基于单目视觉车辆姿态角估计和逆透视变换的车距测量
2018-08-10后士浩晏晓娟
刘 军,后士浩,张 凯,晏晓娟
基于单目视觉车辆姿态角估计和逆透视变换的车距测量
刘 军,后士浩,张 凯,晏晓娟
(江苏大学汽车与交通工程学院,镇江 212013)
针对一般的单目视觉测距方法忽略汽车在行驶过程中姿态角变化的问题,该文提出了一种基于变参数逆透视变换和道路消失点检测的单目视觉测距模型,实现了车辆在相对运动过程中的纵向距离和横向距离实时测量。首先,该文通过基于纹理方向估计的道路消失点检测算法计算出汽车运动的偏航角和俯仰角,然后运用变参数的逆透视变换和几何建模分析方法,建立车辆测距模型。对不同道路环境和测距方法的2组对比试验分析该文方法的可行性和有效性,结果表明,该文所提出的测距模型能够有效测量纵向70 m、横向4 m以内的目标车辆距离,测量误差在5%以内,且道路环境越好,误差越小,道路良好的平坦道路测距误差在3%以内;该文算法的平均处理速度达到了40帧/s。
算法;模型;车辆;单目视觉;逆透视变换;道路消失点检测;单目测距
0 引 言
在智能车和高级驾驶辅助系统中,车辆检测和测距是对道路交通信息理解的关键内容,也是汽车避免危险而做出响应的前提条件。视觉机器学习方法被广泛运用在车辆检测任务上,而车辆测距技术是在车辆检测任务的基础上发展而成的一项技术。测量车辆的纵向距离和横向距离可以对车辆进行准确定位,而且还可以为汽车行驶过程中纵向、横向提供安全距离控制[1-5]。
目前基于毫米波雷达和激光雷达等主动式传感器的测距方法[6-7]价格昂贵,扫描范围和速度有限,同时易受外界信号干扰。而基于视觉类被动式传感器的测距方法,价格低廉,信息丰富,具有更广泛的应用范围。现有的视觉测距方法主要为单目视觉和立体视觉测距。基于立体视觉的测距方法[8-11]直观明了,测量精度较高,但这种方法需融合匹配多个摄像头的信息,计算量大,实现实时测距的成本相对较高,使其在汽车上的应用受到限制。
此外,基于单目视觉的测距方法算法简单,计算量小,成本低廉且实时性能更好。近年来国内外对单目视觉测距方法的研究取得了一些成果[12-15],主要分为拟合建模法、逆透视变换法、成像几何关系法以及光学投影特性法。徐超等[16]提出了一种通过特征变换匹配算法估计坦克的姿态角,从而用匹配的模板和目标图像来模拟立体视觉,将单目测距转化为双目视觉的平面测距方法,但是其需要大量的姿态角匹配模板,模板匹配不佳时会造成很大的测距误差,并且需要消耗大量的匹配时间。余厚云等[17-18]提出了一种基于车道线消失点的几何模型测量前方目标车辆的纵向距离的方法,但其只适用于结构化的道路,未考虑汽车运动的偏航角、俯仰角的变化,也没有考虑横向距离测量的问题。许宇能等[19]提出了一种基于道路消失点计算摄像机偏航角和俯仰角的6自由度变换测距模型,把整个测距模型建立在考虑摄像机畸变的针孔模型上,其需要标定大量的摄像机内外参数而带来了测量误差。吴骏等[20]提出了一种基于检测车辆位置信息的车辆纵向距离测量几何模型,但未考虑到偏航角、俯仰角的实时补偿,只适用于结构化道路。
Tuohy等[21]提出了一种基于逆透视变换的测距方法,通过逆透视变换还原出道路平面的信息,并且该平面与真实道路平面具有线性的比例关系,该方法简单易行,但是其没有考虑汽车运动的偏航角和俯仰角补偿,导致在汽车产生偏航和俯仰运动时会产生较大的测距误差。Nakamura等[22]提出了一种基于水平方向和垂直方向三角几何关系联合估计车宽长度的单目视觉车辆测距方法;Han等[23]提出了基于车宽长度估计的单目视觉车辆测距方法,并综合考虑了结构化道路和非结构化道路2种测距环境;文献[22-23]通过卡尔曼滤波算法减少由于车辆俯仰角变化引起的测距误差,但是对非正前方目标的车宽长度估计存在较大误差,且并没有从俯仰角变化的机理上进行建模分析,只是在跟踪过程中减小车宽长度的估计误差。Bao等[24]提出了一种基于车宽的平均长度与检测车辆的实际距离之间存在的线性关系的单目视觉车辆测距方法,但是其没有考虑到汽车运动过程中的姿态角变化,同时统计得到的车宽平均值只能保证平均的测距精度,对单个车辆目标的测距误差较大。
上述逆透视变换测距方法没有考虑汽车运动的偏航角、俯仰角补偿,成像几何关系测距方法需要标定大量的摄像机内外参数。为提高车辆单目视觉测距在复杂应用场景的精度和稳定性,在已有目标检测算法的基础下,本文提出了基于汽车姿态角估计的单目视觉车辆测距算法,利用基于纹理的道路消失点检测跟踪方法建立实时的车辆纵向和横向距离检测几何模型。本文叙述了算法的实现过程,并以某型号的试验车为例,进行了测距试验,最终给出了相应的结果和分析。
1 道路消失点的检测与跟踪
根据透视投影原理,所有平行的直线经过透视投影后都会相交于一点,该点称为消失点。道路消失点是道路环境的重要信息,其总是指向道路的尽头,可以为智能车导航系统提供重要的方向信息和道路边界信息,同时可用来估计汽车运动的姿态角[25-28]。


