基于变距光电传感器的小麦精播施肥一体机监测系统设计
2018-08-10赵立新张增辉王成义荐世春崔东云丁筱玲
赵立新,张增辉,王成义,荐世春,刘 童,崔东云,丁筱玲
基于变距光电传感器的小麦精播施肥一体机监测系统设计
赵立新1,张增辉1,王成义2,荐世春3,刘 童1,崔东云1,丁筱玲1※
(1. 山东农业大学机械与电子工程学院,泰安 271018; 2. 山东农业大学信息科学与工程学院,泰安 271018; 3. 山东省农业机械科学研究院,济南 250100)
为实现小麦精播施肥过程的实时监测,确保播种作业质量,该文设计了一种基于变距光电传感器的小麦精播施肥一体机监测系统。该监测系统以STM32单片机硬件系统为下位机,通过反射式光电传感器和旋转编码器分别获取种肥流动与种肥轴转动信息,判断精播机运行状态,并通过Modbus通讯协议将信息传输至MCGS触摸屏上位机人机交互界面实时显示。下位机排种监测电路仿真测试结果表明,放大电路对种管光电传感器检测距离的改变值为4~7 mm;上下位机通讯测试结果表明,数据传输内容准确率为100%;监测系统样机试验测试结果表明,故障报警准确率≥92.5%,种肥缺失、堵塞、泄漏响应时间分别≤0.2、≤0.3、≤0.3 s。该监测系统实现了对小麦精播施肥机作业的实时高精度监测,有助于提高小麦精播机作业质量。
监测;设计;传感器;精播施肥机;变距;MCGS触摸屏
0 引 言
精密播种已成为现代播种技术的主要发展方向[1],播种机作业质量会直接影响小麦的生长和产量。面对复杂的田间墒情、机器震动、嘈杂噪声等不利因素以及种肥管的全封闭环境,仅采用视听方式难以实时了解播种机的运行状态,当出现种肥管堵塞或种肥缺失等问题时会造成大面积缺苗断垅的状况从而导致减产[2-5],同时机具在地头转向过程中会因种肥掉落而造成浪费。因此研制与精播机配套的监测系统具有重要的生产意义和经济效益。
目前,国外对精播机监测系统进行了较多研究,美国Precision Planting公司设计的基于光电传感器的MeterMAx试验台功能齐全,可迅速准确地检测播种故障以及播种参数,但该产品在国内使用时需配备专属电源[6-7],该公司研制的WaveVision监测器解决了排种过程中多粒种子同时通过导种管无法区分的问题,提高了排种性能监测的可靠性及准确性[8]。Karayel等[9]设计的高速摄像系统实现了对小麦和大豆布种粒距与落种速度的检测,但该系统图像的处理过程无法做到在线监测。Navid等[10]在Karayel的研究基础之上增加图像数量并结合MATLAB处理数据的方法获取更加准确的监测结果。美国John Deere公司基于光电传感器研发的SeedStar系列监测仪将播种监测推向实用化,该公司的第二代产品还可实时进行播种参数设置[11-12]。