湍流场多柱体绕流形态和水动力特性研究❋
2016-06-28于定勇张广成马朝晖
于定勇, 张广成, 马朝晖
(中国海洋大学工程学院,山东 青岛 266100)
湍流场多柱体绕流形态和水动力特性研究❋
于定勇, 张广成, 马朝晖
(中国海洋大学工程学院,山东 青岛 266100)
摘要:为研究间距比对多柱体在湍流场下的互扰效应影响,利用Fluent软件模拟了雷诺数为3 900,柱间距比L/D为1.6~6.0情况下正方形排列四圆柱绕流过程。通过模拟得到了不同间距比下的升、阻力系数值以及涡量图,利用快速傅里叶变换法得到了漩涡脱落频率。结果表明,当柱间距比L/D为1.6~2时,4个圆柱后都没有漩涡脱落,随间距比增加,上游圆柱平均升力系数增大,平均阻力系数减小,下游圆柱平均升、阻力系数减小,斯特鲁哈数增大;当L/D为2~3.5时,随间距比增大,下游圆柱后开始出现漩涡脱落,平均升、阻力系数减小,斯特鲁哈数增大;当L/D为3.5~6时,随间距比增大,四个圆柱后都发生漩涡脱落,上游圆柱平均升、阻力系数减小,下游圆柱平均升力系数减小,平均阻力系数增大,斯特鲁哈数不变。L/D<3.5时互扰效应逐渐增强,L/D>3.5时互扰效应逐渐减弱;考虑到工程安全性和经济性,本文研究成果对于海洋工程设计具有一定的参考价值。
关键词:四圆柱;湍流;升力、阻力系数;漩涡脱落形态;斯特鲁哈数
引用格式:于定勇, 张广成, 马朝晖. 湍流场多柱体绕流形态和水动力特性研究[J].中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(6):52-59.
YU Ding-Yong, ZHANG Guang-Cheng, MA Zhao-Hui. Study on flow pattern and hydrodynamic characteristics of multi-cylinder in turbulent field [J].Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(6): 52-59.
柱体绕流现象在航空航天、海洋、石油工程等领域普遍存在,如海洋工程中的输油管道、海洋平台中的各种立管等。在工程中柱体绕流引起的事故会造成巨大的经济损失和环境破坏。圆柱绕流是柱体绕流现象中的经典问题,圆柱状结构广泛存在于海洋工程和建筑工程中,因此成为人们研究的热点问题。
通过大量的研究,学者们对于单圆柱和双圆柱绕流的认识已经比较充分,但是对于多圆柱绕流过程的认识相对不足。多圆柱绕流问题涉及更多复杂的流体力学问题,影响因素众多,研究难度较大,目前对四圆柱绕流的研究相对较少。
虽然对于多圆柱绕流现象认识不足,但是依然有学者对多圆柱绕流问题进行了一定的研究,为进一步开展研究提供了指导。考虑到多圆柱绕流的特点,现存研究多以四圆柱排列方式为研究对象。
Lam等对于四圆柱绕流过程进行了大量的研究。对于层流过程,Lam等采用有限体积法进行了二维和三维数值模拟,同时进行了实验研究,验证了数值模拟的可行性[1-3];对于雷诺数处于亚临界区的湍流过程,Lam等采用三维大涡模拟的方法进行了数值模拟,同时利用多普勒测速和数字粒子图像测速技术进行了物理模型实验,揭示了湍流状态下四圆柱绕流形态,同时验证了大涡模拟方法的准确性[4-5]。
Farrant等利用单元边界元法得到了2种排列方式下二维流场特征和水动力参数,计算结果和Lam的实验结果比较吻合[6],验证了单元边界元法的准确性。Wang等在雷诺数为8 000时,对不同间距比和来流角度进行了物理模型实验,详细研究了间距比和角度对升、阻力系数以及漩涡脱落形态的影响[7]。
Zou等对钻石型排列的四圆柱进行了低雷诺数(Re=200)数值模拟,利用SIMPLE算法求解了不可压缩N-S方程,通过研究得到了不同间距比下尾流形态和圆柱的受力特性[8]。韩兆龙等利用谱单元法对低雷诺数(Re=200)时正方形排列的四圆柱绕流过程进行了计算模拟,并将结果与Lam等进行了对比,结果表明谱单元法可以得到比较准确的结果[9]。
由上述可知,目前对于四圆柱绕流的研究主要集中在低雷诺数,层流条件,对亚临界区雷诺数的研究不多。研究的方法主要以物理模型实验为主,数值模拟相对较少。
真实的流场大多是湍流流态,因此对于湍流的研究更有实际意义。本文进行了湍流数值模拟,研究的雷诺数取为3 900,属于亚临界区,虽然和实际雷诺数相差较大,但能为以后进行更高雷诺数的研究提供参考。
1计算模型
1.1 控制方程
假设流体为黏性不可压缩流,因此密度不变。又假设温度变化不大,因此能量方程可以忽略。故N-S方程只考虑连续方程和动量方程。
连续方程:

(1)
动量方程:

(2)
1.2 湍流模型
本文选用RNG κ-ε湍流模型。该模型来源于严格的统计意义,和标准的κ-ε模型相比,考虑了湍流漩涡,改善了精度,同时RNG理论为湍流Prandtl数提供了一个解析公式。
湍流动能κ方程:

(3)
湍流耗散率ε方程:
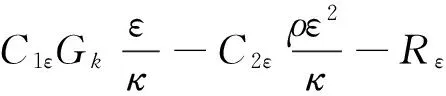
(4)

(5)
式中:η=Sκ/ε,η0=4.38,β=0.012;Gk是由层流速度梯度而产生的湍流能;C1ε,C2ε是常量;αk,αε是κ方程和ε方程的湍流Prandtl数。
2模型设置
2.1 计算参数
本文共进行10个组次的计算模拟,各组次计算参数设置如表1所示。
本文参数设置为直径D=0.01m,速度U=0.39m/s,两圆柱中心距离为L。计算区域大小为30D×45D。计算区域和圆柱布置如图1所示。
本文利用有限体积法离散控制方程,压力速度耦合采用SIMPLE算法,压力计算采用二阶格式,动量计算采用二阶迎风格式,湍流动能和耗散率采用二阶迎风格式。瞬态求解采用二阶隐式格式。采用非结构化网格,首先模拟了雷诺数为3 900时的单圆柱绕流过程,并和已有成果进行了验证。进而验证了较低雷诺数的四圆柱绕流,和已有成果进行了对比验证,通过验证可知本文选择的模型能够较准确的模拟四圆柱绕流过程。在此基础上进行了雷诺数为3 900的四圆柱绕流过程模拟,分析了其水动力参数和漩涡脱落形态随间距比的变化。
