Training indicators and quantitative criteria for emergency nurse specialists*
2017-07-05ManJiangXinAo
Man Jiang,Xin Ao
Medical School of Yangtze University,Jingzhou,Hubei 434023,China
Training indicators and quantitative criteria for emergency nurse specialists*
Man Jiang,Xin Ao*
Medical School of Yangtze University,Jingzhou,Hubei 434023,China
a r t i c l e i n f o
Article history:
Emergency nurse specialist
Continuing education system
Evaluation indicators
Quality standard
Delphi
Objective:By constructing a training system of quality evaluation standards for emergency nurse specialist(ENS),we can ensure smooth operations and quality training for ENS.
Methods:First,the frame structure of indicators was designed on the basis of system theory and the balanced scorecard method.Meanwhile,corresponding quantitative standard indicators were compiled through literature analysis and a review of training characteristics.Next,screening indicators were collected through consultation with experts and statisticalcalculations.The indicators weight coef fi cient was calculated using the analytic hierarchy process(AHP).Finally,indicators were validated in two groups of nurses in two different training courses.
Results:(1)We created a three-levelindicator system:level-Ⅰdimensions have 4 indicators,while level-Ⅱdimensions and level-Ⅲdimensions have 13 and 34 indicators,respectively;(2)The coef fi cient of expert's judgment is 0.840,familiarity is 0.914 and authority is 0.877,and the three rounds of coordination coef fi cient are 0.456,0.553 and 0.715,respectively;(3)There are at least 56 indicators in alternative quantitative standards;and(4)The alpha reliability value of the indicator system in the two training course had no signi fi cant difference(P>0.05).The same result was observed when examining two groups of nurses in one training course(P>0.05).
Conclusions:This study established a training system of quality evaluation standards for emergency nurse specialists that is objective,reliable,easy to operate and representative according to scienti fi c selection and veri fi cation.This system can therefore provide a basis for quality evaluation and targeted improvement for ENS training in addition to promoting health.
©2017 Shanxi Medical Periodical Press.Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
1.Introduction
Since the implementation of ENS training program in China, cities,hospitals and universities atalllevels responded quickly,and many quali fi ed people have been trained to meet the needs of hospitals.Many problems with training remain,however, including1:limited teaching resources and limited ability at many training institutions;and weak foundational knowledge among students that is dif fi cult to mitigate,which leads to unsatisfactory training effects.This factor is closely correlated with the lack of quality standards for training institutions and ENS programs. Therefore,it is particularly important to establish a system of quantitative standards for ENS.This study examines ENS training as a whole from the perspective of system theory,2which is based on management guru Robert's balanced scorecard method,3to build a system based on evaluation indicators,which is conducive to the coordinated development ofa training system.This study also uses many other methods,such as the expert consultation method,4the correlation coef fi cient calculation method,AHP5and paired comparison method to select and verify the evaluation indicators and their quantitative standards.The ultimate goal of this study is to provide a quantitative basis for identifying the problems existing in the training of ENS,evaluate and monitor the training quality.
2.Methods
In this study,the construction of an indicator system and the quantization of indicators consist of four factors:designindicators,screening indicators,indicators'weight and veri fi able indicators.
2.1.Design indicators and their quantitative standards
First,the frame structure of the indicator system is designed on the basis of system theory and the balanced scorecard method in order to determine the level-Ⅰdimension.Second,four academic literature databases,i.e.,CNKI,PUBMED,VIP,and Wanfang,were searched using the keyword“specialist nurse training”to collect the relevant data.The frequency of elements,which are closely related to level-Ⅰindicators in the statistical data,ranked in the frequency of occurrence,and the high frequency elements were selected as metrics to form level-Ⅱindicators and level-Ⅲ indicators.Finally,the level-Ⅲindicators were quantized individually. The fi nal design of the alternative indicators included 16 level-Ⅰdimensions indicators,39 level-Ⅱdimensions indicators and 61 level-Ⅲdimensions indicators.An additional 61 items formed the alternative quantitative standards.
