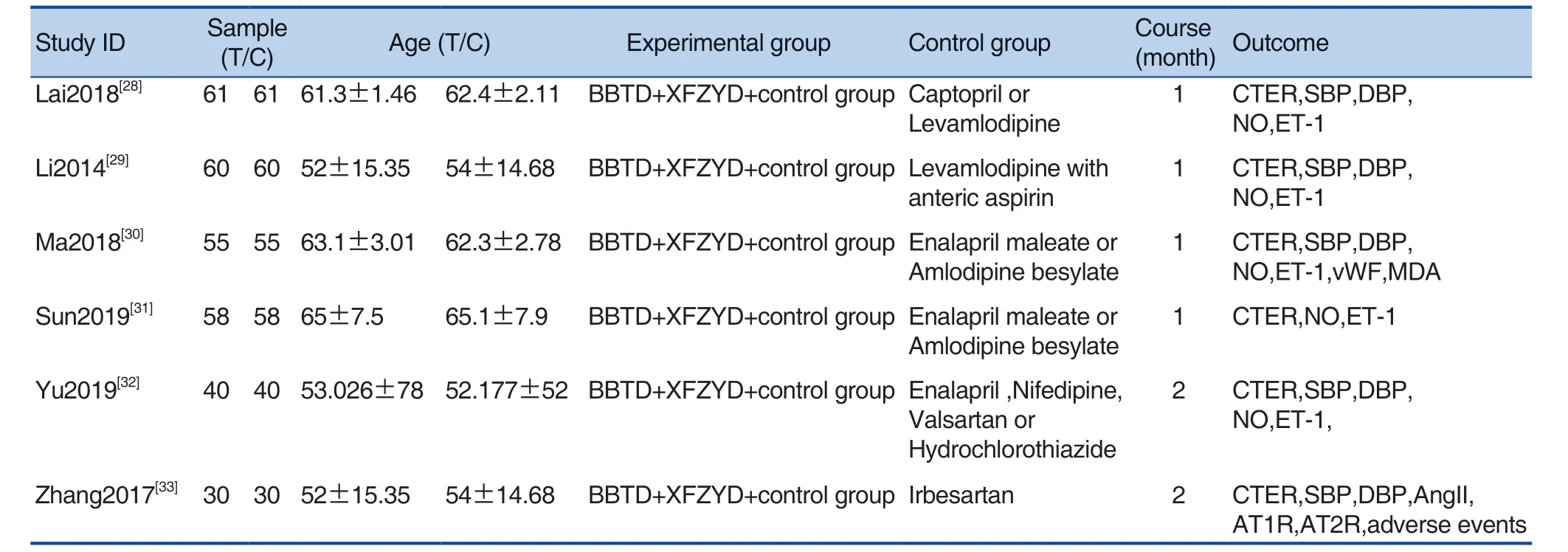
Table 1.The Characteristics of Eligible Studies
Methodological Quality
All of these studies indicated randomization,but most of them did not describe it clearly.5 studies described specific random methods, 4 studies[33,35-37]used random number table, 1 study[38]used the way to choose random numbers, 1 study[34]did not mention the detail of random methods.Otherwise,all of these studies did not describe the method of allocation concealment.None of the six studies described blinding and placebo in the control group.Although there was no patient dropped out of the 6 studies, but none of studies had a pre-trial estimation of sample size.The risk of bias was shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
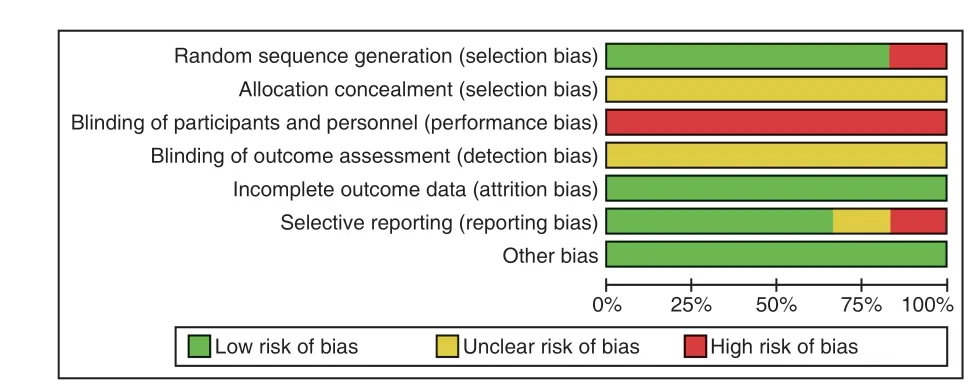
Figure 2.Risk of Bias Graph

Figure 3.Risk of Bias Summary
Outcomes Measurements
Primary outcomes
Clinical total effective rate was reported in all the 6 studies, and there was no heterogeneity in the included studies (P=0.90; I2=0%) using the fixedeffect model.According to RR statistics, the clinical effective rate of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group (RR=1.27, 95%CI[1.18,1.38], Z=6.13,P<0.00001), and the difference was statistically significant, as shown in Figure 4.
