Development of noncontacting mechanical measurement system for instruments in laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery with digital image correlation technology
2011-05-16XUAnanZHUJiangfanSUJinZHANGDongshengWANGQiang
XU An-an,ZHU Jiang-fan,SU Jin,ZHANG Dong-sheng,WANG Qiang
1.Department of General Surgery,East Hospital of Tongji University,Shanghai,200120,China;
2.Department of Mechanics Shanghai University,Shanghai200444,China
Development of noncontacting mechanical measurement system for instruments in laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery with digital image correlation technology
XU An-an1,ZHU Jiang-fan1,SU Jin1,ZHANG Dong-sheng2,WANG Qiang2
1.Department of General Surgery,East Hospital of Tongji University,Shanghai,200120,China;
2.Department of Mechanics Shanghai University,Shanghai200444,China
ObjectiveAnalysis of mechanical measurements in laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery(LESS)is an important instrument design and surgical simulator.Aims of this study was to set up and evaluate the reliability and stability of noncontacting mechanical measurement system for instrument of LESS in company with digital image correlation technology.MethodsThe noncontacting mechanical measurement system was connected to a digital image correlation devices and a LESS manipulation platform(set up with a SILS Port and an inanimate laparoscopic trainer box).The correlation between the changes of deformation measurements(displacement and strain calculated by digital image correlation technology)and the change of workload(workout by the universal material testing machine)were evaluated.The experiment was repeated 8 times.ResultsA strong correlation was noticed between the changes of deformation measurements and the change of workload.The correlation coefficient was statistical significant(P <0.001).A high stability was well shown in all repetitions.Conclusions A noncontacting mechanical measurement system has been developed for LESS.Comprehensive mechanical parameters of SILS port can be obtained precisely by the digital image correlation technology.It is reliable and stable for the evaluation of instruments and manipulations in laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery by this system.
Laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery;Noncontacting measurement system;Digital image correlation technology
Since the introduction oflaparo-endoscopic single-sitesurgery(LESS)in 2007,it has rapidly gained popularity with surgeonsaswellasthe industry.Almost all traditional laparoscopic surgeries can be performed by the LESS approach,including surgeries for morbid obesity,liver,spleen,and gastrointestinal diseases[1].However,the procedure is more difficult than traditional laparoscopic surgeries due to associated technicalchallenges including laparoscope and instruments crowding around the umbilicus,lossoftriangulation between the two instruments in the operative field and the required ambidexterity ofthe surgeons to adopt relatively difficult maneuvers[2].To overcome these problems in LESS,new instruments and manipulations have been developed[3-4].Although these instrumentations may seem beneficial,they leave one vital question:Do these concepts really benefit laparo-endoscopic singlesite surgery?The aim of our study was to try to set up and evaluate the reliability and stability ofthe noncontacting mechanical evaluation system based on digital image correlation technology for an objective assessment of instrumentations in laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery.
Materials and Methods
The noncontacting mechanical measurement system was composed ofthe LESS manipulation platform,a charge-coupled device camera(type:JAI CV-A1),and a straight grasper(YIDA Medical DeviceCo.,Ltd.,Hangzhou,Zhejiangprovince,China).The LESS manipulation platform was set up by a box trainer(Model 200,RUIHONG laboratory equipment Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai,China)and a SILS PortTM(Covidien, Mansfield, MA, USA). A microcomputer-controlled electronic universal testing machine was used to measure the forces trailing the grasper(BZ2.5/TSIS,ZWICK Co.,Ltd.,German.)
MechanicalTest by the Universal Material Testing Machine
The grasper,which was inserted in the SILS Port,was connected with the universal testing machine by a fishing wire,and was trailed 50mm with a constant speed of 0.33 mm/s.The traction forces per second were obtained and saved by the attached software.
Noncontacting Mechanical Test based on Digital Image Correlation Technology.
The noncontacting mechanical test contained the following steps:
1.Formation of speckle on the SILS port(Fig.1).
2.Selection of dominant-points(the right point and the left point,Fig.2).
