甜菜硝酸还原酶基因编码氨基酸偏好及功能预测分析
2011-07-26丁广洲马凤鸣
丁广洲 ,侯 静 ,马凤鸣
(1.中国农业科学院甜菜研究所,哈尔滨150080;2.黑龙江大学农作物研究院,哈尔滨150080;3.东北农业大学农学院,哈尔滨150030)
在高等植物氮代谢过程中,与NO3-还原有关的基因包括NR基因(nia)和NiR基因(nii)。高等植物的NR由nia编码。至今,nia或nia cDNA至少已在下列植物中被克隆:菠菜(Prosser&Lazarus,1990;Tamura等,1997;Kubo 等,1998)、笋瓜(Crawford 等,1986;Hyde 等,1991)、烟草(Cherel等,1990;Vaucheret等,1989;Yamamoto 等,2006)、 拟南芥 (Cheng 等,1988;Crawford 等,1988;Wilkinson&Crawford,1991,1993)、 水稻(Choi等,1989;Matsumoto 等,2005;Ohyanagi等,2006;Itoh 等,2007)、 大豆 (Wu 等,1995)、 玉米(Campbell等,1995;Katagi等,1999)、番茄(Daniel-Vedele 等,1989;王利群,2003)、桃(Nakamura 等,2001)、菜豆(Hoff等,1991;Jensen 等,1994,1996)、 大麦 (Miyazaki等,1991,Schnorr等,1991)、 马铃薯 (Harris 等,1997;Yamamoto 等,2003)、甘蓝型油菜(Fukuoka,1996)、蓖麻(Tsai等,2003)、矮牵牛(Salamoubat&Budang,1993)等。目前,还没有其他的关于甜菜硝酸还原酶基因全序列被克隆注册的报道。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试品种
实验采用黑龙江省甜菜(Beta vulgaris L.)主栽二倍体纯系品种甜研7号(Ty7),原种由中国农科院甜菜研究所提供。种子在室温下浸种7h,置于培养皿中25℃恒温培养24~48h萌发,定植至营养钵中,置于光照培养箱中培养,待植株长到2~4对真叶时进行硝酸钾(30mmol/L KNO3)诱导处理,然后用于实验操作。
1.2 采用RACE技术克隆甜菜硝酸还原酶基因
取硝酸钾诱导后的甜菜叶片0.1 g,使用Trizol试剂盒(Invitrogen,USA)提取总RNA,电泳检测其质量,置-70℃保存。前期利用同源序列克隆技术筛选拼接得到一个1438bp NR基因片段。采用SMARTTMRACE cDNA Amplification Kit(Clontech,USA)进行5′端和3′端的RACE反应。根据中间片段设计基因特异性引物(GSP)(表 1)。 以 5′GSP 与 UPM 引物扩增基因的 5′端,反应程序为:5 个循环(94℃ 30 s,72℃ 3 min);5个循环(94℃ 30 s,70℃ 30 s,72℃ 3 min);20 个循环(94℃ 30 s,58.7℃ 30 s,72℃ 3 min),4℃保存。 以 3′GSP与UPM引物扩增基因的3′端,反应程序为:5个循环(94℃ 30 s,72℃ 3 min);5 个循环(94℃ 30 s,70℃ 30 s,72℃ 3 min);25 个循环 (94℃ 30 s,62℃30 s,72℃3 min),4℃保存。将PCR产物电泳条带切下,按照 TIAN gel Midi Purification Kit使用说明书回收PCR产物。将回收产物连接到pEASY-T1载体上,转化连接产物到Trans1-T1感受态细胞中。挑取白色单克隆培养,使用通用引物正反向引物(表1)鉴定阳性克隆。
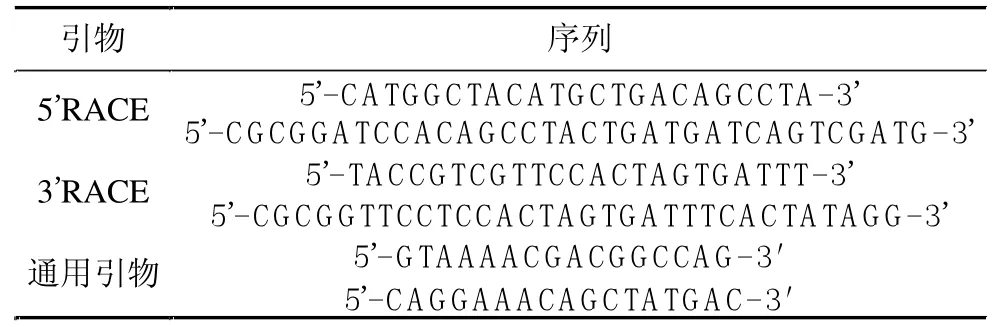
表1 试验中采用的引物及序列
1.3 生物信息学分析
将选取的阳性克隆测序,根据测序结果拼接出基因的全长序列。应用NCBI的ORF finder软件对全长cDNA序列进行可读框架分析;利用BLAST P程序在NCBI网站通过同源性比对验证基因的完整性,并进行保守结构域分析;蛋白质等电点和分子量计算 http://www.expasy.ch/cgi-bin/pi;利用DNASTAR中的EditSeq计算cDNA序列的GC含量;利用ClustalX 1.83和BOXSHADE 3.21在线软件(http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/BOX_form.html)进行氨基酸序列相似性比对分析。
2 结果与讨论
