Clinical study on Jin’s three-needle therapy for post-stroke cognitive impairment
2020-02-28YaoRui姚睿GongZunke巩尊科
Yao Rui (姚睿), Gong Zun-ke (巩尊科),2
1 Xuzhou Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Jiangsu 221000, China
2 Department of Rehabilitation Science of Xuzhou Central Hospital, Jiangsu 221000, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Jin’s Three-needle; Scalp Stimulation Areas; Post-stroke Syndrome; Cognitive Dysfunction;Neuropsychological Scale; Psychiatric Status Rating Scales; Event-related Potential, P300
Stroke is a major cause of adult death in China and approximately 30% of the stroke survivors have long-term neurological deficit[1].Among the factors that limit the functional recovery of patients after stroke,cognitive impairment is the most unfavorable one.According to statistics, the incidence of post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) is as high as 40%-70%[2],and about 1/3 of PSCI patients will develop dementia[3].
According to literature review, acupuncture can significantly improve cognitive impairment in stroke patients[4].Jin’s three-needle therapy is a branch in the development of modern acupuncture.Modern research has suggested that Jin’s three-needle therapy is effective for PSCI[5], but there are few clinical studies on its physiological mechanism.In this study,neuropsychological scales and potential 300 (P300)event-related potential (ERP) were used as evaluation items to observe the clinical efficacy of Jin’s threeneedle therapy for PSCI and associated neuroelectrophysiology and to further explore the mechanism of Jin’s three-needle therapy in treating PSCI.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
1.1.1 Diagnostic criteria in Western medicine
According to the specific diagnostic criteria of PSCI proposed inExpert Consensus on Management of PSCI[6], post-stroke dementia (PSD) diagnostic criteria:based on baseline cognitive impairment; ≥1 cognitive domain; the severity affected the activities of daily living (ADL).
Diagnostic criteria of post-stroke cognitive impairment no dementia (PSCIND): based on the assumption of baseline cognitive impairment; at least one cognitive domain is damaged; the instrumental ADL can be normal or slightly damaged.
The above two types of diagnostic criteria should meet the corresponding three requirements and at least 4 cognitive domains (executive function/attention,memory, language and visuospatial ability) should be evaluated.Impairment of ADL should be independent of motor/sensory impairment of secondary vascular events.
1.1.2 Diagnostic criteria in Chinese medicine
Score according to theSyndrome Differentiation Standard of Vascular Dementia(SDSVD) inCriteria for the Diagnosis, the Differentiation of Syndrome and the Evaluation of Efficacy of Vascular Dementia for Research Studies[7].
Score explanation: The score of each syndrome was the highest score of each factor for diagnosis of this syndrome, and the total score was 30.
Syndrome diagnosis explanation: Syndrome diagnosis score ≥7 points meant that the syndrome diagnosis was correct.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Those who met the above diagnostic criteria; those personally or the legal guardian agreed and signed the informed consent; confirmed by CT scan or MRI examination after hospitalization; confirmed by minimental state examination (MMSE), illiteracy group<19 points, the primary school (education period≤6 years) <22 points, the middle school or above(education period >6 years) group <26 points; the Montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA) score<23 points; the first stroke, course ≤6 months; age≥45 but ≤75 years old; no gender limitation; those having a clear consciousness, stable vital signs and condition.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those who suffered from cognitive impairment due to other reasons (frontotemporal dementia, Alzheimer's disease, brain trauma, Parkinson's disease,hypothyroidism, brain tumors, brain parasites, etc.)before the onset of stroke, as confirmed by previous medical records, clinicians or family members; those with depression, delirium, consciousness or mental disorder; those with a history of alcohol and drug abuse;patients with severe heart, liver, kidney, endocrine and hematopoietic system diseases; patients who were participating in other trials that may affect the evaluation of the results of this study; patients with severe visual, auditory or speech disorders that cannot cooperate with the assessment and test; those who cannot tolerate or accept acupuncture and manipulation (including pregnant women); those with scar, tumor, severe infection, ulcer or trauma on the scalp, or without skull repair after osteotomy.
1.4 Statistical methods
The SPSS 21.0 statistical software was used for data analysis.The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s) and checked byt-test.The counting data were checked by Chi-square test.Pearson analysis was used for correlation analysis.TheP-value of less than 0.05 meant a statistical significant difference.