国内对精播机监测系统的研究起步较晚,但成果显著[13],张继成等[14-15]设计了一种基于光敏电阻的监测装置能够实现大型精密播种施肥机在播种施肥作业过程中对每个作业单体的实时监测;Lu等[16-20]基于对射式红外检测方法设计的播种质量监测系统可对播种过程出现的故障情况发出声光报警信号;丁幼春等[21-24]利用光纤传感器法、聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)压电薄膜法以及时间间隔法分别对油菜等小粒径排种器的排种性能监测进行了研究;周利明等[25-26]基于电容器电容随板间介质变化原理开发的电容式传感器可对小麦、玉米的排种性能进行在线监测;陈进等[27-28]运用高速摄像系统对精密排种器的种子排种过程进行图像采集进而处理得到排种器性能的方法;胡少兴等[29]提出了基于神经网络的种子位置智能检测方法,该方法可全面监测种子的运动情况。
实际应用中,图像处理法虽可高精度监测落种过程,但设备昂贵、数据量大,难以实现实时监测;电容法和压电感应法面对机具震动以及复杂的田间墒情难以保证精度;光电感应法成本低廉、便于维护,但传统的对射式光电传感器安装对精度要求较高,易受机具震动影响。实验室前期设计研究了电控宽幅小麦精播施肥机,达到了均匀播种的目的[30]。本研究在此基础上设计了基于变距光电传感器的小麦精播施肥一体机监测系统,该系统以反射式光电管为监测传感器,通过单片机控制传感器根据需要改变检测距离,结合通过MODBUS传输协议接收主控系统利用旋转编码器测取的种肥轴转速,同时监测排种施肥状况,安装方便、运行稳定,实现了免耕精播施肥机在作业过程中对排种、排肥器单体的实时监测。
1 系统结构与工作原理
1.1 监测系统结构方案
监测系统的结构分为下位机STM32F103硬件电路与上位机触摸屏人机交流界面2部分。下位机硬件电路由OH-1021光电传感器(日本ALEPH公司生产,检测距离2~30 mm)、信号整形放大电路、编码器转速采集模块、通讯模块、中央处理器及外围电路组成。上位机人机交流部分采用MCGS触摸屏,触摸屏放置于驾驶室内便于驾驶员及时观察机具运行状况。系统结构如图1所示。

图1 小麦精播施肥一体机监测系统结构示意图
1.2 监测原理
图2为传感器安装及工作过程示意图。监测系统排种管与排肥管均采用PVC-U管,该管壁厚2 mm,外径28 mm,该管内壁光滑,对流体阻力小,透光性强,不会因为内壁堆积少量的灰尘而影响红外光线的透过性。排种与排肥监测传感器均采用OH-1021反射式光电传感器,可通过改变传感器供电电压来改变探测距离,传感器的检测距离与供电电压成正相关,如图3所示。当有物体阻挡红外光线时,传感器输出低电平;无物体阻挡红外光线时,传感器则输出高电平。
排种管中小麦颗粒处于充满状态,小麦颗粒经排种管流入排种器(如图4a所示)。设定排种传感器的初始检测距离为5 mm,即管壁厚度(2 mm)与单粒小麦短径(3 mm)的总和。正常工作时,颗粒流动经过光电传感器监测位置时反射红外光线,传感器输出经历高电平-低电平-高电平的变化过程。
红外光线照射于种管壁上2个颗粒之间的空隙时,故障类型无法区分。通过单片机控制IO口输出电平控制三极管的导通,改变传感器检测距离。当单片机输出高电平时,三极管导通,传感器电压提升,检测距离增加,进而了解种管种子存量情况,确定故障类型。
