RP-HPLC法同时测定十种五加属植物叶中三萜Chiisanoside和Chiisanogenin
2013-02-10刘向前戴秀珍
刘向前,戴 玲,戴秀珍
1湖南省中药现代化研究重点实验室湖南中医药大学药学院,长沙410208;2中南大学制药工程系,长沙410083
Introduction
The plants of Acanthopanax Miq.are richly distributed in Asia,growing about 26 kinds and 18 varieties in China,11 kinds and 3 varieties in Korea,and 9 kinds in Japan.A large number of Acanthopanax Miq.plants have shown somemedical values,including nourishing,anti-rheumatic, anti-stress, anti-fatigue, and antitumor[1,2].Chiisanosidewas reported to have anti-cancer,anti-hepatotoxic and anti-diabetic activities[6].It had been isolated from A.chiisanensis,A.divaricatus var allbeofructus and other Acanthopanax genus[3-5].While,chiisanogenin,a metabolite of chiisanoside by human intestinal bacteria[7],also showed some biological activities such as protection of ulcer of stomach and liver damage[8-10].In order to further develop and utilize of these plants,a RP-HPLCmethod for quantitative analysis of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin was devel-oped and optimized in thismanuscript[10,11].Thismethod was validated for its precision,stability and repeatability.In addition,chiisanoside and chiisanogenin from leaves of ten kinds of Acanthopanax Miq.plants were simultaneously determined and quantified to provide a basis for the follow-up study of Acanthopanax Miq.plants.
M aterials and M ethods
Chem icals and reagents
tandards of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin(Fig.1)were internally prepared in the laboratory(purities and structures were determined by HPLC,NMR,MS,etc;and their puritieswere above 98.5%).Acetonitrile(CH3CN,HPLC grade)and methanol(CH3OH,HPLC grade)were both purchased from Tianjin Kermel Chemical Reagent Co.Ltd;double-distilled water for the chromatography was purified by using the automatic double pure water distillatory.The solventswere filtered through 0.45 μm membranes and degassed in an ultrasonic bath before use.

Fig.1 Chem ical structures of chiianoside(A)and chiisanogenin(B)
Ten plantmaterials were A.gracilistylus W.W.Smith(Ningxiang county,Hunan Province);A.senticosus(Fusong county,Jilin province);A.henryi(Oliv.)Harms and A.sessiliflorus(Xinhua county,Hunan Province);A.seboldianus Makino,A.koreanum,A.divaricatus var.albeofructus,A.divaricatus f.distimatis,A.divarcatus f.inermis and A.chiisanesis,which were all collected from the herb garden of Kyung Hee University,Korea.All samples were random ly divided into three batches and were identified by one of authors,Professor Liu Xiang-qian.The voucher specimens of these samples were kept in Herbarium of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine.
The ten kinds of A.Miq.plants chosen in this study were distributed widely and richly in China and Korea.Among them,the dried roots and stem barks of A.gracilistylus W.W.Smith and A.senticosus were listed officially in Chinese Pharmacopoeia as Acanthopanacis Cortex(Wujiapi)and Acanthopanacis Senticosi Radix et Rhizoma seu caulis(Ciwujia),respectively[12].Moreover,A.sessilifluous was examined and approved as a new resource of food.A.henryi(Oliv.)Harmswas collected into the local standards of Hunan Province.
Instrum ental and chrom atographic conditions
A HPLC system(Shimadzu,Japan,LC-10AT)consisted of a SPD-10A UV-Vis detector and a CBM-102 chromatography workstation was used for the quantitative analyses.Chromatographic separation was achieved with an ODS-C18column(250 mm × 4.6 mm,5 μm)at40 ℃,and CH3CN-H2O(55∶45)was employed as themobile system.The flow rate was kept constantly at 1.0 mL/min.The UV detection wavelength was selected as 205 nm.The injection volume was 10 μL.
Preparation of standard solution
Standard stock solutionswere prepared by dissolving an appropriate amount of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin in methanol to give a final concentration of330μg/mL and 195 μg/mL.A serial of mixed standard solutions were then prepared at concentrations of 16.5,49.5,82.5,115.5,148.5,181.5 μg/mL and 4.88,19.5,34.1,48.8,63.4,78.0 μg/mL for chiisanoside and chiisanogenin,respectively.