对存在显著纹理方向的像素点取最大2个Gabor能量响应值计算显著纹理方向,估计方程[28]如下。
1)最大的2个Gabor能量响应方向若为1=0和4=135º,则

2)其他情况,则


显著纹理方向()定义为

为了降低每帧图片里的敏感噪声对消失点检测的干扰,对当前帧消失点的位置与之前20帧的位置取平均值,同时通过帧间消失点位移的大小来调节候选消失点的分布,大大增加了消失点检测的稳定性。在不同光照和道路环境下道路消失点检测的试验效果示例如图1所示。
2 汽车姿态角估计模型



式中1为存在偏航角时成像平面中消失点的横坐标。
新的像平面(粗线矩形区域)是由于摄像机偏航角的存在,导致标准成像平面(细线矩形区域)向左偏移得到的,但这并不会导致视场角的改变,因此水平视场角仍然存在如下关系

由式(5)和(6)可知

同理,对于摄像机的俯仰角,也和消失点存在着类似的关系,即

式中1为存在偏航角时成像平面中消失点的纵坐标。
注:为成像平面的水平方向像素数量,为摄像机的焦距,2为摄像机水平视场角范围,为摄像机偏航角。在摄像机没有偏航角和俯仰角时成像平面中消失点坐标为(0,0),当存在偏航角时成像平面中消失点的坐标为(1,1),为水平方向的偏移量。
Note:is the number of horizontal pixels in the imaging plane,is the camera focal length, 2is the horizontal field angle of camera,is the yaw angle of camera. When the camera has no yaw and pitch angle, the vanishing point coordinates are(0,0). While having a yaw angle, the coordinates of the vanishing point in the imaging plane are(1,1);is an offset in the horizontal direction.
图2 摄像机偏航角估计示意图
Fig.2 Diagram of camera yaw angle estimation
3 基于道路消失点的逆透视变换
当摄像机存在偏航角和俯仰角时,固定参数的逆透视变换不能恢复道路平面的平行关系,而存在很大的横向或者纵向的畸变。假设世界坐标系的原点位于光心处,建立如图3所示的摄像机偏航角、俯仰角对逆透视变换的影响示意图,摄像机偏航角会使得逆透视变换俯视图存在一定的旋转,但是准确恢复了道路平面俯视图的平行关系;俯仰角的存在则会使逆透视变换俯视图不能恢复实际道路俯视图的平行关系[29],使得在实际测距时,存在较大的误差,不能满足使用要求。因此,必须提出一种方法能够对摄像机俯仰角进行实时的补偿以消除这种畸变对测距的影响。

