伏硫西汀对首发抑郁症主观认知功能的影响及相关因素
2022-04-28刘林晶朱程潘安乐杨智英
刘林晶 朱程 潘安乐 杨智英
[摘要] 目的 探討伏硫西汀对首发抑郁症主观认知功能的影响及相关因素,为抑郁症的康复寻找新的视角。方法 选取温州医科大学附属康宁医院临床心理科首发抑郁症患者100例,随机分为研究组和对照组,研究组采取伏硫西汀治疗,对照组采取选择性5-羟色胺再吸收抑制剂(SSRIs)类抗抑郁药治疗,进行8周治疗。搜集一般资料、治疗前和治疗8周临床量表和认知量表。 结果 完成研究94例,研究组48例,对照组46例,研究组主观认知功能PDQ减分为(25.47±6.28)分,明显高于对照组的(16.49±5.83)分,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),研究组治疗前后主观认知功能差值与文化程度、抑郁症状(HAMD17)、客观认知功能(RBANS和P300)差值无明显相关性,与自杀意念(SIOSS)、创伤体验(PCL-C)、职位呈正相关。结论 相比于SSRIs类抗抑郁药,伏硫西汀对首发抑郁症患者主观认知功能障碍更好,这种效果独立于抑郁症状和客观认知功能,可能通过伏硫西汀独特的机制。
[关键词] 伏硫西汀;首发抑郁症;主观认知功能;相关因素
[中图分类号] R749.4 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2022)09-0103-04
Effects of vortioxetine on subjective cognitive function of patients with first-episode depression and related factors
LIU Linjing ZHU Cheng PAN Anle YANG Zhiying
Department of Clinical Psychology,the Affiliated Kangning Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325007, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effect of vincristine on subjective cognitive function of patients with first-episode depression and related factors, so as to find a new perspective for the rehabilitation treatment of depression. Methods A total of 100 patients with first-episode depression were selected and randomly divided into the study group (treated with vortioxetine) and the control group (treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) antidepressants). All patients were treated for 8 weeks. General data, the clinical scales and cognitive scales before treatment and after 8 weeks of treatment were collected. Results A total of 94 patients completed the study, including 48 patients in the study group and 46 patients in the control group. After treatment, the score of subjective cognitive function (personality diagnostic questionnaire, PDQ) decreased was (25.47±6.28) points, which was higher than that of (16.49±5.83) points in the control group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). In the study group, the difference of subjective cognitive function before and after treatment was not significantly correlated with literacy, depressive symptoms (Hamilton depression scale-17, HAMD17), and objective cognitive function (repeatable battery for the assessment of Neuropsychological Status [RBANS] and P300), but was positively correlated with suicidal ideation (self-rating idea of suicide scale, SIOSS), traumatic experience (the posttraumatic stress disorder checklist - civilian version, PCL-C), and job position. Conclusion Compared with SSRIs antidepressants, vortioxetine has better effects in treating subjective cognitive dysfunction in patients with first-episode depression, and this effect is independent of depressive symptoms and objective cognitive function, which may be related to the unique mechanism of vortioxetine.
