Chlorpyrifos Determined in Human Blood by UPLC-MS/MS and Its Application in Poisoning Cases
2015-12-23QIAOZhengYANHuiZHUOXianyiSHENBaohua
QIAO Zheng,YAN Hui,ZHUO Xian-yi,SHEN Bao-hua
(Shanghai Key Laboratory of Forensic Medicine,Institute of Forensic Science,Ministry of Justice,P.R.China,Shanghai 200063,China)
Chlorpyrifos Determined in Human Blood by UPLC-MS/MS and Its Application in Poisoning Cases
QIAO Zheng,YAN Hui,ZHUO Xian-yi,SHEN Bao-hua
(Shanghai Key Laboratory of Forensic Medicine,Institute of Forensic Science,Ministry of Justice,P.R.China,Shanghai 200063,China)
Objective To determine the chlorpyrifos in human blood by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and to validate its application in poisoning cases.Methods The samples were extracted by a simple one-step protein precipitation procedure.Chromatography was performed on a Capcell Pack C18MGII column(250mm×2.0mm,5 μm)using an isocratic elution of solvent A(0.1%formic acid-water with 2mmol/L ammonium acetate)and solvent B(methanol with 2mmol/L ammonium acetate)at 5∶95 (V∶V).Results The linear ranged from 5 to 500 ng/mL(r=0.998 7).The limit of detection(LOD)and the lower limit of quantification(LLOQ)were 2ng/mL and 4ng/mL,respectively.For this method,the precision and accuracy of intra-day and inter-day were<10%and 97.44%-101.10%,respectively.The results in stability test of long-term frozen were satisfied.The matrix effect,recovery and process efficiency were 64.97%-86.81%,76.70%-85.52%,and 55.57%-66.58%,respectively.Conclusion This method can provide a rapid approach to chlorpyrifos extraction and determination in toxicological analysis of forensic and clinical treatment.
forensic toxicology;chlorpyrifos;chromatography,high pressure liquid;tandem mass spectrometry;blood
Article IC:1004-5619(2015)02-0112-05
Introduction
Chlorpyrifos,[O,O-diethyl-O-(3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl)phosphorothioate],also named as dursban or lorsban,is one of the organophosphorus pesticides, which is widely used in agriculture around the world, characterized by efficient,broad spectrum and medium toxicity.Although it is unstable in alkaline media,its residue could be easy to spread in environment and food consumables[1].The previous researches focused on the issues of environment pollution and food residues[2-3].
Humans are exposed to chlorpyrifos,absorbing directly through inhalation and transdermal absorption or food consumables,which increases the risk of acute and chronic poisoning[4].The chemical mainly distributes in the viscera with high blood flow, such as the kidney,liver and spleen[5-6].Humans have already noticed the toxic reactions caused by organophosphoruspesticides,theneurotoxicity becoming a potential risk of the disability and death[7]. As in the case of other organophosphate insecticides,chlorpyrifoscouldinhibittheactivitiesof cholinesterase(ChE)and pseudo-cholinesterase activities,and affect neuromuscular function[8].It could combine with acetylcholinesterase enzyme and change it to phosphorylcholinesterase enzyme,which couldnot disintegrate acetylcholinesterase(AchE),thus causing accumulation[9].This irreversiblereaction happens after 24-48 hours.It has also been reported thatchlorpyrifoscausesalargeinhibitionof protein synthesis and DNA synthesis[10-11].The symptoms of chlorpyrifos poisoning,which are similar with those of dichlorvos poisoning,include vomiting,dizziness,loss of reflexes,mental disorders and so on.
Most of chlorpyrifos could be metabolized,and the metabolites,excreted in urine.Such biological specimen have been analyzed in organophosphorus pesticides poisoning cases,as serum,blood,urine, gastric contents,infant hair,and meconium[12].Various analytical methods have been reported,including enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,UV spectrophotometerdetermination,gaschromatography coupled with electron capture detector,flame ionization detector,flame photometric detector,and mass spectrometry[2,13-16].Some determination techniques may not be specific enough to provide positive results.Theliquid-chromatog raphycombinedwith mass spectrometry could achieve the requirements of speed,selectivity and sensitivity in biochemistry analysis.This technique has been reported in chlorpyrifos analysis of blood or serum under different sample preparations[17].The objective of the current research was to establish an effective approach to qualifying and quantifying chlorprifos under a simple sample preparation so that a reliable theoretical foundation can be provided for clinic therapeutic application and forensic science.