注:θ为摄像机俯仰角。
假设世界坐标系轴与轴位于地平面上,两轴的交点与摄像机光心在地面上的正投影重合,文献[29]建立了摄像机存在俯仰角时的动态逆透视变换方程,用以消除摄像机俯仰角的存在导致的透视畸变效果。其变换方程如下


4 车辆测距模型
首先,标定实际道路俯视图与逆透视变换俯视图之间的纵向比例系数,如图4a所示,在透视图中每隔3 m的实际距离作等距横向标线,然后进行逆透视变换,如图4b所示,纵向比例系数可以描述为

式中d为某一横向标线至本车车头的实际距离,h′为逆透视变换俯视图对应的像素高度,e1为标定出的纵向比例系数。
进一步,假设不考虑检测车辆与本车的形状大小,为求道路方向上摄像机存在偏航角时目标车辆与本车的纵向距离及横向距离,对图像进行抽象简化分析。如图5所示,当摄像机偏航角为时,假定棋盘格为路面,其透视图如图5a所示,实际道路平面俯视图如图5b所示,逆透视变换俯视图如图5c所示,图5b与图5c中的点一一对应。图5b中为透视图下边界所对应的道路上的线段,点为中点,过点作直线垂直于车道线即棋盘格网格线(车道线只用来说明摄像机存在偏航角的参考),过点作直线平行于车道线;为检测车辆在地面上的位置点,作垂直于,则为道路方向上检测车辆目标点与摄像机之间的纵向距离,为横向距离,垂直于,垂足为;连接交于点,垂直于。
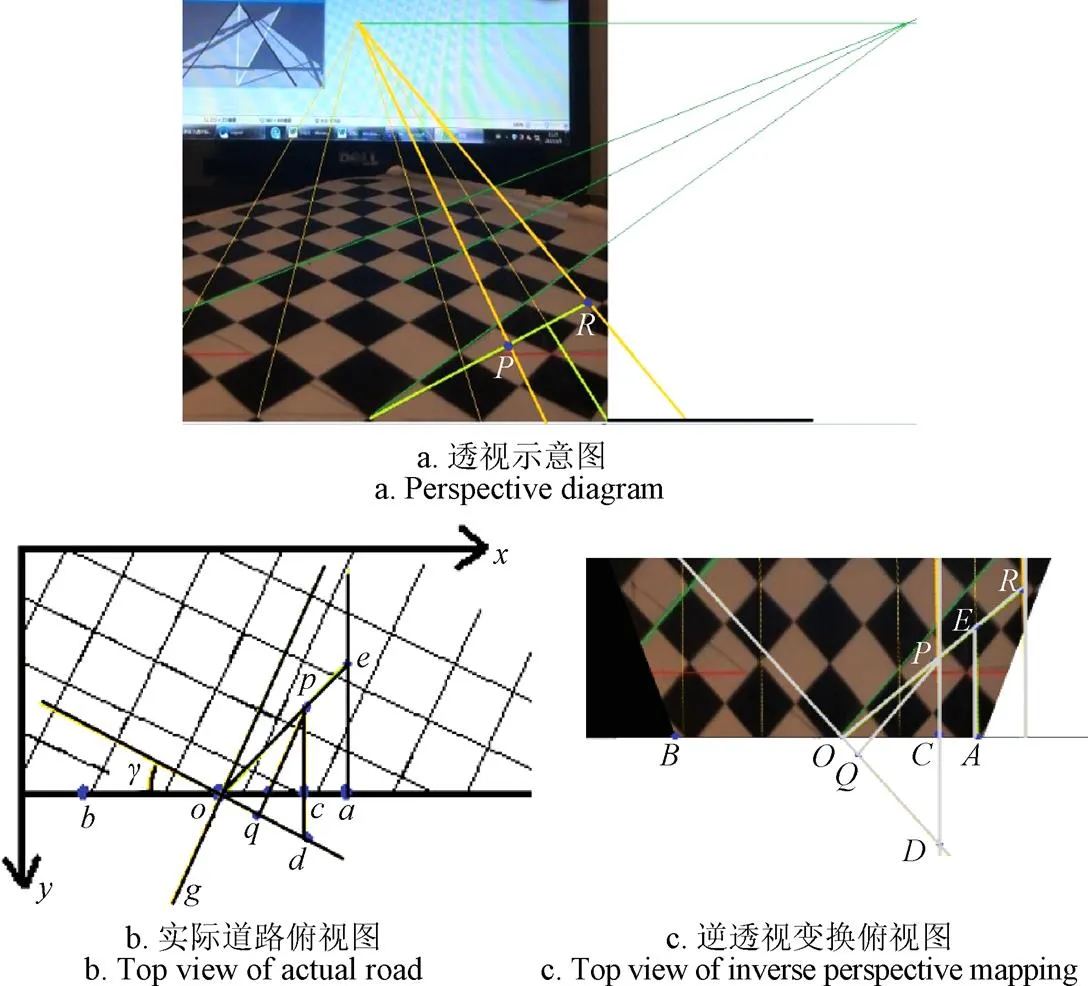
图5 单目视觉测距模型分析示意图
在图5c中,已知(x,y)、(x, y)、(x, y),则点的坐标为(x,y),根据透视图与逆透视变换俯视图之间的关系,设对应的为d,对应的为d,则