[Key words] Vortioxetine; First-episode depression;Subjective cognitive function; Related factors
认知功能障碍是抑郁症的核心病理特征[1]。目前認为,抑郁症患者的认知症状包括主观认知功能和客观认知功能两个方面[2],主观认知障碍指自我报告出现记忆等认知功能改变,但客观认知测验的结果在正常范围内[3]。Shi等[4]采用抑郁症认知缺陷自评量表(perceived deficits questionnaire depression,PDQ-D)评估中国抑郁症患者发现,PDQ-D与数字符号替换测验(digital symbol conversion test,DSST,客观认知功能比较精确的检查方法之一)无明显相关性,提示主观认知功能独立于客观认知功能。抑郁症主观认知功能障碍造成患者主观感受不良,无法回到病前状态[2],但在诊断和治疗中经常被忽视和低估[5]。目前国外研究显示,伏硫西汀在抑郁症患者主观认知功能方面的优势[6-7],国内主观认知功能影响研究尚少见诸报道。本研究特选取温州医科大学附属康宁医院门诊或住院抑郁症患者100例,旨在分析伏硫西汀对首发抑郁症主观认知功能的影响及相关因素,为抑郁症的康复寻找新的视角,现报道如下。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
选择温州医科大学附属康宁医院门诊或住院抑郁症患者100例,年龄18~50岁,性别不限,初中以上文化程度;符合国际疾病分类第10版(International Classification of diseases ,Tenth Edition,ICD10)精神与行为障碍[8]中抑郁症诊断标准,病程≤12个月;未用过抗抑郁药。除外中枢神经系统或严重的躯体疾病者;未经许可的伴随治疗者。入组患者均签署知情同意书,研究经医院医学伦理委员会批准。
1.2方法
本研究为前瞻性开放对照研究。入组患者收集一般资料、文化程度、职务,按随机数字表法分为两组,研究组使用伏硫西汀每天10 mg[灵北(北京)医药信息咨询有限公司,国药准字H20170382,规格10 mg,片剂]治疗,对照组使用5-羟色胺再吸收抑制剂(SSRIs)类中任一药物治疗,最大剂量不超过说明书用量,疗程8周。
1.3观察指标及评价标准
治疗前和治疗8周分别评估临床量表,包括汉密尔顿抑郁量表(Hamilton’s depression scale,HAMD17)、自杀意念自评量表(Self-rating idea of suicidal scale,SIOSS)、创伤后应激障碍自评量表(the PTSD cheeklist-civilianversion,PCL-C);认知量表包括PDQ-D-20和可重复的成套神经心理状态测验(repeatable battery for assessment of neuropsychological status,RBANS)。本研究量表由不参加本课题的两名主治医师评定,研究开始前对研究人员进行量表一致性培训,组内相关系数(ICC≥0.82)。
1.3.1临床量表 HAMD17量表总分为评定抗抑郁药疗效的金标准[9]。SIOSS总分≥12分为存在自杀意念, SIOSS的信度与效度均达到心理测验的要求[10]。PCL-C由17项条目组成,作为症状诊断和疗效评价标准[11]。
1.3.2认知量表及认知检测 PDQ-D是目前抑郁症患者主观认知功能评定的最为常用工具,RBANS是评估客观认知功能的测验方法,具有很好的信度和效度[12-13]。
1.3.3 诱发电位P300潜伏期 反映大脑对外部目标刺激作出反应的神经传导速度,波幅反映患者大脑感受刺激信息时神经投入资源的多少,是客观认知功能的重要检测方法。
1.4统计学方法
所有资料用Epidata3.0输入,采用SPSS 23.0统计学软件进行分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验;非正态资料采用U检验。所有的统计检验均采用双侧检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1一般情况
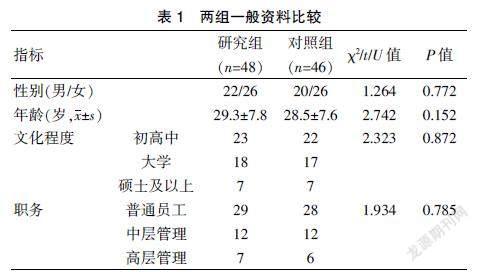
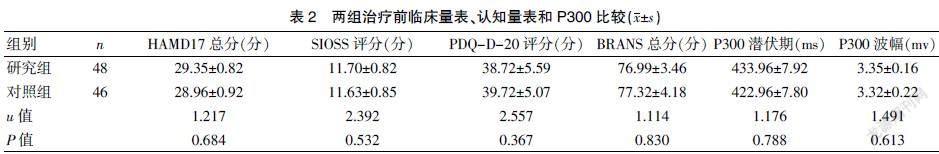
