三种干扰素γ释放试验在不同年龄结核病患者中的应用比较
2020-10-29美朗曲措陈民黄丽萍边玛措
美朗曲措 陈民 黄丽萍 边玛措

摘要:目的 比較三种干扰素γ释放试验在不同年龄结核病(TB)患者中的应用效果。方法 选取2016年6月~2019年11月西藏自治区人民医院确诊为TB患者425例,按照年龄分为≤29岁61例,30~49岁145例,50~69岁130例,≥70岁89例,均进行三种IGRAs(QFT Plus、QFT-GIT及T-SPOT.TB)检测,比较三种方法检测结果及其在各年龄组灵敏度和特异性,并分析IGRAs检测不同年龄段TB患者免疫指标结果。结果 不同IGRAs方法的灵敏度、特异性、阳性预测值比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),而QFT-GIT方法的阴性预测值低于QFT Plus和T-SPOT.TB方法,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。不同IGRAs方法检测各年龄段的灵敏度和特异性比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);根据双变量回归分析,灵敏度、特异性与年龄均呈负相关(P<0.05)。不同年龄组TB患者WBC数和白蛋白/球蛋白比值比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。≥70岁年龄组TB患者淋巴细胞数、淋巴细胞百分比、血清白蛋白数较其他年龄组TB患者下降(P<0.05),CRP较其他年龄组TB患者上升(P<0.05)。结论对于<70岁TB患者,QFT Plus及T-SPOT.TB可用于TB早期诊断工具,而≥70岁TB患者,仍需结合痰涂片、痰结核菌DNA、影像学检查等手段综合判断。
关键词:IGRAs;QFT Plus;QFT-GIT;T-SPOT.TB;结核诊断
中图分类号:R52 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.18.055
文章编号:1006-1959(2020)18-0164-04
Application Comparison of Three Kinds of Interferon γ Release Test
in Tuberculosis Patients of Different Ages
MEILANG Qu-cuo,CHEN Min,HUANG Li-ping,BIAN Ma-cuo
(Department of Respiratory Medicine,People's Hospital of Tibet Autonomous Region,Lhasa 850000,Tibet,China)
Abstract:Objective To compare the effects of three interferon gamma release tests in tuberculosis (TB) patients of different ages.Methods From June 2016 to November 2019, 425 patients with TB diagnosed in the People's Hospital of Tibet Autonomous Region were selected. According to age, 61 cases were ≤29 years old, 145 cases were 30-49 years old, 130 cases were 50-69 years old, and 89 were ≥70 years old. In each case,3 types of IGRAs (QFT Plus, QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB) were tested,compare the detection results of the three methods and their sensitivity and specificity in each age group, and analyze the results of IGRAs detecting immune indicators in TB patients of different ages.Results The sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value of different IGRAs methods were not statistically different (P>0.05), while the negative predictive value of QFT-GIT method was lower than that of QFT Plus and T-SPOT.TB methods,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). The sensitivity and specificity of different IGRAs methods for detecting each age group were compared,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05); according to the bivariate regression analysis, the sensitivity and specificity were negatively correlated with age (P<0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in WBC count and albumin/globulin ratio in TB patients of different age groups (P>0.05). The number of lymphocytes, the percentage of lymphocytes, and the number of serum albumin in TB patients in the age group ≥70 years were lower than those in TB patients in other age groups (P<0.05), and CRP was higher than that in TB patients in other age groups (P<0.05).Conclusion For TB patients under 70 years of age, QFT Plus and T-SPOT.TB can be used as early diagnostic tools for TB, while TB patients ≥ 70 years of age still need to be combined with sputum smears, sputum tuberculosis DNA, imaging examination and other methods to make comprehensive judgments.