Materials and methods
Chemicals and reagents
Chlorpyrifos standard solution(100 μg/mL in acetone[GSB05-1869-2005])was obtained from Argo-environmental Protection Institute,the Ministry of Agriculture(Beijing,China).Internal standard diazepam(1 mg/mL in methanol)was purchased from Cerilliant(TX,USA);methanol and acetonitrile (both for HPLC grade),from Sigma-Aldrich(St. Louis,MO,USA);and formic acid(50%,for HPLC grade)and ammonium acetate,from Fluka(Buchs, Switzerland).Deionized water was purified with a Milli-Q system(Millipore,MA,USA). Ultra-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry(UPLC-MS/MS)conditions
The samples were analyzed with an AcquityTMUltra Performance Liquid Chromatography(Waters, USA),combined with an API 4000 Q-Trap mass spectrometer(Applied Biosystems,USA).The UPLC analytical column was a Capcell Pack C18MGII column(250 mm×2.0 mm,5 μm,Shiseido,Japan), combined with a guard column of C18(12.5 mm× 2.1 mm,5 μm,Phenomenex,USA).Chromatographic separation was conducted using an isocratic elution of solvent A(0.1%formic acid-water with 2 mmol/L ammonium acetate)and solvent B(methanol with 2 mmol/L ammonium acetate)at 5:95(V:V),the flow rate was 0.2mL/min at room temperature.The total chromatographic analysis took 10min per sample.
Tandem mass spectrometer was operated on the positive electrospray ionization mode and multiple reaction monitoring(MRM).The optimum conditions were as follows:collision activated dissociation(CAD)medium,nebulizing gas(GS1)60 psi, heater gas(GS2)65 psi,curtain gas(CUR)25 psi, ion spray voltage(IS)4 500 V,and ion source temperature(TEM)550℃.The mass transitions were m/z 352.0→200.0,m/z 352.0→324.3 for chlorpyrifos, and m/z 285.1→193.3,m/z 285.1→154.1 for internal standard.
Working solution and sample preparation
Chlorpyrifos standard working solution was prepared by diluting the chlorpyrifos standard solution (100 μg/mL).Calibration curve samples were preparedusing 1 mL aliquotof bloodspikedwith chlorpyrifos standard solution at the different concentrations of 5,10,20,50,100,200,500 ng/mL, and quality control samples,at 10,80,400 ng/mL. The samples were mixed on a vortex mixer,and 100 μL of the sample was added to 900 μL acetonitrile,containing internalstandarddiazepamat 100 ng/mL,which were mixed and centrifuged at 13000r/min in the micro centrifuge for 3mins.Then 200μL organic layer was collected before analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS.The data were collected for analysis. All the samples and solutions were stored at-20℃until analyzed.
Method validation
The selectivity of this method was assessed for potential endogenous interference by analyzing blank blood samples from ten different persons without being exposed to chlorpyrifos.
Seven different concentrations of spiked samples ranging from 5 ng/mL to 500 ng/mL were analyzed to build up the calibration curve.Each concentration was prepared by six replicates.The calibration curveinbloodwasconstructedbyplottingthe spiked chlorpyrifos concentration versus the rations of peak area for chlorpyrifos and internal standard. A weighted linear regression model(1/x)was used.
The limit of detection(LOD)and the lower limit of quantification(LLOQ)are the lowest concentration of an analyte in a sample that can be qualified and quantified with acceptable precision and accuracy.LOD is three times of signal to noise (S/N)and LLOQ is five times response[18].
The intra-day and inter-day precision were expressed as the relative standard deviation(RSD,%)of measured concentration.The accuracy was calculated by the ration of measured concentration with target concentration.Three quality control samples at the low,medium,high concentration were analyzed on four consecutive days by six replicates and calculated using the calibration curves obtained on the day of analysis.