肥料从排肥器排出后落入排肥管(如图4b所示),肥料颗粒运动至光电传感器监测位置时反射红外光线,传感器输出经历高电平-低电平-高电平的变化过程,单片机监测传感器的输出状态。具体故障判断类型如表1所示。
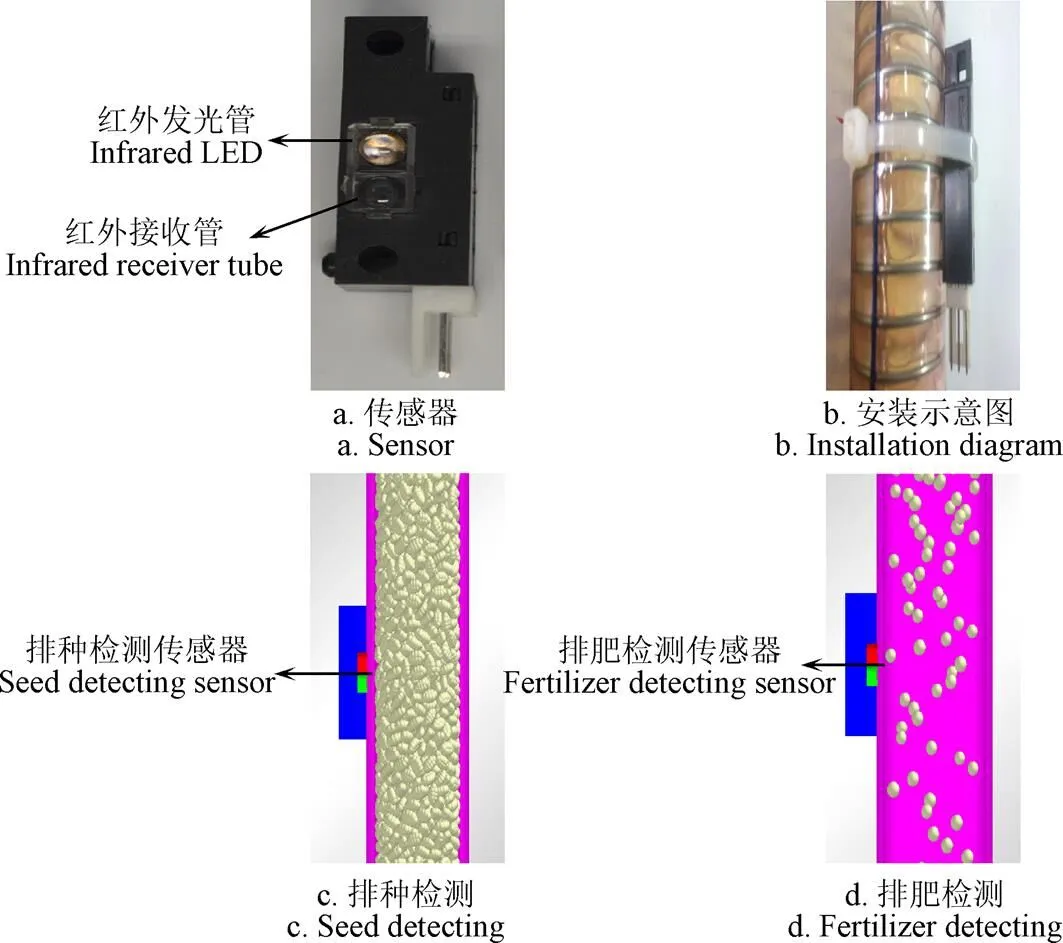
图2 传感器安装及工作过程示意图
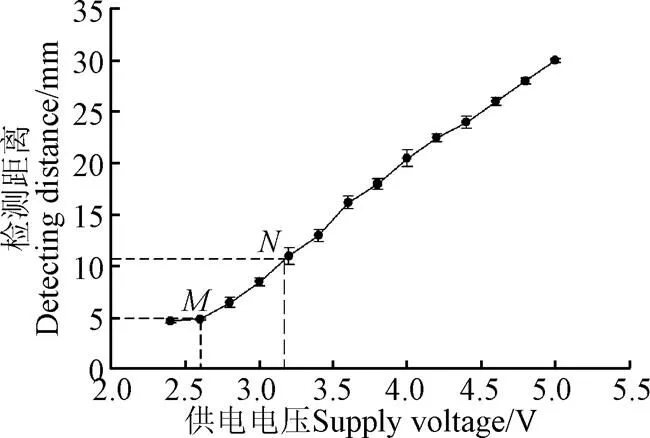
图3 传感器检测距离与供电电压关系

图4 传感器监测示意图

表1 故障监测判断
注:堵种:排种器故障造成堵转;缺种:种箱中麦种缺失;漏种:因毛刷磨损造成的种子泄漏。堵肥:排肥器故障造成堵转;缺肥:肥箱肥料缺失;漏肥:因排肥器毛刷磨损造成的肥料泄漏。
Note: Blocking wheat: Lock-rotor in case of seeding device fault; Lack wheat: lack of seeds in seed box; Leaking wheat: leaking of wheat in case of brush worn. blocking fertilizer: Lock-rotor in case of fertilizing device fault; lacking fertilizer: lack of fertilizer in fertilizer box; leaking fertilizer: leaking of fertilizer in case of brush worn.
主控系统采用1 000线欧姆龙旋转编码器采集排种轴转速和排肥轴转速。系统驱动直流电机属于感性负载,转速突变的可能性较小,为最大程度降低监测滞后性对监测系统程序故障判断过程造成的影响,主控系统以100 Hz频率向监控系统发送种肥轴转速。
2 下位机监测系统电路设计
监测系统硬件电路包括排种检测变距电路、排肥监测硬件电路、STM32F103微处理器最小系统和TTL转485通讯模块。排种故障监测电路的放大器件选取9013NPN三极管,三极管基极连接单片机I/O口。传感器监测供电部分对于三极管放大电路属于有源负载。单片机输出低电平时,传感器电压和检测距离均初始设置;单片机输出高电平时,三极管处于放大状态,负载电压提升,检测距离增加;单片机再次输出低电平时,负载电压与监测距离再次回到初始状态。排种监测电路如图5a所示。
排肥监测电路包括信号采集部分和电压比较放大电路,如图5b所示。为避免传感器输出电平与单片机输入引脚电平不匹配,本研究采用日本Sonteen公司的LM339芯片对传感器的输出信号进行整形滤波,单片机采集比较器的输出信号从而获取排肥管中肥料下落情况。
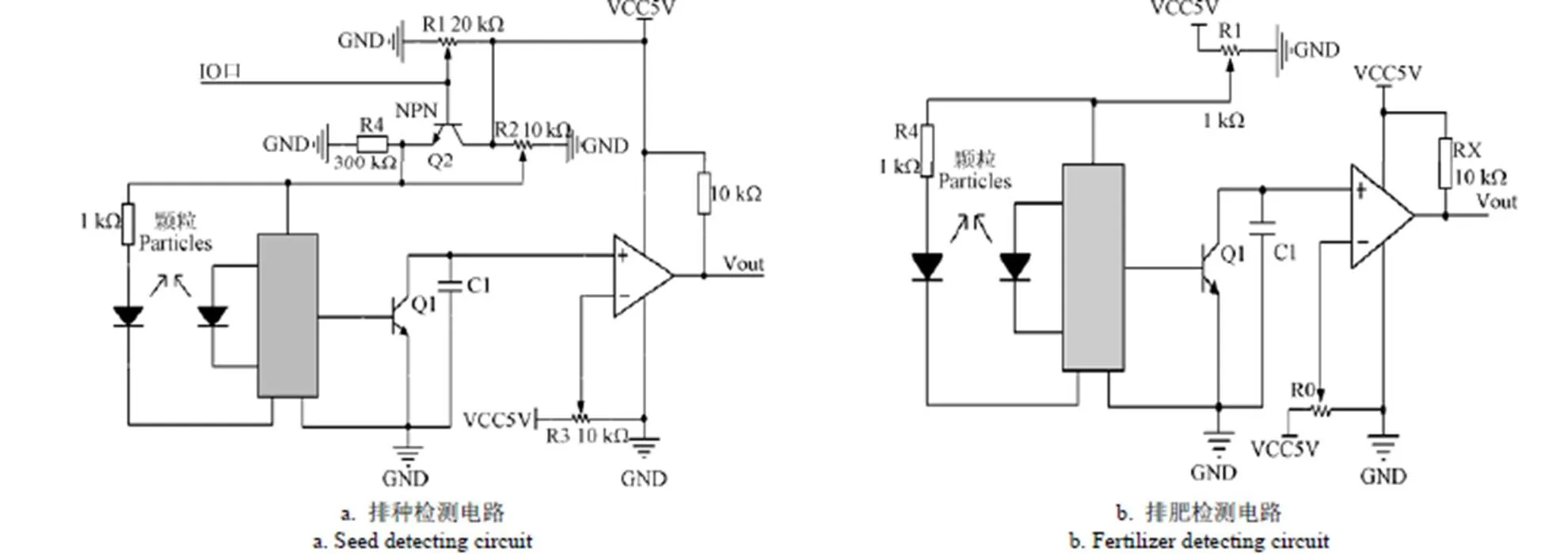
图5 下位机电路原理图
3 系统软件设计
该监控系统的软件由下位机监测处理程序和上位机程序组成。下位机监测处理程序采用C语言编写,易于移植,可读性强;上位机程序采用图形化界面,用于显示播种机排种和排肥的工作状况。
3.1 下位机排种、排肥监测流程