1.5 General data
Sixty PSCI inpatients in the Department of Rehabilitation Science of Xuzhou Central Hospital were selected between December 2017 and December 2018.According to the method of random number table, they were divided into a treatment group and a control group, with 30 cases in each group.There were no significant differences in the baseline data between the two groups (allP>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable (Table 1).
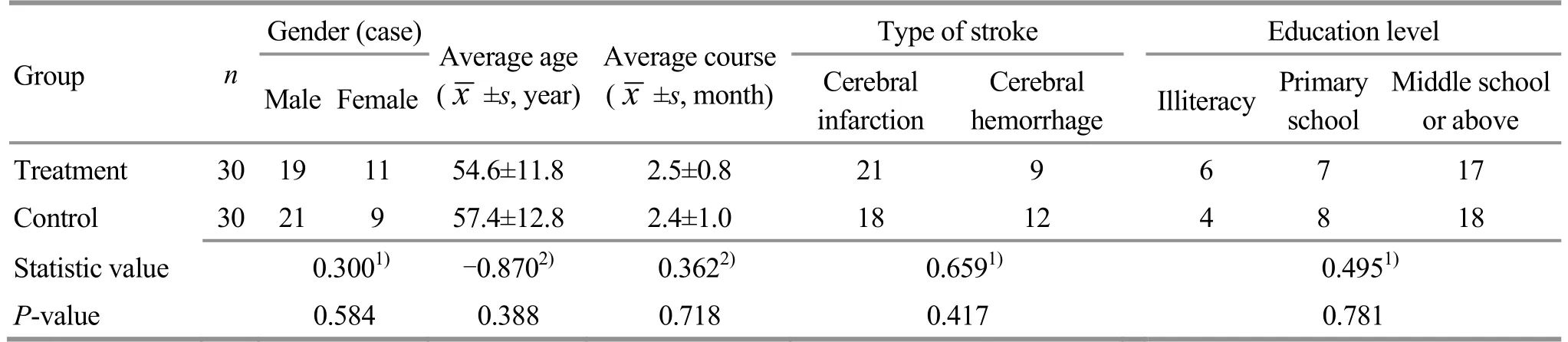
Table 1.Comparison of general data between the two groups
2 Therapeutic Methods
2.1 Treatment group
2.1.1 Routine treatment
After hospitalization, according to the results of clinical examination, referring toGuidelines for Primary Prevention of Cerebrovascular Diseases(2015, China)[8]andGuidelines for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients with Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack(2014 AHA/ASA edition)[9], the patients received the basic treatment for internal diseases, including hypertension,hyperlipidemia, poor circulation, malnourishment,nerve problems, etc.The routine rehabilitation training was based on theGuidelines for Stroke Rehabilitation Treatment in China(2011 full version)[10].The same rehabilitation team was responsible for the rehabilitation plan according to the patients' functional status.These included normal limb position, sports function training, occupational therapy training, speech training and cognitive training.
2.1.2 Jin’s three-needle therapy
Major acupoints: Three temporal points (Figure 1),four spiritual points (Figure 2), three cerebral points(Figure 3) and three intelligent points (Figure 4).
Routine combination of acupoints: Three arm points(Figure 5) and three leg points (Figure 6).
