切换网络下加速分布式在线加权对偶平均算法
2018-10-26王俊雅
王俊雅
切换网络下加速分布式在线加权对偶平均算法
王俊雅
(安徽理工大学数学与大数据学院,安徽,淮南 232000)
研究了切换网络下加速分布式在线加权对偶平均算法,提出了A-DOWDA算法。首先利用加权因子对对偶变量进行加权,其次在有向切换网络是周期强连通,且对应的邻接矩阵是随机的而非双随机的条件下,加速了算法的收敛速率,最后通过数值实验验证了算法的可行性。
分布式;加权;切换网络;对偶平均;Regret界
0 引言
近些年来,随着网络规模的增长,复杂网络成为人们研究的热点领域。通过增加这些系统的规模和复杂性,需要分散控制方案,以降低数据传输速率和确保本地故障时的鲁棒性,这使得分布式网络受到了越来越多的重视,在并行计算、机器学习和通信系统等多个方面具有广泛的应用[1-3]。文献[4-6]提出了基于次梯度的分布式优化算法,但其成本函数是不变的,而网络的拓扑结构允许变化。然而,环境中的不确定性往往会对成本函数产生重大影响,难以建立易于处理的优化问题。文献[7-9]通过随机框架来提高算法鲁棒性,但随机优化方法难以解决动态问题。
本文考虑基于在线优化的分布式权重对偶平均算法,不仅能处理复杂系统的动态模型,而且节约了网络成本和存储空间,避免了资源浪费。文献[10]提出了基于交替乘子法的分布式在线算法,对网络数据流进行实时采集和分析,增强了网络的鲁棒性。

文章在第一部分介绍了图论和Regret相关知识,第二部分介绍了切换网络,第三部分提出了加速分布式在线加权对偶平均算法(A-DOWDA),第四部分给出了证明,第五部分给出了数值实验,在第六部分总结了本文工作,并提出了未来值得进一步研究的问题。
1 图论和Regret

2 切换网络


3 加速分布式在线加权对偶平均算法

算法1 加速分布式在线加权对偶平均算法(A-DWDA)
11) end
14) end for
4 收敛性分析








证明 由引理2,引理4得:
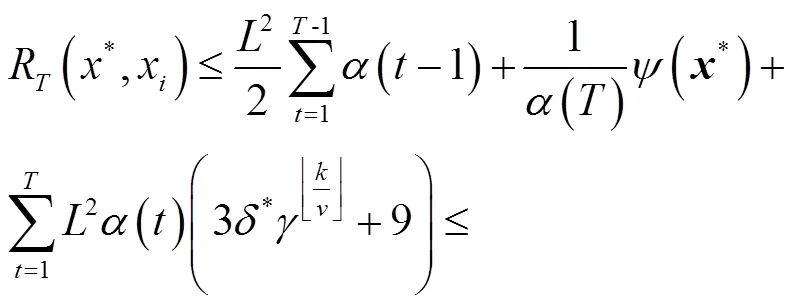



证明:由文献14中定理2得静态网络Regret界:

又根据文献14中定理2知:
故可得静态网络情形下的Regret界收敛速度为:


证明:由定理1易证。
对比(8)式和(9)式,可以看出,当网络是切换网络时,带有加权的分布式在线对偶平均算法收敛速度变快,变快的速率可以由(9)式右边第二项衡量。
5 数值实验
通过数值实验验证A-DWDA的可行性,评价指标为平均损失函数:即
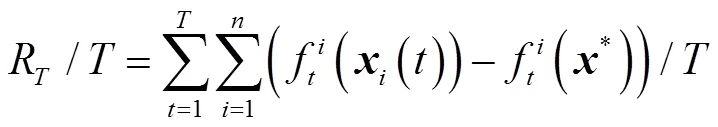
图1 不同迭代次数和步长下加速与不加速算法的对比
Fig.1 Comparison between accelerated and unaccelerated algorithms with different number of iterations and step sizes