下位机监测处理程序采用时间间隔任务循环程序设计方法,以TIM2作为基准时间划分任务时间片段,循环执行数据采集和数据通信等任务。
排种管光电传感器安装于排种器上方,当红外光线照射在紧贴管壁的2个小麦颗粒空隙时,无法准确判定故障类型,此时启动变距任务函数改变传感器检测距离,检测排种管小麦颗粒数量,若有小麦剩余则传感器输出为低电平,此时排种管出现堵种故障;若无小麦剩余则传感器输出为高电平,此时为缺种故障。排种检测处理算法流程如图6a所示。
排肥光电传感器安装于排肥器下方,根据数据采集函数和排肥轴转速判定排肥器的运行状态,排肥故障监测流程如图6b所示。

注:VS为排种轴转速,r·min-1;VF为排肥轴转速,r·min-1。
3.2 上位机触摸屏报警界面设计
上位机触摸屏人机交流界面的功能是帮助驾驶员实时了解播种施肥过程的种肥状态信息,及时处理故障问题。
上位机的后台数据更新采用循环策略中的ReadP(批量读取)命令以100 Hz频率向下位机发送机具运行状态请求,界面脚本程序以500 Hz频率刷新来自下位机的应答信号,保证下位机的数据能实时显示在上位机报警界面。
本研究中样机设计中排种器与排肥器各有8个,在报警界面中分别用8个指示灯代表各排种器和排肥器的工作状态,每个指示灯下方均有3个动画标签代表不同的故障类型(堵种,缺种,漏种;堵肥,缺肥,漏肥)。当指示灯显示绿色时代表机具工作正常,当指示灯显示红色时代表有故障发生,同时具体故障类型显示于指示灯下方。
4 排种监测电路仿真
为确定电路设计中2个电位器的最佳比例值,在试验之前进行了电路仿真。
利用Multisim电路仿真软件建立下位机电路模型,如图7所示。开关S1初始状态下连接GND(ground,大地)(即IO输出低电平),电位器A的比例值为0,三极管处于截止状态。调节电位器B的值,负载电压即为变距前的传感器电压,结果表明负载电压与电位器B的比例值呈正相关。根据传感器供电电压与检测距离关系得知,当传感器检测距离为5 mm时,负载端电压为2.646 V(如图3点所示),此时电位器B的比例值为92%(如图8a所示)。
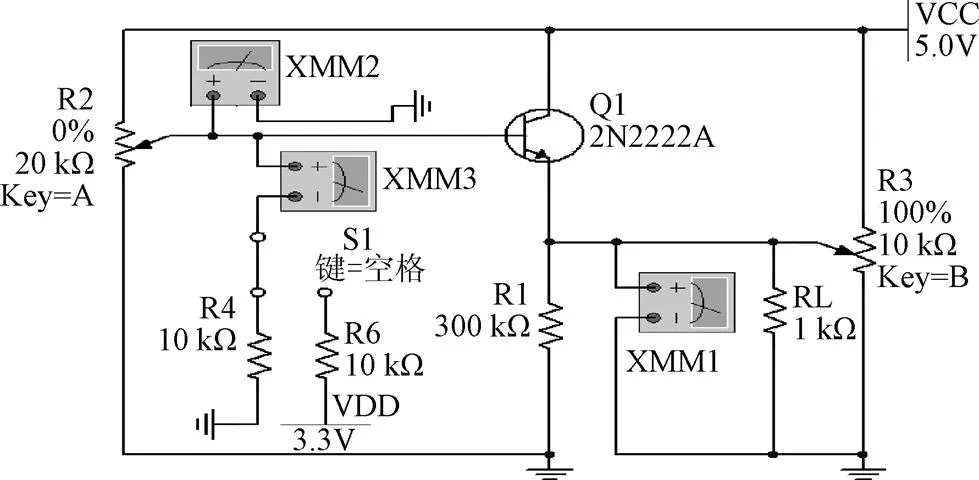
注:2N2222A代表实际电路的9013NPN三极管;开关S1模拟单片机输出电平状态;XMM1、XMM2与XMM3为电压表;Key=A和Key=B分别表示通过键盘A和B调整电位器比例值。
调节电位器A的比例值,分别记录不同比例值时开关1连接3.3 V电源和GND(I/O输出高低电平)时的负载电压,电位器A比例值与负载电压关系如图8b所示,由图8b可知电位器A的比例值为84%时负载压差最大,此时可最大程度改变探测距离。
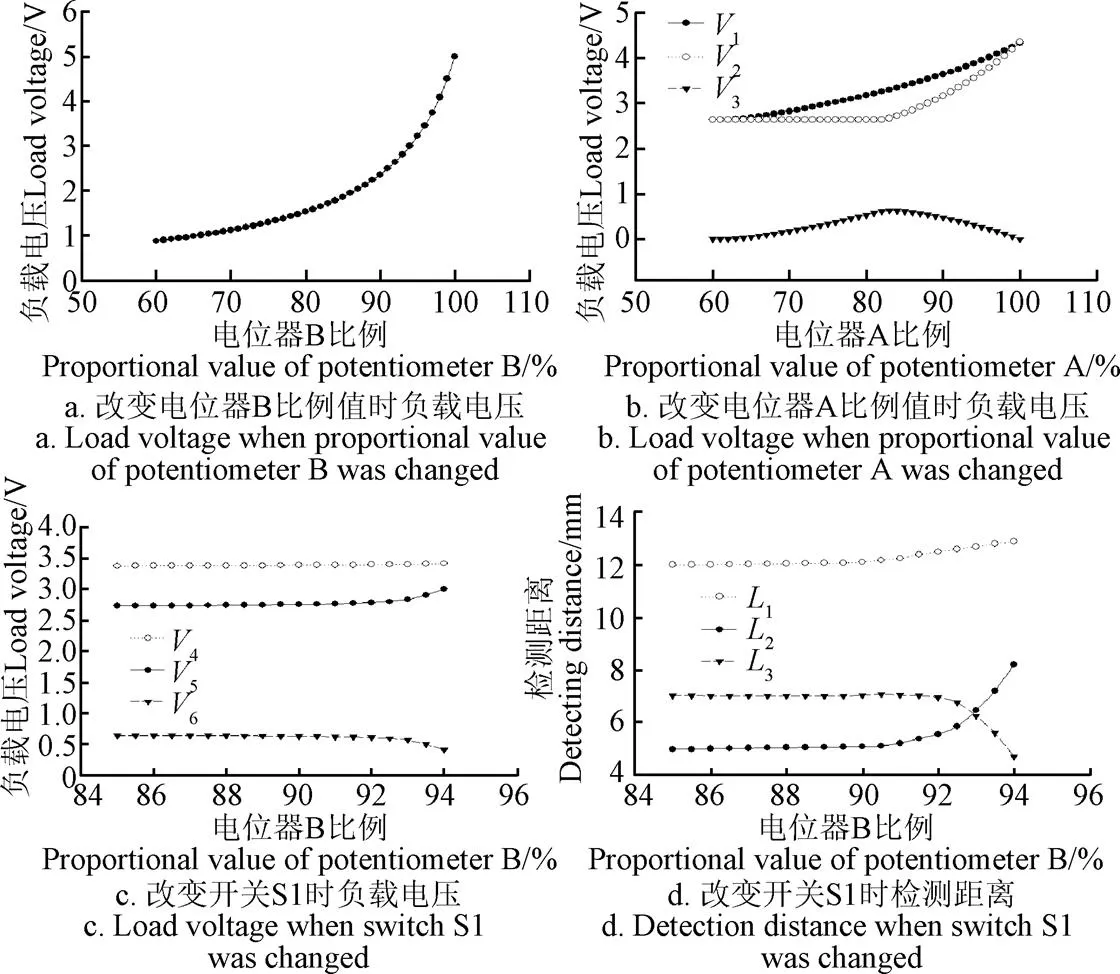
注:V1为开关S1连接至3.3 V电源时负载电压;V2为开关S1连接至GND(Ground)时负载电压;V3为V1与V2的电压差值;V4为开关S1连接至3.3 V电源时负载电压;V5为开关S1连接至GND时负载电压;V6为V4与V5的电压差值;L1为开关S1连接至3.3V电源时传感器检测距离;L2为开关S1连接至GND时传感器检测距离;L3为L1与L2的距离差值。
