不同金属3D打印增材制造技术对比分析
2016-05-12李素丽陕西国防工业职业技术学院陕西西安710300
李素丽(陕西国防工业职业技术学院,陕西西安 710300)
不同金属3D打印增材制造技术对比分析
李素丽
(陕西国防工业职业技术学院,陕西西安 710300)
随着3D打印增材制造技术的发展,不同种类的成形技术有各自不同的特点和分类方法,按照成形材料不同沉积状态,金属件的成型工艺主要有SLS技术、SLM技术、LCD技术、3D P技术及EBM技术。通过不同金属3D打印增材制造方式的对比,可以看出没有一种技术可以同时满足精度高、力学性能优异、成本低的要求。各工艺优缺点明显,应用领域显著不同。
金属3D打印;增材制造技术;SLS技术;SLM技术;LCD技术;3DP技术;EBM技术
0 引言
金属3D打印技术增材制造(Additive Manufacturing,AM)是基于离散—堆积原理的新型数字化成形技术,被誉为“具有工业革命意义的制造技术”,极大地缩短了产品的研发周期和成本,对制造业的发展有着十分重要的意义[1]。
1 不同金属3D打印增材制造技术成形特点
不同的3D打印增材制造技术有各自不同的特点和分类方法,按照成形材料不同沉积状态,金属件的成型工艺主要有[2-4]:选择性激光烧结(Selected Laser Sintering,SLS)技术,选区激光熔化(Selective Laser Melting,SLM)技术,激光熔敷沉积(Laser Cladding Deposition,LCD)技术,三维打印(3D Printing,3DP)技术,电子束熔融(Electron Beam Melting,EBM)技术以及三维微焊接(3D Micro Welding,3DMW)成形技术。
1.1 选择性激光烧结(Selective Laser Sintering,SLS)成形技术
图1为SLS成形原理示意图,激光对均匀铺展于工作台面的粉末材料进行扫描、烧结,每扫描一层后成型活塞下降一个层高,继续进行后续层的成形,直至完成零件。其中SLS激光快速成形技术工艺具有可采用多材料成形;成形工艺简单;成形精度高等优点。该工艺成形精度平均可以达到0.05~2.5 mm的公差。并且无需设计支撑结构,未烧结的粉末可以直接作为成形过程中悬空层的支撑。因此材料利用率高,是常见几种AM工艺中利用率最高的,且价格较便宜的工艺。
