世界主要深水含油气盆地烃源岩特征
2011-01-09范玉海屈红军张功成冯杨伟关利群
范玉海,屈红军,张功成,冯杨伟,关利群,雷 露
(1西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室,地质学系;2中国海洋石油研究中心)
世界主要深水含油气盆地烃源岩特征
范玉海1,屈红军1,张功成2,冯杨伟1,关利群1,雷 露1
(1西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室,地质学系;2中国海洋石油研究中心)
对墨西哥湾、巴西东部大陆边缘、西非被动大陆边缘、澳大利亚西北陆架、挪威中部陆架、南海等六个地区的22个深水含油气盆地烃源岩特征(主力烃源岩形成的时代、构造背景、沉积环境、类型、地球学化指标等)的综合研究结果表明,世界深水含油气盆地主力烃源岩主要集中在白垩系,其次为第三系和侏罗系;裂谷期烃源岩占绝对优势,其次为被动陆缘期;沉积环境以湖相和海陆过渡相为主,其次为海相。墨西哥湾、巴西东部大陆边缘和非洲西海岸的烃源岩以Ⅰ—Ⅱ型干酪根为主,澳大利亚西北陆架、挪威中部陆架和南海的烃源岩以Ⅱ—Ⅲ型干酪根为主。
全世界;深水盆地;含油气盆地;烃源岩特征;沉积相;成熟度指标
随着技术的进步和能源需求的增长以及陆上和浅海老油区新发现难度的增大,世界深水盆地成了近几十年来勘探的重点区域[1-3],尤其是在巴西坎波斯(Campos)盆地发现了Albacora、Marlim等大型油气田以后,深水勘探更是不断升温,如今已成为世界上最热的勘探领域[4-8]。据 USGS和国际能源机构估计,全球深水盆地潜在石油储量可能超过(1 000~1 500)×108bbl[9]。目前,全球有 60 多个国家进行深水油气勘探,累计发现的石油地质储量超过250×108bbl,天然气达到 160×108bbl油当量[10-11],所探明油气主要分布在墨西哥湾、巴西东部边缘、非洲西海岸、澳大利亚西北陆架、挪威中部陆架及南海的深水盆地中[4,7,12-13](图1)。
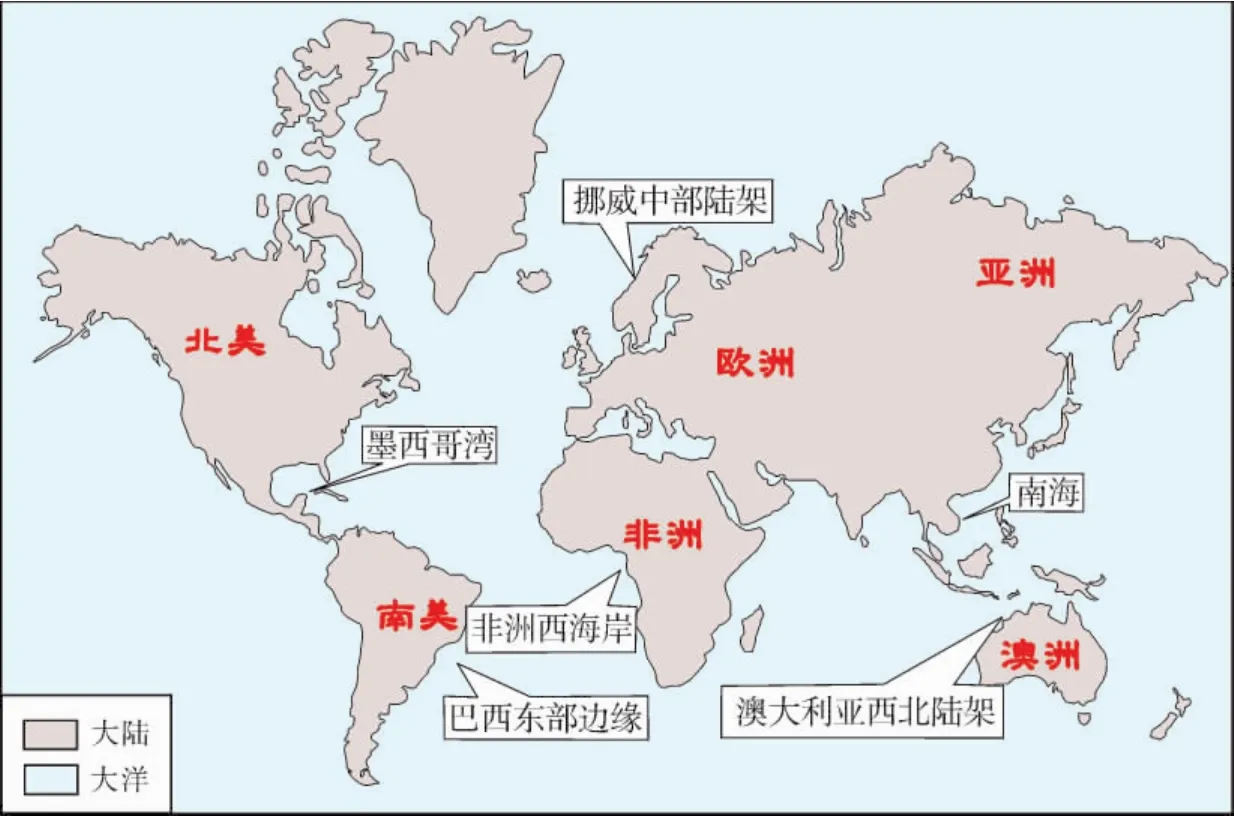
图1 世界主要深水含油气盆地位置图[6]
烃源岩好坏直接决定生烃强度、烃源丰富程度即烃源供给条件的优劣[14]。因此,归纳总结世界主要深水含油气盆地烃源岩形成的时代、构造背景、沉积环境、类型、地球化学指标等特征及其分布规律,对下一步深水盆地油气勘探具有一定的借鉴意义。
1 深水盆地烃源岩的特征