图2 不同函数在迭代次数和步长下加速与不加速算法的对比

6 结论
本文在切换网络所对应的邻接矩阵是随机的情况下,对分布式在线权重对偶平均算法进行加速,提出了A-DWDA算法,不仅提高了算法的收敛速度,而且改进了Regret界。未来将考虑相应的量化算法或异步问题。
[1] Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J].Foundations & Trends in Machine Learning, 2010, 3(1):1-122.
[2] Dorfler F, Chertkov M, Bullo F. Synchronization in complex oscillator networks and smart grids[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(6): 2005-2010.
[3] Blatt D, Hero A O, Gauchman H. A convergent incremental gradient method with a constant step size[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2007, 18(1): 29-51.
[4] Nedic A, Ozdaglar A. Distributed subgradient methods for multi-agent optimization[C]. Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Automatic Control, Piscataway, 2009:48-61.
[5] Lobel I, Ozdaglar A. Distributed subgradient methods for convex optimization over random networks[C]. Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Automatic Control, Piscataway, 2011: 1291-1306.
[6] Lee S, Nedic A. Distributed random projection algorithm for convex optimization[C]. Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE conference on Selected Topics in Signal Processing, Piscataway, 2013:221-229.
[7] Ram S, Nedic A, Veeravalli V. Incremental stochastic subgradient algorithms for convex optimization[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2009, 20(2):691-717.
[8] Sundhar R S, Nedi A, Veeravalli V V. Distributed Stochastic Subgradient Projection Algorithms for Convex Optimization[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications,2010, 147(3):516-545.
[9] Agarwal A, Duchi J. Distributed delayed stochastic optimization[C]. Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Piscataway, 2012:5451-5452.
[10] Lin P, Ren W. Distributed Constrained Consensus in the Presence of Unbalanced Switching Graphs and Communication Delays[C]. Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Piscataway, 2012: 2238-2243.
[11] Tsianos K I, Rabbat M G. Distributed dual averaging for convex optimization under communication delays[C]. Proceedings of the 2012 American Control Conference, Piscataway, 2012:1067-1072.
[12] Tsianos K I, Lawlor S, Rabbat M G. Push-sum distributed dual averaging for convex optimization[C]. Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Piscataway, 2012:5453-5458.
[13] Hosseini S, Chapman A, Mesbahi M. Online Distributed Convex Optimization on Dynamic Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 61(11):3545-3550.
[14] Duchi J C, Agarwal A, Wainwright M J. Dual Averaging for Distributed Optimization: Convergence Analysis and Network Scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(3):592-606.
[15] Liu S J, Chen P Y, Heri A O. Accelerated Distributed Dual Averaging over Evolving Networks of Growing Connectivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 66(7):1845-1859.
ACCELERATE DISTRIBUTED ONLINE WEIGHTED DUAL AVERAGE ALGORITHM IN SWITCHED NETWORKS
WANG Jun-ya
(College of Mathematics and Big Data, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Huainan, Anhui 232000, China)
We studies the distributed online weighted dual average algorithm is accelerated under switched network and an A-DWDA algorithm is proposed. Firstly, weighting factors are used to weight dual variables. Secondly, the directed switched network is periodically strongly connected, and the corresponding adjacency matrix is stochastic rather than doubly stochastic, the convergence speed of the algorithm is accelerated. Finally, a numerical experiment is performed to verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
distributed; weighted; switched network; dual average; Regret bound
1674-8085(2018)04-0006-05
TP-301.6
A
10.3969/j.issn.1674-8085.2018.04.002
2018-05-05;
2018-06-27
安徽省级精品资源共享课程(11528);硕士研究生创新基金项目(2017CX2046)
王俊雅(1994-),女,安徽阜阳人,硕士生,主要从事分布式优化研究(E-mail:784836893@qq.com).