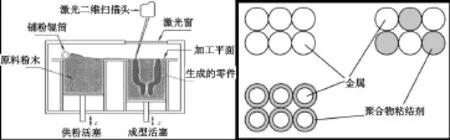
图1 SLS成形原理示意图
选择性激光烧结(SLS)技术的主要缺点为:①表面质量差。制件成形是由粉末状的原料通过加热熔化实现逐层粘结的,因此,制件表面严格讲是粉粒状的,因而表面粗糙;②力学性能差。原型结构疏松、多孔,制件致密度低,因而力学性能较差。
1.2 选区激光熔化(Selective Laser Melting,SLM)技术
SLM技术使用的金属材料主要包括铁基合金、TiC4合金、316L不锈钢粉、铜合金、钛合金、工具钢等[5]。其中很多材料需要进口。表面成形精度可达30~60 μm,尺寸精度可达±0.1 mm,可以完全熔化金属粉末,得到全致密结构,具有较好的机械性能(表1)。
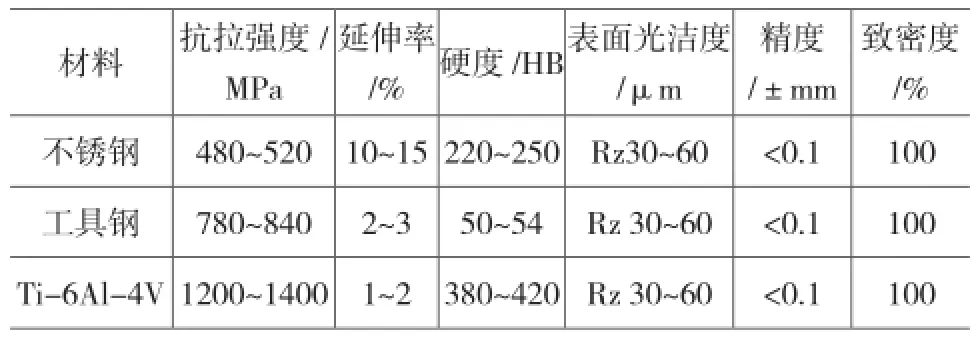
表 1 选择性激光熔化成形制件机械性能[5]
1.3 激光熔敷沉积(Laser Cladding Deposition,LCD)技术
该技术可使用铁基合金、不锈钢粉、铜合金、钛合金等作为成形材料进行成形,同时还可使用WC/ Co、TiC4、VC 等硬金属及Al2O3、TiO2 等陶瓷材料进行成形,是复杂零件快速成形的有效方法。另外,该技术可利用激光在工件表面局部产生瞬间的高能量使熔化粉体材料和基层产生冶金结合,且比传统焊接工艺(如:钨极气体保护焊,氩弧焊等)产生的残余热应力小,是修复损坏的叶片、汽轮机、涡轮盘的理想技术。
1.4 三维打印(3D Printing,3DP)技术
3DP工艺采用液态粘结剂,通过喷嘴将液态粘结剂喷在铺于工作台上的粉末层上,喷有粘结剂的区域凝固后就将金属粉末粘结到了一起。成形件也不是真正意义上的“纯”金属零件,“绿件”的致密度大约为60%[6],图2为3DP工艺的原理图。
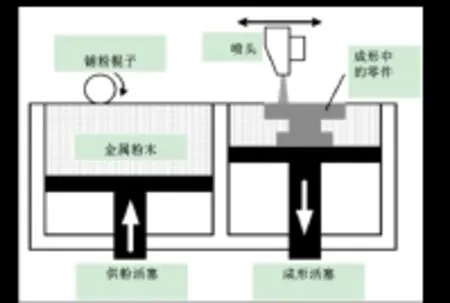
图2 3DP成形原理示意图
3DP工艺与SLS工艺类似,是采用粉末材料(陶瓷粉末,金属粉末等)通过喷嘴用粘接剂(如硅胶)将零件的截面“印刷”在材料粉末上面成形,而不是通过烧结连接起来的。因而零件强度较低,须后处理。3DP技术可以通过减小粉末直径、减小粉末层厚度等方式来提高成形精度,其制件精度也很高。成形件需要采取与间接SLS相似的后处理工艺来提高致密度,成形件也多用于注塑模具等低载荷的场合。由于没有采用激光等昂贵的设备,使设备的成本远低于与其他采用激光、电子束等的金属成形设备[7]。