2.2.Screening indicators through expert consultations
The criteria for selecting experts for consultation were as follows6:(1)Engaged in emergency nursing or teaching,hospital or teaching management for more than 20 years;(2)Senior professional title;(3)Holding a bachelor's or higher degree.After selecting experts at random in different cities and regions according to the admittance criteria,a totalof 31 experts were selected.7Thirty of those returned a paper survey form containing their feedback for a response rate of 96.78%.Of the selected experts,9 were teaching management experts,6 specialist nursing experts,8 education experts and 7 hospital management experts,these experts aged from 43 to 60;senior professional titles accounted for 100%,and 86%held a master's or higher degree.The expert consultation phase was completed after three rounds of letter consultations.8The purpose of the fi rst round was to learn the individuals'perspectives on the research problems by introducing them to the background and signi fi cance.This allowed us to better understand how an expert's practical experience,theoretical analysis,background knowledge,intuitive feelings and other personalfactors mightimpacthis or her judgments.We also submitted allthe indicators to them.Each indicator was evaluated on a 9 point Likert scale(1:extremely unimportant,9:extremely important) with answers indicated by checking the appropriate box.The quantitative standards for each level-Ⅲindex were evaluated using a fi ve-point Likert scale(1:completely disagree,5:completely agree),with answers once again indicated by a check box.The indicators were evaluated on the basis of the experts'assessment of their relative importance,while the quantitative standards were evaluated based on approval ratings.The study,according to the standards ofthe related researches abroad,regards the importance score that is greater than or equalto the average and the approval rate thatis greaterthan or equalto 80%as the selection standards of indicators and quantitative standards.9The second round was based on the statisticalresults ofthe fi rstround.After eliminating 2 level-Ⅱdisagreement indicators,5 level-Ⅲ indicators and their corresponding quantization standards,the remaining indicators were resubmitted to experts again to supplement and modify. Three level-Ⅱindicators were supplemented in total,however: because the importance scores are lower than average,2 level-Ⅲindicators could not be selected in the third consultation round. This third round took the higher scores indicators from the statistical results of the second round and resubmitted them to the experts in conjunction with the supplementary indicators to observe the stability of the results.
2.3.Screening indicators through statistical calculations
Five institutions engaged in ENS training,comprising 2 ClassⅢGrad A hospitals,2 Class IIGrade A hospitaland one ordinary school ofhigher education were selected.The originaldata were evaluated for quality with the indicators after the fi rstscreening,according to the collected data,after which the score of each indicator was counted and the correlation coef fi cient between the two indicators was calculated,fi nally the T test was carried out.Correlation was judged as follows10:a correlation coef fi cient less than 0.3 was regarded as low correlation;between 0.3 and 0.7 is the medium correlation;and correlation exceeding 0.7 was regarded as high correlation.Any two highly correlated indicators must be further integrated and re fi ned into a single indicator.
2.4.Calculating indicators'weight coef fi cient
Indicators'weight coef fi cient was calculated by AHP.First,the judgment matrix was designed according to the average scores obtained from the early expert consultation on the importance of indicators.The scale was designed to follow the relative importance of proportional scaling of the AHP method11(Table 1).Then,the weight coef fi cients of the indicators were calculated based on the judgment matrix,and the consistency of the judgment matrix was fi nally tested to verify the rationality of the judgment matrix.
2.5.Verifying indicators
Considering that there is no mature correlation index system, we could not perform the comparison between indicators.The consistency,stability and reliability of the test results of the index system were validated through the self-contrast method.Through convenience sampling,2 institutions that were carrying out ENS training were taken as the research subjects to perform a quality evaluation.A total of 10 judges,four men and six women with an average age of 42±0.971 years participated in the evaluation.All were professors.They were randomly divided into two groups. Neither education,professional level,professional experience nor other aspects showed any signi fi cant difference.Based on the information provided by the training courses,live lectures,small sample surveys and related personnel questionnaires,seminars orother methods were used to implement evaluation.During the evaluating,we used the designed quantitative criteria.All that reached the quali fi ed standards were scored at 65 points,those who achieved the good standard record were scored at 80 points, and the indicators that reached the standard of excellence werefi nalweight coef fi cientofeach indicator)÷indicator number.Ifthe total score fell between 60 and 79,the program has some good qualities but still needs to make targeted improvements;a total score ranging from 80 to 89 suggested good quality,butwith a need for some further improvements;and total score over 90 points suggested excellent quality.Then,statistical analysis was carried out on the evaluation results.The scores for the a reliability coef fi cients of the two groups were calculated by SPSS software,and the average values ofthe reliability values were compared with the T test.