设定电位器A的比例值为84%,微调电位器B的比例值,对比开关S1分别连接GND与3.3V电源时的负载电压。仿真结果如图8c所示,电压差值为0.413~0.646 V,可使光电传感器检测距离增加4~7 mm(如图8d所示,即图3中点到点的变化),此压差的变化足以解决红外光线位于管壁上2个颗粒之间的空隙时,无法判定故障的问题。
5 田间试验与结果分析
为检测精播施肥一体机监测系统的技术指标与可靠性,在课题组前期研制的宽幅小麦免耕精播施肥一体机的基础上,安装了基于变距光电传感器的监测系统。于2016年10月在山东大华机械有限公司试验田内进行监测系统的检测试验。试验所用小麦品种为“济麦17”,其含水率为11.8%;肥料选取齐商化肥厂生产的控释掺混肥料。图9为试验现场。
图9 试验现场
1)种肥缺失监测试验
在种肥箱内分别放置0.5 kg麦种与5 kg复合肥料,启动播种机进行播种施肥试验,当出现种肥缺失时,人为添加同等质量种肥颗粒,持续播种。拖拉机带动机具以不同速度向前行进,使用毫秒计时器记录各排种器和排肥器种肥实际缺失到系统种肥缺失报警的时间间隔,并统计报警次数,测试重复5次。
2)种肥堵塞监测试验
种肥堵塞监测试验采用塑料袋堵塞落种口和落肥口的方式进行。启动播种机进行播种试验,使用毫秒计时器记录各排种器和排肥器种肥实际堵塞到系统种肥堵塞报警的时间间隔,并统计报警次数,机具以不同速度进行测试,试验重复5次。
3)种肥泄漏监测试验
种肥泄漏监测试验采用人为制造种肥泄漏故障的方式进行,将种肥管与排种器和排肥器分离,模拟种肥泄漏洒落过程。启动监测系统,使用毫秒计时器记录各排种器和排肥器种肥实际泄漏到系统泄漏报警的时间间隔,并统计报警次数,模拟不同种肥泄漏流速,试验重复5次。
试验结果如表2所示,由试验数据得知,种肥缺失报警监测准确率均≥95%,响应时间均≤0.2 s;监测系统种肥堵塞监测准确率均≥95%,响应时间均≤0.3 s;监测系统种肥泄漏监测准确率均≥92.5%,响应时间均≤0.3 s,系统能够迅速准确的对各种运行故障进行报警。
注:监测精度=系统检测次数/人工统计次数×100%,即系统监测准确率。
Note: Check =Check by system/Check by artificial ×100%, that is, the system check accuracy.
6 结论与讨论
1)该研究设计了一种基于变距光电传感器的小麦精播施肥一体机监测系统,该系统下位机采用反射式光电传感器和旋转编码器分别获取种肥流动与种肥轴转动信息,判断精播机运行状态(正常、堵塞、缺失和泄漏),并通过Modbus通讯协议将状态信息传输至人机界面显示,实现精播施肥一体机作业过程的实时监测。
2)运用Multisim对监控系统排种监测电路进行仿真与试验测试,结果表明:放大电路对排种管光电传感器检测距离的改变值为4~7 mm,该距离能有效调整传感器检测距离。