完成研究94例,研究组48例,对照组46例,两组的性别、年龄、文化程度、职务比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。见表1。治疗前研究组和对照组的HAMD17总分、SIOSS评分、PDQ-D20评分、BRANS总分、P300潜伏期和波幅比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1~2。
2.2 两组治疗前后认知功能差值和事件诱发电位比较
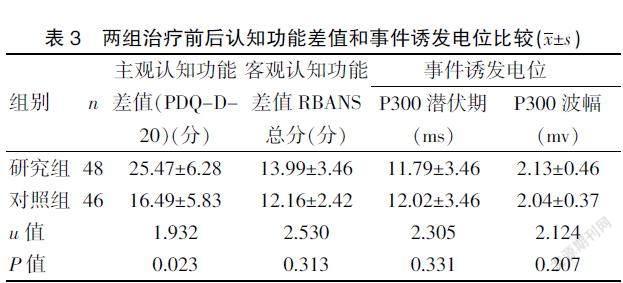
研究组和对照组治疗前后主观认知功能评分差值比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组客观认知功能差值和事件诱发电位比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表3。
2.3研究组治疗前后主观认知功能差值的相关因素
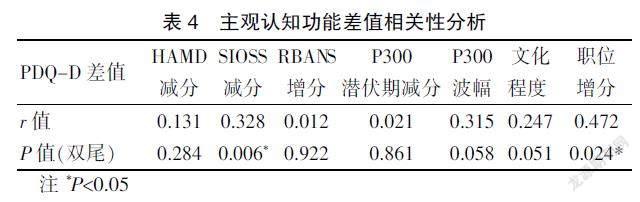
主观认知功能差值与文化程度、抑郁症状、客观认知功能差值(RBANS和P300)无相关性。与自杀意念、创伤体验、职位呈正相关。见表4。
3 讨论
不同于其他抗抑郁药,伏硫西汀为5-羟色胺(5-HT)多模式作用机制,具有5-HT转运体抑制和5-HT多受体(5HT1A受体激动、5HT1B受体部分激动、5HT1C受体拮抗、5HT3受体拮抗、5HT7受体拮抗)调节作用[14-16]。伏硫西汀通过抑制5-HT3受体介导的GABA中间神经元兴奋从而增加锥体神经元活性,进而增加谷氨酸能神经元的兴奋性,增加额叶皮质中多种递质系统的神经传递,促进突触可塑性改变,改善认知症状[17],是第首个有重复证据证明发挥直接和独立的改善认知功能作用,目前唯一批准用于抑郁症认知症状的抗抑郁药[18-19]。有研究显示,伏硫西汀对患者主观认知功能有明显改进[20],尤其对于经理/行政人员等脑力工作者[21-22]。
本研究结果显示,与SSRI类抗抑郁药相比,伏硫西汀对主观认知功能的改善更明显,且与抑郁症状、客观认知功能的改善无明显相关性,提示为独立于以上因素独特的作用,与相关研究结果一致[23]。
本研究结果表明,伏硫西汀对主观认知功能的影響与自杀意念及创伤体验相关,有报道早年创伤在抑郁和自杀意念中起作用[24]。抑郁发作将以往的创伤重新激活,而在抑郁症状改善后,被激活的创伤相关的体验会长期存在,主观认知功能下降并难以恢复。但当有任务(如客观认知测验)进行时,患者较好地完成客观认知功能的测验,这是有创伤史的抑郁症患者在抑郁症状好转后客观认知功能改善而主观认知功能仍不能同步恢复的可能因素之一。本研究结果提示,主观认知功能的改善与患者的文化水平无关,而与职位相关,考虑与高职位特殊人群对主观认知功能的需求更明显。
综上所述,伏硫西汀对主观认知功能的改善更明显,相关因素如职务、创伤体验,自杀意念等均与心理社会因素相关,提示从生物学角度伏硫西汀对主观认知功能具有特殊治疗作用,而在社会心理因素方面可以尝试进行心理治疗的干预,相关的研究还在进一步进行中。
[参考文献]
[1] 陆林.沈渔邨精神病学[M].6版,北京:人民卫生出版社,2017:382,416.
[2] 肖乐,朱雪泉,丰雷,等.抑郁症急性期治疗结局对残留症状变化的影响:一项来自全国、多中心的随访调查研究[J].中华精神科杂志,2021,54(1):9-16.
[3] Reisberg B,Gauthier S.Current evidence for subjective cognitive impairment(SCI) as the pre-mild cognitive impairment(MCI)stage of subsequently manifest Alzheimer’s desease[J].Int Psychogeriatr,2008,20(1):1-16.
[4] Shi C,Wang G,Tian F,et al. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of perceived deficits questionnaire for depression in patients with MDD[J].Psychiatry Research,2017, 252:319-324.
[5] Metternich B,Kosch D,Kriston L,et al.The effects of nonpharmacological intervention on subjective memory complaints:A systematic review and meta-annlysis[J].Psychother Psychosom,2010,79(1):6-19.