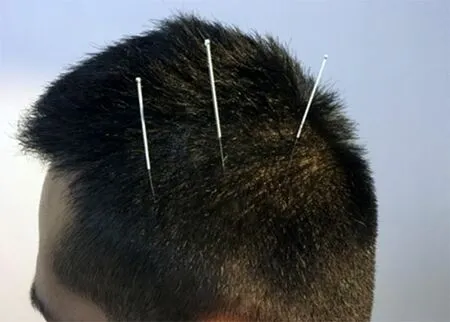
Figure 1.Three temporal points
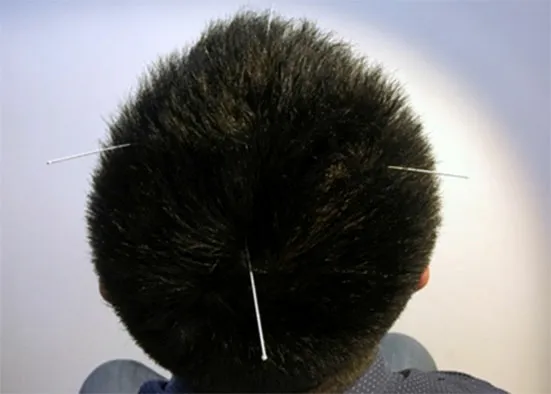
Figure 2.Four spiritual points

Figure 3.Three cerebral points

Figure 4.Three intelligent points
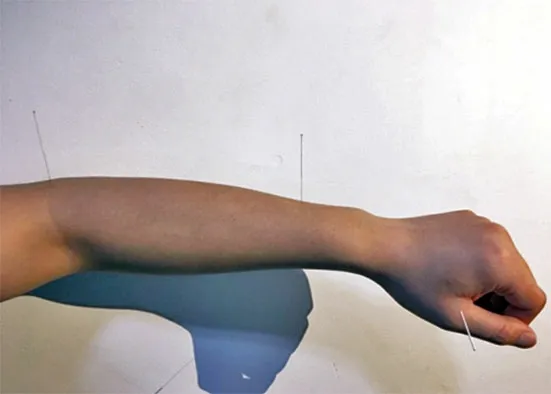
Figure 5.Three arm points
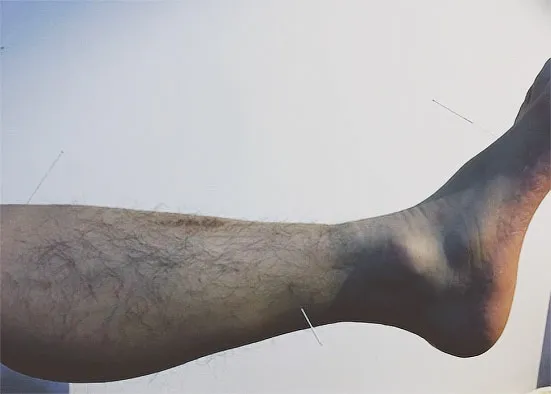
Figure 6.Three leg points
Combination of acupoints based on pattern differentiation: Added Shenshu (BL 23) and Sanyinjiao(SP 6) for kidney essence deficiency; Qihai (CV 6) and Geshu (BL 17) for deficiency of qi and blood; Fenglong(ST 40) and Zhongwan (CV 12) for turbid phlegm obstructing orifices; Geshu (BL 17) and Weizhong (BL 40)for blood stasis obstructing meridians; and three tongue points for speech difficulties.
Methods: The acupoint locations and operations were all in accordance with theMethods for Acupoint Combination of Jin's Three-needle[11].
Course of treatment: The patients were treated once a day, six days a week and one day off, four weeks as a course of treatment.The curative efficacy was observed after one course of treatment.
2.2 Control group
The patients in the control group received the same routine treatment as the treatment group alone.
3 Observation of Therapeutic Effects
3.1 Observed items
Before and after the treatment, the patients in both groups received MMSE, MoCA and auditory P300 detections.The scores of the two scales and the measurement of auditory P300 were performed by the same experienced rehabilitation physician.
3.1.1 Score of MMSE[12]
MMSE mainly involves the fields of timing and orientation, executive function, short-term and delayed memory, calculation, language expression and attention.There are 30 questions in total, 1 point for correct answer, 0 point for wrong answer or no answer, and the total score is 30 points.The higher the total score, the better the overall cognitive function of the patient.
3.1.2 Score of MoCA[13]
MoCA involves 7 items and 11 aspects, which can be divided into visual space and executive function,naming, memory, attention, language, abstract thinking,delayed memory and orientation.The total score is the sum of all scores.If the number of years of education≤12 years, 1 point will be added and the total score is 30 points.The higher the total score, the better the overall cognitive function of the patient.
3.1.3 Auditory P300 potential detection
The Oddball program of electromyography (EMG)-evoked potential (EP) equipment was used to record the latency and amplitude of P300.The electrodes were placed at CZ point, and the target stimulation of high frequency (2 000 Hz) and 25% low probability was given.The stimulation intensity was 80 dB, the filtering bandwidth was 1-50 Hz, and the superposition was 50 times[14].Repeated the test twice for each test and took the average value.
