An Empirical Analysis of the Export Competitiveness of Agricultural Products in Hubei Province Based on Inter-provincial Comparison
2016-01-11
School of Economics, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, China
AnEmpiricalAnalysisoftheExportCompetitivenessofAgriculturalProductsinHubeiProvinceBasedonInter-provincialComparison
LingWANG*
School of Economics, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, China
With the six provinces of Central China and China’s six major provinces of exporting agricultural products as the reference objects, this paper uses revealed comparative advantage index and export growth advantage index to perform the empirical analysis and comparison on the export competitiveness of agricultural products in Hubei Province, and finally makes the corresponding policy recommendations in order to enhance the export competitiveness of agricultural products in Hubei Province.
Six provinces of Central China, Export competitiveness of agricultural products, Comparative advantage
1 Introduction
Hubei is a province of China, located in the easternmost part of Central China. The Jianghan Plain takes up most of central and southern Hubei, while the west and the peripheries are more mountainous, with ranges such as the Wudang Mountains, the Jing Mountains, the Daba Mountains, and the Wu Mountains. Thousands of lakes dot the landscape of Hubei’s Jianghan Plain, giving Hubei the name of "Province of Lakes". Hubei has a humid subtropical climate, with four distinct seasons. Winters are cool to cold, with average temperatures of 1 to 6 °C in January, while summers are hot and humid, with average temperatures of 24 to 30 °C in July. The favorable climate and geographical conditions create prominent advantages in developing agriculture. Hubei is an important commodity grain, cotton, oil production base and the largest freshwater production base in China. There are certain advantages in the export of livestock and poultry products, aquatic products and bee products, but the province’s overall export scale of agricultural products is not large, and the export value of agricultural products in Hubei Province accounted for only 2.8% of the total export value of agricultural products in China in 2014. With the six provinces of Central China and China’s six major provinces of exporting agricultural products as the reference objects, this paper performs the empirical analysis and comparison on the export competitiveness of agricultural products in Hubei Province. In this paper, data are from China Agriculture Yearbook, China Statistical Yearbook, the United Nations Commodity database, and the United Nations Food and Agriculture database from 2010 to 2014.
2 The export of agricultural products in Hubei Province
In 2009, the export value of agricultural products was $ 720 million in Hubei Province, accounting for 1.84% of the national total export value of agricultural products. In 2014, the export value of agricultural products was $ 1.995 billion in Hubei Province, accounting for 2.8% of the national total export value of agricultural products, an increase of 177.1% compared with 2009, with the average annual growth rate of 35.4%. In 2013, Hubei was ranked eighth in China in terms of export value of agricultural products. The export value of agricultural products in Hubei Province during 2009-2014, and its share in the national total export value of agricultural products are shown in Fig. 1. As can be seen from Fig.1, except 2012 when the weak overseas market demand and the abolition of export tax rebate policy for some agricultural products caused decline in the exports of agricultural products, Hubei’s export value of agricultural products shows an overall upward trend, and its share in national total export value of agricultural products is also rising. Clearly, the export of agricultural products in Hubei Province shows a good trend of development. The six provinces of Central China are China’s major agricultural provinces, with food production accounting for about 40% of total national food production and oil production accounting for more than 40% of total national oil production. To better understand the export of agricultural products in Hubei Province, this paper selects six provinces of Central China (Hubei, Henan, Shanxi, Anhui, Hunan and Jiangxi) and top six provinces (Shandong, Fujian, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Liaoning, and Jiangsu) in terms of agricultural exports in 2013 as the object for comparative analysis. Table 1 shows the export of agricultural products in various provinces. As can be seen from Table 1, the export value of agricultural products is large in Shandong, Fujian, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Liaoning and Jiangsu, and the total export value of agricultural products in the six provinces accounted for about 70% of the national total export value of agricultural products in 2013 (25% for Shandong). The six provinces of Central China are all important production bases of agricultural products in China, but the export value of agricultural products is small. In 2013, the total export value of agricultural products in six provinces of Central China accounted for only 8.74% of the national total export value of agricultural products, and the export value in Hubei was higher than in other provinces but far less than in the major exporters such as Shandong and Fujian.