在大量调研资料的基础上,本文对墨西哥湾、巴西东部大陆边缘(坎波斯盆地、桑托斯盆地)、西非被动大陆边缘(阿尤恩-塔尔法亚盆地、塞内加尔盆地、尼日尔三角洲盆地、木尼河盆地(Rio Muni Basin)、加蓬盆地、下刚果盆地、宽扎盆地、纳米比亚盆地、西南非盆地)、澳大利亚西北陆架(卡那封盆地、布劳斯盆地、波拿巴盆地)、挪威中部陆架、南海(珠江口盆地、琼东南盆地、文莱—沙巴盆地、北巴拉望盆地、曾母盆地、万安盆地)的主要烃源岩特征进行了综合分析(表1),归纳总结这些深水含油气盆地中主力烃源岩形成的时代、构造背景、沉积环境、类型、地球化学指标及成熟度等特征,并探讨其分布规律。
2 深水盆地烃源岩的分布时代
经大量的资料分析发现,世界主要深水含油气盆地的烃源岩从志留纪到第三纪都有分布,但主要集中在白垩纪,其次为第三纪和侏罗纪,侏罗纪之前的地层中烃源岩的生烃潜力较差(图2,表1)。

图2 世界深水含油气盆地主力烃源岩分布时代
墨西哥湾烃源岩从侏罗纪到第三纪都有分布,上侏罗统烃源岩被认为是最重要的烃源岩[15-17,21-22];巴西坎波斯及桑托斯盆地的烃源岩主要为下白垩统Lagoa Feia组页岩[4,28](表1);西非的绝大部分油气来自下白垩统盐下湖相页岩和盐上上白垩统―第三系海相页岩(表1),其中以下白垩统的烃源岩为主[4,30,32,36,40];澳大利亚西北陆架的烃源岩时跨整个中生代(表1),下—中侏罗统海相、海陆交互相碳质泥岩和煤系为主要烃源岩[42-43,45,47];挪威中部大陆边缘盆地中的烃源岩为早侏罗世的海陆过渡相煤及页岩和晚侏罗世的海相页岩(表1),主要为晚侏罗世海相页岩[55,61,63];南海的烃源岩主要为第三纪页岩,从始新世到中新世都有分布[64-65,68,70,74](表1)。
3 深水盆地烃源岩的构造背景
离散大陆边缘盆地的发育一般都经历前裂谷期(裂前期)、裂谷期(裂陷期)以及被动陆缘期(热沉降期或漂移期)三个大的构造演化阶段。世界深水含油气盆地的烃源岩在各个构造演化阶段均有分布,其中裂谷期占绝对优势,其次为被动陆缘期(图3,表1)。
墨西哥湾盆地烃源岩全部为被动陆缘期的海相页岩[15-18,22-23];巴西东部大陆边缘盆地烃源岩主要为裂谷期湖相页岩,局部地区发育被动陆缘期的海相页岩[25,27-29];西非的绝大部分油气来自裂谷期盐下湖相页岩,其次为被动陆缘期盐上上白垩统—第三系早期海相页岩[30,33-37];澳大利亚西北大陆架含油气盆地主要的烃源岩为裂谷期下—中侏罗统海相、海陆交互相碳质泥岩和煤系,其次为被动陆缘期白垩系海相泥页岩[42,44,46-51];挪威中部陆架主要烃源岩位于裂谷期[52,54];南海主要烃源岩为裂谷期海陆过渡相泥岩,但在南海南部北巴拉望盆地、万安盆地及曾母盆地也发育被动陆缘期的海相泥页岩[64,66-74]。