3.The grasper was trailed by the universal testing machine(the forces exerted followed the displacement control algorithm).Meanwhile,the transformation of the port was captured by the CCD camera.
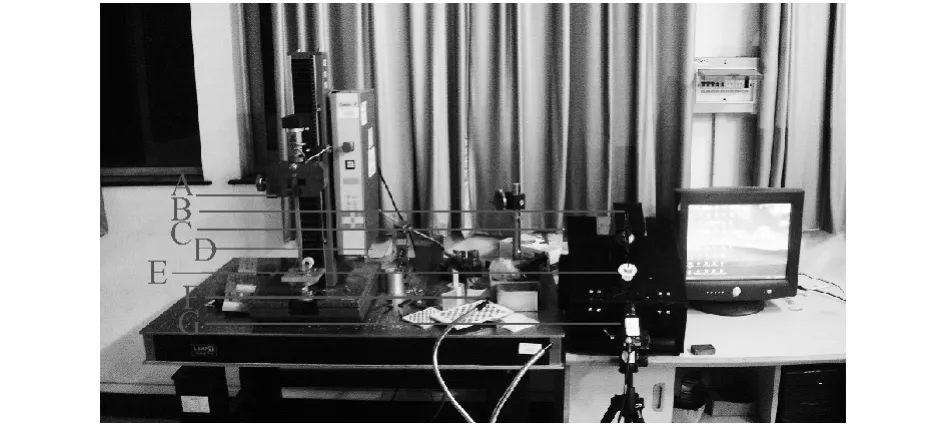

Fig.1 Mechanical test by theuniversal testing machine and the digital image correlation(A:Universal material testing machine,B:grasper,C:box trainer,D:fishing wire,E:SILS port,F:fiber optic lights,G:camera)图1 万能材料试验机水平牵引实验与数字图像相关技术测试实验(A:万能材料试验机,B:抓钳C训练箱 D 牵引线,E:SILS port,F:光源,G:摄像机)
Fig.2 Formation of speckle and selection of dominant-points in the SILS port图2 散斑制作和红点选取
As the grasperwas trailed by the universal testing machine,transformation of the SILS Port’s surface was captured by the CCD camera with the frequency of 1 Hz.Then,the commercialsoftware (the MATFOLT CO Ltd,Shanghai)was used to store a series of images acquired by the camera in digital form and perform image analysis to extract full-field shape and deformation measurements(vertical and horizontaldisplacement and strain data).This experiment was repeated for 8 times.
Statistical analysis
Although different vertical and horizontal displacements were obtained for the left and right dominant-points,the changing trends were the same as the dominant-points in the SILS port.Due to this,statistical analyses were conducted only for the left dominant-point.As allthe measurements were continuous variables,The Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to investigate the relationship between the changes of deformation measurements(displacement and strain calculated by digital image correlation technology)and the change of workload(workout by the universal material testing machine).
All statistical analyses were conducted by using SPSS statistical software(version 15.0;SPSS,Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA).Statistical significance was set,and p-value was defined as<0.05.
Results
Table1 shows the results of the experiments which were repeated for8 times.The Pearson correlation coefficients between the changes of deformation measurements(displacement and strain)and the change of workload were very high(│r│ >0.8,P < 0.01).Extremely similar stability results appeared in all repetitions of the procedure as shown in table 1.Due to the high similarity of the results,we chose one of the repetitions(the fifth one)to visualize it in scatterdiagrams as seen in Fig.3 -5.