3.2 Results
3.2.1 Comparison of MMSE score Before treatment, there was no significant betweengroup difference in the MMSE score (P>0.05).After treatment, the scores were significantly improved in both groups (bothP<0.05).The score of the treatment group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.05).Check Table 2 for details.
Table 2.Comparison of MMSE score between the two groups(±s, point)

Table 2.Comparison of MMSE score between the two groups(±s, point)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Treatment 30 13.63±5.00 21.67±6.32 -18.676 0.000 Control 30 13.43±4.78 18.13±5.74 -11.160 0.000 t-value 0.158 2.268 P-value 0.875 0.027
3.2.2 Comparison of MoCA score
Before treatment, there was no significant betweengroup difference in MoCA score (P>0.05).After treatment, the scores were significantly improved in both groups (bothP<0.05).The score of the treatment group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.05).Check Table 3 for details.
Table 3.Comparison of MoCA score between the two groups(±s, point)
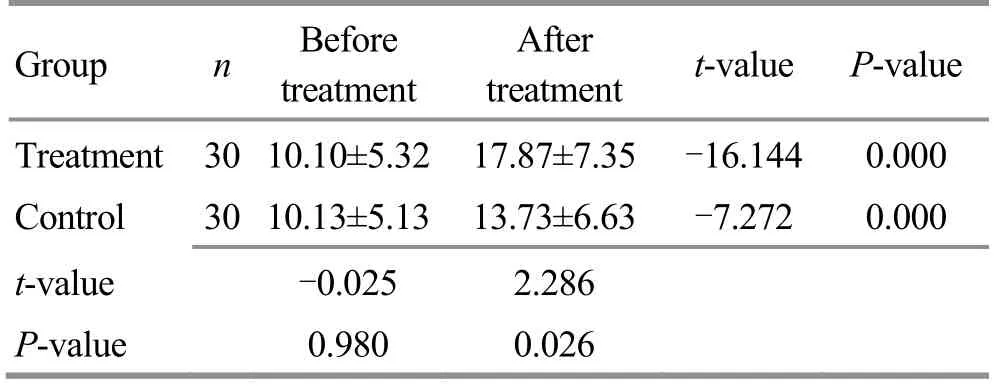
Table 3.Comparison of MoCA score between the two groups(±s, point)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Treatment 30 10.10±5.32 17.87±7.35 -16.144 0.000 Control 30 10.13±5.13 13.73±6.63 -7.272 0.000 t-value -0.025 2.286 P-value 0.980 0.026
3.2.3 P300 latency and amplitude
Before treatment, there was no between-group statistical difference in P300 latency (P>0.05).After treatment, the latencies of P300 were significantly decreased in both groups (bothP<0.05).The latency of the treatment group was significantly shorter than that of the control group (P<0.05).Check Table 4 for details.
Table 4.Comparison of P300 latency (±s, ms)

Table 4.Comparison of P300 latency (±s, ms)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Treatment 30 363.08±22.59 324.95±25.84 12.328 0.000 Control 30 362.72±21.90 346.10±31.54 6.484 0.000 t-value 0.063 -2.841 P-value 0.950 0.006
Before treatment, there was no significant betweengroup difference in P300 amplitude (P>0.05).After treatment, the amplitudes of P300 were significantly increased in both groups (bothP<0.05).The amplitude of the treatment group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.05).Check Table 5 for details.
Table 5.Comparison of P300 amplitude (±s, μV)
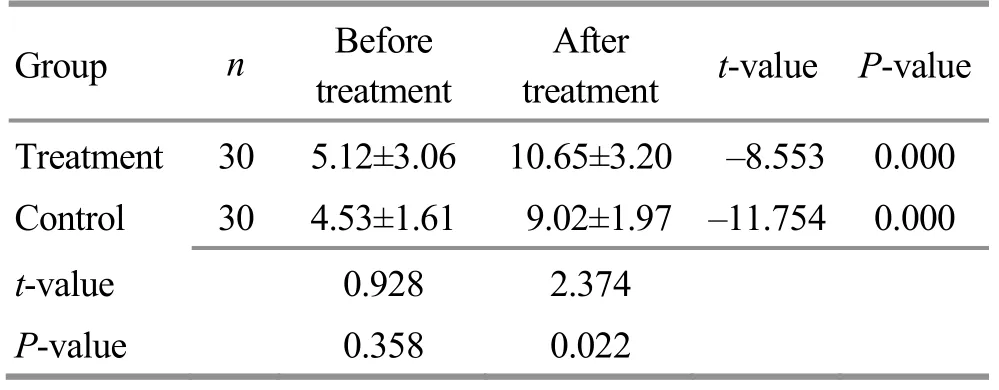
Table 5.Comparison of P300 amplitude (±s, μV)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Treatment 30 5.12±3.06 10.65±3.20 -8.553 0.000 Control 30 4.53±1.61 9.02±1.97 -11.754 0.000 t-value 0.928 2.374 P-value 0.358 0.022
3.2.4 Correlation between MMSE and MoCA scores and P300
By correlation analysis, MMSE, MoCA scores and P300 latency have significant negative correlation (r<0,P<0.05).However, MMSE and MoCA scores have no significant correlation with P300 amplitude (P>0.05).Check Table 6 for details.