图3 世界深水含油气盆地主力烃源岩形成时的构造背景
4 深水盆地烃源岩的沉积相类型
世界深水含油气盆地的烃源岩发育海陆过渡相、海相和湖相三种沉积相类型,其中以湖相和海陆过渡相为主,其次为海相(图4,表1)。

表1 世界深水含油气盆地主要烃源岩特征(据文献[4,15―73])
墨西哥湾盆地烃源岩几乎都为海相页岩[15-17,19-23];巴西东部大陆边缘盆地烃源岩主要为湖相页岩[24-26,27-29];西非的绝大部分油气来自盐下湖相页岩,北部的阿尤恩—塔尔法亚盆地、塞内加尔盆地、尼日尔三角洲盆地发育盐上海相页岩[30-32,35-39]。澳大利亚西北大陆架主要的烃源岩为海相页岩,局部发育湖相泥页岩[42-44,46-54];挪威中部陆架盆地主要烃源岩为海相页岩,也发育海陆过渡相的泥页岩及煤层[53,56-60];南海主要烃源岩为裂谷期海陆过渡相泥岩及煤层,也发育少量的湖相或海相泥页岩[64-69]。

图4 世界深水含油气盆地主力烃源岩沉积相类型
5 深水盆地烃源岩的类型、地球化学指标
不同沉积环境形成的烃源岩,其干酪根类型不同。生油为主的Ⅰ—Ⅱ型干酪根和生气为主的Ⅱ—Ⅲ型干酪根在世界深水盆地中都有分布(图5,表1),其中Ⅰ—Ⅱ型干酪根数量较多。
墨西哥湾、巴西东部大陆边缘和非洲西海岸的烃源岩以Ⅰ—Ⅱ型干酪根为主[15-23,25,27,30-36]。澳大利亚西北大陆架、挪威中部陆架和南海的烃源岩以Ⅱ—Ⅲ型干酪根为主[42-44,46,48,55-57,59-63,65-69]。

图5 世界深水含油气盆地主力烃源岩干酪根类型
墨西哥湾主要烃源岩为上侏罗统的海相钙质页岩、灰质泥岩,TOC达1%~2%,Ⅰ—Ⅱ型,为富氢油源岩[15-17,21]。
巴西东部盆地湖相黑色钙质页岩生油岩遍及整个盆地,TOC一般为2.0%~6.0%,最高达9.0%,HI最高达900mg/g,干酪根为I型,它们于始新世进入生油窗,至今仍处于生油窗之内[28]。
西非木尼河及其南部盆地主要为湖相页岩,Ⅰ—Ⅱ型干酪根,TOC值1%~5.9%;尼日尔三角洲及其北部盆地主要为海相页岩,II—III型干酪根,TOC值 3%~10%[30-41]。
澳大利亚西北陆架被动陆缘深水盆地的主力烃源岩为中生界海陆交互相碳质泥页岩与煤系和海相泥岩,生气为主,生油次之,干酪根类型为Ⅱ或Ⅲ型[54]。
挪威中部陆架烃源岩以晚侏罗世海相泥页岩为主,具有高放射性,TOC为5%~8%,是一套富油的烃源岩[55],干酪根类型为Ⅱ或Ⅲ型[63]。
