Effect of electroacupuncture on the learning and memory abilities in type 2 diabetic model rats with cognitive impairment
2020-02-28CaoJiangpeng曹江鹏YuanAihong袁爱红YangJun杨骏SongXiaoge宋小鸽ZhaBixiang查必祥LiuZhen刘振
Cao Jiang-peng (曹江鹏), Yuan Ai-hong (袁爱红), Yang Jun (杨骏), Song Xiao-ge (宋小鸽), Zha Bi-xiang (查必祥),Liu Zhen (刘振)
1 Graduate School, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230012, China
2 The First Affiliated Hospital, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
3 Institute of Acupuncture and Meridian of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230012, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2; Cognitive Disorders; Maze Learning;Apoptosis; Caspases; Rats
Cognitive impairment (CI) caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a diabetic complication characterized by the acquired cognitive behavioral deficiency.In recent years, as one side effect of the living standard improvement, aging population, high sugar and energy diet, the incidence of T2DM has been increasing.Studies have reported that by 2030, the global diabetics will reach 366 million[1].The incidence of T2DM with CI is also increasing, seriously affecting the patient's physical health and quality of life.At present, the management of this disease is mainly to prevent risk factors and improve symptoms, without precise,complete and unified strategy.Acupuncture, as one of the therapies of traditional Chinese medicine, can improve various CI, including the CI caused by diabetes mellitus, vascular dementia, etc.[2-3]Diabetes mellitus mainly induces apoptosis through chronic high glucose and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways, thereby impairing cognitive function[4-5].Our previous studies showed that electroacupuncture (EA) at Zusanli (ST 36),Neiting (ST 44) and Yishu (Extra) significantly reduced the blood glucose of patients with T2DM[6-7].Other related studies have also shown that acupuncture inhibits apoptosis[8-9].In this study, based on the related research, the effects of EA on the learning and memory abilities and apoptosis were investigated in T2DM model rats with CI, thus to explore the mechanism of EA in the treatment of this medical condition.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Animals and groups
One-hundred clean grade adult male Sprague-Dawley(SD) rats, weighing (160±20) g, were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Anhui Province[License No.: SCXR (Anhui) 2011-002].Rats were housed in a SPF laboratory at (23±2) ℃, with humidity at (60±10)% and natural light.Every 5 rats were housed in a cage with free access to the standard laboratory food and water.After 1 week of adaptive breeding, 100 rats were divided into a normal group (n=10) and a model group (n=90) according to the random number table method.Rats in the model group were intraperitoneally injected with a small dose of streptozotocin (STZ) to establish the T2DM models,after being fed with high-fat and high-sugar diet for 1 month.Only 50 T2DM rat models were successfully established due to the low success rate of the T2DM model.Twenty CI rats were selected from the 50 successful modeled rats by the Morris water maze(MWM) experiment and randomly divided into a model group and an EA group according to the blood glucose level and MWM data (n=10).The experimental processes strictly complied with the relevant regulations in theGuiding Opinions on the Treatment of Experimental Animals.
1.2 Main instruments and reagents
1.2.1 Main instruments
Tianxie brand acupuncture needles (Suzhou Tianxie Acupuncture Needle Apparatus Co., Ltd., China);KWD-808-Ⅰ pulse acupuncture treatment instrument(Shanghai Huayi Medical Equipment Co., Ltd., China);OneTouch Wenhao blood glucose monitor and test strip(Shanghai Johnson Medical Equipment Co., Ltd., China);MWM and Morris animal behavior experiment software (Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, China); JW-3021HR high-speed refrigerated centrifuge (Anhui Jiawen Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd., China); PIKOREAL 96 fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction(qPCR) instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA);MINI-P25 microplate mini centrifuge (Hangzhou Aosheng Instrument Co., Ltd., China); K960 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) instrument (Hangzhou Lattice Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., China); electrophoresis instrument, electrophoresis tank and transfer membrane instrument (Shanghai Tianneng Technology Co., Ltd., China); JS-1070P automatic exposure meter(Shanghai Peiqing Technology Co., Ltd., China);10212432C PIKO plate illuminator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA); biological tissue automatic dehydrator,embedder and spreader (Hubei Yaguang Medical Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., China); RM2016 Leica microtome (Leica, Germany); CX43 Olympus microscope (Olympus, Japan).