[6] McIntyre RS,Lophaven S,Olsen CK. A randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled study of vortioxetine on cognitive function in depressed adults[J].Int J Neuropsychopharmacol,2014,17(2):1557-1567.
[7] Mahableshwarkar AR,Zajecka J,Jacobson W,et al.A randomized placebo-controlled, active-reference doubleblind,flexible-dose study of the efficacy of vortioxetine on cognitive function in major depressive disorder[J].Amenran College of Neuropsychophar-Macology,2015,40(5):2025-2037.
[8] 范肖东,汪向东,于欣,等.ICD-10精神与行为障碍分类[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1993:97-100.
[9] Gordon Parker,Dusan Hadzi-Pavlovic. Do Hamilton depression scale items have the capacity to differentiate melancholic and non-melancholic depressive sub-types?[J].J Affect Disord,2020,274:1022-1027.
[10] 夏朝云,王东波,吴素琴,等.自杀意念自评量表的初步制定[J].临床精神医学杂志,2002,12(2):100-102.
[11] 吴咏梅,姜红娟,杨娟,等.创伤后应激障碍测评量表因子结构的跨性别等值性[J].中国临床心理学杂志,2020, 28(1):37-40,45.
[12] Srisurapanont M, Suttajit S, Eurviriyanukul K,et al.Discrepancy between objective and subjective cognition in adults with major depressive disorder[J].Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):3901.
[13] 张保华,谭云龙,张五芳,等.重复性成套神经心理状态测验的信度、效度分析[J].中国心理卫生杂志,2008,22(12):865-869.
[14] Pehrson AL, Sanchez C. Serotonergic modulation of glutamate neurotransmission as a strategy for treating depression and cognitive dysfunction[J].CNS Spectr,2014, 19(2):121-133.
[15] Leiser SC,Li Y,Pehrson AL,et al.Serotonergic regulation of prefrontal cortical circuitries involved in cognitive processing:A review of individual 5-HT receptor mechanisms and concerted effects of 5-HT receptors exemplified by the multimodal antidepressant vortioxetine[J]. ACS Chemical Neuroscience,2015,6(7):970-986.
[16] Bennabi D,Haffen E,Van Waes V. Vortioxetine for cog- nitive enhancement in major depression:From animal models to clinical research[J].Frontiers in Psychiatry,2019, 10:771.
[17] Nierenberg AA,Loft H,Olsen CK. Treatment effects on residual cognitive symptoms among partially or fully remitted patients with major depressive disorder:A randomized, double-blinded,exploratory study with vortioxetine[J]. J Affect Disord,2019,250:35-42.
[18] Levada OA,Troyan AS. Cognitive-functional relation ships in major depressive disorder: Crucial data from a Ukrainian open-label study of vortioxetine versus escitalopram[J]. J Affect Disord,2019,250:114-122.
[19] 王賢斌,白录东,邹连勇,等.伏硫西汀改善抑郁障碍患者临床症状、社会功能及认知功能的对照研究[J].精神医学杂志,2019,32(4):277-280.
[20] McIntyre RS,Xiao HX,Syeda K,et al. The prevalence,measurement, and treatment of the cognitive dimension/domain in major depressive disorder[J].CNS Drugs,2015, 29(7):577-589.
[21] Al-Sukhni M,Maruschak NA,McIntyre RS. Vortioxetine:A review of efficacy,safety and tolerability with a focus on cognitive symptoms in major depressive disorder[J].Expert Opin Drug Saf,2015,14(8):1291-1304.
[22] McIntyre RS,Florea I,Tonnoir T,et al. Efficacy of vortio xetine on cognitive functioning in working subjects with major depressive disorder[J].J Clin Psychiatry,2017,78(1):115-121.
[23] 余青云,王文,伍新春,等.创伤暴露对青少年暴力行为和自杀意念的影响:创伤后应激障碍和抑郁的中介作用[J].心理发展与教育,2021,37(1):101-108.
[24] Xie P,Wu K,Zheng Y,et al. Prevalence of childhood trauma and correlations between childhood trauma,suicidal ideation,and social support in patients with depression,bipolar disorder,and schizophrenia in southern China[J].J Affect Disord,2018,228(1):41-48.
(收稿日期:2021-06-21)