3)对监控系统进行样机故障模拟测试,结果表明:系统报警响应准确,故障监测准确率≥92.5%;报警响应速度快,种肥缺失、堵塞、泄漏响应时间分别≤0.2、≤0.3、≤0.3 s。
田间试验过程中,偶尔会出现漏种(漏肥)的误报、响应延迟等现象,分析原因:1)外界环境噪声干扰了数据的传输;2)机器振动影响了反射式光电传感器的固定位置。因此后续工作主要为研究噪声干扰滤除算法、设计具有防震功能的传感器固定装置进而提高系统监测准确率。
[1] 李洁,赵立新,毕建杰,等. 小麦双线精播智能控制系统的设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(增刊1):134-140.
Li Jie, Zhao Lixin, Bi Jianjie, et al. Design of intelligent control system for two-row precise seeding of wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(Supp.1): 134-140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 刘翔宇,丛锦玲,坎杂,等. 基于反射式光电感应的精量播种机漏播监测系统研究[J]. 江苏农业科学,2017,45(11):164-167.
[3] 张晓辉,赵秀珍,李法德,等. 精密播种机工况自动监控及播量数显系统的研制[J]. 农业工程学报,1997,13(2):169-172.
Zhang Xiaohui, Zhao Xiuzhen, Li Fade, et al. Development of automatic monitor and digital seed rate display system of precision drill[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1997, 13(2): 169-172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张锡智,李敏,孟臣. 精密播种机智能监测控制系统的研制[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报,2002,14(4):28-31.
Zhang Xizhi, Li Min, Meng Chen. Research on aptitude watch and control system for precision seeder[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2002, 14(4): 28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张锡志,李敏,孟臣. 精密播种智能监测仪的研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2004,20(2):136-139.