由式(11)得

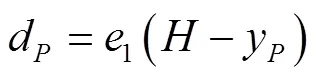
根据式(12)~(13)可知
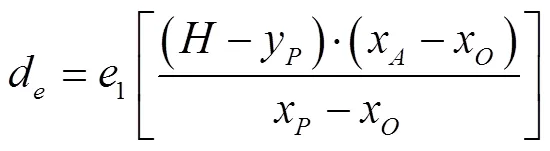

式中为透视图下边界所对应的实际距离的一半。


在Rt△中,∠=,则检测车辆的纵向、横向距离分别为
纳入标准:①以上患者均符合糖尿病肾病的临床诊断标准[2];②所有患者均同意该次研究,并签订知情同意书。
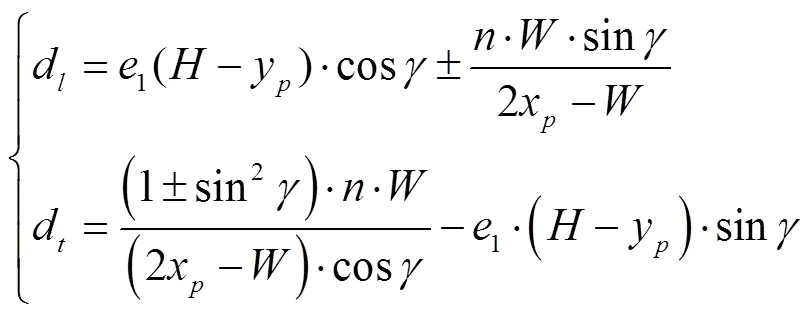
式中(x,y)为逆透视变换俯视图中所求目标车辆的坐标,+、-分别为检测车辆在本车纵向轴线的右侧和左侧。
而实际测距时,车辆的形状大小是不能被忽略的。根据检测车辆的位置信息,当车辆包围框右下角横坐标小于/2时,检测车辆在本车纵向轴线的左侧,根据包围框右下点坐标计算式(19);当车辆包围框左下角横坐标大于/2时,检测车辆在本车纵向轴线的右侧,根据包围框左下点坐标计算式(19);反之,则说明检测车辆在本车的正前方,此时横向距离为0,式(19)的纵向距离计算公式可简化为