Key words:IGRAs;QFT Plus;QFT-GIT;T-SPOT.TB;Tuberculosis diagnosis
结核病(tuberculosis,TB)是一种威胁人类健康的传染性疾病,世界范围内每年新增约610万结核病例,其中约有180万例死亡[1],因此结核病的早期准确诊断对控制其传播至关重要。干扰素γ释放试验(IGRA)是一种能够克服传统结核菌素皮肤试验(TST)局限性的诊断方法[2-4]。目前常见商品化IGRA试剂盒有QuantiFERONTB Gold Plus(QFT Plus)、QuantiFERON-TB-GoldIn-Tube(QFT-GIT)和T-SPOT.TB试剂盒。QFT Plus是新一代QFT-GIT,于2015年推出[5],QFT-GIT含有一个TB特异性抗原管,通过酶联免疫吸附试验测定γ干扰素(IFN-γ)的浓度[6],而QFT Plus试剂盒由两个TB特异性抗原管组成[7,8];T-SPOT.TB则是通过酶联免疫斑点试验测量IFN-γ分泌的T细胞数量[9]。这三种IGRA均与IFN-γ紧密相关,而IFN-γ的产生与人体免疫相关,随着年龄的增长,人体的免疫反应强度下降[10,11]。本研究旨在比较三种干扰素γ释放试验在不同年龄结核病(TB)患者中的应用效果,现报道如下。
1资料与方法
1.1一般资料 选取2016年6月~2019年11月西藏自治区人民医院确诊(门诊及住院)的肺结核(TB)患者425例,该研究经我院医学伦理委员会批准,参与研究者均签署知情同意书。所有患者均未服用免疫抑制药物,符合《结核病诊断和治疗指南》中两次痰涂片抗酸杆菌阳性及影像学检查显示结核征象,排除精神及认知障碍者。其中男219例,女206例;≤29岁61例,30~49岁145例,50~69岁130例,≥70岁89例;TB感染情况:肺结核269例,肺外结核156。
1.2仪器与试剂 QFT Plus及QFT-GIT试剂盒(澳大利亚Cellestis公司),T-SPOT.TB试剂盒(英国Oxford Immunotec公司),SPX-150B-Z型生化培养箱(上海博讯医疗生物股份有限公司),TD-12K型离心机(湖南湘仪离心机仪器有限公司),HY-3型振荡器(常州国华电器有限公司),伯乐-550型酶标仪(美国Bio-Rad公司),Elispot Classic型酶联斑点分析仪(德国AID公司),OLYMPUS SZX10型显微镜(日本Olympus公司)。
1.3方法
1.3.1 QFT Plus方法 取受试者全血2 ml分别置于特异性试管(TB1和TB2)中,37℃培养16~20 h。25℃离心15 min(4000 rpm;14.6 cm)后取上清液,采用ELISA测定血浆中IFN-γ的浓度。采用Ascent 2.6(Thermo Scientific)进行判定(阳性、阴性或不确定)。
1.3.2 QFT-GIT方法 取受试者全血3 ml分别置于A、B、C 3个特异性试管,A为TB抗原管,B为阳性对照管,C为阴性对照管,于37℃培养16~20 h。25℃离心15 min(4000 rpm;14.6 cm)后取上清液,采用ELISA测定血浆中IFN-γ的浓度。采用Ascent 2.6(Thermo Scientific)进行判定(阳性、阴性或不确定)。