In the current method,thelong-termfrozen stabilitytestsofthespikedsampleswereperformed.Three different concentrations of the quality control samples were analyzed twice,interrupted by one-month storage at-20℃.The measured concentrations were compared,expressed as deviation.
Matrix effect,recovery and process efficiency were measured to value the method,according to the previous researches[19-20].Three quality control samples were analyzed in six replicates.The calculation procedures and equations went as follows: Matrix effect(%)=Set 2/Set 1×100%;Recovery (%)=Set 3/Set 2×100%;Process efficiency(%)= Set 3/Set 1×100%.Set 1 was indicated as the peak area of standard solution;Set 2,as the peak area of spiked sample post-extraction;and Set 3,as the peak area of spiked sample pre-extraction.
Results and discussion
Thefullscanspectraindicateddeprotonated molecules of chlorpyrifos at m/z 352.0.In MS-MS spectra the major fragments were observed at m/z 324.2,m/z 200.2,m/z 153.3,m/z 115.0.In consideration of the potential interference from blank or endogenous interference in blank blood matrix,and analysis of MRM,the ions of m/z 324.3 and m/z200.0 were selected to monitor in the determination of chlorpyrifos.The ion of m/z 200.0 was selected as quantitative transition with a greater intensity. The mother ion of internal standard diazepam was m/z 285.1,and the daughter ions were m/z 193.3 and m/z 154.1.The ion of m/z 193.3 was selected as quantitative transition.
Several different chromatographic columns were evaluated for chlorpyrifos achievement.The Capcell Pack C18MGII column(250 mm×2.0 mm,5 μm)proved to achieve a good separation of analyte and internalstandardwithsuitableretentiondurations and peak shapes.As for the chemical properties of organophosphorus pesticides,the mobile phase consisted of a high percentage of methanol with water. And 0.1%formic acid and 2 mmol/L ammonium acetate were added to the mobile phase to adjust the pH values to enhance the ionization effect and increase intensity of target compound[21].This mobile phase was also suitable for the internal standard.
As indicated by the simple one-step protein precipitationsampleextractionprocedure,acetonitrile developed a better deproteinization of blood samples than methanol.
The selectivity of this current method was assessed for potential endogenous interference by analyzing blank blood samples from ten different people without being exposed to chlorpyrifos.No significant peaks or responses were detected at the retention durations of the target compound or internal standard.The chromatograms of blank blood and spiked blood samples were presented(Fig.1).
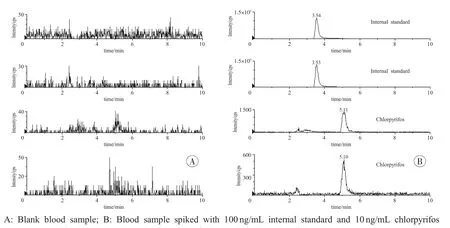
Fig.1 The chromatograms of blank blood and spiked blood samples
The standard calibration equation was y=0.00168x-0.00115,r=0.9987,y as the peak area ration of chlorpyrifoswithinternalstandard,xasseven spiked chlorpyrifos concentration,ranging from 5 to 500ng/mL(n=6).Correlation coefficient was>0.995, and the linearity was good;thus the method was acceptable.Based on the definition,the LOD and LLOQ were estimated at 2 ng/mL and 4 ng/mL,respectively.
Asindicatedbytheintra-dayandinter-day precision and accuracy tests of quality control samples,all the RSD values were less than 10%,and the accuracy was 97.44%-101.10%(Table 1),hence an acceptable precision and accuracy of the method.
From the long-term frozen stability test at-20℃of three quality control samples to determine an appropriatestoragerequirementofsamples,itwas found that three deviations,expressed as the ration of frozen spiked sample concentration with spiked sample concentration,were-8.48%,-3.54%and 1.54%,respectively,less than±15%.This indicated thatthebloodsamplesspikedwithchlorpyrifos were considered to be stable when stored at-20℃in one month.