3 Empirical analysis of the export competitiveness of agricultural products in Hubei Province
3.1Revealedcomparativeadvantage(RCA)indexRevealed comparative advantage index was first proposed by the American economist Bela Balassa in 1976. It is an index for meas-uring competitiveness with high economic value. The formula is as follows:
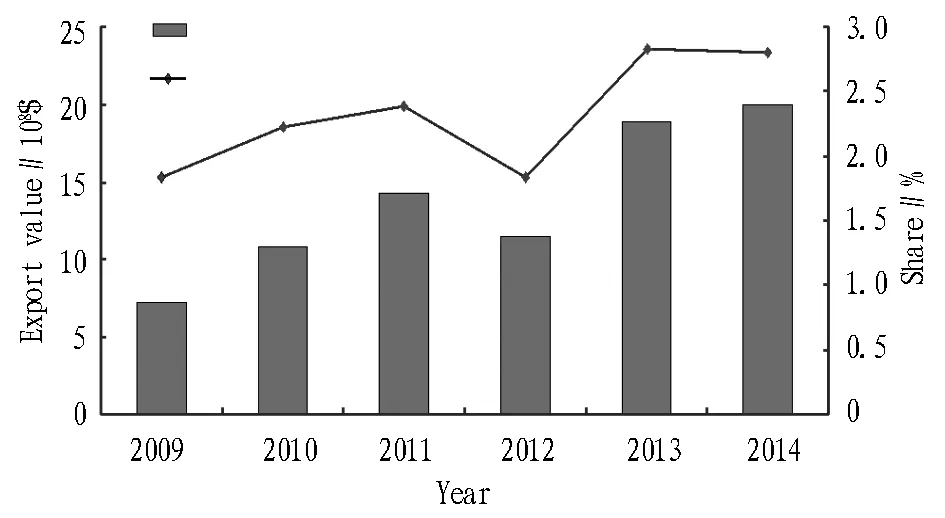
Fig.1 The export value of agricultural products in Hubei Province and its share in the total export value of agricultural products in China during 2009-2014

Table 1 Comparison of the export value of agricultural products and its proportion between Hubei Province and other provinces Unit: 108$, %
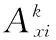
Table2ComparisonofRCAofagriculturalproductsbetweenHubeiProvinceandotherprovinces
Table3ComparisonofcomparativeadvantageindexofmajoragriculturalproductsbetweenHubeiProvinceandotherprovinces
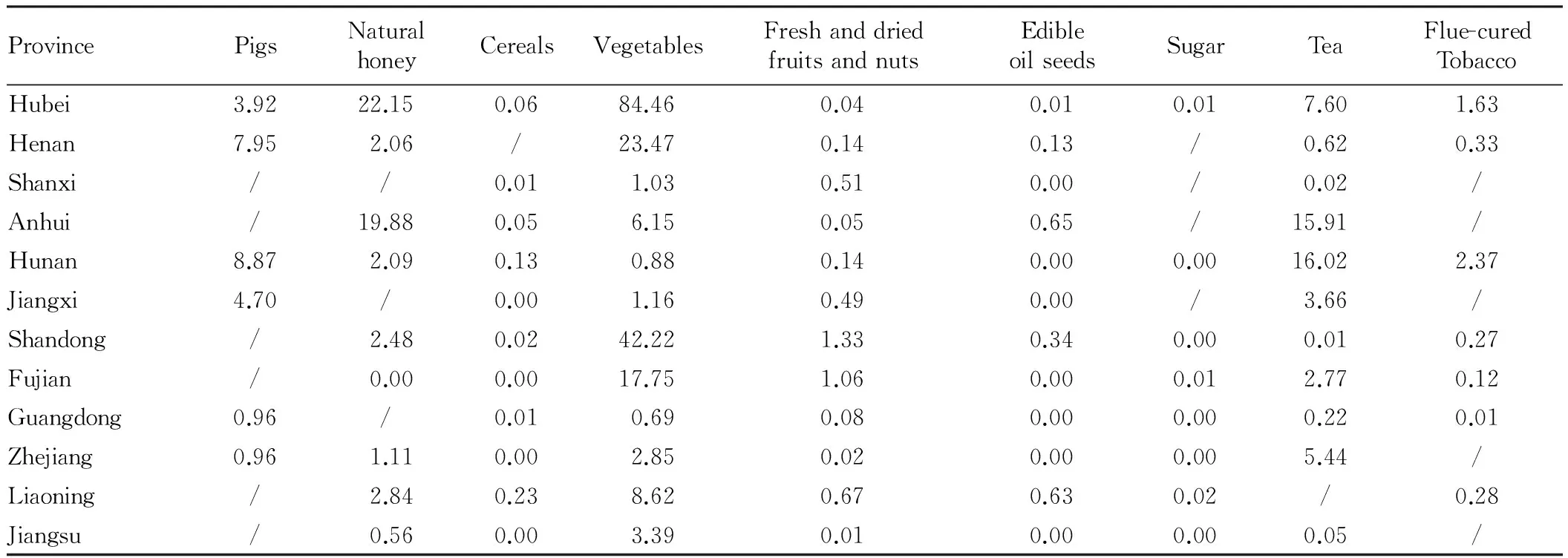
ProvincePigsNaturalhoneyCerealsVegetablesFreshanddriedfruitsandnutsEdibleoilseedsSugarTeaFlue-curedTobaccoHubei3.9222.150.0684.460.040.010.017.601.63Henan7.952.06/23.470.140.13/0.620.33Shanxi//0.011.030.510.00/0.02/Anhui/19.880.056.150.050.65/15.91/Hunan8.872.090.130.880.140.000.0016.022.37Jiangxi4.70/0.001.160.490.00/3.66/Shandong/2.480.0242.221.330.340.000.010.27Fujian/0.000.0017.751.060.000.012.770.12Guangdong0.96/0.010.690.080.000.000.220.01Zhejiang0.961.110.002.850.020.000.005.44/Liaoning/2.840.238.620.670.630.02/0.28Jiangsu/0.560.003.390.010.000.000.05/
Note: The "/" indicates that the data is missing.
3.2ExportgrowthadvantageindexThe export growth advantage index is the difference between the export growth rate of one commodity and the export growth rate of all commodities in one region, reflecting changes in the product export advantage. The formula is as follows:
Dt=(gi-gt)×100
whereDtis the export growth rate;giis the export growth rate of productiin one region;gtis the export growth rate of all commodities in one region.
WhenDt>0, the export competitiveness of this product will rise during the reporting period; on the contrary, the export competitiveness of this product will fall. The larger the index, the faster the export growth of producti. The export growth advantage index of agricultural products in Hubei Province and other provinces during 2009-2013 is shown in Table 4. Due to changes in the index value in various provinces, it is not easy to compare, and we take the average of the index during 2009-2013 to reflect the overall changes in the export advantage of agricultural products in various provinces. TheDtindex of agricultural products in Hubei in the past 5 years was greater than zero, indicating that its export competitiveness was gradually increased; theDtindex was higher than in China’s six major exporters of agricultural products-Shandong, Fujian, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Liaoning and Jiangsu and also higher than in five other provinces of Central China, indicating that Hubei’s export competitiveness of agricultural products was gradually increased and the potential for export growth was large.
