Diffuse large B cell lymphoma with bilateral adrenal and hypothalamic involvement:A case report and literature review
2019-04-22PingAnKangChenGuoQingYangJingTaoDouYuLongChenXinYeJinXianLingWangYiMingMuQuanShunWang
Ping An, Kang Chen, Guo-Qing Yang, Jing-Tao Dou, Yu-Long Chen, Xin-Ye Jin, Xian-Ling Wang, Yi-Ming Mu,Quan-Shun Wang
Ping An, Kang Chen, Guo-Qing Yang, Jing-Tao Dou, Yu-Long Chen, Xin-Ye Jin, Xian-Ling Wang,Yi-Ming Mu, Department of Endocrinology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853,China
Quan-Shun Wang, Department of Hematology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853,China
Abstract
Key words: Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; Bilateral adrenal glands; Hypothalamus;Panhypopituitarism; Case report
INTRODUCTION
The clinical manifestations of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) are not specific.When other organs are involved, the clinical manifestations of NHL are complex and diverse; this makes accurate diagnosis difficult[1-3].The synchronous involvement of two endocrine organs is rare in NHL.Until now, only four cases of NHL with bilateral adrenal and sellar involvement have been reported, and all the patients presented with pituitary involvement.Here, we describe a case of a middle-aged male patient with bilateral adrenal masses, who was finally diagnosed with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with bilateral adrenal gland and hypothalamic involvement.We also discuss the diagnostic and treatment approaches available when a patient with NHL presents with multiple endocrine organ involvement.This report can help physicians avoid misdiagnosis of this disease.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
The patient was a 52-year-old man who complained of intermittent fever, sweating,thirst, polyuria, anorexia, abdominal distension and dizziness for 20 d.Three days before he presented to us, and impaired liver function and bilateral adrenal masses were found in a local hospital.
History of present illness
His symptoms persisted for 20 d prior to his arrival at the local hospital.He subsequently underwent extensive examinations which indicated a low blood pressure of 90/60 mmHg.His blood biochemical tests demonstrated elevated aminotransferase levels, and the abdominal ultrasound revealed hypoechoic bilateral adrenal gland masses.Symptomatic treatment resulted in no relief.
那晚我梦见克里斯蒂娜又吊在栏杆上,这次是双脚倒挂,悬于峡谷半空。突然,一个声音喊道:“只有分歧者才能救她。”我二话没说就跑上去拉她,但就在这时,我被人推下护栏,跌落山崖,就在快要撞得粉身碎骨时,猛地惊醒过来。
History of past illness
The patient was diagnosed with hypertension a year ago, with the highest blood pressure of 135/105 mmHg, and he had never been treated systematically.Family history of the patient was negative.
Physical examination
On admission, he was hypovolemic, with a blood pressure of 88/68 mmHg, a pulse rate of 122 beats/min and a temperature of 37.6ºC.No superficial lymphadenopathy was noted.Although physical hypothermia was effective, intermittent fever persisted.After admission for a week, he developed rashes on his chest, back, and abdomen.
Laboratory examinations
On admission, his blood biochemical tests were indicative of impaired liver function,with significant elevation of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase,glutamyl transferase, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase levels.Routine blood tests showed a significantly decreased platelet count and slightly elevated red and white blood cell counts.The coagulation function test showed a marked elevation in plasma fibrinogen and D-dimer levels.Moreover, serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and β2-microglobulin were elevated significantly.The results are shown in Table 1.
We also evaluated the function of the pituitary-target gland axes.The plasma adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) and cortisol values at 0 AM, 8 AM, and 4 PM,are shown in Table 2.Despite the cortisol level decline, the ACTH levels failed to increase via a feedback mechanism.In addition, the diurnal rhythm of cortisol and ACTH were disturbed.The results of the thyroid and gonadal function tests are shown in Table 3.The serum total thyroxine, free thyroxine, free triiodothyronine, and thyroid stimulating hormone values, were all lower than normal ranges.Hormones in the pituitary-gonadal axis, including testosterone, luteinizing hormone, and follicle stimulating hormone, were also markedly lower.The 24-h urinary catecholamine and vanillylmandelic acid levels were within the normal range.
Imaging examinations
Computed tomography (CT) of the urinary system showed bilateral adrenal gland space occupying lesions with retroperitoneal lymphadenectases.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pituitary gland revealed a space occupying lesion in the hypothalamus with an enlarged pituitary stalk.18Fluorine-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/CT (PET/CT) images showed lesions with high metabolism in both adrenal glands, the sellar area, left supraclavicular lymph nodes,retroperitoneal lymph nodes, left tonsil, and the left testis (Figure 1).Metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scintigraphy showed normal bilateral adrenal glands uptake.