式中y为透视图检测车辆包围框底边中点的纵坐标对应到逆透视变换俯视图中的值。
5 车辆测距结果与分析
为了便于验证本文提出的方法,本文通过安装在某型号别克车上的单目摄像机抓取已知摄像机偏航角、俯仰角和车辆距离的图片,进行试验结果分析验证。试验中利用陀螺仪测量偏航角和俯仰角,卷尺测量目标车辆距本车的纵向、横向距离。摄像机安装情况:安装在车内后视镜处,离地高度为1.3 m,摄像机分辨率为×=720×576 像素,焦距为8 mm,透视图下边界所对应的实际距离的一半=1.58 m,纵向比例系数1=0.1453。
本文试验程序的运行平台为英特尔酷睿i7 7700K @ 3.0GHz,显卡为NVIDIA GTX 1060。软件的运行平台为Windows 10、Caffe以及Visual Studio 2013,使用C++代码实现了本文算法和基于Caffe框架的SSD目标检测算法[30]的融合,本文测距算法流程如图6所示。

图6 本文测距算法流程图
5.1 汽车姿态角的验证
本文分别使用8个不同的偏航角和俯仰角度值,通过陀螺仪测得的真实数值(测量角度)和本文所述的计算角度对比,验证本文提出的方法,结果如表1所示。从表1数据可知,除了1°左右的偏角由于本身实际角度值很小而造成的误差百分比较大外,其余汽车姿态角的计算值与实际测量值误差均在10%以内。

表1 本文计算角度与测量角度对比
5.2 测距模型验证与分析

表2 两组试验的计算距离与实际距离对比
注:横向距离是检测的车辆目标到摄像头的距离,纵向距离是其到本车车头的距离,表示为(横向距离,纵向距离),文献[22-23]的横向距离由车宽长度估计的方法计算得到。
Note: Horizontal distance is distance from detected vehicle object to the camera and longitudinal distance is the distance from detected vehicle object to the front of the host vehicle. They are expressed as (horizontal distance, longitudinal distance). The horizontal distance in [22-23] is calculated from the vehicle width estimation.
图7所示为本文测距算法在不同路况下的检测结果,图中包围框上方左边表示横向距离,右边表示纵向距离,可以看出,本文算法的平均处理速度达到了40帧/s,符合实时性测距的要求。文献[22-23]方法同本文在相同车辆检测算法下的平均处理速度分别达到了80和55帧/s,主要是因为本文在道路消失点检测和跟踪部分增加了算法耗时的缘故。
进一步分析,本文测距方法产生误差的主要原因有:
1)摄像机的安装误差和测量误差。根据本文试验算法,摄像机光心应该安装在本车纵向轴线上;用卷尺测量摄像机的离地高度D以及值时存在误差,以及地面地砖之间存在的缝隙,试验中均未考虑在内。
2)摄像机标定和畸变产生的误差。摄像机的焦距本文未进行标定,而是采用仪器厂家提供的数据;摄像机畸变会产生轻微的透视失真,在逆透视变换的过程中产生误差。
3)消失点检测存在误差,直接造成了摄像机偏航角、俯仰角的计算存在误差,进一步导致逆透视变换存在透视畸变。消失点检测产生误差的原因主要有道路环境恶劣,以及阳光强烈照射下的晕光会使道路显著纹理方向误检,带来很大的检测误差。
其中1)是本文试验的固有误差,试验中基本保持不变,而2)、3)属于可以通过优化方法减少的误差来源,也是本研究后续应该关注的内容。摄像机的内参数可以通过标定来减少误差;轻微的畸变可以通过矫正减少误差;消失点的检测是本文研究的基础,因此也是改进的主要方向。虽然本文考虑了摄像机俯仰角的补偿,但是随着道路条件的变化,消失点的检测误差也随之而变化,因此对于基于道路消失点的测距算法,通过提高消失点检测的准确性和稳定性可以提高实时测距的性能,使单目视觉测距算法更具有鲁棒性。