1.2.2 Main reagents
Streptozotocin (STZ) (Cat.No.: BJBAG2001, Sigma,USA); trizol (Cat.No.: 15596018, Life Technogies, USA);DEPC (Cat.No.: D1007, Generay Biotech, China);Novostart SYBR qPCR SuperMix plus (Cat.No.:E096-01A, Novoprotein, China); reverse transcription kit(Cat.No.: K1622) and ECL ultrasensitive luminescence kit (Cat.No.: 34094), (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA);Bcl-2 antibody (Cat.No.: ab182858) and Bax antibody(Cat.No.: Ab32503), (Abcam, USA); Caspase-3 antibody(Cat.No.: 9665T, CST, USA); terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)reaction kit (Cat.No.: 11684817910, Roche, USA); DAB color development kit (Cat.No.: ZLI-9018, Zsbio, China);hematoxylin staining solution (Cat.No.: BA-4041, Baso,China); xylene (Cat.No.: 20180310, Shanghai Sujing Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., China).
1.3 Model establishment and evaluation method
A small dose of STZ was intraperitoneally injected to establish the T2DM rat model based on previous research[6-7].All rats had free access to food and water.Food, litter and water were changed once a day.Ten rats in the normal group were fed with normal food.Ninety rats in the model group were fed with high-fat and high-sugar food (20% sucrose, 0.25% pig bile salt,10% lard, 2.5% cholesterol and 67.25% regular food) for 1 month, a small dose of STZ [25 mg/(kg·bw)] was intraperitoneally injected (fasted for 10 h before injection) for 2 consecutive days.Random blood glucose(RBG) ≥16.7 mmol/L was diagnosed as T2DM.
Criteria for successful modeling: The average rat evasion latency tested by the MWM positioning navigation experiment in the normal group was used as the reference value.The ratio, the difference between the average rat escape latency in the model group and the reference value to the average escape latency of the rat, were calculated.A value greater than 20% indicated the successful establishment of rat model with CI[10].
1.4 Intervention methods
Rats in each group received specific intervention and had free access to the ordinary food and water.
1.4.1 EA group
Acupoints: Zusanli (ST 36), Neiting (ST 44) and Yishu(Extra).
Methods: After successful modeling, each rat in the EA group was placed in a rat holder (30 cm×11 cm×10 cm for 150-500 g rats) to treat with EA.The acupoints were located according to the drawings of commonly used acupoints for experimental animals in theExperimental Acupuncture Science[11].Zusanli (ST 36)is located posterior-lateral of the knee joint,approximately 5 mm below the fibula head, and in the tibiofibular space; Neiting (ST 44) is located in the depression in front of the 2nd and 3rd metatarsal junction; Yishu (Extra) is located about 5 mm below the 8th thoracic vertebra).The skin of the acupoint area was disinfected with 75% alcohol.A disposable sterile acupuncture needle with a diameter of 0.20 mm and a length of 25 mm was used to pierce into each selected acupoint.The twirling needle manipulation for even reinforcing-reducing was performed at Zusanli (ST 36)and Yishu (Extra) for 1 min, and the twirling needle manipulation for reducing was performed at Neiting(ST 44) for 0.5 min.The KWD-808-Ⅰ EA instrument was then connected to Zusanli (ST 36) and Neiting (ST 44)(continuous wave, an intensity of 1 mA, a frequency of 10 Hz).Acupuncture was performed at one side of acupoints each time for 20 min, once a day.The two sides were alternately treated for 6 d per week and 4 consecutive weeks.
1.4.2 Model group Rats in the model group only received the same fixation as in the EA group without treatment.
1.4.3 Normal group Rats in the normal group only received the same fixation as in the EA group without treatment.
1.5 Observation items and detection methods
1.5.1 RBG determination
Blood was taken from the rat tail vein 3 d after the modeling, before and after the treatment, and the RBG level was measured with a blood glucose meter and recorded.
1.5.2 MWM test
The MWM experimental device consisted of a circular stainless steel pool [120 cm in diameter and 50 cm in height; the water depth was 25 cm and the water temperature was maintained at (28±1) ℃during the experiment], a transparent platform (9 cm in diameter and 29 cm in height, 30 cm away from the edge of the pool), an automatic photographic recording and analysis system under water.The following 2 items were tested.