1.5 电子束熔融(Electron Beam Melting EBM)技术
EBM技术原理为:在真空环境中,采用电子束焊接工艺熔化金属丝材或金属粉末材料,然后按照设定的路径逐层堆积而成形出金属制件。可用于电子束自由成形的材料广泛,如工具钢、钛合金、镍合金,甚至耐火的钼合金等导电金属材料都可用于电子束沉积成形。电子束还可用于对光能具有较高反射作用的金属沉积成形:如在室温下,Ti-6Al-4V材料对激光反射较为严重,采用激光烧结工艺,能量利用率很低,而此材料对电子束的反射率只有10%左右,具有较高的能量利用率[8-10]。
但电子束沉积需要具有较高真空度的真空环境,设备的成本昂贵;且电子束在沉积过程中会伴随伽玛射线的发射,如果装置设计不合理会造成射线的泄露,导致环境的污染。另外,电子束只能沉积导电材料,不能沉积塑料、陶瓷等不导电材料[11]。
1.6 不同金属3D打印增材制造技术对比分析
表2为金属3D打印增材制造方式的对比,可以看出没有一种技术可以同时满足精度高、力学性能优异、成本低的要求。各工艺优缺点明显,应用领域显著不同。
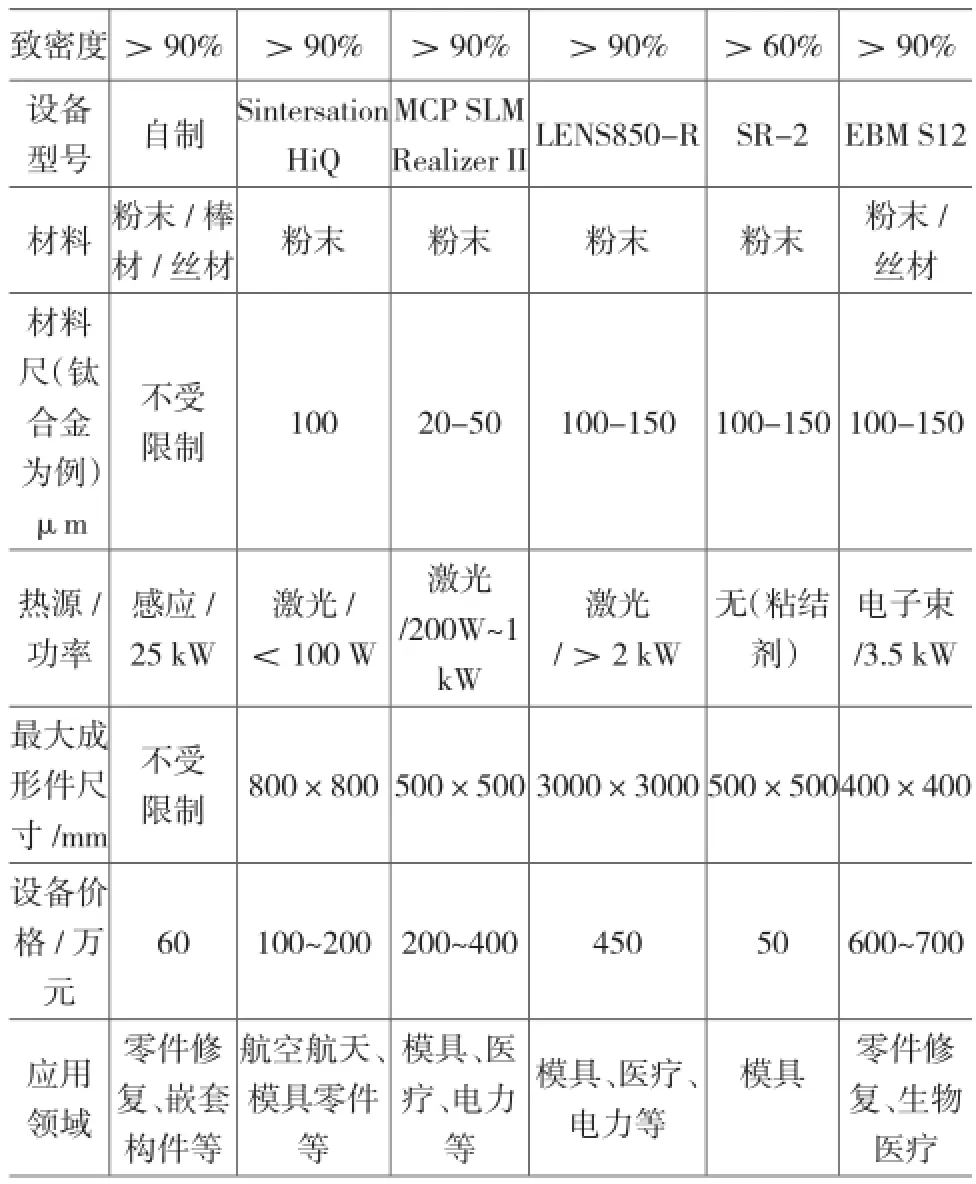
表2 七种增材制造技术比较[12-15]
2 结束语
金属3D打印增材制造技术的这些特点顺应了现代制造业快速化、个性化、柔性化发展的需求,因此,对采用直接金属3D打印的研究成为了AM研究的热点,已经在电力、生物、医疗、航空等制造领域得到了广泛的应用,并显示出了非常好的应用前景[16-17]。
[1] F. Gao, A. Sonin, P recise deposition of molten microdrops:the physics of digital microfabrication, Proc. R. Soc.Lond. A 444 (1994) 533–554.
[2] L.J. Zarzalejo, K.S. Sc hmaltz, C.H. Amon, Molten dropletsolidification and s ubstrate remelting in m icrocasting PartI: Numerical modeling and experimental verification, HeatMass Transfer 34 (1999) 477–485.