采用RACE技术对前期研究获得的1438bp的中间片段进行全长序列克隆,3′RACE克隆获得了1109bp的序列;5′RACE克隆获得了803bp的序列,回收产物利用通用引物鉴定,显示克隆结果较好。使用 Contig Express软件将5′RACE序列、中间序列和3′RACE序列拼接,获得全长序列3247bp,找到了完整的ORF。甜菜Ty7 nia cDNA全序列共3247bp,含有一个2718bp的开放阅读框(ORF);包括147bp的5′非翻译区(UTR)和382 bp的3′非翻译区。该序列编码905个氨基酸,分子量大小为102kD(ExPaSy的分子量分析),等电点为6.12。将全序列提交NCBI的GenBank注册,注册序列号为:EU163265。
2.1 基因的密码子偏好和编码产物氨基酸组成
在cDNA编码蛋白的氨基酸序列中,Gly含量最多为7.85%,其次为Glu 7.62%,第三为Val 7.29%,Cys含量最少为1.55%(见表2)。因此,甜菜硝酸还原酶基因编码氨基酸具有甘氨酸偏好。编码蛋白的氨基酸序列中含有14个Cys,说明编码产物中可能含有二硫键。现有的研究表明,植物NR蛋白C'端都具有二肽 (Cys-Gly)保守的基序。

?
2.2 基因编码产物的功能预测
参照Daniel的方法,推测甜菜硝酸还原酶基因编码的氨基酸残基及其功能。表3是对该基因编码的氨基酸残基及其功能的分析。
从甜菜硝酸还原酶基因编码蛋白的结构域分析,从第93个氨基酸开始进入3个氧化还原中心的功能区(MoCo、Fe-血红素、FAD),其中 93~478为钼辅因子功能区(eukary NR Moco),含有386个氨基酸残基;535~608 为 Fe-血红素结合区(Cyt-b5),含 75个氨基酸;653~760为 FAD结合区(FAD binding 6)。 从 779~888 为 NADH 绑缚区(NADH binding 1)。 详见图 1。

?
2.3 可能的酶水解位点和磷酸化位点
在连接3个氧化还原中心的两个绞链区中,绞链区I有3个可能被胰蛋白酶(trypsin)水解(hydrolysis)的精氨酸位点(-475、-510、-522);两个可能被金黄葡萄球菌 V8 蛋白水解酶 (S.aureus V8 pro-tease)水解的谷氨酸位点(-487、-513);另外含有4个容易被磷酸化的-Ser位点,(-502、-515、-525、-533)。绞链区Ⅱ也有 3 个可能被胰蛋白酶(trypsin)水解(hydrolysis)的精氨酸位点(-642、-649、-651);一个可能被金黄葡萄球菌 V8 蛋白水解酶(S.aureus V8 pro-tease)水解的谷氨酸位点(-606)(见图 2)。

3 结论

克隆获得甜菜硝酸还原酶基因,该基因编码905个氨基酸,具有甘氨酸偏好,含有高等植物硝酸还原酶所特有的功能结构域:3个氧化还原中心的功能区(MoCo、Fe-血红素、FAD)。在连接3个氧化还原中心的两个绞链区中,分别具有若干可被胰蛋白酶水解的酶切位点和磷酸化位点。
[1]Crawford N M,H N Arst.The molecular genetics of nitrate assimilation in fungi and plants[J].Annu.Rev.Genet., 1993,27:115-146.
[2]Crawford N M,Campbell W H,Davis R.Nitrate reductase from squash:cDNA cloning and nitrate regulation[J].Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA,1986,83(21):8073-8076.
[3]Melzer J M,A Kleinhofs and R L Warner.Nitrate reductase regulation:effects of nitrate and light on nitrate reductase mRNA accumulation[J].Molecular and General Genetics,1989,217(2-3):341-346.
[4]Crawford N M.Nitrate:nutrient and signal for plant growth[J].Plant Cell,1995,7:859-868.
[5]Dawn E.Tucker,Damian J.Allen,Donald R.Ort.Control of nitrate reductase by circadian and diurnal rhythms in tomato[J].Planta,2004,219(2):277-285.