注:FPS(frames per second)为帧速,描述动态视频的流畅度,帧·s-1。
6 结 论
本文将道路消失点的检测用于单目视觉车辆测距,提出了一种基于变参数逆透视变换的几何测距模型,对摄像机俯仰角进行了动态补偿,同时在测距模型中将摄像机由于车辆变道超车等引起的偏航角进行建模分析,建立了统一的数学模型。对提出的基于道路消失点的汽车姿态角估计模型进行了试验验证,同时对本文完整的测距模型进行了验证分析,试验结果表明,本文提出的测距模型能有效测量纵向70 m以内、横向4 m以内的车辆距离,对不同道路环境的车辆测距误差在5%以内,且算法的平均处理速度达到了40帧/s,实时性能好,鲁棒性高,满足智能车系统对算法实时性和准确性的要求,有一定的工程应用价值。
[1] Park K Y, Hwang S Y. Robust range estimation with a monocular camera for vision-based forward collision warning system[J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2014, 2014(2): 923632.
[2] 刘庆华,邱修林,谢礼猛,等. 基于行驶车速的车辆防撞时间预警算法[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(12):99-106.
Liu Qinghua, Qiu Xiulin, Xie Limeng, et al. Anti-collision warning time algorithm based on driving speed of vehicle[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(12): 99-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] Ding P, Zhang J, Zhou Y, et al. Anti-collision warning algorithm based on visual perception in front of vehicle[C]// International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic, Control and Automation Engineering, 2017: 51-55.
[4] Lin H Y, Chen L Q, Lin Y H, et al. Lane departure and front collision warning using a single camera[C]//International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communications Systems, IEEE, 2013: 64-69.
[5] Wu C F, Lin C J, Lin H Y, et al. Adjacent lane detection and lateral vehicle distance measurement using vision-based neuro-fuzzy approaches[J]. Journal of Applied Research & Technology, 2013, 11(2): 251-258.
[6] 方建超,周兴林,毛雪松. 利用多普勒激光雷达实现距离和速度同步测量[J]. 光电工程,2016,43(12):212-218.
Fang Jianchao, Zhou Xinglin, Mao Xuesong. Doppler laser radar for measuring range and speed simultaneously[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(12): 212-218. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 刘军辉,陈宏滨. 基于FMCW雷达测距的车辆防碰撞系统[J]. 桂林电子科技大学学报,2016,36(5):349-354.
Liu Junhui, Chen Hongbin. A vehicle anti-collision system based on FMCW radar ranging[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Electronic Technology, 2016, 36(5): 349-354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] Lim B, Woo T, Kim H. Integration of vehicle detection and distance estimation using stereo vision for real-time AEB system[C]//International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems, 2017: 211-216.
[9] Lü X Z, Wang M T, Qi Y F, et al. Research on ranging method based on binocular stereo vision[C]//Advanced Materials Research, 2014: 2075-2081.
[10] Long H M, Guo H Y, Liang F, et al. Distance measurement algorithm based on binocular stereo vision[C]//Applied Mechanics & Materials, 2014: 948-952.
[11] 项荣,应义斌,蒋焕煜,等. 基于双目立体视觉的番茄定位[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(5):161-167.
Xiang Rong, Ying Yibin, Jiang Huanyu, et al. Localization of tomatoes based on binocular stereo vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(5): 161-167.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] Li B, Zhang X, Sato M. Pitch angle estimation using a Vehicle-Mounted monocular camera for range measurement[C]// International Conference on Signal Processing, IEEE, 2015: 1162-1168.
[13] Rezaei M, Terauchi M, Klette R. Robust vehicle detection and distance estimation under challenging lighting conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(5): 2723-2743.
[14] Adamshuk R, Carvalho D, Neme J H Z, et al. On the applicability of inverse perspective mapping for the forward distance estimation based on the HSV colormap[C]// IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, IEEE, 2017.
[15] Ho H W, Croon G D, Chu Q P. Distance and velocity estimation using optical flow from a monocular camera[J]. International Journal of Micro Air Vehicles, 2017, 9(3): 198-208.
[16] 徐超,高敏,曹欢. 单目图像中姿态角估计的坦克目标测距方法[J]. 光子学报,2015,44(5):140-147.
Xu Chao, Gao Min, Cao Huan. The attitude angle estimation-based distance measurement of tank target in monocular image[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2015, 44(5): 140-147. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 余厚云,张为公. 基于单目视觉传感器的车距测量与误差分析[J]. 传感器与微系统,2012,31(9):10-13.