Zhang Xizhi, Li Min, Meng Chen. Research and development of precision seeding intelligent monitor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2004, 20(2): 136-139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 和贤桃,郝永亮,赵东岳,等. 玉米精量排种器排种质量自动检测仪设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(10):19-27.
He Xiantao, Hao Yongliang, Zhao Dongyue, et al. Design and experiment of testing instrument for maize precision seed meter’s performance detection[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(10): 19-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 刘广玉,胡和兴,杨丽娜,等. MeterMax精密排种器试验台简介[J]. 农业机械,2011(17):102-104.
[8] 丁幼春,王雪玲,廖庆喜. 基于时变窗口的油菜精量排种器漏播实时检测方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(24):11-21. Ding Youchun, Wang Xueling, Liao Qingxi. Method of real-time loss sowing detection for rapeseed precision metering device based on time changed window[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(24): 11-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] Karayel D, Wiesehoff M, Ozmerzi A, et al. Laboratory measurement of seed drill seed spacing and velocity of fall of seeds using high-speed camera system[J]. Computers & Electronics in Agriculture, 2006, 50(2): 89-96.
[10] Navid H, Ebrahimian S, Gassemzadeh H R, et al. Laboratory evaluation of seed metering device using image processing method[J]. Australian Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 2: 1-4.
[11] 车宇,伟利国,刘婞韬,等. 免耕播种机播种质量红外监测系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(增刊1):11-16.
Che Yu, Wei Liguo, Liu Xingtao, et al. Design and experiment of seeding quality infrared monitoring system for no-tillage seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(Supp.1): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] John D. Monitoring and documentation [EB/OL]. (2015-08-04) [2016-01-08]. http://www.deere.com/en_US/parts/parts_by_ industry/ag/seeding/monitoring/monitoring.page
[13] 宋鹏,张俊雄,李伟,等. 精密播种机工作性能实时监测系统[J]. 农业机械学报,2011,42(2):71-74.
Song Peng, Zhang Junxiong, Li Wei, et al. Real-time monitoring system for accuracy for precision seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(2): 71-74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张继成,陈海涛,欧阳斌林,等. 基于光敏传感器的精密播种机监测装置[J]. 清华大学学报自然科学版,2013,53(2):265-268,273.
Zhang Jicheng, Chen Haitao, Ouyang Binlin, et al. Monitoring system for precision seeders based on a photosensitive sensor[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University Science and Technology, 2013, 53(2): 265-268, 273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 窦钰程,欧阳斌林,陈海涛. 光敏式气吸播种机监测装置研究[J]. 东北农业大学学报,2010,41(9):133-137.
Dou Yucheng, Ouyang Binlin, Chen Haitao. Study on photosensitive-type suction planter monitoring apparatus[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2010, 41(9): 133-137. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
[16] Lu Caiyun, Fu Weiqiang, Zhao Chunjiang, et al. Design and experiment on real-time monitoring system of wheat seeding[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(2): 32-40.
卢彩云,付卫强,赵春江,等. 小麦播种实时监控系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(2):32-40. (in English with Chinese abstract)
[17] 张晓辉,赵百通. 播种机自动补播式监控系统的研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(7):119-123.
Zhang Xiaohui, Zhao Baitong. Automatic reseeding monitoring system of seed drill[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(7): 119-123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 纪超,陈学庚,陈金成,等. 玉米免耕精量播种机排种质量监测系统[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(8):1-6.
Ji Chao, Chen Xuegeng, Chen Jincheng, et al. Monitoring system for working performance of no-tillage corn precision seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(8): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 陈广大,马占辉,马超,等. 基于ARM的玉米免耕播种施肥机监控系统设计[J]. 中国农机化学报,2016,37(5):209-212.
Chen Guangda, Ma Zhanhui, Ma Chao, et al. Design on monitoring system for no-tillage corn planter based on ARM[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2016, 37(5): 209-212. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 吴南,林静,李宝筏,等. 免耕播种机漏播补偿系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(7):69-77.
Wu Nan, Lin Jing, Li Baofa, et al. Design and test on no-tillage planter reseeding system for miss-seeding[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(7): 69-77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 丁幼春,杨军强,朱凯,等. 油菜精量排种器种子流传感装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(9):29-36.
Ding Youchun, Yang Junqiang, Zhu Kai, et al. Design and experiment on seed flow sensing device for rapeseed precision metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(9): 29-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] Ding Youchun, Wang Xueling, Liao Qingxi, et al. Design and experiment of performance testing system of multi-channel seed-metering device based on time intervals[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(7): 11-18.
丁幼春,王雪玲,廖庆喜,等. 基于时间间隔的多路精量排种器性能检测系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(7):11-18. (in English with Chinese abstract)
[23] 黄东岩,贾洪雷,祁悦,等. 基于聚偏二氟乙烯压电薄膜的播种机排种监测系统[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(23):15-22.
Huang Dongyan, Jia Honglei, Qi Yue, et al. Seeding monitor system for planter based on polyvinylidence fluoride piezoelectric film[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(23): 15-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 黄东岩,朱龙图,贾洪雷,等. 基于GPS和GPRS的远程玉米排种质量监测系统[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(6):162-168.