[3] J.P. Krut h, Material incress ma nufacturing by rapidprototyping techniques, Ann. CIRP 40 (2) (1991) 603–614.
[4] M. Orme, A novel technique of rapid solidification netformmaterials synthesis, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2 (3)(1993) 399–405.
[5] M. Orme, C. Huang, J. Courte, Deposition strategies forcontrol of microstructures microporosity and surfaceroughness i n dropletbased solid freeform fabrication ofstructural materials, in: E.F. Matthys, W.G. Truckner(Eds.), Melt Spinning, Strip Casting and Slab Casting, TheMinerals, Metals a nd Materials Society, Warrendale, PA,1996, pp. 125–143.
[6] M.E. Orme, C. Huang, J. Courter, Precision dropletbasedmanufacturing and material s ynthesis, Atomization Sprays6 (1996) 305–329.
[7] Liu Q, Orem M. J Eng.Manufacture [J], 2001, 215(10): 1333
[8] 晁艳普,齐乐华,罗俊,等. 金属熔滴沉积制造中STL模型切片轮廓数据的获取与试验验证[J]. 中国机械工程,2009,22:2701-2705.
[9] 高琛,黄孙祥,陈雷,等. 液滴喷射技术的应用进展[J]. 无机材料学报,2004,04:714-722.
[10] AMON.C.H,SCHM ALTZ.K.S,MERZ.R,et.al.Numerical and experimental investigate of interface bonging via substrate remelting of an im pinging molten metal droplet[J].Journal of heat transfer,1996,118(1):164-172.
[11] NEAGU.M. Study of remelting process during the droplet-based solid freeform fabrication [J].The annals dungaree de jobs University of Galati, fascicle v: technologies in mechanical engineering, 2004, 5:35-39.
[12] John D. Benrnardin, Clinton J. Stebbins, IssamMudawar. Mapping of impact and heat transfer regimes of water drops impining on a polished surfa ce. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfe r. 1997, 40 (2):247-267.
[13] G. E. Cossali, M. Marengo, M. Santini.Thermally induced secondarydrop atomisation by single drop impactonto heated surface. International Journalof Heat and Mass Transfer. 29 (2008):167-177.
[14] M. Pasandideh-Fard, S. D. Aziz, S. Chandra, J. Mostaghimi. Cooling effectiveness of a water drop im pinging on a hot s urface. International Journal of Heat andFliud Flow. 22 (2001):201-210.
[15] N. Nikolopoulos, A. Theodorakakos, G. Bergeles. A numerical investigation of the evaporation process of a liquiddroplet impinging onto a hot substrate.International J ournal of Heat and Mas s Transfer.50 (2007):303-319.
[16] George Strotos,ManolisGavaises,Andreas.Numerical investigation on the evaporation of droplets depositing on heated surfaces at low Weber numbers. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer.45 (2007):213-216.
[17] Fukai, J.,Shiliba, Y.,Yanmaoto et al. wetting effects on the spreading of a liquid droplet colliding with a surface:experiment and modeling. Phys. Fluids 1995, 7 (2):236-247.
[18] 耿佩.浅析3D打印技术在铸造成形中的应用[J].中国铸造装备与技术,2016(1).
Comparative analysis of different 3D printing technology
Li SuLi
(Shaanxi institute of technology,Xi'an 710300, Shaanxi ,China)
With the development of 3D printing technology, different kinds of technologies have different characteristic and classification methods. According to the different sedimentary condition, the technique of metal parts mainly include∶ SLS technology, SLM technology, LCD technology, 3DP technology and technology of EBM. Through different metal 3D printing material manufacturing way of contrast, it can be seen that there isn’t a technology can satisfy the high precision at the same time, excellent mechanical properties, and low cost requirements. Each technological advantages and disadvantages, application fi eld is signi fi cantly different.
3D printing; metal material manufacturing technology;SLS technology;SLM technology;LCD technology;3DP technology; EBM technology
TQ021;TG249;
A;
1 006-9 658(201 6)06-0006-03
10.3969/j.issn.1 006-9 658.2016.06.002
陕西国防工业职业技术学院课题(编号:Gfy16-14)
2016-05-20
稿件编号:1605-1382
李素丽(1981—),女,讲师,主要从事3D打印以及模具设计相关的研究工作.