Further diagnostic work-up
A biopsy of the left supraclavicular lymph nodes was carried out subsequently and the result showed lymphoid hyperplasia.Immunohistochemistry demonstrated lesion positivity for Bcl-2, Bcl-6, CD 20, PAX-5 and MUM-1, and negativity for CD10 (Figure 2); the levels of C-myc and Ki-67 were 70% and 80%, respectively.
According to the results of pituitary-target gland hormone measurement, the patient was diagnosed with anterior pituitary hypofunction.After hydrocortisone replacement therapy, posterior pituitary hypofuntion appeared.
MULTIDISCIPLINARY EXPERT CONSULTATION
Jing-Tao Dou, MD, PhD, Professor and Chief, Department of Endocrinology,Chinese PLA General Hospital
The patient developed hypernatremia after hydrocortisone treatment for two possible reasons:first, a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone was prominent, leading to polyuria with a relative high blood sodium concentration; second, hydrocortisone played a partial role of a mineralocorticoid; therefore we decided to replace hydrocortisone by prednisone.
Guo-Qing Yang, MD, PhD, Professor and Chief, Department of Endocrinology,Chinese PLA General Hospital
The patient developed acute-onset impaired liver function, a fever, a rash, and according to the biopsy and PET/CT results, bilateral adrenal and sellar occupying lesions were more likely to be NHL, causing panhypopituitarism.Therefore, the patient was treated in the endocrinology department with hormone replacement therapy for panhypopituitarism.
Quan-Shun Wang, MD, PhD, Professor and Chief, Department of Hematology,Chinese PLA General Hospital

Table 1 Results of laboratory test on admission
The diagnosis of NHL in this patient was clear, and therefore chemotherapy should be administered as soon as possible.In addition, in view of the multiple organs involved, an intrathecal injection was administered to prevent central neurological symptoms.Due to the multiple organ involvement of the tumor and poor prognosis according to the results of immunohistochemistry, an autologous stem cell transplantation was recommended.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The patient was finally diagnosed with DLBCL, Ann-Arbor stage IVB, a type of nongerminal center B-cell tumor, involving the bilateral adrenal glands, hypothalamus,left supraclavicular lymph nodes, retroperitoneal lymph nodes, left tonsil, and left testis.With hypothalamic and bilateral adrenal involvement, the condition also led to panhypopituitarism.
TREATMENT
The patient was treated with the R-CHOP immunochemotherapy regimen (rituximab:0.7 g on day 0, and cyclophosphamide:1.3 g, doxorubicin:60 mg, and vincristine:4 mg on day 1, and methylprednisolone:80 mg on days 1–5).He also received intrathecal dexamethasone and cytarabine at doses of 5 mg and 50 mg, respectively.A total of 6 courses of chemotherapy were delivered, and the interval between each course was 1 mo.After the 6 courses of chemotherapy, autologous stem cell transplantation was carried out.
For panhypopituitarism, the patient was prescribed desmopressin acetate, and hydrocortisone was replaced with prednisone acetate at a dose of 0.05 mg and 5 mg,twice a day, respectively.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
A time line of this case is shown in Table 4.After immunochemotherapy, the patient recovered from his intermittent fever, the transaminase levels decreased significantly,and the platelet count returned to a normal range.After 4 courses of chemotherapy,PET/CT indicated that the lesions disappeared including the hypothalamus and adrenal gland lesions (Figure 1).After replacement therapy with prednisone acetate and desmopressin acetate twice a day at a dose of 5 mg and 0.05 mg, respectively, the serum sodium level declined to a normal range, and the symptoms relieved.
We evaluated the risk for central nervous system (CNS) relapse by calculating the CNS-International Prognostic Index (CNS-IPI) score, which was 4.Therefore, the patient had a high risk for CNS relapse.We then recommended a pituitary MRI every year and endocrine hormone measurement every 3 mo.

Table 2 Results of pituitary-adrenal function test
DISCUSSION
Pheochromocytomas, lymphomas, and metastatic carcinomas are all common types of adrenal space occupying lesions[4-6].In this case, the presence of pheochromocytoma and metastatic carcinoma were excluded by MIBG scintigraphy, CT scans, and laboratory examination.Lymphoma is the most common malignant cause of fevers of unknown origin[7].The patient had intermittent fever for 20 d; infection and autoimmune diseases could therefore be excluded.A rash developed at a later stage and the results of the laboratory examination showed abnormal elevations in serum LDH, serum β2-microglobulin, and transaminases.All these symptoms and findings suggested a diagnosis of lymphoma, which was finally confirmed by biopsy and PET/CT.PET/CT also showed that the standardized uptake values (SUV) in bilateral adrenal gland and the hypothalamus were higher than those of the background; they were as high as those of the left supraclavicular lymph nodes.The findings indicated that DLBCL had bilateral adrenal gland and hypothalamic involvement in this case.