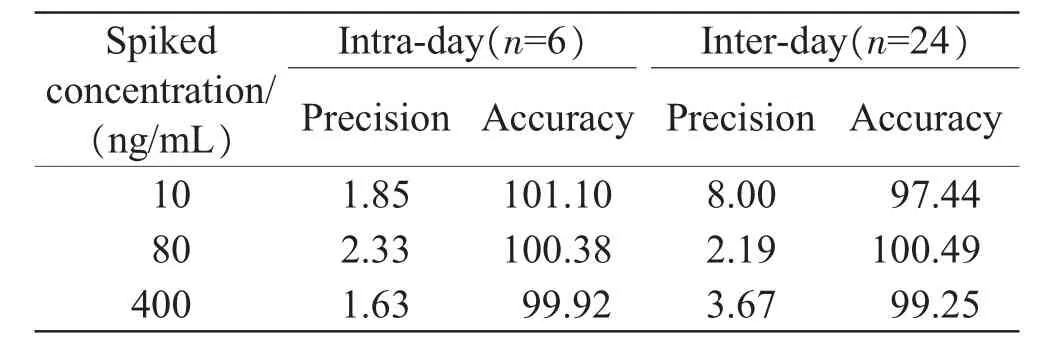
Table1 The intra-day and inter-day precision and accuracy results(%)
According to the results of matrix effect,recovery and process efficiency(Table 2),the recovery and process efficiency were all over than 50%, which indicated that the one-step protein precipitation extraction with acetonitril of blood sample was suitable and effective.The matrix effect of 10ng/mL was 64.97%,suggesting that the lower spiked concentration could be more likely to be influenced bythe blood matrix of signal inhibiting.Previous researches had indicated that protein impurities still existed after protein precipitation and provided a solid phase extraction or supercritical fluid extraction before pesticide analysis,which could minimize thematrixeffectandincreasetherecoveryof method[3,16,22].
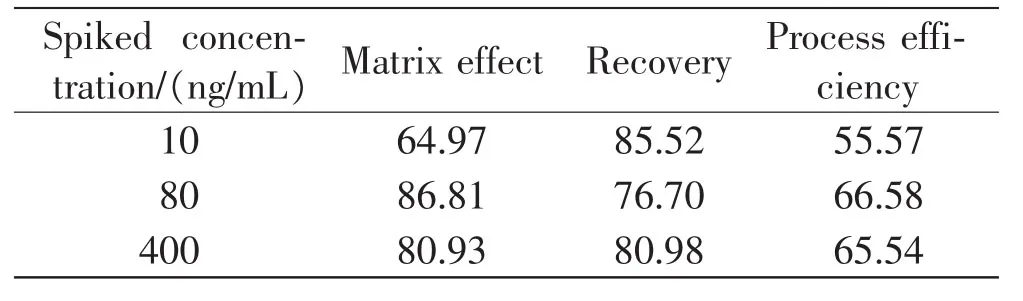
Table2 Matrix effect,recovery and process efficiency results(n=6,%)
Application
Case1:Afteraconflictinthefamily,a 31-year-old man attempted to suicide by swallowing a bottle of pesticide marked with the Chinese characters meaning chlorpyifos.After vomiting a kind of milk-white liquid,he was sent to the hospital immediately.Obviously,the symptoms of organophosphorus intoxication were miosis,polypnea,and loss of reflexes.The cholinesterase value was under 100 U/L. His blood and gastric lavage fluid,with a strong odor of organophosphorus pesticide,were analyzed and determined at 0.941μg/mL and 2.377mg/mL of chlorpyrifos,respectively.The samples had been diluted suitability before analyzed.After a 4-day treatment,the vital signs became stable.The cholinesterase value was still 100-120 U/L,and the concentration of chlorpyifos decreased to 0.054μg/mL in blood.
Case 2:A 6-year-old boy was sent to the hospital and a diagnosis was made of acute organophosphorus poisoning.He was confirmed to be close to a bottle of chlorpyrifos by mistake while playing outside. The blood sample was quantified at 0.096 μg/mL. Three days later,the blood sample was collected again for determination.Although no obvious clinical symptoms developed,chlorpyrifos could still be detected,under the LLOQ.