Positioning navigation experiment: The rats were placed into the water facing the pool wall from the entry point at the first, second, third and fourth quadrants in the clockwise direction, and the time to find a platform within 2 min (escape latency) was recorded.A rat was introduced onto the platform and stayed for 10 s if it did not find a platform within 2 min.The escape latency was then recorded as 2 min.
Space exploration experiment: The space exploration experiment was conducted the next day after the positioning navigation experiments were all completed.The platform was then removed, the rats were placed into the water facing the pool wall from the same entry point in the first quadrant, and the number of times that rats crossed the original platform within 2 min was recorded.
1.5.3 Protein and gene expressions of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 in rat prefrontal cortex
Western blot (WB) was used to detect the expressions of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 in the rat prefrontal cortex in each group.Rats were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate[3 mL/(kg·bw)].The rats in each group were sacrificed by neck relocation after the blood sample was taken,and the brain tissues were immediately isolated on the freezing table.The cerebral cortex was isolated, placed in a cryovial, quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen, and transferred to a -80 ℃ refrigerator after 5 min.A piece of 100 mg cerebral cortex tissue was lysed by 1 mL of RIPA cell lysate, and centrifuged at 12 000 r/min for 10 min to collect the supernatant; added 5×SDS-PAGE protein loading buffer at 1:4 and heated in a boiling water bath for 10 min to fully denaturize the protein followed by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis,transferring to membrane, rinsing for 5 min, and blocking with 5% skimmed milk for 2 h at room temperature; primary antibodies were diluted with the primary antibody diluents according to the specific ratio(1:2 000 for Bcl-2, 1:1 000 for Bax, 1:1 000 for Caspase-3,1:1 000 for β-actin); incubated the membrane in horseradish peroxidase (HRP) diluted with secondary antibody diluents (1:15 000) at room temperature for 2 h, and washed with TBST for 3 times and 10 min/time;ECL luminescence kit was used to detect the protein level following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Fluorescent real-time qPCR (RT-qPCR) method was used to detect the gene expressions of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 in rat cortical tissues of each group: primer sequences were designed according to the Genebank nucleotide sequence data (NM-031144), (Table 1).The gene expressions of the rat cerebral cortex tissues were detected strictly following the kit instructions, and analyzed using the relative quantification study method.The relative expression of the target gene in the test sample was calculated and expressed as 2-△△Ct.

Table 1.Primer sequences and product lengths
1.5.4 Apoptosis
TUNEL assay for apoptosis detection: The paraffin sections were routinely dewaxed, rinsed with ddH2O and 0.05 mol/L PBS (pH=7.6); digested in a 37 ℃water bath with 20 mg/L proteinase K working solution for 30 min, rinsed 3 times with PBS, and blocked with peroxidase for 30 min; after standing at room temperature for 10 min, 500 μL of TUNEL reaction solution (50 μL TdT plus 450 μL dUTP) was added dropwise to each section, and the reaction was performed in a wet and dark box at 37 ℃ for 1 h; after rinse in PBS for 3 times, 50 μL of POD was added to the specimen to react in a wet and dark box at 37 ℃ for 30 min.After wash with PBS for 3 times, DAB was added for color development; rinsed with distilled water to stop the color development followed by counterstaining with hematoxylin, differentiating with hydrochloric acid and alcohol for 3 s, bluing with lithium carbonate for 1 min, transparence and seal.After the color development by DAB, the apoptotic cells(brown-yellow stained particles in the nuclei) were observed under light microscope (×400), and the number of apoptotic cells in 5 non-repeating fields was counted.
1.6 Statistical processing
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 17.0 statistical software.The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s).Comparisons among groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA.Comparisons between groups and comparisons between different time points within the same group were performed by the least significant difference (LSD)test.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2 Results
2.1 RBG level comparison
There was no significant difference in RBG levels of rats among groups before modeling (P>0.05); there was no significant difference in RBG levels of rats before modeling, after modeling and after 4 weeks of treatment in the normal group (P>0.05).After modeling,the RBG levels of the model and the EA groups were significantly increased compared with the normal group(bothP<0.001); there was no significant difference in the RBG level between the model and the EA groups(P>0.05).After 4 weeks of treatment, the RBG level of the model group was significantly higher than that of the normal group (P<0.001); the level of the EA group was significantly reduced than that of the model group(P<0.05), (Figure 1).