The diagnosis of panhypopituitarism was complicated.Since hormones levels of pituitary-target gland were all lower than the normal ranges, the patient was diagnosed with anterior pituitary hypofunction.He was accordingly received hydrocortisone replacement therapy.However, after treatment, the urine osmotic pressure and specific gravity declined to 151 mOsm/L and 1.005, respectively, while the serum sodium and chloride levels increased to 155.4 mmol/L and 117.3 mmol/L,respectively.In view of the hypovolemia, polyuria, and thirst on admission, his posterior pituitary function was also considered to be impaired, and he was diagnosed with panhypopituitarism.
Synchronous bilateral adrenal gland and hypothalamic–pituitary axis involvement has never been reported in patients with NHL.Literature review reveals 4 similar cases of NHL with bilateral adrenal gland and pituitary involvement.Two patients, 1 Chinese and 1 Japanese, presented with adrenal insufficiency and panhypopituitarism[8,9].A Chinese patient presented with adrenal insufficiency and only anterior pituitary hypofunction[10].A British patient presented with adrenal insufficiency and mild diabetes insipidus[11].
The most common pathological type of bilateral adrenal lymphoma is DLBCL,which causes adrenal insufficiency to varying degrees[12-15].However, this case was extraordinary in that the ACTH level was lowered instead of being raised due to the hypothalamic involvement.In previous literature, only a few patients with lymphoma presented with panhypopituitarism secondary to hypothalamic involvement[16].Previous reports noted that DLBCL was the most common type of NHL involving the hypothalamic–pituitary axis[17,18].In addition, cases of NHL with pituitary involvement often presented with variable clinical manifestations including anterior pituitary hypofunction, posterior pituitary hypofunction, visual disturbances, and acromegaly[19-24], and few cases presented with hyperprolactinemia[25,26].In the current case, prolactin level also increased slightly in addition to developing panhypopituitarism.A study suggested that as the pituitary gland has a considerable reserve capacity, most cases of NHL with hypothalamus and pituitary involvement usually present with posterior pituitary hypofunction, and only a few patients present with anterior pituitary hypofunction[27].A few previous reports have also shown that chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation has a substantial effect on hypothalamic-pituitary lymphoma, which led to sustained remission and restoration of hormone levels, but the mechanism remains unclear[28,29].However, this restoration of endocrine hormones has not been seen in this patient.Therefore,continued evaluation of endocrine hormones should be conducted during follow-up period.
CNS-IPI is an index used to evaluate the risk for CNS relapse in patients with DLBCL treated with R-CHOP.The index consists of 5 risk factors (age > 60; elevated LDH; Easter Cooperative Oncology Group status > 1; stage III/IV; extranodal site > 1)with additional kidney or adrenal involvement.The CNS-IPI score divides patients with DLBCL into 3 groups, low risk (0-1 factor), intermediate risk (2-3 factors) andhigh risk (4-5 factors) with a 2-year risk for CNS relapse of 0.6%, 3.4% and 10.2%,respectively[30].The CNS-IPI score in this case was 4, which represents a high risk of CNS relapse.Therefore, prophylactic interventions are recommended to prevent CNS relapse.In addition, endocrine hormones measurement and pituitary MRI should be conducted regularly to identify CNS relapse.

Table 3 Results of pituitary-thyroid function test and pituitary-gonadal function test
The presented patient was diagnosed with DLBCL based on the left supraclavicular lymph nodes biopsy.Significantly increased SUVs were also noted in the left supraclavicular lymph nodes, bilateral adrenal area, sellar area, retroperitoneal lymph nodes, left tonsil, and left testis.Our experience with this case suggests that biopsy and PET/CT are effective for the diagnosis of NHL with multiple organ involvement[31].
CONCLUSION
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of DLBCL with bilateral adrenal hypothalamic involvement.When NHL involves endocrine organs, patients are predisposed to hypofunction of endocrine organs.Therefore, hormone replacement therapy is necessary.The case demonstrates the necessity of biopsies in combination with PET/CT in the diagnosis of NHL with involvement of extralymphatic organs.