Table4TheexportgrowthadvantageindexofagriculturalproductsinHubeiProvinceandotherprovinces
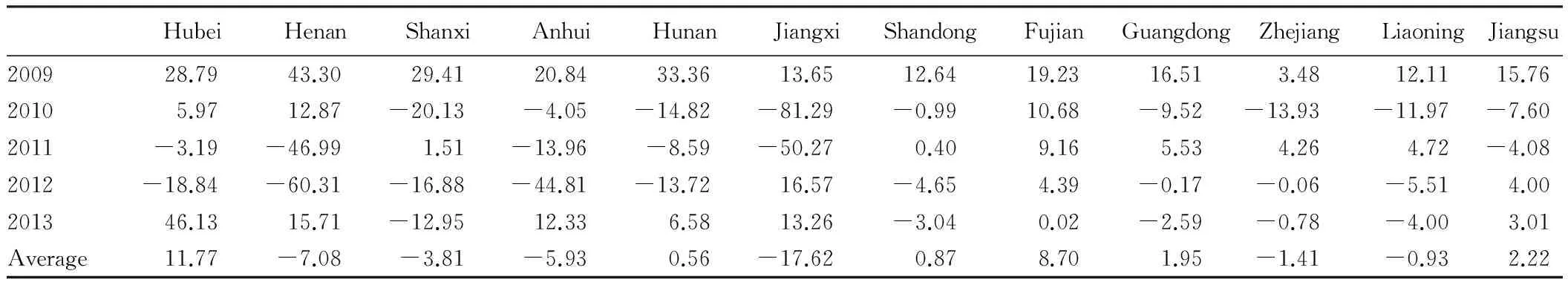
HubeiHenanShanxiAnhuiHunanJiangxiShandongFujianGuangdongZhejiangLiaoningJiangsu200928.7943.3029.4120.8433.3613.6512.6419.2316.513.4812.1115.7620105.9712.87-20.13-4.05-14.82-81.29-0.9910.68-9.52-13.93-11.97-7.602011-3.19-46.991.51-13.96-8.59-50.270.409.165.534.264.72-4.082012-18.84-60.31-16.88-44.81-13.7216.57-4.654.39-0.17-0.06-5.514.00201346.1315.71-12.9512.336.5813.26-3.040.02-2.59-0.78-4.003.01Average11.77-7.08-3.81-5.930.56-17.620.878.701.95-1.41-0.932.22
4 Conclusions and policy recommendations
With the six provinces of Central China and China’s six major provinces of exporting agricultural products as the reference objects, this paper uses revealed comparative advantage index and export growth advantage index to perform the empirical analysis and comparison on the export competitiveness of agricultural products in Hubei Province. Results show that compared with China’s major agricultural provinces and exporters of agricultural products such as Shandong, Fujian and Liaoning, Hubei’s export competitiveness of agricultural products lags behind, but is higher than that of six provinces of Central China and stronger than that of the other five provinces. At the same time, the export growth advantage index results show that Hubei’s export competitiveness of agricultural products is gradually increased, with strong export competitive potential. Hubei has favorable geographical conditions and temperate climate, and the advantages of agricultural development are prominent. There are numerous types of agricultural products and the exports of some products (such as livestock products, aquatic products, bee products, edible mushrooms, wild vegetables and konjac) grow rapidly, becoming the new competitive agricultural products in Hubei Province. But at the same time, Hubei is faced with some problems during agricultural development and agricultural export. Currently, Hubei’s export of agricultural products is still based on general trade export while the processing trade export occupies a small share, resulting in low added value of agricultural exports and less brand-name products, which is not conducive to the Hubei’s agricultural industrialization. Hubei Province should give full play to the comparative advantage in agriculture, and vigorously develop the deep