南海各沉积盆地主要发育始新统湖相泥岩、渐新统滨岸沼泽相煤系和中新统海相泥岩、碳质泥岩等3套烃源岩。始新统湖相泥岩有机碳含量在1.5%~2.0%之间,母质类型以Ⅱ1型干酪根为主;渐新统滨岸沼泽相煤系地层中泥岩、碳质泥岩的有机碳含量在1.0%~2.0%之间,以Ⅱ2型干酪根为主,煤层有机碳含量高达80%,平均为23.18%,主要为Ⅲ型干酪根,以生气为主;中新统浅海—半深海相泥页岩有机碳平均为0.5%~0.7%,主要为Ⅱ—Ⅲ型干酪根[40-50]。
6 认识及结论
(1)世界深水主要含油气盆地烃源岩从志留系到第三系都有分布,但主要集中在白垩系,其次为第三系和侏罗系,侏罗纪之前的地层中烃源岩的生烃潜力较差;
(2)世界深水含油气盆地的烃源岩在各个构造演化阶段均有分布,其中裂谷期占绝对优势,其次为被动陆缘期;
(3)世界深水含油气盆地的烃源岩发育海陆过渡相、海相、湖相三种沉积相类型,其中以湖相和海陆过渡相为主,其次为海相;墨西哥湾、巴西东部大陆边缘和非洲西海岸的烃源岩以Ⅰ—Ⅱ型干酪根为主,澳大利亚西北大陆架、挪威中部陆架和南海的烃源岩以Ⅱ—Ⅲ型干酪根为主。
[1]白云程,周晓惠,方群,等.世界深水油气勘探现状及面临的挑战[J] .特种油气藏,2008,15(2):7-10.
[2]江怀友,赵文智,闫存章,等.世界海洋油气资源与勘探模式概述[J].海相油气地质,2008,13(3):5-10.
[3]何家雄,夏斌,施小斌,等.世界深水油气勘探进展与南海深水勘探前景[J].天然气地球科学,2006,17(6):747-752.
[4]吴时国,袁圣强.世界深水油气勘探进展与我国南海深水油气前景[J].天然气地球科学,2005,16(6):693-699.
[5]Pinder D.Offshore oil and gas:Global resource knowledge and technological change[J].Ocean&Coastal Management,2001,44(9-l0):576-600.
[6]Pettingill H S,Weimer P.Worldwide deepwater exploration and production:Past,present,and future[J].The Leading Edge,2002,21(4):371-376.
[7]金春爽,乔德武,姜春艳.国内外深水区油气勘探新进展[J].海洋地质动态,2003,19(10):20-23.
[8]娄承.世界深水油气勘探开发展望[J].国际石油经济,2003,11(8):43-44.
[9]金秋,张国忠.世界海洋油气开发现状及前景展望[J].国际石油经济,2005,13(3):43-44.