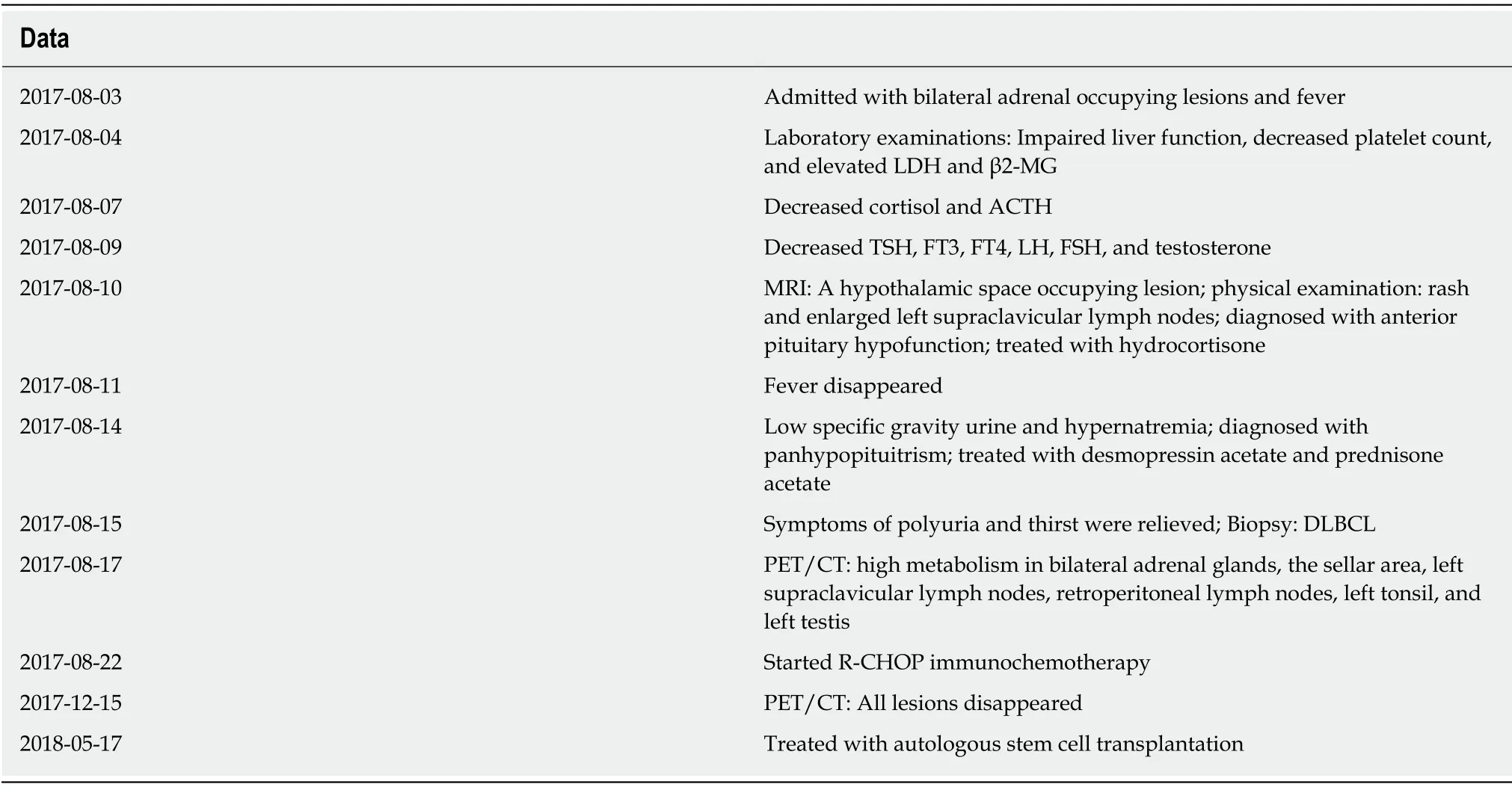
Table 4 Time line
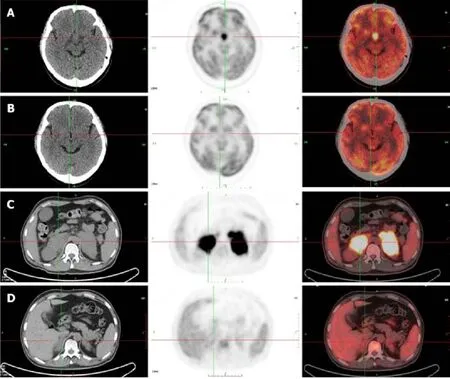
Figure 1 Images of positron emission tomography/computed tomography scan.

Figure 2 Results of the left supraclavicular lymph nodes biopsy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank all of the treatment groups of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital.
杂志排行
World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Overview of organic anion transporters and organic anion transporter polypeptides and their roles in the liver
- Value of early diagnosis of sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury by renal contrast-enhanced ultrasound
- Value of elastography point quantification in improving the diagnostic accuracy of early diabetic kidney disease
- Resection of recurrent third branchial cleft fistulas assisted by flexible pharyngotomy
- Therapeutic efficacy of acupuncture combined with neuromuscular joint facilitation in treatment of hemiplegic shoulder pain
- Comparison of intra-articular injection of parecoxib vs oral administration of celecoxib for the clinical efficacy in the treatment of early knee osteoarthritis