Case 3:A 20-year-old female was confirmed to be self-poisoning by swallowing a kind of organophosphorus pesticide,whose the samples of blood,urine and gastric lavage fluid were collected.Following a full screening method of organophosphorus detection, chlorpyrifos was detected,and the samples of the blood and gastric lavage fluid were quantified,the concentrations were 0.013 μg/mL and 10.933 μg/mL, respectively.No specific peak response of chlorpyrifos was observed in the urine sample.
Case 4:A 42-year-old female reported that she had drunk four bottles of pesticide.She was treated with gastric lavage and catheterization.The sample of blood was collected for toxicological analysis. Although no obvious clinical symptoms were observed,except for vomiting,the previous screening methodindicatedtherewaschlorpyrifosinthe blood sample.Chlorpyrifos was detected using the method to be quantified at 0.369μg/mL in blood.
Reported acute chlorpyrifos poisoning was mostly caused by mistake or suicide.Suicide attempts are mainly due to domestic or emotional conflicts. A suicidal attempt due to ingestion of chlorpyrifos was reported in a teenage girl,whose serum and gastric content contained 5.3 and 9.4 μg/mL of chlorpyrifos[23].In several death cases,toxic concentration of chlorpyrifos ranged from 0.2 to 88 μg/mL in blood,0.003 to 0.09μg/mL in urine[24].In a poisoning case the chlorpyrifos concentration in blood was 3 300,3 000,2 200,1 000,600,300 ng/mL on day 1,3,6,8,10 and 12,respectively[25].In the previous studies,no unchanged chlorpyrifos was found in the urine following either route of administration. It was cleared from the blood and eliminated in the urine with a mean half-life of twenty-seven hours after oral intake[5].Therefore,it is reasonable to explain the negative result of urine sample in Case 3. In four cases,all the patients were treated with gastrolavageandhemoperfusion.Andpralidoxime chloride,atropine and penehyclidine hydrochloride are first-line therapy for chlorpyrifos posioning in China[26].The samples had been proved to be without diazepam in the previous screen method.This method could also be applied in urine,gastric lavage fluid and other specimens.
Conclusion
A UPLC-MS/MS analytical technique with onestep extraction was established for the qualification and quantification of chlorpyrifos.The linearity of standard curve proved to be satisfying.The current method could be used as an effective approach to addressing poisoning cases in forensic science and provide a technical support to the clinical treatment of acute chlorpyrifos intoxication.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the 12th Five-year Plan National Key Technology R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of P.R.China(2012BAK16B02),the National Natural Science Foundation of China(81302614),the Science and Technology Committee of Shanghai Municipality(14DZ2270800,13ZR1443000)and grants from Ministry of Finance,P.R.China(GY2015G-3).
[1]郑璐,卢振兰.杀虫剂毒死蜱的研究进展[J].轻工科技,2013,(1):77,79.
[2]Wei Y,Zhang X,Li J,et al.Comparisons of two methods for extraction and determination of chlorpyrifos in water[J].Shangdong Science,2010,23(6): 44-47.
[3]Xu D,Chen A,Yu X,et al.Determination of chlorpyrifos in fish tissue by supercritical fluid extraction and gas chromatography[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2005,33(4):451-454.
[4]Sinha SN.Liquid chromatography mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS)study of distribution patterns of base peak ions and reaction mechanism with quantification of pesticides in drinking water using a lyophilization technique[J].American Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2011,(2):511-521.
[5]Nolan RJ,Rick DL,Freshour NL,et al.Chlorpyrifos: pharmacokinetics in human volunteers[J].Toxicol Appl Pharmacol,1984,73(1):8-15.
[6]郑光,周志俊.毒死蜱的毒理学研究进展[J].中国公共卫生,2002,18(4):496-498.
[7]Wang H,Wu Y.Neurotoxicity and mechanisms of chlorpyrifos[J].J Environ Occup Med,2008,25(3): 314-318.
[8]Wacksman MN,Maul JD,Lydy MJ.Impact of atrazine on chlorpyrifos toxicity in four aquatic vertebrates[J]. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol,2006,51(4):681-689.