[6]Vaucheret H,Vincenta M,Kronenberger J,et al.Molecular cloning and characterization of the two homeologous genes coding for nitrate reductase in tobacco[J].Mol.Gen.Genet.,1989,216(1):10-15.
[7]Jensen P E,Hoff T,Moiler M G,et al.Identification and characterization of a nitrate reduetase gene from bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) contgxning four introns[J].Physiol.Plant.,1994,92:613-623.
[8]Hoff T,Stummann B M,Henningssen K W.Cloning and expression of gene encoding a root specific nitrate reductase in bean(Phaseolus vulgaris)[J].Physiol.Plant.,1991,82(2):197-204.
[9]Prosser I M and Lazarus C M.Nucleotide sequence of a spinach nitrate reductase cDNA[J].Plant Mol.Biol., 1990,15(1):187-190.
[10]Tamura N,Takahashi H,Takeba G,et al.The nitrate reductase gene isolated from DNA of cultured spinach[J].Biochim.Biophys.Acta.,1997,1338(2):151-155.
[11]Hyde G E,W H Campbell.Highlevel expression in Escherichia coli of the catalytically active flavin domain of com leaf NADH:nitrate reductase and its comparison to human NADH:cytochrome b5 reductase[J].Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun.,1990,168(3):1285-1291.
[12]Cherel I,Gonneau M,Meyer C,et al.Biochemical and immunological characterization of nitrate reduetese-defieient nia mutants of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia[J].Plant Physiol.,1990,92(3):659-665.
[13]Yamamoto-Katou A,Katou S,Yoshioka H,et al.Nitrate reductase is responsible for elicitin-induced nitric oxide production in Nicotiana benthamiana[J].Plant Cell Physiol.,2006,47(6):726-735.
[14]Cheng C L,G N Acedo,J Dewdney,et al.Differential expression of the two Arabidopsis nitrate reductase genes[J].Plant Physiol.,1991,96(1):275-279.
[15]Wilkinson J Q and Crawford N M.Identification and characterization of a chlorate-resistant mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana with mutations in both nitrate reductase[J].Mol.Gen.Genet.,1993,239 (1-2):289-297.
[16]Choi H,Kieinhofs A,An G.Nucleotide sequence of rice nitrate reductase genes[J].Plant Mol.Biol.,1989,13(6):731-733.
[17]Wu S,Lu Q,Kriz A L and Harper J E.Identification of cDNA clones corresponding to two inducible nitrate reductase genes in soybean:analysis in wild-type and nr1 mutant[J].Plant Mol.Biol.,1995,29 (3):491-506.
[18]Daniel-Vedele F,Dorbe M F,Caboche M,et al.Cloning and analysis of the tomato nitrate reductase-encoding gene:protein domain structure and amino acid homologies in higher plants[J].Gene.,1989,85(2):371-380.
[19]Jensen P E,Hoff T,Stummann B M,et al.Functional analysis of two bean nitrate reductase promoters in transgenic tobacco[J].Physiol.Plant.,1996,96(3):357-358.
[20]Miyazaki J,Juricek M,Angelis K,et al.Characterrization and sequence of a novel nitrate reductase from barley[J].Mol.Gen.Genet.,1991,228(3):329-334.
[21]Schnorr K M,Juricek M,Huang C,et al.Analysis of barley nitrate reductase cDNA and genomic coones[J].Mol.Gen.Genet.,1991,227(3):411-416.
[22]Fukuoka H,Ogawa T,Minami H,et al.Developmental stage-specific and nitrate independent regulation of nitrate reductase gene expression in rapeseed[J].Plant Physiol.,1996,111(1):39-47.
[23]Tsai CB,Kaiser WM,Kaldenhoff R.Molecular cloning and characterization of nitrate reductase from Ricinus communis L.heterologously expressed in Pichia pastoris[J].Planta.,2003,217(6):962-700.
[24]Fei-Fei Sun,Xi-Lin Hou,Ying Li,Xue-Dong Yang.Molecular cloning and characterization of nitrate reductase gene from nonheading Chinese cabbage[J].Scientia Horticulturae.,2008,119(1):1-10.
[25]Thomas Hettmann,Roman A.Siddiqui,Christa Frey et al.Mutagenesis study on amino acids around the molybdenum centre of the periplasmic nitrate reductase from Ralstonia eutropha[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.,2004,320(4):1211-1219.
[26]王利群,王勇,董英,等.硝酸盐对硝酸还原酶活性的诱导及硝酸还原酶基因的克隆[J].生物工程学报,2003,19(5):632-635.
[27]Mesnard F,Ratcliffe R G.NMR analysis of plant nitrogen metabolism[J].Photosynthesis Research.,2005,83(2):163-180.
[28]Jie Li,Lexun Xue,Hongxia Yan,et al.The nitrate reductase gene-switch:A system for regulated expression in transformed cells of Dunaliella salina[J].Gene.,2007,403(15):132-142.