[10]吕福亮,贺训云,武金云,等.世界深水油气勘探现状、发展趋势及对我国深水勘探的启示[J].中国石油勘探,2007,12(6):28-31.
[11]吕福亮,贺训云,武金云,等.世界深水油气勘探形势分析及对我国深水油气勘探的启示[J].海洋石油,2007,27(3):41-45.
[12]杨川恒,杜栩,潘和顺,等.国外深水领域油气勘探新进展及我国南海北部陆坡深水区油气勘探潜力[J].地学前缘,2000,7(3):247-256.
[13]吕福亮,贺训云,武金云,等.全球深水油气勘探简论[J].海相油气地质,2006,11(4):22-28.
[14]张厚福,方朝亮,高先志,等.石油地质学[M].北京:石油工业出版社,1999.
[15]Guzmán-Vega M A,Ortiz L C.Classification and origin of petroleum in the Mexican Gulf Coast Basin :An Overview[J].AAPG Memoir,2001,75:127-142.
[16]Dow W G,Yuker M A,Senftle J T,et al.Miocene oil source beds in the East Breaks Basin,flex-trend,off shore Texas:Their characteristics,origin,distribution,and exploration and production significance[C]//Society of economic paleontologists and mine alogists foundation,Gulf Coast Section.9th Annual Re search Conference Proceedings.Austin,1990:139-150.
[17]Salvador A.Origin and development of the Gulf of Mexico Basin[C]//Salvador A.The Gulf of Mexico Basin.Geological Society of America,Decade of North American Geology,1991:389-444.
[18]陈国威,董刚,龚建明.从地质演化特征探讨墨西哥湾地区油气富集的基本规律[J].海洋地质动态,2010,26(3):6-13.
[19]成海燕,龚建明,张莉.墨西哥湾盆地石油的来源和分类[J].海洋地质动态,2010,26(3):40-46.
[20]孙萍,王文娟.持续沉降是墨西哥湾油气区优质烃源岩形成的重要条件[J].海洋地质动态,2010,26(3):22-27.
[21]龚建明,文丽,李慧君,等.墨西哥湾南部晚侏罗纪主力烃源岩的形成条件[J].海洋地质动态,2010,26(3):1-5.
[22]Nehring R.Oil and gas resources [C]//Salvador A.The Gulf of Mexico Basin,the geology of North America.The Geological Society of America,1991,15:445-493.
[23]Magoon L B,Hudson T L,Cook H E.Pimienta-Tamabra(!)-A giant supercharged petroleum system in the Southern Gulf of Mexico,onshore and offshore Mexico,the Western Gulf of Mexico Basin[J].AAPG Memoir,2001,75:83-125.
[24]Alan R C,Kevin M B.Lake-type controls on petroleum source rock potential in nonmarine basins[J].AAPG Bulletin,2001,85(6):1033-1053.
[25]C&C.Deep water reservoirs exploration and development[DB].C&C Reservoirs Research Report,2004.
[26]Jackson M P A,Cramez C,Fonck J M.Role of subaerial volcanic rocks and mantle plumes in creation of South Atlantic margins:implications for salt tectonics and source rocks[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology,2000,17:477-498.
[27]Mello M R,Ordonhez A R,Gallango O,et al.Comparative geochemical characterization of south American oils derived from carbonate and siliciclastic source rocks[C]//Anonymous.A Paleo-environmental and biological marker approach.AAPG Annual Convention,Annual Meeting Abstracts,1993:150.
[28]Guardado L R,Spadini A R,Brandão J S L,et al.Petroleum system of the Campos Basin[C]//Mello M R,Katz B J.Petroleum systems of South Atlantic margins.AAPG Memoir,2000,73:317-324.
[29]Trindade L A F,Dias J L,Mello M R.Sedimentological and geochemical characterization of the Lagoa Feia Formation,rift phase of the Campos Basin,Brazil[C]//Katz B J.Petroleum source rocks.New York:Springer-Verlag,1995:149-165.