Table 1 Proportional scaling regarding the level of importance.
2.6.Statistical methods
Data were collected using Excel to establish a database,while Excel,SPSS11.5 and AHP were used to complete the statistics.The T test was used to analyze the continuous data andХ2test for the categoricaldata.
3.Results
3.1.Indicators structure and authority coef fi cient on the basis of system theory and the balanced scorecard method
After the initial design of the alternative indicators and two rounds ofselection that removed 3 level-Ⅱindicators and 6 level-Ⅲindicators while adding 1 level-Ⅲindicator,the fi nal form of the indicator system is shown in Table 2.
3.2.To analyze the reliability of expert consultation
The various coef fi cients obtained are shown in Table 3.
3.3.Quantitative standards and quality standards ofeach indicator
After the submission ofthe 61 quantitative standards,the level-III indicators changed:6 indicators were eliminated and oneindicator was supplemented,including two establishment rates,a model updating rate,a new method coverage rate and a new knowledge coverage rate for a total of 5 criteria.Because of 6%of the experts felt that the description and de fi nition are not reasonable,they were re fi ned and completed by the research group based on the opinions of the experts after discussion.The quantifi cation standards,standards speci fi cation and quality standards of each indicator are shown in Table 4.
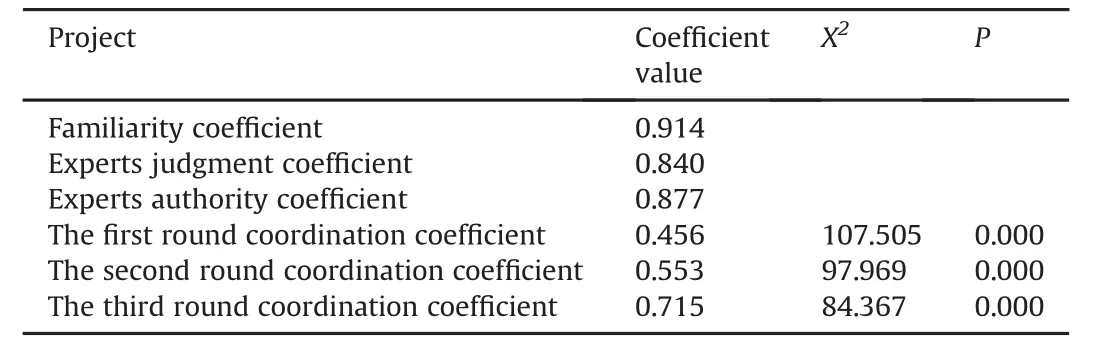
Table 3 The calculation results of the coef fi cients after expert consultation.
3.4.The comparison of the average value of a reliability and the results of T test of the two groups
It has been demonstrated that there were no signi fi cant differences in the a reliability value of the T test in the evaluation of the two training classes;in the same class,there were also no signi ficant differences between the two groups for a reliability coef fi cients with the T test.These results suggest that the index system is of high reliability.The results are shown in Table 5.