Subgroup analysis was performed according to the duration of treatment.4 studies' duration were 1 month[33-36], and there was no heterogeneity in these studies (P=0.87; I2=0%), so the fixed-effect model was adopted.Meta analysis results showed that the clinical efficiency of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group (RR=1.28,95%CI[1.18, 1.40], Z=5.64,P<0.00001), and the difference was statistically significant.The duration of treatment in 2 studies[37,38]was 2 months, and there was no heterogeneity in the included studies (P=0.70;I2=0%).The fixed-effect model was used for analysis,and the analysis results showed that the clinical effective rate of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group (RR=1.24, 95%CI[1.05,1.47], Z=2.48,P=0.01<0.05), and the difference was statistically significant, as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 4.Comparison of the Clinical Total Effective Rate between Experimental Groups and Control Groups Under Fixed Effects Model
Secondary outcomes
SBP
Systolic blood pressure comparisons were reported in 4 studies[33,34,37,38], but none of the studies compared blood pressure by grade.There was moderate heterogeneity in the studies (P=0.09,I2=54%), using the random effect model.According to the statistics of MD, the SBP in the experimental group was lower than that in the control group(MD=-4.80, 95%CI[-7.46, -2.14], Z=3.54,P=0.0004), and the difference was statistically significant, as shown in Figure 6.Sensitivity analysis was carried out, and there was a large heterogeneity in these studies, which was related to the duration of treatment.1 month and 2 months duration of treatment were analyzed respectively.The duration of treatment of 2 studies[33,34]was 1 month, and there was no heterogeneity in the included studies (P=0.35; I2=0%), using the fixed effect model.The result showed that the contraction of the experimental group was lower than that of the control group (MD=-2.96, 95%CI[-5.24,-0.66],Z=2.53,P=0.01), and the difference was statistically significant.The treatment duration of the two studies was 2 months[37,38].There was no heterogeneity in the inclusion studies (P=0.33; I2=0%).The fixed effect model was used for analysis.The analysis results showed that the SBP in the experimental group was lower than that in the control group (MD=-7.01, 95%CI[-9.89, -4.12], Z=4.76,P<0.00001), and the difference was statistically significant, as shown in Figure 7.
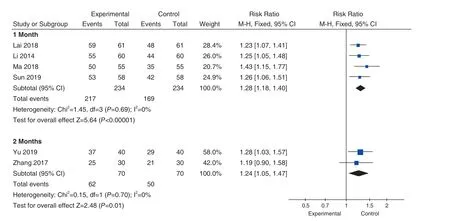
Figure 5.Comparison of the 1 or 2 Months Duration's Clinical Total Effective Rate between Experimental Groups and Control Groups Under Fixed Effects Model
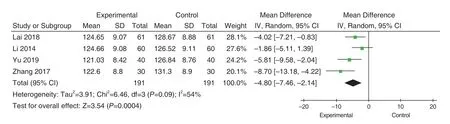
Figure 6.Comparison of the SBP between Experimental Groups and Control Groups Under Random Effects Model
DBP
4 studies[33,34,37,38]reported DBP comparisons, and there was no significant heterogeneity in these studies(P=0.17; I2=41%).Using the fixed-effect mode, we found diastolic depression in the experimental group was lower than that in the control group (MD=-3.08,95%CI[-4.66, -1.50], Z=3.82,P=0.0001), and the difference was statistically significant, as shown in Figure 8.Analyzed according to the duration of treatment.Two studies'duration[33,34]was 1 month, and there was moderate heterogeneity in the included studies (P=0.14; I2=54% ), using the random effect model.Meta analysis results showed that there was no statistical difference between the experimental group and the control group (MD=-2.30,95%CI [-5.24, -0.64], Z=1.53,P=0.13), as shown in Figure 9.Two studies'duration was 2 months[37,38].There was no heterogeneity in the inclusion studies(P=0.26; I2=20%).The results showed that the DBP in the experimental group was lower than that in the control group (MD=-4.43, 95%CI[-7.04,-1.82], Z=3.32,P=0.0009), and the difference was statistically significant, as shown in Figure 10.