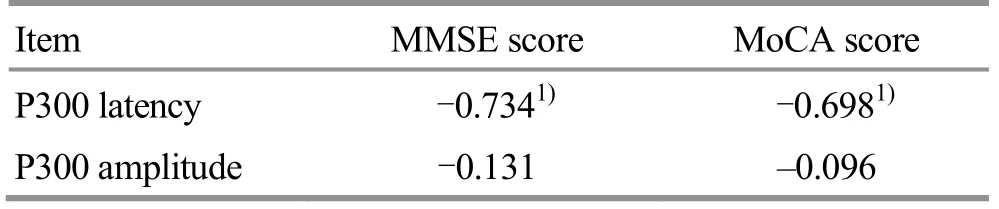
Table 6.Analysis of correlation between MMSE, MoCA scores and P300 before treatment (n=60)
4 Discussion
PSCI has a high incidence and can seriously affect the patients’ social adaptability, ADL and quality of life.In addition, PSCI patients generally have problems such as inattention, clumsiness, poor understanding,forgetfulness, emotional volatility, and lack of patience.Patients often fail to cooperate well with limb function training, which may delay the rehabilitation process and impair the comprehensive rehabilitation of other dysfunctions.Therefore, it is of important clinical significance to early diagnose, early treat and delay the development of PSCI.
At present, PSCI is mainly treated with Western medicine; however, these medications are expensive and may cause adverse reactions[15].Therefore, it is urgent to find a simple, effective and low-cost optimal rehabilitation scheme for PSCI[16].Acupuncture is a therapy recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the treatment of stroke.Since it can also benefit PSCI without causing adverse reactions,it has become a popular research point in recent years.
PSCI belongs to mental problems in traditional Chinese medicine, belonging to the same category as dementia, amnesia and depression.It is located in the brain, but closely associated with the kidney, heart, liver and spleen.The basic pathogenesis of this condition is brain marrow failing to nourish the mind.The pathological nature can be summarized as deficiency in root cause (deficiency of kidney essence, qi and blood)but excess in clinical manifestations (stagnation of qi,fire and phlegm).As a result, the treatment strategies should be to supplement marrow, refresh the mind,resolve phlegm, calm the liver, reduce fire, and circulate blood.
Jin’s three-needle therapy, created by Professor Jin Rui at the Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, is a representative of Lingnan School of acupuncture.This method is simple, practical and easy to learn.