4.Discussion
4.1.Theoretical basis of building indicators
System theory was fi rst conceived by Austrian American biologist L.von Bertalanffy in the 1920s.According to system theory,any complicated thing in the world can be seen as a system and any system is an organic whole.Each system is made up ofa number of elements,each of which can affect others and even the whole system.Only by analyzing the structure and the function of the whole system can we fi nd the rules of change,which can help thesystem reach the optimalstate.12ENS training is a complex project. On the one hand,it is in fluenced by many elements,such as policy support,teaching teams,students'status,resource availability,and training methods and means,etc.;on the other hand,there are many steps in the process of training and each element and link interacts and in fluences the others.Training therefore represents a process of dynamic change,and leads to particular training results which are not easy to control.In particular,ENS training in China remains in the initialstages ofexploration atpresent.Some training courses emphasize the improvement of the training model,means and method,but ignore students'learning ability.Other training courses devote their attention to students'access standards,but ignore the management and construction of training institutions. Viewing these problems from a single angle leaves us unable to make real improvements in training effects.To combat this problem,we draw on the basic idea of system theory and viewed ENS training as a system.From the overallpoint ofview,we created the overalldesign of the index structure.Viewing the system from the outside,the government has a high degree of support for the training of specialist nurses and has created relevant policies, helping to usher in new opportunities for ENS training.Analyzing the system from the inside,good training outcomes require suf ficient material resources,human resources and various teaching software packages,which are similar to the training scheme and plan,for security.Programs must also be able to screen the eligible students,seeking students with the professionalbackground,work ethically and with professional experience to meet the training requirements.Successful programs also require strong teaching management and constant monitoring ofboth program operations and program outcomes.It is clear that the training guarantee is the basic element,student quality is the key element,and good program management is the main line in the ENS training.This is the reason why we regard the training guarantee,student quali fi cations,process and effect as fi rst level indicators.

Table 2 Indicator structure and authority coef fi cient on the basis of system theory and the balanced scorecard method.

Table 4 Quantitative standards and quality standards of each indicator.

Table 4(continued)

Table 5The average value of a reliability and the results of t tests of the two groups.
The balanced scorecard is a method for designing a comprehensive evaluation index system fi rstproposed by Robert,a famous management scholar at Harvard University,and Norton,the president of international enterprises,in 1992.It uses four different perspectives,such as fi nancial security,securing customers,internalmanagement,learning and growth,to examine and evaluate the performance and development of an enterprise.Its characteristics are mainly embodied in its balance,emphasizing the balanced development of enterprises.3ENS training both a complex and long-term project that requires sustainable development and a virtuous circle.In view of this,compared with the index structure, we made further improvements to the structure of the training system and added the development oftraining as a level-indicator. The fi nal indicator system is comprehensive,complete and conducive to the control,management,transformation and development of training that was able to promote the continued development of ENS training.
4.2.Indicators screening method analysis
Analysis was performed from the following two aspects:(1)the reliability ofexpert consultation.A.Authority:the reliability of the consulting results is closely related to the authority of experts themselves.To increase the authority ofexperts,the study targeted experts'selection criteria and set clear provisions regarding the necessary degrees,professional titles,professional experience and professionalbackground to be considered an expert in this setting. In the fi rst round of letter consultation,we carried out a selfassessment survey of experts in order to both learn how experts understand indicators and understand how different criteria affect experts'judgments.Then,according to the self-scoring score,the experts'mean familiarity coef fi cient(Cs)was calculated as 0.914, and the mean judgment coef fi cient(Ca)was 0.840.The calculation formula for degree ofauthority[Cr¼(CsþCa)/2,when Cr>0.7 can be accepted],13and the mean coef fi cient of experts'authority is 0.877.It can be seen that the coef fi cient of experts'judgment,familiarity and authority are all higher than 0.7.Especially in the observed value,71%of experts'familiarity coef fi cients are one. Sixty-three percent of the experts'judgment coef fi cients are one, which can further explain the high credibility of experts and the reliable results.B.Consistency:the reliability of the consultation results has a positive correlation with the consistency of the experts'opinions.The indicator commonly used to evaluate the degree of judgment consistency is the Kendall coordination coef fi cient(W).Its value falls between zero and one such that the greater the W value,the better the consistency.14In this study,after three rounds of letter consultation and calculating the importance score level of the coordination coef fi cient(W)in each round,the average coordination coef fi cients are 0.456,0.553 and 0.715 for each of the three rounds,respectively.Calculating the approval rates of each round of quantitative standards returned 91%,90.5% and 95%,which all met the inclusion criteria,and the agreement score levels of coordination coef fi cient(W)are 0.803,0.822 and 0.867.The results show that although there were differences in the selection ofindicators at alllevels in the fi rstround ofconsultation, the differences gradually shrank and the consistency tended to be good.Further,from the beginning,experts tended to agree with the quantitative criteria we submitted,and the consistency of opinions was high.