1.3.3 T-SPOT.TB方法 取受试者全血4 ml于室温放置20 min,密度梯度离心法提取纯化外周血单个核细胞,稀释至2.5×106/ml。培养板中加入50 μl阳性对照、抗原A、抗原B、AIM-V培养基,于37℃培养16~20 h。在与碱性磷酸酶结合的第二抗体和底物显色后,采用CTL-ImmunoSpot S5 Versa Analyzer(USA)对形成色斑的细胞进行计数并进行结果判定(阳性、阴性或不确定)。
1.4观察指标 比较三种IGRAs检测方法的灵敏度、特异性、阳性预测值、阴性预测值。所有受试者均于清晨空腹采集EDTA抗凝血,TB组血样除IGRAs检查外,仍检查了白细胞(white blood cell,WBC)计数、淋巴细胞百分比、绝对淋巴细胞计数、血清白蛋白数、血清球蛋白数、白蛋白/球蛋白比值以及C反应蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP)数。灵敏度=真阳性/(真阳性数+假阴性)×100%,特异性=真阴性/(真阴性+假阳性)×100%,阳性预测值=真阳性/(真阳性+假阳性)×100%,阴性预测值=真阴性/(真阴性+假阴性)×100%。
1.5统计学方法 应用SPSS 21.0统计软件进行数据分析,计数资料以[n(%)]表示,比较采用?字2检验,采用双变量回归分析进行灵敏度与年龄、特异性与年龄的相关性分析。各年龄组间包括WBC计数、淋巴细胞百分比、绝对淋巴细胞计数等变量,采用ANOVA的LSD法进行多重比较。以P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2结果
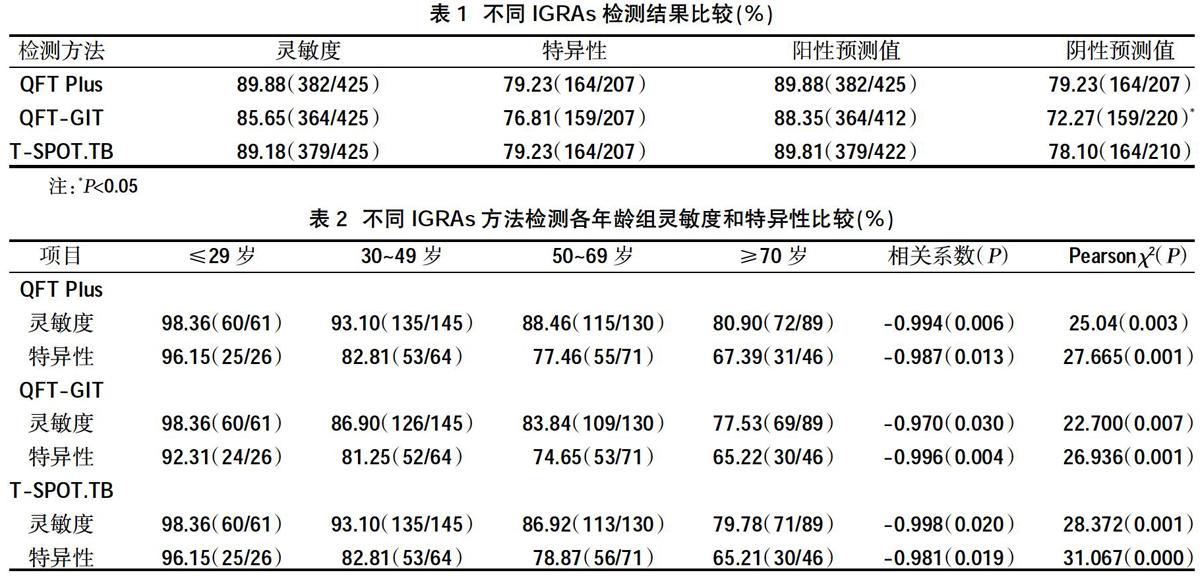
2.1不同IGRAs检测结果比较 不同IGRAs方法的灵敏度、特异性、阳性预测值比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),而QFT-GIT方法的阴性预测值低于其他两种,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。
2.2不同IGRAs方法检测各年龄段的灵敏度和特异性比较 不同IGRAs方法检测各年龄段的灵敏度和特异性比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);根据双变量回归分析,灵敏度、特异性与年龄均呈负相关(P<0.05),见表2。
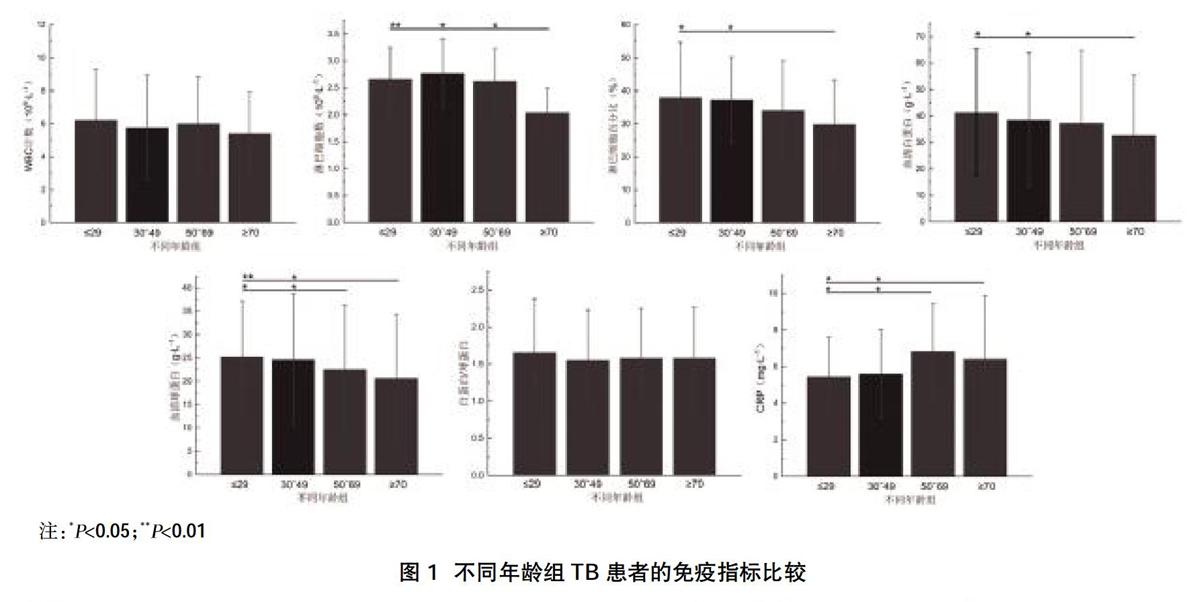
2.3不同年龄段TB患者免疫指標比较 不同年龄组TB患者WBC数和白蛋白/球蛋白比值比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。≥70岁年龄段TB患者淋巴细胞数、淋巴细胞百分比、血清白蛋白数较其他年龄段TB患者下降(P<0.05),CRP较其他年龄段TB患者上升(P<0.05),见图1。
3討论