本文采用非结构化三角形网格,为了精确模拟边界层处流场特征,对圆柱周围网格进行了加密处理,网格如下图所示。
2.2 边界条件及初始条件
边界条件进口条件为均匀来流u=0.39m/s,v=0;出口条件为自由出流;圆柱表面为无滑移壁面边界;上下条件为对称边界。
初始条件 本次模拟采用瞬态模拟,为提高计算精度,先进行300步稳态模拟,使全流场具有更接近真实物理条件的初始条件,然后进行瞬态模拟。
3模型验证
3.1 单圆柱模型验证
本文选择的是κ-ε模型中的RNG模型,为了验证本文选择的湍流模型、参数设置和网格划分的准确性,首先进行了雷诺数为3900的单圆柱绕流过程的模拟,将模拟结果与雷诺数相同的实验结果[10-11]和数值模拟结果[12,14-15]进行了对比,结果如表2所示。
已有的研究表明,雷诺数处于亚临界区时,斯特鲁哈数稳定在0.2附近,平均阻力系数稳定在1.0附近。
本文St数为0.19,和已有成果相比较小,但和稳定值的误差仅为0.01,在可接受范围内;平均阻力系数为0.95,和已有研究成果较吻合,因此可以认为本文进行的单圆柱绕流过程模拟是准确的。
3.2 四圆柱模型验证
Lam对低雷诺数四圆柱绕流进行了数值模拟和物理模型实验,取得了大量可靠的结论,因此本文首先验证κ-ε模型在低雷诺数下的准确性。
根据图1可知,四圆柱排列具有对称性,因此本文只选择圆柱1和3进行对比验证,低雷诺数验证结果如表3所示。
根据表3可知,间距比为2.5时,平均阻力系数值和文献2符合较好,圆柱1没有稳定的漩涡脱落,故没有斯特鲁哈数,圆柱3漩涡脱落的斯特鲁哈数较小。间距比为3.5时,平均阻力系数值和有限体积法得到的结果符合较好,但和谱单元法的结果差距较大,圆柱1和3的斯特鲁哈数和已有结果符合较好。
雷诺数为200时,圆柱后开始出现漩涡脱落,但没有稳定的涡街,而本文雷诺数3900属于亚临界区,尾流已转变为稳定湍流涡街,为了充分验证本文模型的准确性,选择较高雷诺数研究成果进行对比验证。验证结果如表4所示。
根据已有研究成果可知,雷诺数为300~2.5×105属于亚临界区,剪切层开始转捩为湍流,St≈0.2。如表4所示,表中雷诺数均属于亚临界区,流态相似,因此可以用来验证本文结果。由验证结果可知,本文得到的St和已有实验结果较吻合,但是Cd结果存在一定误差,下游圆柱Cd较实验结果偏大。
表3和4分别对低雷诺数和高雷诺数进行了模型对比,充分验证了本文模型的可靠性,因此可以用 κ-ε模型进行雷诺数为3 900的四圆柱绕流过程模拟。
4计算结果及分析
4.1 漩涡脱落形态
Wang进行的物理模型实验[7]表明,上游剪切层的分离对下游圆柱产生的影响可以根据间距比分为3种不同模式,分别是:(1)遮蔽模式;(2)再附着模式;(3)漩涡拍击模式。下文分别称为模式1、2、3。
本文模拟选取的雷诺数为3900,计算间距比为1.6~6.0,各组次漩涡脱落形态如图4所示。
根据本文结果可知,当L/D≤2时,由图4中(a)和(b)可以发现,下游圆柱完全处于上游圆柱剪切层的包裹中,4个圆柱都没有明显的漩涡脱落,属于模式1;当2 根据分析可知模式1到模式2转化的临界间距比为2.0,模式2到模式3转化的临界间距比为3.5。 4.2 升、阻力系数 升力系数和阻力系数是反映圆柱水动力特性的重要参数,分别表征圆柱横向和纵向受力变化。本文通过模拟得到了不同间距比下各圆柱的升、阻力系数,并计算了平均阻力、升力系数和均方根升力系数。并将结果与单圆柱进行了对比,分析了四圆柱和单圆柱水动力系数的差别。 各圆柱平均阻力系数结果如图5所示。 由图5可知,上游圆柱的阻力系数大于下游圆柱。在间距比很小时,由于上游圆柱的阻挡作用,使得下游圆柱受到的阻力很小,随着间距比增大,阻挡作用减弱,因此阻力明显变大,但是依然远小于单圆柱受到的阻力。上游各圆柱和下游各圆柱的平均阻力系数几乎相等。 平均升力系数的结果如图6所示。 由上图可知,在模式1时,圆柱的平均升力系数随间距比的增大而增大,在模式2和3时,平均升力系数随间距比增加而减小,逐渐趋于和单圆柱相等。 均方根升力系数结果如图7所示。 升力系数均方根(Clrms)是有效升力系数,它表示的是各圆柱升力系数的幅值大小。 由图7可知,各圆柱均方根升力系数均随间距比的增大呈现先增后减的趋势,间距比为3.5时达到最大值。本文各圆柱升力系数幅值都大于单圆柱,在模式2和3时,由于漩涡的拍打作用,下游圆柱横向受力变大,升力系数明显大于单圆柱,因此圆柱3和4的均方根升力系数明显大于单圆柱。 4.3 斯特鲁哈数St St(Strouhal Number)数反应的是漩涡脱落频率的大小,St的变化与漩涡脱落形态的变化相对应。 St=fD/U。 (6) 式中:f为漩涡脱落频率;D为圆柱直径;U为流体速度。 由于漩涡脱落的周期和升力变化的周期相同,因此对升力系数进行快速傅里叶变换可以求得漩涡脱落频率,进而得到St数。图8给出了各圆柱St数随间距比的变化。 由图8可知,St数随着间距比的增大逐渐增大,4个圆柱St数变化规律基本一致,当间距比L/D=3.5时,漩涡脱落频率和单圆柱几乎相同,此时上下游圆柱都开始发生漩涡脱落。此后St数值保持稳定,几乎和单圆柱相等,说明各圆柱以稳定的频率泄送漩涡,这和图4的涡量图变化规律是相符的。 5结论 本文利用Fluent软件中的κ-ε湍流模型,模拟了湍流场四圆柱绕流过程,通过分析其升力、阻力系数和漩涡脱落形态随间距比的变化,得到了如下结论: (1)漩涡脱落随间距比的变化呈现3种不同的模式。在模式1时,4个圆柱都没有漩涡脱落,在模式2时,下游圆柱开始有漩涡脱落,在模式3时,4个圆柱都产生规律性的漩涡脱落。模式1转化为2的临界间距比为2,模式2转化为3的临界间距为3.5。 (2)上游圆柱平均阻力系数大于下游圆柱,但下游圆柱平均阻力系数随间距比的增大明显增大。模式1时平均升力系数随间距比增大而增大,模式2和3时,平均升力系数随间距比增大而减小,并趋于和单圆柱相同;升力系数的幅值随间距比的增大先增加后减小,最大值出现在间距比为3.5时,上游圆柱数值和单圆柱较接近,但下游圆柱明显大于单圆柱。 (3)在模式1和模式2时,St数小于单圆柱,但是随着间距比增大而增加,在临界间距比3.5时和单圆柱相同,在模式3时,各圆柱漩涡脱落频率和单圆柱几乎相同。 (4)当柱间距比小于3.5时,各圆柱之间互扰效应较强;当间距比大于3.5时,各圆柱之间互扰效应逐渐减弱。因此,在设计中考虑到工程安全性和经济性,建议取间距比为5.0左右。 参考文献: [1]Lam K, Li J Y, So R M C. Force coefficients and Strouhal numbers of four cylinders in cross flow [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2003, 18: 305-324. [2]Lam K, Gong W Q, So R M C. Numerical simulation of cross-flow around four cylinders in an in-line square configuration [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2008, 24: 34-57. [3]Lam K, Zou L. Three-dimensional numerical simulations of cross-flow around four cylinders in an in-line square configuration [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2010, 26: 482-502. [4]Lam K, Zou L. Experimental and numerical study for the cross-flow around four cylinders in an in-line square configuration [J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2007, 21: 1338-1343. [5]Lam K, Zou L. Experimental study and large eddy simulation for the turbulent flow around four cylinders in an in-line square configuration [J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2009, 30: 276-285. [6]Farrant T, Tan M, Price W G. A cell boundary element method applied to laminar vortex shedding from circular cylinders [J]. Computers & Fluids, 2001, 30: 211-236. [7]Wang X K, Gong K. Flow around four cylinders arranged in a square configuration [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2013, 43: 179-199. [8]Zou L, Lin Y F, Lu H. Flow patterns and force characteristics of laminar flow past four cylinders in diamond arrangement [J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2011, 23(1): 55-64. [9]韩兆龙, 周岱, 陈亚楠, 等. 谱单元法及其在多圆柱绕流分析中的应用[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2014, 32(1):21-29. HAN Z L, ZHOU D, CHEN Y N, et al. Numerical simulation of cross-flow around multiple circular cylinders by spectral element method[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2014, 32(1): 21-29. [10]Norberg C. Effects of Reynolds number and low-intensity free-stream turbulence on the flow around a circular cylinder [D]. Goteborg: Chalmers University of Technology, 1987. [11]Ong L, Wallace J. The velocity field of the turbulent very near wake of a circular cylinder [J]. Experiments in Fluids, 1996, 20: 441-453. [12]Franke J, Frank W. Large eddy simulation of the flow past a circular cylinder at Re=3900 [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2002, 90: 1191-1206. [13]Lam K, Lo S C. A visualization study of cross-flow around four cylinders in a square configuration [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1992, 6: 109-131. [14]詹昊, 李万平, 方秦汉, 等. 