Yu Houyun, Zhang Weigong. Vehicle distance measurement and its error analysis based on monocular vision sensor[J]. Transducer & Microsystem Technologies, 2012, 31(9): 10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 顾兆伦,邵雨辰,谢扬振,等. 多环境下的实时前车检测与车距测量[J]. 信号处理,2015,31(9):1188-1194.
Gu Zhaolun, Shao Yuchen, Xie Yangzhen, et al. Real-time Vehicle detection and distance measurement in multi- environment[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(9): 1188-1194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 许宇能,朱西产,马志雄,等. 基于单目摄像头的车辆前方道路三维重建[J]. 汽车技术,2014(2):48-52.
Xu Yuneng, Zhu Xichan, Ma Zhixiong, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the road ahead of vehicle based on mono-vision[J]. Automobile Technology, 2014(2): 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 吴骏,李文杰,耿磊,等. 基于单目视觉的前方车辆检测与测距[J]. 计算机工程,2017,43(2):26-32.
Wu Jun, Li Wenjie, Geng Lei, et al. Preceding vehicle detection and ranging based on monocular vision[J]. Computer Engineering, 2017, 43(2): 26-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] Tuohy S, O’Cualain D, Jones E, et al. Distance determination for an automobile environment using inverse perspective mapping in OpenCV[C]// Signals and Systems Conference. IET, 2010: 100-105.
[22] Nakamura K, Ishigaki K, Ogata T, et al. Real-time monocular ranging by Bayesian triangulation[C]// Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. IEEE, 2013: 1368-1373.
[23] Han J, Heo O, Park M, et al. Vehicle distance estimation using a mono-camera for FCW/AEB systems[J]. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2016, 17(3): 483-491.
[24] Bao D, Wang P. Vehicle distance detection based on monocular vision[C]// International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing. IEEE, 2017: 187-191.
[25] Moghadam P, Starzyk J A, Wijesoma W S. Fast vanishing-point detection in unstructured environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing A Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2012, 21(1): 425-430.
[26] Kong H, Audibert J Y, Ponce J. Vanishing point detection for road detection[C]// Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 2009: 96-103.
[27] Nguyen L, Phung S L, Bouzerdoum A. Enhanced pixel-wise voting for image vanishing point detection in road scenes[C]// IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. IEEE, 2017: 1852-1856.
[28] Shi J, Wang J, Fu F. Fast and robust vanishing point detection for unstructured road following[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(4): 970-979.
[29] Zhang D, Fang B, Yang W, et al. Robust inverse perspective mapping based on vanishing point[C]//International Conference on Security, Pattern Analysis, and Cybernetics, IEEE, 2014: 458-463.
[30] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham, 2016: 21-23.
Vehicle distance measurement with implementation of vehicle attitude angle estimation and inverse perspective mapping based on monocular vision
Liu Jun, Hou Shihao, Zhang Kai, Yan Xiaojuan
(,,212013,)
Due to the change of vehicle steering attitude caused by road conditions and driver’s intention during driving, location information of detected vehicles relative to the host vehicle is also changed. Aiming at the problem that the method of monocular vision ranging ignores changes in attitude angle in the process of driving, this paper presents a monocular vision ranging model based on inverse perspective mapping (IPM) of variable parameters and road vanishing point detection, which achieves a real-time measurement of longitudinal and horizontal distance during vehicle relative movement by taking advantage of location information of vehicle detection so that it can locate and detect the vehicle on the ground plane as well as provide a good environment perception for advanced driver assistance