Figure 7.Comparison of the SBP About 1 or 2 Months Duration between Experimental Groups and Control Groups Under Fixed Effects Model
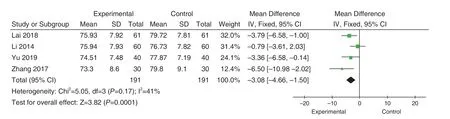
Figure 8.Comparison of the DBP between Experimental Groups and Control Groups Under Fixed Effects Model
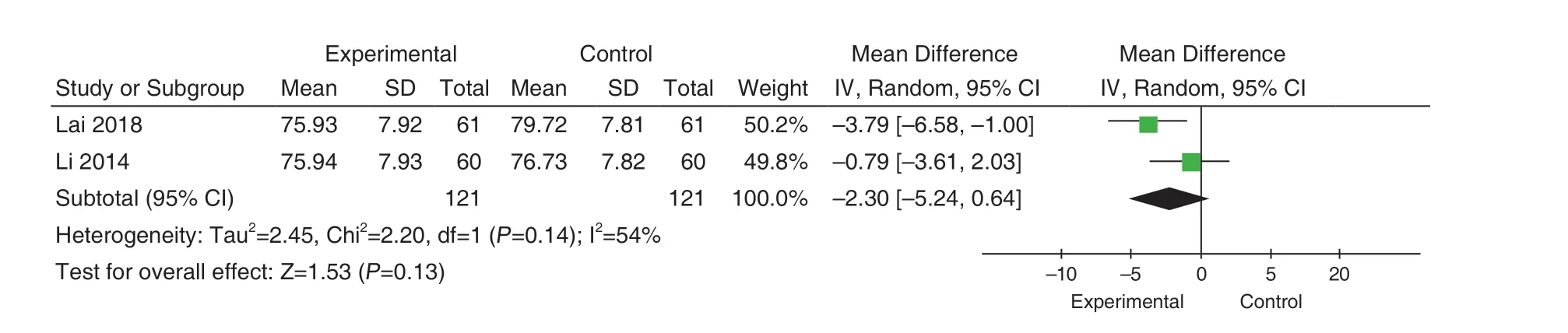
Figure 9.Comparison of the DBP of 1 Month Duration between Experimental Groups and Control Groups Under Random Effects Model
NO
5 studies[33-37]reported NO comparisons.Heterogeneity test was performed on the included study, showing high heterogeneity (P=0.0002;I2=82%).By sensitivity analysis, we considered that one study[8]induces high heterogeneity.After the exclusion of this literature, no obvious heterogeneity exist (P=0.71; I2=0%), using the fixed effect model.According to the statistics of MD, NO of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group.(MD=0.95, 95%CI[0.69, 1.21],Z=7.17,P<0.00001), the difference was statistically significant, as shown in Figure 11.
ET-1
5 studies[33-37]reported ET-1.There was no heterogeneity in the included study (P=0.46; I2=0%),using the fixe effect model.According to the statistics of MD, ET-1 of the experimental group was lower than that of the control group.(MD=-9.86, 95%CI[-11.63, -8.09], Z=10.92,P<0.00001), the difference was statistically significant, as shown in Figure 12.