The major acupoints in this study are three temporal points, four spiritual points, three cerebral points and three intelligent points.The three temporal points are located in the temporal region with dense bone structures and abundant nerves and blood vessels.They are the distribution areas of the Triple Energizer and Gallbladder Meridians: the first treatment option for stroke and its sequelae[17].The selected points include Shuaigu (GB 8) and Jiaosun (TE 20) as the first point of three temporal points, Xuanli (GB 6) and Qubin (GB 7)as the second points of three temporal points, and Tianchong (GB 9) as the third point of three temporal points.The three points of the Gallbladder Meridian are crossing points of the Bladder and Gallbladder Meridians.Jiaosun (TE 20) is a crossing point of the Triple Energizer and Gallbladder Meridians.The point Xuanli (GB 6) is a crossing point of the Triple Energizer,Gallbladder and Stomach meridians.Therefore,needling the three temporal points can unblock the qi of Liver and Gallbladder Meridians and help with the recovery of stroke sequelae[17].The three intelligent points are Shenting (GV 24) and bilateral Benshen(GB 13).The point Shenting (GV 24) is a crossing point of Governor Vessel and Bladder Meridian, the residence of spirit.The point Benshen (GB 13) is a crossing point of Governor Vessel and Yang Link Vessel, the root of vital spirit.These acupoints are located in the projection area of the frontal lobe of the brain, which is closely related to intelligence, and can strengthen the brain and improve intelligence.The four spiritual points are developed from Sishencong (EX-HN 1), which has the function of regulating original spirit and ascending yang qi.The first spiritual point is Qianding (GV 21) and the second spiritual point is Houding (GV 19).The third and forth spiritual points are located on the pathway of Bladder Meridian.Both Governor Vessel and Bladder Meridian enter the brain.Therefore, needling this group of acupoints can stimulate the brain in a large area and regulate the spirit and refresh the mind.The three cerebral points consist of Naohu (GV 17) and bilateral Naokong (GB 19): two points that contain the word‘brain’ in Chinese.The point Naokong (GV 17) means the orifice of the brain, while the point Naohu (GB 19)means the gate to the brain.The combination of the two can regulate and refresh the mind.
The combination of these four groups can regulate spirit, benefit marrow, and refresh the mind[18].The three arm points consist of Hegu (LI 4), Quchi (LI 11) and Waiguan (TE 5).The three leg points consist of Zusanli(ST 36), Sanyinjiao (SP 6) and Taichong (LR 3).The three tongue points consist of Lianquan (CV 23), along with the other two points: 0.8 cun bilateral to Lianquan(CV 23).
In order to further explore the clinical effect of Jin’s three-needle therapy on PSCI and its influence on neuroelectrophysiology, MMSE and MoCA cognitive function screening scales and P300 were used as evaluation items to observe its effect and mechanism.The results have shown that after 4 weeks of treatment,the MMSE and MoCA scores, and P300 amplitude were increased, and P300 latency was shorter, indicating that cognitive function of both groups was improved after treatment.The improvement of the treatment group was more noticeable than that of the control group,indicating that Jin’s three-needle therapy had a definite effect on PSCI.The action mechanism is probably through its regulation on the neuroelectrophysiology.Moreover, the scores of MMSE and MoCA were negatively correlated with P300 latency, but not with P300 amplitude, which indicated that P300 was correlated with MMSE and MoCA, and P300 latency could objectively reflect the cognitive function of patients to a certain extent.P300 amplitude showed no specificity in cognitive function.P300 combined with MMSE and MoCA could evaluate the cognitive impairment of stroke patients more timely, objectively and comprehensively.
Jin’s three-needle therapy is often adopted to treat encephalopathy.The results of this study have suggested that Jin’s three-needle therapy can improve the cognitive function of PSCI patients and improve P300 latency and amplitude.The mechanism is probably associated with its effect in improving the hemorheological state of the brain[19], counteracting free radical injury, protecting nerve cells, preventing apoptosis, and regulating the neuroelectric activity of the brain[20].These hypothetic mechanisms are in line with Jin’s three-needle's functions of refreshing the mind, opening orifices, regulating the spirit and supplementing marrow.
To sum up, Jin’s three-needle therapy plus routine treatment can improve the cognitive impairment in patients after stroke by regulating their neuroelectrophysiology.Combined with modern rehabilitation, Jin’s three-needle therapy is an effective therapy for PSCI.Considering the tolerance of points, a better therapeutic effect can be achieved by using Jin’s three-needle alternately with acupuncture methods such as awaking brain and opening orifices, scalp acupuncture, and unblocking the Governor Vessel and regulating the spirit.
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effect of electroacupuncture on the learning and memory abilities in type 2 diabetic model rats with cognitive impairment
- Effects of electroacupuncture of different frequencies on electromyography, NOS and ICC of colon in rats with slow transit constipation
- Effects of electroacupuncture on conjunctival cell apoptosis and the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins Caspase-3, Fas and Bcl-2 in rabbits with dry eye syndrome
- Acupuncture for premature ovarian insufficiency:a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of heat-sensitive moxibustion for adjuvant treatment of depression in Parkinson disease
- Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of heat-sensitive moxibustion for vascular dementia