system (ADAS) and intelligent vehicle system. Firstly, owing to the relationship between changes in attitude angle and the coordinates of road vanishing point, the yaw angle and pitch angle of vehicle motion are calculated in real time through the algorithm for road vanishing point detection, which is based on texture orientation estimation. The algorithm, which possesses a better robustness under different light and road conditions, estimates dominant texture orientation of pixels according to joint activities and confidence measure of Gabor filter with 4 directions, and vanishing point candidates are confirmed by the modified locally adaptive soft voting and particle filter tracking algorithm. On account of the yaw angle which leads to a certain degree of rotation in the top view of IPM and the existence of the pitch angle which leaves the top view of IPM unable to restore the parallel relationship of thetop view of actual road, IPM of variable parameters based on the coordinate of road vanishing point is used to compensate for the pitch angle to eliminate the influence of inverse perspective distortion, thereby restoring the parallel relationship of road plane and measuring longitudinal distance between the detected vehicle and the host vehicle using calibrated longitudinal scale factor. Then a modeling analysis of the yaw angle of vehicle motion during the process of IPM is made and the effects of the shape and size of the detected vehicle on ranging model are considered. When the horizontal axis in the lower-right bounding box of detected vehicle is less than half of the number of horizontal pixels in the imaging plane, the detected vehicle would be on the left of the host vehicle and its longitudinal and horizontal distance are calculated in accordance with the coordinate in the lower-right bounding box, while the horizontal axis in the lower-left bounding box of detected vehicle is greater than half of the number of horizontal pixels in the imaging plane, the detected vehicle would be on the right of the host vehicle and its longitudinal and horizontal distance are calculated in accordance with the coordinate in the lower-left bounding box; otherwise, it would be directly in front of the host vehicle with the horizontal distance being zero, and its longitudinal distance is calculated in accordance with the coordinate in the middle base of bounding box. Finally, the vehicle ranging model on the basis of location information of vehicle detection is established to consider compensating for attitude angle. The feasibility and effectiveness of this method are analyzed from 2 groups of contrast experiments on different road environments and ranging methods, and the results show that the proposed ranging model can effectively measure the distance of detected vehicles within about 70 m in the longitudinal direction and 4 m in the horizontal direction, having a measurement error of less than 5%; and the better the road environment, the smaller the error; the ranging error of a good flat road is within 3%, and the average processing speed of this algorithm reaches 40 frames/s.
algorithms; models; vehicles; monocular vision; inverse perspective mapping; road vanishing point detection; monocular ranging
刘 军,后士浩,张 凯,晏晓娟. 基于单目视觉车辆姿态角估计和逆透视变换的车距测量[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(13):70-76.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.13.009 http://www.tcsae.org
Liu Jun, Hou Shihao, Zhang Kai, Yan Xiaojuan. Vehicle distance measurement with implementation of vehicle attitude angle estimation and inverse perspective mapping based on monocular vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(13): 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.13.009 http://www.tcsae.org
2017-11-08
2018-04-10
国家自然科学基金项目(51275212)
刘 军,教授,博士,主要研究方向为汽车主动安全。Email:Liujun@ujs.edu.cn
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.13.009
TP391;U491.6
A
1002-6819(2018)-13-0070-07