IGRAs是基于IFN-γ产生的一种免疫学诊断方法,与机体免疫紧密相关[12]。随着年龄的增长,人体免疫细胞数量减少、分化增殖及免疫能力减低,T细胞数量及功能的降低可能是导致T-SPOT.TB灵敏度下降的重要原因之一[13,14]。同时,老年TB患者营养不良、低蛋白血症的比例较高,CD4细胞数量减少可能导致QFT Plus及QFT-GIT灵敏度下降[15,16]。Santos JA等[17]研究报道,年龄(≥65岁)是IGRAs不确定结果的预测因素之一。田瑞雪等[18]研究报道,在老年TB患者诊断中T-SPOT.TB方法敏感度下降。Bae W等[19]研究报道,WBC、淋巴细胞数等免疫指标对不同年龄段患者的QFT-GIT和T-SPOT.TB方法的灵敏度影响较大,但由于研究对象来自不同医院的不同患者,结果存在一定偏差与不确定性。
IGRAs法灵敏度高,且不受卡介苗和大部分非致病分枝杆菌的影响,近年来在TB的诊断中脱颖而出[20],但在老年TB患者诊断中IGRAs敏感度降低[21]。本研究结果显示,不同IGRAs方法的灵敏度、特异性、阳性预测值比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),而QFT-GIT方法的阴性预测值低于其他两种,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),说明QFT-GIT方法在TB诊断中的对真正未患病者的诊断准确率低于其他两种方法;三种IGRAs方法检测各年龄段的灵敏度和特异性比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);根据双变量回归分析,灵敏度、特异性均与年龄呈负相关(P<0.05),说明随着年龄增加,三种IGRAs的灵敏度及特异性均降低,且除了≤29年龄组三种IGRAs的灵敏度相似外,在其他年龄组中QFT-GIT方法的灵敏度及特异性均低于其他两种方法;相较于其他年龄组,≥70岁组患者的淋巴细胞数、淋巴细胞百分比、血清白蛋白数、血清球蛋白数等指标下降,CRP数上升,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),说明随年龄增加,≥70岁TB患者的淋巴细胞数等免疫指标下降及CRP数的上升可能与IGRAs灵敏度降低相关[22,23]。
综上所述,对于<70岁的患者,QFT Plus及T-SPOT.TB可用于TB早期诊断工具,灵敏度和特异性高。而≥70岁的患者,对其结果应当结合临床谨慎解读,可结合痰涂片、痰结核菌DNA、影像学检查进行综合判断。
参考文献:
[1]Zumla A,George A,Sharma V,et al.The WHO 2014 global tuberculosis report--further to go[J].Lancet Glob Health,2015,3(1):e10-e12.
[2]Diel R.Long-term Effect of Bacille Calmette-Guérin Vaccination in Tuberculin Skin Testing:A New Reality for TB Prevention[J].Chest,2017,152(2):235-236.
[3]Hermansen TS,Lillebaek T,Kristensen KL,et al.Prognostic value of interferon-γ release assays,a population-based study from a TB low-incidence country[J].Thorax,2016,71(7):652-658.