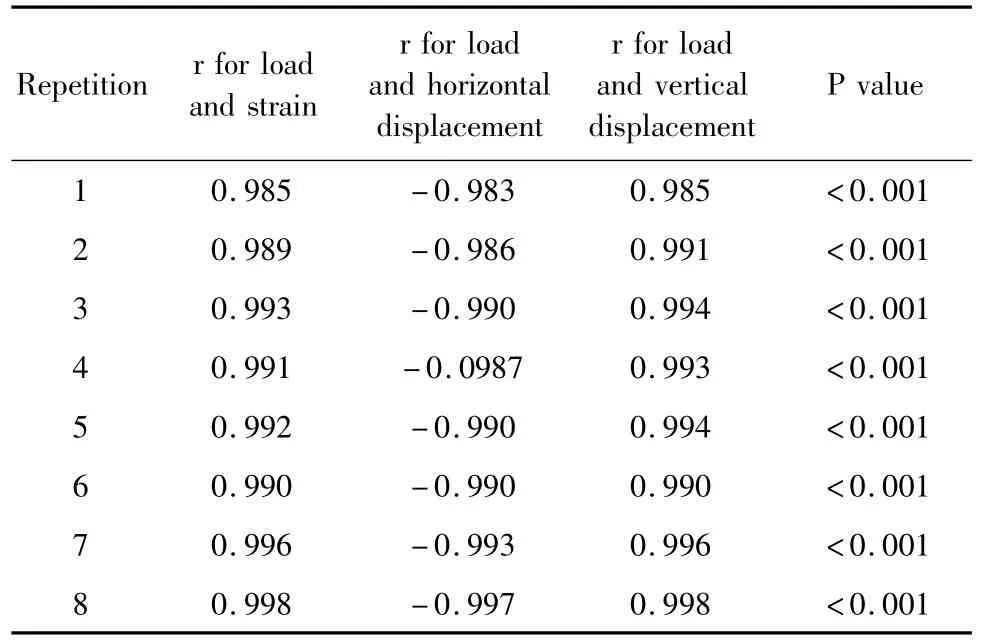
Table.1 The Pearson correlation analysis(correlation coefficient:r)between the changes of displacement andstrain and the change of workload in all repetitions of the experiment表1 8次重复实验载荷与应变及位移的Pearson相关分析
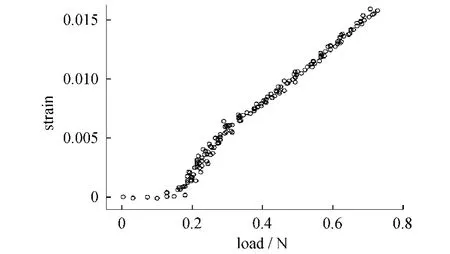
Fig.3 Scatterdiagram of the fifth experiment showing the linear correlation between load and strain图3 载荷与应变的散点图
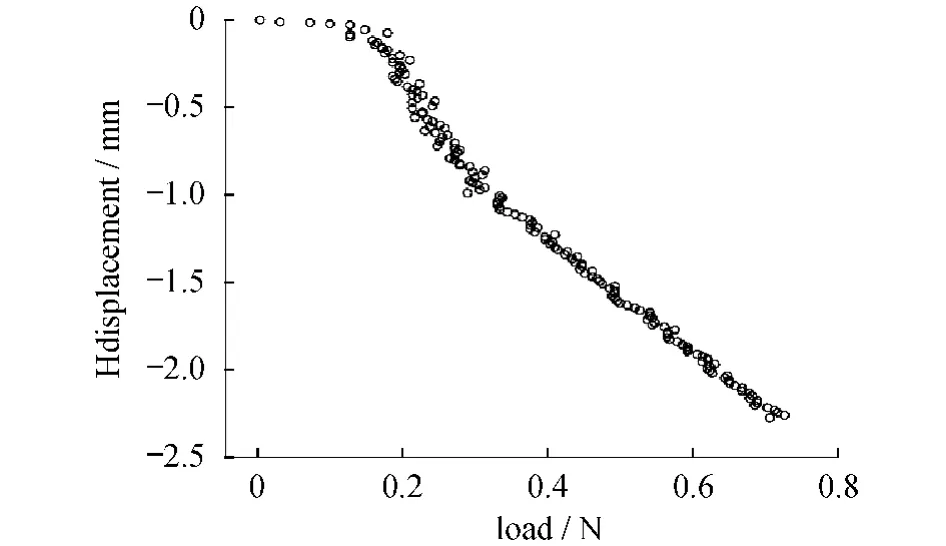
Fig.4 Scatterdiagram of the fifth experiment showing the linear correlation between load and horizontal displacement(Hdisplacement)图4 载荷与水平位移的散点图
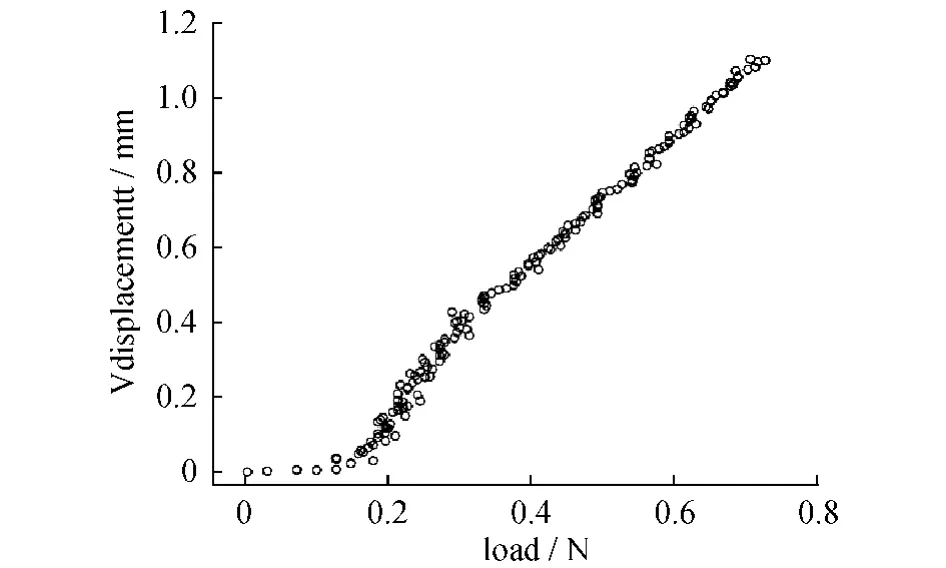
Fig.5 Scatterdiagram of the fifth experiment showing the linear correlation between load and vertical displacement(Vdisplacement)图5 载荷与垂直位移的散点图
Discussion
As with most new surgical techniques,the early development oflaparo-endoscopic single-site surgery(LESS)was fraught withproblems:alossof triangulation,clashing of instruments and the instruments with the telescope and camera head,and a lack of maneuverability.New instruments and manipulations were developed by the pioneers to enable surgeons to overcome these difficulties.However,whether these improvements benefit LESS was lacking of objective evaluation.There have been several researches attempted to assess the benefit[5-6],as the measurements were subjective indexes included the operation success rates,errors,and so on,lacking of definite and objective assessment criteria.We set up a contacting mechanical evaluation platform to compare the articulating instruments and the crosshanded manipulation with conventional instruments.Study indicates that more force and time are needed by using cross-handed manipulation in LESS[7].However,contacting mechanicalcomponentslike sensor or gauge used in aforementioned researches were vulnerable to external environmental interference during measurement.Therefore,as a whole they can’t reflect more comprehensive Mechanics changes.
Digital image correlation(DIC),an advanced noncontacting measurement system,has seen explosive growth in the past two decades.In recent years,the method has been modified and extended to encompass a breathtaking number of novel measurement systems.The term digital image correlation refers to the class of noncontacting methods that acquire images of an object,store images in digital form,and perform image analysis to extract full-field shape and deformation measurements.Within the broad field of image analysis,digital image correlation is generally considered a sub-set of digital image registration techniques.The technique can be used to measure and observe the local mechanical behavior(displacement and strain)in natural and semi-natural texture of different materials like metals,ceramics and polymers[8-9].In biomechanics,DIC are widely used in evaluation for dental restorations and prosthesis,bone repair materials[8-9].
In this study,basing on the DIC technology,we aimed to set up a reliable noncontacting mechanical measurement system to evaluate instruments in LESS.According to the repeated experimental results of currentstudy,two importantconclusionscan be drawn. First, the noncontacting mechanical measurement system based on DIC technology system is proven to be reliable,as the measurement results almost show a perfect linear correlation with the objective criteria (the universalmaterialtesting machine).Second,an extreme similarity of the results appeared in all repetitions of the experiment demonstrating the high stability of the measurement system.