[30]熊利平.西非构造演化及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J].石油与天然气地质,2005,25(6):25-29.
[31]Jacquin T.Cyclic fluctuations of anoxia during Cretaceous time in the South Atlantic Ocean[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology,1999,5:59-69.
[32]林卫东,陈文学,熊利平,等.西非海岸盆地油气成藏主控因素及勘探潜力[J].石油实验地质,2008,30(5):451-455.
[33]Turner J P.Detachment faulting and petroleum prospectivity in the Rio Muni Basin,Equatorial Guinea,West Africa[C]//Cameron N R,Bate R H,Clure V S.The oil and gas habitats of the South Atlantic.London:The Geological Society of Special Publication,1999,153:303-320.
[34]Katz B J,Dawson W C,Lira L M,et al.Petroleum systems of the Goose Delta,offshore Gabon[C]//Mello M R,Katz B J.Petroleum systems of South Atlantic margins.AAPG Memoir,2000,73:247-256.
[35]Burwood,R.Angola:source rock control for Lower Congo Coastal and Kwanza Basin petroleum systems[C]//Cameron N R,Bate R H,Clure V S.The oil and gas habitats of the South Atlantic.London:The Geological Society of Special Publication,1999,153:181-194.
[36]Braecini E,Denison C N,Seheevel J R,et al.A revised chronolitho stratigraphic framework for the pre-salt(Lower Cretaceous)in Cabinda,Angola[J].Bulletin Centre de Reeherches Exploration-Production Elf Aquitaine,1997,21(1):125-151.
[37]Cole G A,Requejo A G,Yu Z,et al.Petroleum geological assessment of the Lower Congo Basin[C]//Mello M R,Katz B J.Petroleum systems of South Atlantic margins.AAPG Memoir,2000,73:325-339.
[38]Harris N B,Katherine H F,Richard D P,et al.The character and origin of latchstring source rocks in the Lower Cretaceous synrift section,Congo Basin,West Africa[J].AAPG Bulletin,2004,88(11):1163-1184.
[39]刘剑平,潘校华,马君,等.西非被动大陆边缘Walvis Ridge以南纳米比亚盆地的地质特征及油气意义——兼与Walvis Ridge以北盆地比较[J].中国石油勘探,2007,4:67-74.
[40]Davies C P N,Van der Spuy D.Chemical and optical investigations into the hydrocarbon source potential and thermal maturity of the Kudu 9A-2 and 9A-3 boreholes[C]//Hoal B.The Kudu offshore drilling project.Communs Geol Surv Namibia,1990,6:49-58.
[41]侯高文,刘和甫,左胜杰.尼日尔三角洲盆地油气分布特征及控制因素[J].石油与天然气地质,2005,26(3):374-378.
[42]白国平,殷进垠.澳大利亚北卡那封盆地油气地质特征及勘探潜力分析[J].石油实验地质,2007,29(3):251-258.
[43]张建球,钱桂华,郭念发.澳大利亚大型沉积盆地与油气成藏[M].北京:石油工业出版社,2008.
[44]Thomas B M,Smith D N.A summary of the petroleum geology of the Carnarvon basin[J].Australian Petroleum Exploration Association Journal,1974,14(1):66-76.
[45]Jablonskl D,Saltta A J.Permian to lower Cretaceous plate tectonics and its impact on the tectono-stratigraphic development of the western Australian margin[J].APPEA Journal,2004,(1):287-328.
[46]Maung T U,Cadman S,West B.A review of the petroleum potential of the Browse Basin[C]//Purcell P G,Purcell R R.The sedimentary basins of Western Australia:Proceedings of the West Australian Basins Symposium.Perth,1994:333-346.
[47]Daniel D,Kliti G,Robert A,et al.The effect of source and maturity on the stable isotopic compositions of individual hydrocarbons in sediments and crude oils from the Vulcan Sub-basin,Timor Sea,Northern Australia[J].Organic Geochemistry,2007,38:1015-1038.