(2)The importance of the correlation coef fi cient.The selection of indicators is not scienti fi c if it is purely dependent on subjective or objective methods.The expert consultation method is a subjective method,with the result that the fi rst screening index has two problems:one is thatthe experts'views on the importance of indicators has a certain subjective tendency,which is remedied with four indicators,namely,the coef fi cient of experts'judgment, familiarity,authority and coordination.The second problem is that itis impossible to judge the correlation degree between the indexes through the expert consultation method,as it renders the independent discrimination of indicators insuf fi cient.Taking into account the large number of indicators in this study,there may be a certain degree of correlation between indicators such that the observed information can overlap and affect the results of the overall evaluation.Therefore,it is necessary to use the statistical method to compare the relationships between the level-Ⅱand level-Ⅲ indicators,in order to objectively determine the representative of the indicators.Using statistical calculations,in the level-Ⅲindicators,the correlation coef fi cient between the training model and the model innovation is 0.97,which suggests that the information ofthe two indicators is highly overlapped and must be integrated.Because the score of the importance of the model innovation is higher than the training model,we removed the“training model”index.The correlation coef fi cients of the remaining indicators are all less than 0.5,indicating that the relationships between these indicators are not close and that they therefore exhibit better independence and representation,so they are retained.
4.3.Characteristics of indicator system
The indicator system in this study has the following three characteristics:(1)To follow the principles of building indicators. Because the indicators were formulated under different principles, their performance is not the same.Therefore,before the construction of the indicators,based on the normal principles of designing indicators and combined with the characteristics and requirements of the ENS training,the research group worked exhaustively and formulated fi ve principles.The fi rst is the principle of comprehensive development;that is,to regard the ENS training as a whole with the developmentofa vision that considers all aspects of the training process.The second is the principle of objectivity,which means to objectively analyze the meaning of indicators and screen them objectively as far as possible to overcome the impact of subjective factors.The third is the principle of independence,which refers to avoid any overlap in the indicators' content,which renders the comparison of indicators dif fi cult and affects the accuracy of the evaluation results.In other words,we should try to choose the independent indicators to enhance the typicality of the indicators.Fourth is the principle of realization. This refers to the process in the quantization ofindicators.We must grasp the quantitative degree with the current existing conditions and resources as the basis in order to improve the level of the standards appropriately,which leads to the implementation of the standards and further training development,and notbecause ofthe high requirements and cannot be achieved.Fifth is the principle of feasibility.This states that the construction of indicators must be measurable using data,so that the conditions are practicaland easy to evaluate.(2)The operability of the indicators is good.The indicators ofthis study are allaccompanied by quantitative standards and quality standards.For example:for the indicator regarding teachers'structure of teachers,the teacher's age,professional background,academic degree,professional title,professional source and teacher e student ratio clearly are de fi ned and quantifi ed;we then introduce certain related concepts,such as age coincidence rate,background coincidence rate,academic coincidence rate,title coincidence rate,profession coincidence rate,and teacher e student ratio coincidence rate,to unify the calculation methods(Table 2).When the results reached the quantitative standards of60%e79%they are regarded as being ofaverage quality, as being of good quality upon reaching 80e89%,and excellent quality at 90%or higher rate.The purpose of this design can make the evaluation more objective,easy and accurate.(3)The reliability ofthe indicator system is high.The indicator system constructed in this study notonly has a theoreticalbasis butalso has gone through two rounds of screening and one round of veri fi cation.The feedback from the experts was particularly valuable,and 98%of the experts considered that the design of the indicator system is reasonable,the standards are clear and easy to calculate,indicators are easy to use,and the system overall has high value of use.Two percent of the judges stated that although the indicator system exhibited high reliability and is easy to popularize,room for improvement remains in future iterations.