processing of agricultural products, to increase product’s added value and make the exported agricultural products answer for international market demand. Meanwhile, it is necessary to foster and support leading agricultural enterprises, focus on agricultural deep processing, and form a group of large agricultural export enterprises with good quality, high level of technology and strong market expansion ability. In addition, there is a need to strengthen the study of foreign technical barriers and green barriers to ensure that the exported agricultural products meet international standards, and improve the market competitiveness of agricultural products.
[1] ZHANG YL, JIANG XZ. A comparative analysis on export competitiveness of agricultural products between Jiangsu and Shandong, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Liaoning and Fujian Provinces[J]. Jiangsu Social Sciences,2010(4): 233-237. (in Chinese).
[2] LUO L, CAO H. Empirical analysis and countermeasures research on international competitiveness of agricultural products in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University(Social Science),2007(1): 25-28. (in Chinese).
[3] CHEN Q. Research about the export competitive of Hubei agricultural products[J].Storage Transportation & Preservation of Commodities,2013(10): 169-173. (in Chinese).
[4]ZHANG YY. Analysis on the current situation of export trade of agricultural products and the countermeasures in Hubei Province[J]. Contemporary Economics,2009(1): 108-109. (in Chinese).
[5] LIU SH. An empirical analysis on international competitiveness of agricultural products in Hubei Province[J]. Northern Economy,2009(19): 54-55. (in Chinese).
[6] ZHANG JB, LI B, WANG HJ. Analysis on the current situation of market competitiveness of agricultural products and the promotive countermeasures in Hubei Province[J]. Social Sciences in Hubei,2010(12):46-49. (in Chinese).
December 10, 2015 Accepted: February 24, 2016
Supported by Humanities and Social Sciences Project of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (14Q033); Social Science Fund Project of Yangtze University (2013csq009).
*Corresponding author. E-mail: 414294059@qq.com
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Evaluation of Social Vulnerability to Natural Disasters on a County Scale in Henan Province
- Changes and Influencing Factors of Maize Production Pattern in China
- The Changes in Guilin Paddy Soil Organic Matter and Rice Yield under Long-Term Fertilization
- Study on the Discipline Reputation of Agricultural Colleges and Universities
- Pricing Power of Agricultural Products under the Background of Small Peasant Management and Information Asymmetry
- Backflow of Migrant Workers in Urbanization: Place Selection and Influencing Factors