[48]Ambrose G.Jurassic sedimentation in the Bonaparte and Northern Browse Basins:New models for reservoir-source rock development,hydrocarbon charge and entrapment[C]//Adrian W.Timor Sea petroleum geosciences:Proceedings of the Timor Sea symposium, Northern Territory Geological Survey.Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia Ltd,2004.
[49]Powell D E.Dampier Sub-basin,Carnarvon Basin[J].Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy,1976,(7):155-168.
[50]Barber P M.Sequence stratigraphy and petroleum potential of Upper Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous depositional systems in the Dampier Sub-basin,North West Shelf,Australia [C]//Pur cell P G,Purcell R R.The sedimentary basins of Western Australia:Proceedings of Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia Symposium.Perth,1994:525-582.
[51]McGilvery T A,Polomka S M,Galloway W E.Tectonically controlled paleogeographic evolution of the Barrow Group(Early Cretaceous),Barrow Sub-basin,North West Shelf,Australia[J].AAPG Bulletin,1997:6-80.
[52]Warren J K,Peter T,Paul T.Geological controls on porosity and permeability in reservoir sands,Goodwyn Field,Rankin Trend,Northern Barrow-Dampier Subbasin,Northwest Shelf,Australia[J].AAPG Bulletin,1993,77(9):1675-1676.
[53]Beston N B.Reservoir geological modeling of the North Rankin field,Northwest Australia [J].Australian Petroleum Exploration Association Journal,1986,26(1):426-480.
[54]Longley I M,Buessenschuett C,Clydsdale L,et al.The north west shelf of Australia-a Woodside perspective [C]//Keep M,Moss S J.Sedimentary basins of western Australia:Proceedings of Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia Symposium.Perth,2002,(3):27-88.
[55]Heum O R,Dalland A,Meisingset K K.Habitat of hydrocarbons at Haltenbanken(PVT-modelling as a predictive tool in hydrocarbon exploration)[C]//Spencer A M.Habitat of hydro arbons on the Norwegian Continental Shelf,Proceedings of An International Conference.London:Graham&Trotman,1986:259-274.
[56]Karlsen D A,Nyland B,Flood B,et al.Petroleum geochemistry of the Haltenbanken,Norwegian continental shelf[C]//Cubitt J M,England W A.The geochemistry of reservoirs.London:The Geological Society of Special Publications,1995,86:203-256.
[57]Cohen M J,Dunn M E.The hydrocarbon habitat of the Haltenbanken-Traenabank area,offshore Norway[C]//Glennie K W.Petroleum geology of north west Europe.London:Graham&Trotman,1987:1091-1104.
[58]Hvoslef S,Larter S R,Leythaeuser D.Aspects of generation and migration of hydrocarbons from coal-bearing strata of the Hitra Formation,Haltenbanken area,offshore Norway[J].Organic Geochemistry,1988,13(1/3):525-536.
[59]Khorasani G K.Factors controlling source rock potential of the Mesozoic coalbearing strata from offshore central Norway:Application to petroleum exploration[J].Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology,1989,37(4):417-427.
[60]Mo E S,Throndsen T,Andresen P,et al.A dynamic deterministic model of hydrocarbon generation in the Midgard Field drainage area offshore Mid-Norway[J].Geologische Rundschau,1989:305-317.
[61]Odden W,Patience R L,Van Graas G W.Application of light hydrocarbons(C4-C13) to oil/source rock correlations:A study of the light hydrocarbon compositions of source rocks and test fluids from offshore Mid-Norway[J].Organic Geochemistry,1998,28(12):823-847.
[62]Pittion J L,Gouadain J.Maturity studies of the Jurassic"coal unit"in three wells from the Haltenbanken area[J].Petroleum geochemistry,1985:205-211.