不同雷诺数下圆柱绕流仿真计算 [J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2008, 30(12): 129-132. ZHAN H, LI W P, FANG Q H, et al. Numerical simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder at varies reynolds number [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2008, 30(12): 129-132. [15]Lysenko D A, Ertesvog I S, Rian K E. Large-Eddy Simulation of the flow over a circular cylinder at reynolds number 3900 using the open FOAM toolbox [J]. Flow Turbulence Combust, 2012, 89: 491-518. 责任编辑陈呈超 Study on Flow Pattern and Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Multi-Cylinder in Turbulent Field YU Ding-Yong, ZHANG Guang-Cheng, MA Zhao-Hui (College of Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China) Abstract:Flow around cylinders is a common phenomenon in ocean、aerospace and petroleum engineering, for example, the flow around oil pipelines in ocean engineering and risers in offshore platform. The accidents caused by flow around cylinders can lead to huge economic loss and environmental damage. Flow around circular cylinders is a classic problem in flow around cylinder. Cylinder structures are used in more and more ocean engineering and civil engineering. The study of flow around cylinder structures becomes a meaningful hot issue, especially the study on flow around multi-cylinder. Some researches have been done to investigate the phenomenon of flow around single and two circular cylinders, but few on multi-cylinder. Flow around multi-cylinder is a more complicated phenomenon due to more complex hydrodynamics. In order to investigate the pattern effects of multiple cylinders in turbulent field with different spacing ratio, this paper numerical simulated by using Fluent the flow around 4 cylinders arranged in square configuration, with Reynolds number 3900 and spacing ratio from 1.6 to 6.0. Fluent is a mature and common commercial software, with a feature of stable, accurate in Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) field. Finite Volume Method (FVM) and the Simple algorithm are used to simulate flow around 4 circular cylinder. There are 2 kinds of grid in CFD simulation, i.e., structured and