Figure 1.Comparing RBG levels of rats among groups
2.2 Comparison of spatial memory ability in rats
2.2.1 Comparison of escape latency of rats
There was no statistically significant difference in the rat escape latency tested by MWM before modeling among groups (P>0.05); there was no statistically significant difference in the rat escape latency before modeling, after modeling and after 4 weeks of treatment in the normal group (P>0.05).After modeling,the rat escape latencies tested by MWM in the model and the EA groups were significantly prolonged than the normal group (P<0.05;P<0.01); there was no significant difference between the model group and the EA group(P>0.05).After 4 weeks of treatment, the rat escape latency tested by MWM of the model group was significantly higher than that of the normal group(P<0.001); the latency of the EA group was significantly shortened than that of the model group (P<0.05),(Figure 2).
2.2.2 Comparing the number of times of rat crossing the original platform
There was no significant difference in the number of rat crossing the platform tested by the MWM among groups before modeling (P>0.05); there was no significant difference in the number of rat crossing the platform before modeling, after modeling and after 4-week treatment in the normal group (P>0.05).After modeling, the numbers of times of rat crossing the platform tested by the MWM in the model and the EA groups were significantly decreased compared with the normal group (P<0.05); there was no significant difference in the number of times of crossing the platform tested by the MWM between the model and the EA groups (P>0.05).After 4-week treatment, the number of times of crossing the platform tested by MWM in the model group was significantly lower than that of the normal group (P<0.01); the number of times of crossing the platform in the EA group was significantly increased than that of the model group(P<0.05), (Figure 3).
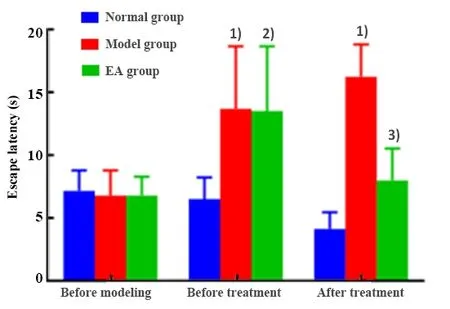
Figure 2.Comparison of the escape latency tested by the MWM test

Figure 3.Comparing the numbers of times of rat crossing the platform tested by the MWM test
2.3 Comparing the protein expressions of Bax,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2
The protein expressions of Bax, Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in the prefrontal cortex of rats in each group were detected by WB assay.After 4-week treatment, the protein expressions of Bax and Caspase-3 were significantly increased (bothP<0.001); Bcl-2 was significantly reduced (P<0.001) in the model group than in the normal group.The protein expressions of Bax and Caspase-3 were significantly reduced (bothP<0.001);Bcl-2 was significantly increased in the EA group than in the model group (P<0.001), (Figure 4).
2.4 Comparing the mRNA expressions of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3
RT-qPCR was used to detect the mRNA expressions of Bax, Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in the rat prefrontal cortex of each group.After 4-week treatment, the mRNA expressions of Bax and Caspase-3 were significantly increased (bothP<0.001); the expression of Bcl-2 was significantly reduced in the model group compared with the normal group (P<0.001).The mRNA expressions of Bax and Caspase-3 were significantly reduced (bothP<0.001); the expression of Bcl-2 was significantly increased (P<0.001) in the EA group compared with the model group (Figure 5).

Figure 4.Comparing the protein expressions of Bax, Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in rat cerebral cortex among groups

Figure 5.Comparing the mRNA expressions of Bax,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in rat cerebral cortex among groups
2.5 Comparison of apoptotic cell number
In the model group, the neurons of the cerebral cortex were densely and neatly arranged with centered and blue stained nucleus.The neurons of cerebral cortex in the model and EA groups were sparse with reduced number and shrunk nucleus.The nucleus was densely and deeply stained brown-yellow.Apoptosis of brain tissues in the model group was more obvious than in the EA group (Figure 6).
After 4-week treatment, there was a significant difference in the number of apoptotic neurons among groups (P=0.000).Compared with the normal group,the number of apoptotic neurons in the cerebral cortex of the model group was significantly increased(P<0.001); compared with the model group, the apoptosis number of neurons in the EA group was significantly reduced (P<0.001), (Figure 7).