[63]Whitley P K.The geology of Heidrun:A giant oil and gas field on the mid-Norwegian shelf[C]//Halbouty M T.Giant oil and gas fields of the decade 1978-1988.AAPG Bulletin,1992,54:383-406.
[64]何家雄,陈胜红,崔莎莎,等.南海北部大陆边缘深水盆地烃源岩早期预测与评价[J].中国地质,2009,36(2):404-416.
[65]马文宏,何家雄,姚永坚,等.南海北部边缘盆地第三系沉积及主要烃源岩发育特征[J].天然气地球科学,2008,19(1):41-48.
[66]米立军,刘震,张功成,等.南海北部深水区白云凹陷古近系烃源岩的早期预测[J].沉积学报,2007,25(1):139-147.
[67]吴时国,董冬冬,袁圣强,等.南海北部陆缘深水区含油气系统研究[C]//中国地球物理学会第二十三届年会论文集.中国地球物理学会,青岛,2007,23:654.
[68]张功成,米立军,吴时国,等.深水区—南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新领域[J].石油学报,2007,28(2):15-21.
[69]朱伟林,张功成,高乐.南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气地质特征与勘探方向[J].石油学报,2008,29(1):1-9.
[70]刘振湖.南海南沙海域沉积盆地与油气分布[J].大地构造与成矿学,2005,29(3):410-417.
[71]Todd S P,Dunn M E,Barwise A J G.Characterizing petroleum charge systems in the Tertiary of SE Asia [C]//Fraser A J,Matthews S J,Murphy R W.Petroleum geology of Southeast Asia.Geological Society Special Publication,1997,126:25-47.
[72]刘伯土,陈长胜.南沙海域万安盆地新生界含油气系统分析[J].石油实验地质,2002,24(2):110-114.
[73]魏喜,邓晋福,陈亦寒.南海盆地中生代海相沉积地层分布特征及勘探潜力分析[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版,2005,35(4):456-461.
[74]姚永坚,吴能友,夏斌,等.南海南部海域曾母盆地油气地质特征[J].中国地质,2008,35(3):503-513.
Characteristics of Hydrocarbon Source Rocks in Major Deepwater Petroliferous Basins in the World
Fan Yuhai,Qu Hongjun,Zhang Gongcheng,Feng Yangwei,Guan Liqun,Lei Lu
Characteristics of hydrocarbon source rocks of 22 major deepwater petroliferous basins in the world are researched and analyzed.The characteristics involve with formation geologic ages,tectonic settings,sedimentary environments and kerogen types as well as geochemical indexes.These basins distribute in the Gulf of Mexico,the eastern continental margin of Brazil,the passive continental margin of West African,the Northwest Shelf of Australia,the continental shelf of Mid-Norway and South China Sea.The comprehensively analysis indicates that the principal source rocks in these basins are mainly Cretaceous and subordinately are Tertiary and Jurassic in geological ages.They dominantly formed in rift stages and next in passive continental margin stage in tectonic settings,and mainly were lacustrine and transitional facies and following marine facies in Sedimentary environment.The kerogen commonly are TypeⅠand TypeⅡin Gulf of Mexico,the eastern continental margin of Brazil,the passive continental margin of West African but TypeⅡand TypeⅢ in the Northwest Shelf of Australia,the continental shelf of Mid-Norway and South China Sea.
Source rock characteristics;Deepwater basin;Oil and gas basin;Sedimentary facies;Maturity index
TE112.113
A
10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2011.02.004
1672-9854(2011)-02-0027-07
2010-06-24;改回日期:2010-11-27
本文为国家科技重大专项“南海深水区油气勘探关键技术”(编号2008ZX05025-06)基金项目
范玉海:1983年生,现为西北大学矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业在读硕士研究生。通讯地址:710069陕西省西安市太白北路229号西北大学地质学系
金顺爱
Fan Yuhai:male,Master student.Add:Geology Department of Northwest University,Xi'an,Shannxi,710069 China