Due to the high reliability and stability,there are several applications for the newly developed noncontacting mechanical measurement system.The objective and comprehensive measurements will provide a good feedback tool for evaluation of new instruments and manipulations in LESS.In addition,the system’s use in experimental practice would help to refine movement and tissue handling in LESS teaching and training purposes.Moreover,it can also be used to define force patterns incurred during certain surgical postures and the effect of muscle fatigue.The combination of force pattern and parameters of mental workload can be used to indicate the levelof psychological stress during surgical procedures.
With the reliable and stablenoncontacting mechanicalmeasurementsystem,LESS willbe spurred on by rapid advances in technology and better instrumentation.
[1] Zhu JF.Scarless endoscopic surgery:NOTES or TUES[J].Surg Endosc,2007,21(10):1898 -1899.
[2] Zhu JF.Transumbilicalendoscopic surgery:History,present situation and perspectives[J].World J Gastrointest Endosc,2011,3(6):107 -109.
[3] Kommu SS,Kaouk JH,Rane A.Laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery:preliminary advances in renal surgery[J].BJU Int,2009,103(8):1034 -1037.
[4] Joseph RA,Goh AC,Cuevas SP,et al.Chopstick surgery:a novel technique improves surgeon performance and eliminates arm collision in robotic single-incision laparoscopic surgery[J].Surg Endosc,2010,24(6):1331 -1335.
[5] Botden S,Strijkers R,Fransen S,et al.The use of curved vs.straight instruments in single port access surgery on standardized box trainer tasks[J].Surg Endosc,2011,25(8):2703 - 2710.
[6] Stolzenburg JU,KallidonisP,Oh MA,etal.Comparative assessment of laparoscopic single-site surgery instruments to conventional laparoscopic in laboratory setting[J].J Endourol,2010,24(2):239 -245.
[7] Zhu JF,Xu An An.Can cross-handed approach improve maneuver in transumbilical laparoscopic surgery?[J].Surg Endosc,2013,27(4):1444 -1445.
[8] Dongsheng Zhang,S Mao,C Lu,ElaineRomberg,etal.Dehydration and the Dynamic Dimensional Changes within Dentin and Enamel[J].Dental Materials,2009,25(7):937-945.
[9] Nazari A,Bajaja D,Zhang D,Romberg E,et al.Aging and the reduction in fracture toughness of human dentin[J].Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials,2009,2(5):550-559.
经脐入路腹腔镜手术操作非接触式力学评估平台的建立*
徐安安1,朱江帆1,苏 金1,张东升2,王 强21同济大学附属东方医院微创外科,上海 200120;2上海大学力学系,上海 200444
目的 本研究旨在建立基于数字图像相关技术的非接触式力学测试评估平台,明确其在经脐入路腹腔镜手术操作评估中的可靠性。方法 用腹腔镜模拟训练箱和SILS Port组建经脐入路腹腔镜手术操作平台。分析基于数字图像相关技术评估平台得到的位移与应变分量改变与客观标准——万能材料试验机水平牵引载荷改变的相关性。结果 本实验中8次重复实验的研究结果均显示,由数字图像相关技术得到的位移与应变分量改变与万能材料试验机牵引实验载荷改变呈强相关,且相关系数有统计学意义(P<0.001)。结论 基于三维数字图像相关技术的非接触式力学测试方法反映了器械进行操作时SILS port发生的综合性力学参数改变,方法可靠,适用于经脐入路腹腔镜手术器械与操作方法评估。
经脐入路腹腔镜手术;力学评估平台;数字图像相关技术
R 656
A
2095-378x(2013)02-0090-04
浦东新区重点发展学科项目资助(PWZxk2010-07)
徐安安(1982-),男,主治医师,硕士研究生,主要从事普外科常见疾病的微创治疗研究。
作者简介:朱江帆(1955-),男,河北人,教授博士生导师,研究腹腔镜外科的临床与实验研究。E-mail:zhujiangfan@hotmail.com