Preparation of sam ple solution
All of the samples were powdered that passed through 40 mesh's sieve.Took about 4 g of each sample,and weighed precisely before extraction.Then,reflux extraction was carried out two times using methanol for 4 hours at65 ℃,and filtered.Finally,after evaporation of themethanol under vacuum,the residue was diluted to 50 mL with methanol and then filtered with 0.45 μm membrane filter.
M ethod validation
Linearity
The linearity of themethod was established by injecting the series of standard mixtures of chiisanoside and chi-isanogenin.The data of peak areas versus concentrations were treated by linear least square regression analysis.
Precision
The precision of the method was determined by injecting one samplewith five replicates.In thismanuscript,five applications of A.divarcatus f.inermis were assayed and the peak areas were recorded.
Stability
The stability study of the sample solution of A.divarcatus f.inermis was carried outover a period of12 h at25℃ (room temperature under laboratory light).The variability was assayed at the same concentration for every 4 hours,during 12 hours.
Repeatability
The repeatability of themethod was detected by extracting one sample of A.divarcatus f.inermis five times,and the areas of the peakswere recorded.
Recovery
To test the extraction recovery,quantified samples of A.divarcatus f.inermis were added with low,middle and high concentrations standards before extraction.The follow-up extractions and HPLC analyses were accomplished in the same manner as detailed above.The recovery was compared with the theoretical concentration.
Results and Discussion
M ethod development
To develop a suitable method for the quantification of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin,differentmobile phases were employed to achieve the best separation and resolution.The method development was initiated with using amobile phase of acetonitrile and water at various ratios(50∶50,55∶45,60∶40,65∶35).Acetonitrile and sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer at different pH were also investigated in this study.However,the pH values ofmobile phase were found to have no effect on the separation of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin.Finally,themobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and water(55∶45)was found to be appropriate allowing good separation of compounds at a flow rate of1 mL/min.In addition,in order to obtain a satisfactory and full detection for this new method,UV-Vis spectra of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin standards were obtained.Based on the maximum UV absorbance of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin,205 nm was selected as the optical detection wavelength.

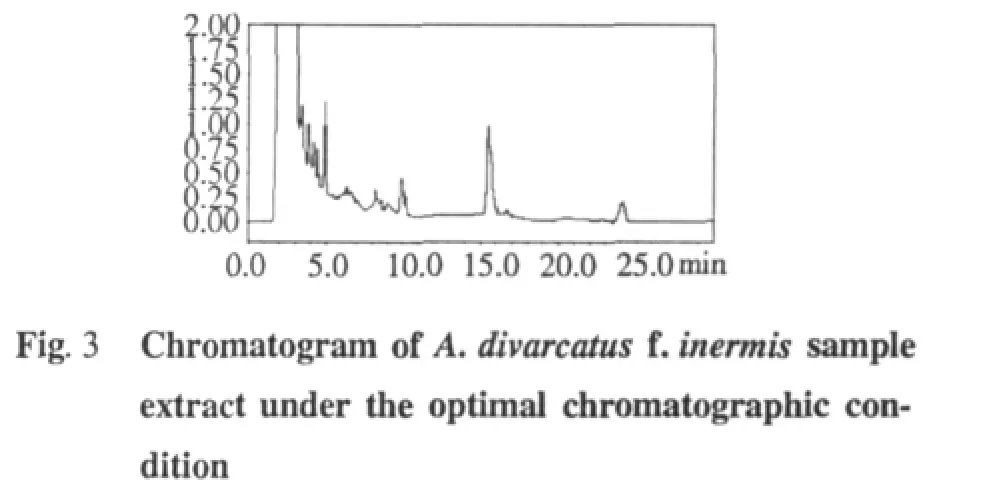
M ethod validation
Calibration curves
The linearity of the detector responseswas investigated for each standard mixture solution by plotting peak areas against concentrations.Good correlation between the peak areas and concentrations at the range of 16.5-181.5 μg/mL for chiianoside and 4.88-78.0 μg/mL for chiisanogenin was achieved.The regression equations and correlation coefficients determined were Y=5498356X-9738(r=0.9995)for chiianoside and Y=5753131X-8289(r=0.9979)for chiisanogenin,respectively.