unstructured grid. In this paper unstructured grid is employed. In order to capture the flow pattern near the wall, the grid is refined in the boundary layer. The results of lift coefficient, drag coefficient and vorticity magnitude in every spacing ratio are obtained according to the numerical simulation. The period of vortex shedding is the same as the occurrence period of lift coefficient, therefore it is easy to get the frequency of vortex shedding by Fast Fourier Transform technology with MATLAB program. The Strouhal number can be then calculated based on the above-obtained frequency. The average and root mean square values of lift and drag coefficient can be also calculated and plotted using MATLAB program. With the spacing ratio changing from 1.6 to 2, the following results are obtained from the simulation: (1) There are no vortex shedding occurrence for pattern of 4 cylinders.(2) The upstream cylinders’ average lift coefficient increases but average drag coefficient decreases, while both the downstream cylinders’ average lift and drag coefficient decrease.(3) The Strouhal number increases. With the spacing ratio changing from 2 to 3.5, the following results are obtained from the simulation: (1) There are vortex begin to shed from downstream cylinders.(2) All cylinders’ average lift and drag coefficient decrease.(3) The Strouhal number increases. With the spacing ratio changing from 3.5 to 6.0, the following results are obtained from the simulation: (1) There are stable vortex shedding from 4 cylinders.(2) The upstream cylinders’ average lift and drag coefficient decrease with spacing ratio, and downstream cylinders’ average lift coefficient decreases but drag coefficient increases.(3) The Strouhal number keeps steady. Besides, the pattern effects of multiple cylinders in turbulent field becomes more obvious with the change of spacing ratio less than 3.5, but when spacing ratio bigger than 3.5 the effect becomes weaker. The obtained results of this paper can be used as design reference in ocean engineering. Key words:four cylinders; turbulence; lift and drag coefficient; vortex shedding pattern;St 基金项目:❋山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2013EEZ002)资助 收稿日期:2015-03-20; 修订日期:2015-10-20 作者简介:于定勇(1964-),男,教授,博导。E-mail: dyyu01@ouc.edu.cn 中图法分类号:TV143 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-5174(2016)06-052-08 DOI:10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20150307 Supported by Natural Science Foundation(ZR2013EEZ002)