Figure 10.Comparison of the DBP 2 Months Duration between Experimental Groups and Control Groups Under Fixed Effects Model
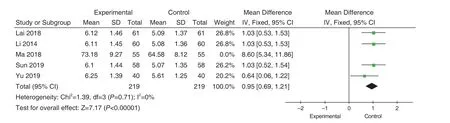
Figure 11.Comparison of the NO between Experimental Groups and Control Groups Under Fixed Effects Model

Figure 12.Comparison of the ET-1 between Experimental Groups and Control Groups Under Fixed Effects Model
Adverse reactions and publication bias
Only 1 study[38]reported the adverse reactions.There were 1 patient had dizziness, nausea,vomiting and chest tightness in the experimental group and 1 patient in the control group.Due to no sufficient number of studies, we failed to perform funnel plot to describe the comparison of adverse reactions and publication bias.
DISCUSSION
This systematic review included 6 RCTs studies and 608 participants.We found that BBTD+XFZYD combined with conventional western drugs had a higher clinical efficiency (P<0.05), which can significantly reduce SBP (P<0.05) and DBP (P<0.05),improve the NO (P<0.05) and reduce the content of ET-1 (P<0.05) compared with conventional western drugs alone for essential hypertension patients.Subgroup analysis for different duration of treatment reveals that no matter 1 month or 2 months treatment,clinical total effective rate was higher (P<0.00001),the SBP was significantly lower (P<0.05)compared with the conventional western drugs used alone.And DBP was significantly lower (P<0.05) at 2 months of treatment.However, due to the quality and limitations of the included studies, it is unable to draw a specific conclusion.
We found that methodological quality of the included studies was not highly compelling.Firstly,although all studies mentioned randomization,one study did not clearly report the method of randomization which might cause the bias of selection.In addition, the allocation concealment as well as the dropout participant were not mentioned for most of the included trials.Secondly, none of these studies reported the method of blinding and using of placebo in control group which might cause the bias of performance or detection.Thirdly,1 study[35]showed a large heterogeneity in the comparison of NO.We thought it might be related to differences in the method of NO detection, the source of kit or the product number.However, these information were not described clearly in the trial,which might lead to bias.Therefore, these issues affected the analyses of BBTD+XFZYD treatment for essential hypertension.
Beyond that, we found some limitations of the study.Firstly, available number of studies was not statistically sufficient to engage in subgroup of NO and ET-1 analysis by duration of treatment.Treatment ranges from 1 to 2 months,and long-term efficacy comparisons are lacking.Secondly, 4 trials[34,35,37,38]specifically stated the grade of essential hypertension, but none reported the outcomes according to the grade of essential hypertension.Thirdly, 24-hour SBP,24-hour DBP and other outcomes which could assess the hypertension were not mentioned in the included studies.Some studies found that 24-hour SBP, 24-hour DBP and 24-hour pulse pressure could predicted mortality in older treated hypertensives[39,40].Similarly, most of the included studies only reported NO and ET-1 as indicator of endothelial function.Only 2 trials[35,38]used other indicator to assess the function, such as AngII,vWF, MDA, etc.There are various methods to assess endothelial function.Some studies shown that endothelial dysfunction could be evaluated by AngII, impaired flow-mediated dilation of the brachial artery or digital reactive hyperemia index in peripheral arterial tonometry[14,41].So, there is a lack of multi-angle verification for hypertension and endothelial function.Finally, only 1 study[38]reported the adverse reactions.The safety of therapeutic drugs cannot be determined.
Therefore, the precise effects of BBTD+XFZYD for treating hypertension remain uncertain given the high overall risk of bias and limitations in our included studies.Thus, well-designed, multicenter and larger sample size RCTs are needed.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, this review provides evidence that Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction combined with Xuefu Zhuyu decoction plus conventional western drugs can reduce blood pressure, improve clinical efficiency and repair endothelial function.However, the benefits and the safety of this therapy for treating essential hypertension are still unclear because of low reporting quality of published studies.High-quality RCTs with larger sample sizes and suitable design project are required to better assess the outcomes of Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction combined with Xuefu Zhuyu decoction as treatment for essential hypertension and endothelial function.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
None.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- The Study of Molecular Mechanisms of Xuanbai Chengqi Decoction(宣白承气汤) in the Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Method
- An Overview on The Antiviral Traditional Chinese Medicines
- Establish a Three-dimensional Fluorescent Fingerprint Database of Traditional Chinese Medicines
- Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Coronavirus Disease 2019(Trial Version 7)
- INSTRUCTION FOR AUTHORS
- World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies Center for Translation