Precision
The RSDs of the peak areas were 0.22%and 0.44%for chiianoside and chiisanogenin respectively,which indicated that the developed and optimized method was precise.
Stability
The RSDs values of the peak areas were 1.04%and 1.17%for chiianoside and chiisanogenin,respectively.It indicated that sample solutions were stable for 12 h at room temperature.
Repeatability
The RSDs values of the peak areas were 0.66%for chiianoside and 1.11%for chiisanogenin,which indicated that the proposed method was repeatable.
Recovery test The average recovery rates were 98.87%(RSD was 1.14%)for chiianoside and 98.83%(RSD was0.72%)for chiisanogenin.The results of recovery tests were shown in Table 1.
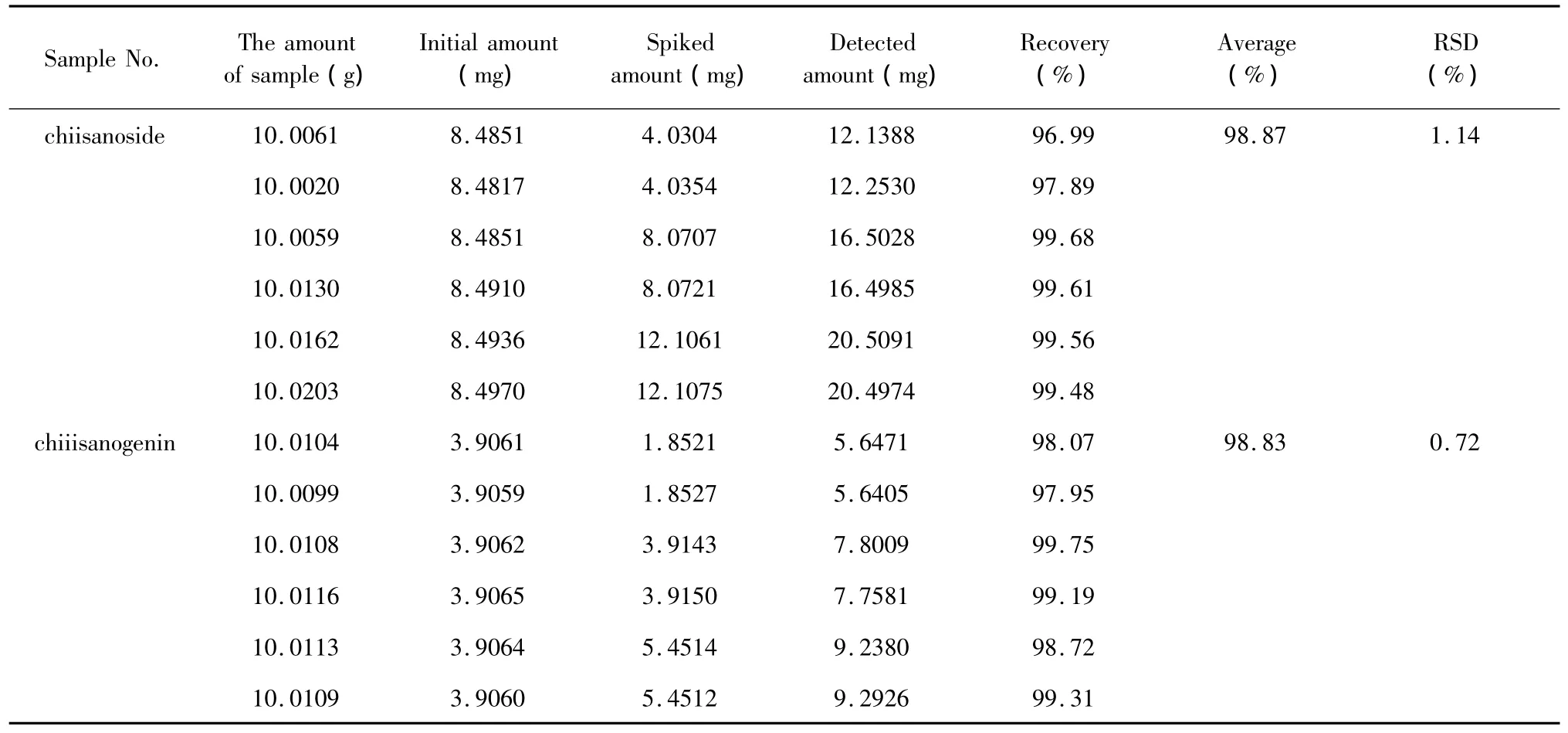
Table 1 Recoveries of chiisanoside and chiiisanogenin
Quantitative determ ination
The validated method was employed to determine the two ingredients in each sample of the ten kinds of Acanthopanax Miq.plants,and every batch of sample was concurrently determined three times.The quantification results of the ingredientswere shown in Table 2.