5.Conclusions
The design of the emergency nurse training quality evaluation index system is in strict accordance with the established fi ve principles.The indicators in this study are all accompanied by quantitative standards and quality standards and the operability of the indicators is good.Finally,after two scienti fi c screenings and a one-time veri fi cation,it has been con fi rmed as being objective, reliable,easy to operate and representative ofnursing training.This evaluation system can therefore provide the basis for quality evaluation and targeted improvement for ENS training,in addition to promoting health.
Conflicts of interest
Allcontributing authors declare no con flicts of interest.
1.Shen H,Chen XY,Wang XJ,Chen L.Research progress on the training and quali fi cation of emergency nurses at home and abroad.J Nurs Sci.2009;24: 91e93(in Chinese).
2.Qian XS.On System Engineering(Expanded Edition).Shanghai:Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press;2007:93(in Chinese).
3.Robert K,David N.Using the balanced scorecard as a strategic management system.Harv Bus Rev.1996;74:75.
4.Li XP,Shen CZ.Application status of Delphi method in nursing research.Chin J Mod Nurs.2012;18:2605e2607(in Chinese).
5.Saaty TL.Decision Making for Leaders:The Analytical Hierarchy Process for Decisions in a Complex World.Belmont:Wadsworth;1982:28e42.
6.Xu ZJ,Xia HO.The Delphi technique and its application in nursing research. J Nurs Sci.2008:78e80(in Chinese).
7.Zeng G.Modern EpidemiologicalMethods and Applications.Beijing:United Press of China Medical University&Beijing Medical University;1994:250e270(in Chinese).
8.Chen LY,He Z,Zhao H,Liu HP,Liu JF.Prediction research on job content and job quali fi cations of community nurses.Chin JNurs.2006;41:490e493(in Chinese).
9.Shrivastava A.Developing a core curriculum for the paediatric component of vocational training for general practice by the Delphitechnique.Arch Dis Child. 2005;90(SupplП):A82e A85.
10.Jiang M.Hypothesis test for the comparison of the overall correlation coef ficient.Chin Health Stat.2010;27:83e84(in Chinese).
11.Xia P,Wang K,Li NX,Wu DR.An improvement of the weight of the analytic hierarchy process.Chin Health Stat.2011;24:152e157(in Chinese).
12.Chen YZ.The difference between the“general system theory”of Bertalanffy and“complex adaptive systems theory”of the Santa Fe Institute.J Shandong Univ Sci Tech.2001;2:5e8(in Chinese).
13.Guo HY,Wang L,Peng JL,Xie H.The construction of evaluation index system of service quality for the aged care institutions.Chin JNurs.2014;49:394e398(in Chinese).
14.Couger JD.Key human resource issues in Is in the 1990s:views of Is executives versus human resource executives in formation and management.Inf Manag. 1988;14:161e174.
How to cite this article:Jiang M,Ao X.Training indicators and quantitative criteria for emergency nurse specialists.Chin Nurs Res.2017;4:24e30.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cnre.2017.03.007
5 December 2016
*This project is supported by the nursing special items of Health and Family Planning Commission Research Fund in Hubei province(No.HL2012-15).
*Corresponding author.
E-mail address:cjdxhlx@126.com(X.Ao).
Peer review under responsibility of Shanxi Medical Periodical Press.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cnre.2017.03.007
2095-7718/©2017 ShanxiMedical PeriodicalPress.Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons. org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Received in revised form 17 December 2016
Accepted 5 January 2017
Available online 30 March 2017
杂志排行
Frontiers of Nursing的其它文章
- Combined debridement in chronic wounds:A literature review
- Resilience as a strategy for struggling against challenges related to the nursing profession
- The application of the necessity-concerns framework in investigating adherence and beliefs about immunosuppressive medication among Chinese liver transplant recipients*
- Changing trends and in fluencing factors of the quality of life of chemotherapy patients with breast cancer*
- Comparative research on the prognostic ability of improved early warning and APACHE II evaluation for hospitalized patients in the emergency department*
- Conversation with presence:A narrative inquiry into the learning experience of Chinese students studying nursing at Australian universities