[9]Jameson RR,Seidler FJ,Slotkin TA.Nonenzymatic functions of acetylcholinesterase splice variants in the developmentalneurotoxicityoforganophosphates: chlorpyrifos,chlorpyrifos oxon,and diazinon[J].Environ Health Perspect,2007,115(1):65-70.
[10]Whitney KD,Seidler FJ,Slotkin TA.Developmental neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos:cellular mechanisms[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol,1995,134(1):53-62.
[11]Qiao D,Seidler FJ,Slotkin TA.Developmental neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos modeled in vitro:comparative effects of metabolites and other cholinesterase inhibitors on DNA synthesis in PC12 and C6 cells[J]. Environ Health Perspect,2001,109(9):909-913.
[12]Ostrea EM Jr,Bielawski DM,Posecion NC Jr,et al. A comparison of infant hair,cord blood and meconium analysis to detect fetal exposure to environmental pesticides[J].Environ Res,2008,106(2):277-283.
[13]Liang Y.Application of immunoassay in organophosphorus pesticide residue analysis[J].Science and Technology of Cereals,Oils and Foods,2013,21(5):89-94.
[14]Sinha SN,Bhatnagar VK.Analysis of toxicants by gas chromatography[J].Advanced Gas Chromatography-Progress in Agricultural,Biomedical and Industrial Applications,137-150.
[15]United States Department of Agriculture Food Safety and Inspection Service,Office of Public Health Science,Screening forpesticides by LC/MS/MS and GC/MS/MS,Instrumentation,2013:1-39.
[16]García-Repetto R,Giménez MP,Repetto M.New method for determination of ten pesticides in human blood[J].J AOAC Int,2001,84(2):342-349.
[17]Salm P,Taylor PJ,Roberts D,et al.Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantitative determination of the organophosphorus pesticides dimethoate,fenthion,diazinon and chlorpyrifos in human blood[J].J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci,2009,877(5-6):568-574.
[18]Shrivastava A,Gupta VB.Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods[J].Chronicles of Young Scientists,2011,2(1):21-25.
[19]Matuszewski BK,Constanzer ML,Chavez-Eng CM. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS[J]. Anal Chem,2003,75(13):3019-3030.
[20]Hall TG,Smukste I,Bresciano KR,et al.Identifying and overcoming matrix effects in drug discovery and development[C].Tandem Mass Spectrometry-Applications and Principles,Chapter 18:389-420.
[21]XieJ,GeQ.Matrixeffectsinbioanalysisby LC/MS[J].Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2008,28(8):1386-1389.
[22]Li J,Wei C,Yuan G,et al.GC-MS simultaneous determinationof8organophosphoruspesticidesin human plasma and its applications[J].Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2009,29(12):2018-2022.
[23]Martínez MA,Ballesteros S,de la Torre CS,et al. Attempted suicide by ingestion of chlorpyrifos:identification in serum and gastric content by GC-FID/GCMS[J].Journal of Analytical Toxicology,2004,28(7): 609-615.
[24]Shen M,Xiang P.Forensic Toxicology Handbook[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2012:178-180.
[25]Sinha SN,Pal R,Dewan A,et al.Effect of dissociation energy on ion formation and sensitivity of an analytical method for determination of chlorpyrifos in human blood,using gas chromatography-mass spectrometer(GC-MS in MS/MS)[J].International Journal of Mass Spectrometry,2006,253(1-2):48-57.
[26]Huang Y,Yin W,Liu C,et al.Therapeutic efficacy of pralidoxime chloride by continuous intravenous infusion in treatment of acute chlorpyrifos poisoning[J]. Guide of China Medicine,2013,11(7):22-23.
(Received date:2014-12-22)
(Editor:LIANG Lu)
DF795.1 Document code:A
10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2015.02.009
Author:QIAO Zheng(1988—),female,postgraduate in pharmaceutical sciences;E-mail:qiaoz@ssfjd.cn
SHEN Bao-hua,male,research fellow,major in forensic toxicology;E-mail:shenbh@ssfjd.cn