Figure 6.Apoptosis of rat cortical neurons in each group (TUNEL, ×400)

Figure 7.Comparing the apoptotic numbers of rat cortical neurons in each group
3 Discussion
The results of this study showed that after EA treatment, the RBG level was significantly reduced, the escape latency tested by MWM was significantly shortened, the number of times of crossing the platforms was increased, the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins and genes in the cerebral cortex were decreased, and the expressions of anti-apoptotic proteins and genes were increased.It’s showed that EA reduced the inflammatory response and apoptosis in rats, reduced the neuron damage,enhanced the learning and memory abilities, and improved the CI.Studies have reported that acupuncture inhibits apoptosis[12], promotes neural regeneration related to learning and memory[13], and improves CI.The results of this study were consistent with the literature.
In recent years, most of the research on T2DM has changed its focus from the peripheral neuropathy to the central nervous system.Among them, the research on CI induced by T2DM has currently become a hot topic at home and abroad, and it has been paid more and more attention by the medical community[14-16].Both the clinical and animal experimental research focuses on observing the diabetic patients or the diabetic rat models to study the CI.Few people made judgments and follow-up studies on the diabetic CI models[17-19].This study aimed to select the CI rat models by MWM test, and to observe the mechanism of EA treatment based on the T2DM rat models [continuous intraperitoneal injection of STZ at 25 mg/(kg·bw) per day for 2 d, and RBG ≥16.7 mmol/L indicated the successful rat modeling][10].
The prefrontal cortex of the brain, as the main execution area of the brain, is related to emotion,cognition, attention control, and memory.This study found that the apoptosis of cerebral cortical cells in rats with diabetic CI was changed, thereby affecting their cognitive function.Studies have shown that the apoptosis of cortical neurons is closely related to the expression of Bcl-2 family and Caspase-3 family[20-21].Bcl-2 is known as an apoptosis inhibitory gene and an important cell regulator in the endogenous pathway of apoptosis signal transduction.It can exert antiapoptotic effects by inhibiting the activity of the Caspase-3 pathway[22].Bax is a major pro-apoptotic protein that induces apoptosis when it forms a Bax-Bax homodimer, and overexpression of Bax also antagonizes the protective effect of Bcl-2, thus to induce cell apoptosis; while the Bax-Bcl-2 heterodimer inhibits apoptosis[23].Caspase-3 is a core member of the Caspase family and plays an irreplaceable role in apoptosis.Caspase keeps a non-activated zymogen state in normal cells.Once the apoptotic program starts,the Caspase will be activated, and the cascade of apoptotic proteases cause irreversible apoptosis.A large number of studies have confirmed that the occurrence of CI is closely related to apoptosis, and EA treatment activates the Bcl-2 expression and inhibits the expressions of Bax and Caspase-3, thereby improving cognitive function[24].In this study, the expressions of apoptotic proteins Bax and Caspase-3 in the prefrontal cortex tissues of rats with CI were lower,and the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 was significantly higher in the EA group than in the model group.It was suggested that EA regulated the apoptosis of T2DM-induced CI in rats and protected the neurons.
Studies have shown that long-term high levels of glucose and lipid in T2DM activate the IRE1α/JNK pathway through endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)and initiate the programmed cell apoptosis[25].Based on previous studies[26-29], this study found that EA at Zusanli(ST 36), Neiting (ST 44) and Yishu (Extra) of rats significantly reduced blood glucose, further inhibited the apoptosis, and improved the learning and memory abilities.
In conclusion, our current study showed that EA at Zusanli (ST 36), Neiting (ST 44) and Yishu (Extra)reduced the blood sugar, promoted Bcl-2 expression and inhibited the expressions of Bax and Caspase-3,thereby inhibiting apoptosis.This may be one of the important reasons that EA improves the learning and memory abilities of T2DM with CI model rats.However,the in-depth mechanism needs to be further explored.
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effects of electroacupuncture of different frequencies on electromyography, NOS and ICC of colon in rats with slow transit constipation
- Effects of electroacupuncture on conjunctival cell apoptosis and the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins Caspase-3, Fas and Bcl-2 in rabbits with dry eye syndrome
- Acupuncture for premature ovarian insufficiency:a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of heat-sensitive moxibustion for adjuvant treatment of depression in Parkinson disease
- Clinical study on Jin’s three-needle therapy for post-stroke cognitive impairment
- Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of heat-sensitive moxibustion for vascular dementia