Table 2 Concentrations of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin detected in the ten kinds of Acanthopanax M iq.(n=3)
Conclusion
A simple and rapid method was successfully developed for simultaneous determination of chiianoside and chiisanogenin from leaves of Acanthopanax Miq.plants.The proposed method was optimized and validated for the various parameters.The results demonstrated the method was highly specific,accurate and precise,which is promising of being used in quality control of Acanthopanax Miq..The concentrations of chiianoside and chiisanogenin of ten kinds of Acanthopanax Miq.plants were quantified using the developed method.The results indicated that the two ingredientswere not detected in A.gracilistylus W.W.Smith and A.koreanum,while A.divaricatus var.albeofructus had the highest concentration of chiianoside,A.senticosus had the highest concentration of chiisanogenin.
1 Liu XQ.Studies on the active constituents of Acanthopanax gracilistylus W.W.Smith.Korea:Kyung Hee University,PhD.2003.
2 Liu XQ,Chang SK,Park SY.A new lupane-triterpene glycoside from the leaves of Acanthopanax gracilistylus.Arch Pharm Res,2002,25:831-836.
3 Liu XQ,Chang SY,Yook CS.Lupane-triterpenoids from the leaves of Acanthopanax gracilistylus,JLanzhou Univ(Natural Sciences),2006,42(4):86-91.
4 Zou QP,Liu XQ,Lee HK.Lupane-triterpenoids from the methanol extracts of leaves of Acanthopanax gracilistylus W.W.Smith.J Lanzhou Univ(Natural Sciences),2011,47:120-127.
5 Liu XQ,Kim IS,Yook CS.Oleanene glycosides from the leaves of Acanthopanax seiboldianus forma albeofolium Yook.Nat Prod Res Dev(天然产物研究与开发),2008,20:66-70.
6 Chang SY,Liu XQ,Chang SY.Lupane-triterpene glycosides from the leaves of A canthopanax gracilistylus.Chem Pharm Bull,2002,50:1383-1385.
7 Chang SY,Yook CS,Nohara T.Two new lupane-triterpene glycosides from leaves of Acanthopanax Koreanum.Chem Pharm Bull,1998,46:163-165.
8 Chang SY,Yook CS,Nohara T.Lupane triterpene glycosides from leaves of Acanthopanax Koreanum.Phytochemistry,1999,50:1369-1374.
9 Li LL,Zheng LS,Liu XQ.Analysis of syringing content in new resource Acanthopanax.sessiliflorus(Rupr,et Maxim.)seem and other seven species of Acanthopanax Miq.by RPHPLC.Food Sci,2009,30:140-143.
10 Ni N,Liu XQ,Zhang XD.Determination of acanthoic acid and kaurenoic acid from rootbarks of eight kinds of Acanthopanax Miq.plants by RP-HPLC.J Central South Univ,Nat Sci(中南大学学报,自科版),2009,40:1216-1221.
11 Zhang BX,Liu XQ,Fan XG.Protective effect of Acanthopanax gracilistylus-extracted acankoreanogenin A on mice with fulminant hepatitis.Inter Immunopharmacol,2011,10:1018-1023.
12 Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee.Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China.Beijing:China Medical Science Press,2010,Vol I,61.