[4]Shu CC,Hsu CL,Wei YF,et al.Risk of tuberculosis among patients on dialysis:the predictive value of serial interferon-gamma release assay[J].Medicine,2016,95(22):e3813.
[5]Rozot V,Patrizia A,Vigano S,et al.Combined use of mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses is a powerful diagnostic tool of active tuberculosis[J].Clinical Infectious Diseases,2015,60(3):432-437.
[6]Tsuyuzaki M,Igari H,Okada N,et al.Variation in interferon-γ production between QFT-Plus and QFT-GIT assays in TB contact investigation[J].Respiratory investigation,2019,57(6):561-565.
[7]Petruccioli E,Chiacchio T,Pepponi I,et al.First characterization of the CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses to QuantiFERON-TB Plus[J].Journal of Infection,2016,73(6):588-597.
[8]Barcellini L,Borroni E,Brown J,et al.First independent evaluation of QuantiFERON-TB Plus performance[J].European Respiratory Journal,2016,47(5):1587-1590.
[9]Zhu F,Ou QF,Zheng J.Application values of T-SPOT.TB in clinical rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis[J].Iranian Journal of Public Health,2018,47(1):18.
[10]Davies JS,Thompson HL,Pulko V,et al.Role of cell-intrinsic and environmental age-related changes in altered maintenance of murine T cells in lymphoid organs[J].The Journals of Gerontology,2018,73(8):1018-1026.
[11]Tsukamoto H,Clise-Dwyer K,Huston GE,et al.Age-associated increase in lifespan of naive CD4 T cells contributes to T-cell homeostasis but facilitates development of functional defects[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2009,106(43):18333-18338.
[12]Pourakbari B,Mamishi S,Benvari S,et al.Can Interferon-γ Release Assays Be Useful for Monitoring the Response to Anti-tuberculosis Treatment:A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis[J].Archivum Immunologiae Therapiae Experimentalis,2020,68(1):4.
[13]Ishikawa S,Igari H,Akutsu N,et al.Comparison of interferon-γ release assays,QuantiFERON TB-GIT and T-Spot.TB,in renal transplantation[J].Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy,2017,23(7):468-473.
[14]Whitworth HS,Badhan A,Boakye AA,et al.Clinical utility of existing and second-generation interferon-γ release assays for diagnostic evaluation of tuberculosis:an observational cohort study[J].The Lancet Infectious Diseases,2019,19(2):193-202.
[15]Pourakbari B,Mamishi S,Benvari S,et al.Comparison of the QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus and QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube interferon-γ release assays:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Advances in Medical Sciences,2019,64(2):437-443.
[16]Lee EH,Kang YA.Successful transition to the QFT-PLUS assay,but more is needed for diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection[J].The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine,2020,35(2):298.
[17]Santos JA,Duarte R,Nunes C.Host factors associated to false negative and indeterminate results in an interferon-γ release assay in patients with active tuberculosis[J].Pulmonology,2019(1422):1-10.
[18]田瑞雪,馬丽萍,武红莉,等.γ-干扰素释放试验在结核诊断中的价值[J].临床荟萃,2017,32(6):507-510.
[19]Bae W,Park KU,Song EY,et al.Comparison of the sensitivity of QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube and T-SPOT.TB according to patient age[J].PLoS One,2016,11(6):e0156917.
[20]董玉兰,谢超,徐冉,等.γ-干扰素释放试验在结核病诊断中的应用[J].医学信息,2019,32(21):66-68.
[21]贾岩,马俊鹏,张春梅,等.结核感染T细胞检测在肺结核尧肺外结核及潜伏性结核感染中辅助诊断的临床运用[J].医学信息,2015,28(32):127.
[22]Latorre I,Mínguez S,Carrascosa JM,et al.Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases differently affect IGRAs'accuracy for latent tuberculosis infection diagnosis in clinical practice[J].PLoS One,2017,12(12):e0189202.
[23]Takasaki J,Manabe T,Morino E,et al.Sensitivity and specificity of QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus compared with QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube and T-SPOT.TB on active tuberculosis in Japan[J].Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy,2018,24(3):188-192.
收稿日期:2020-05-13;修回日期:2020-06-08
编辑/杜帆