Huang Dongyan, Zhu Longtu, Jia Honglei, et al. Remote monitoring system for corn seeding quality based on GPS and GPRS[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(6): 162-168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 周利明,王书茂,张小超,等. 基于电容信号的玉米播种机排种性能监测系统[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(13):16-21.
Zhou Liming, Wang Shumao, Zhang Xiaochao, et al. Seed monitoring system for corn planter based on capacitance signal[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(13): 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 周利明,张小超,苑严伟. 小麦播种机电容式排种量传感器设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(10):99-103.
Zhou Liming, Zhang Xiaochao, Yuan Yanwei. Design of capacitance seed rate sensor of wheat planter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(10): 99-103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 陈进,边疆,李耀明,等. 基于高速摄像系统的精密排种器性能检测试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(9):90-95.
Chen Jin, Bian Jiang, Li Yaoming, et al. Performance detection experiment of precision seed metering device based on high-speed camera system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2009, 25(9): 90-95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 廖庆喜,邓在京,黄海东. 高速摄影在精密排种器性能检测中的应用[J]. 华中农业大学学报,2004,23(5):570-573.
Liao Qingxi, Deng Zaijing, Huang Haidong. Application of the high speed photography checking the precision metering performances[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2004, 23(5): 570-573. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 胡少兴,马成林,张爱武. 排种器性能检测中种子位置智能检测方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2001,32(3):36-39.
Hu Shaoxing, Ma Chenglin, Zhang Aiwu. An intelligent detecting method for seed position in performance detection of seedmeter[J]. Transactions of The Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2001, 32(3): 36-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] Ding X, Li P, Zhao L, et al. Research and design of intelligent control and precision sowing simulation system for wheat[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2016, 31(4): 2313-2320.
Design of monitoring system for wheat precision seeding-fertilizing machine based on variable distance photoelectric sensor
Zhao Lixin1, Zhang Zenghui1, Wang Chengyi2, Jian Shichun3, Liu Tong1, Cui Dongyun1, Ding Xiaoling1※
(1.,271018,; 2.,271018,; 3.,250100,)
Precision seeding has become the main developing direction of the modern seeding technology, and the quality of seeding machine’s operation will directly affect the growth and yield of wheat. Facing complex field moisture, machine vibration, noise and other unfavorable factors as well as the fully closed environment of seeds’ tubes and fertilizer’s tubes, only using audio-visual method is difficult to know the running status of seeder in real time. When the seeds’ tubes and fertilizer’s tubes are plugged or the seeds and fertilizer are lacked, it will cause the question of seedling absence in large areas, and result in yield reduction. Therefore, researching and developing the monitoring system of seeding-fertilizing machine has important significance and benefits both in producing and economy. In the early research stage of the laboratory, an electronically controlled wide wheat fertilization precision seeder was designed to achieve wide precision seeding. In order to realize the real-time monitoring of the process of wheat precision seeding-fertilizing machine and ensure the operation quality, a monitoring system with variable distance photoelectric sensor, which can realize the function of wheat precision seeding-fertilizing machine, was designed based on the previous research. The monitoring system takes the STM32 MCU (micro control unit) hardware detection system as the lower computer, and transmits the information by Modbus communication protocol to man-machine interface of MCGS (Monitor and Control Generated System) touch screen displaying real-time operation status. The lower computer uses a reflective photocell as a monitoring sensor, and determines the malfunction type by combining the information of seeds’ and fertilizer’s flow and shaft rotation measured by master system’s rotary encoder and transferred by Modbus communication. The monitoring sensors of wheat and fertilizer were adopt OH-1021 reflective photoelectric sensor which transmitting terminal and receiving terminal distributed on the same side. When there are particles blocking infrared light, the sensors output low level; when there are no particles, the sensors output high level. The sensor output experiences a high-low-high level change process when the infrared light is reflected while the particles flow through the photoelectric sensor. It is easier to determine the operating status of the fertilizing according to the fertilizer shaft speed and the output of fertilizer sensor data collected by MCU, since the fertilizing sensor was installed under the row fertilizer device. But the seed tube with sensor was installed above the seeding device, in which the wheat particles were full and flowing slowly. The initial detection distance of the seed sensor is set as 5 mm, which is the sum of the short diameter (3 mm) of single wheat particle and the tube thickness (2 mm). In normal operation, the wheat particles reflect the infrared light when flowing through the position of seed sensor, and the sensor output experiences a high-low-high level change process. The MCU determines the operating status of the seeding according to the sensor output and seed shaft speed. During the monitoring of seeding, the type of malfunction cannot be distinguished when the infrared light is located on the gap between 2 particles on the wall of the seed tube. The MCU controls the conduction of the triode via changing the IO (Input /Output) port output by activating the variable pitch task function, and thereby controls the detection distance of the sensor. When the output of the MCU is high, the triode is turned on, then voltage of the sensor is increased, resulting in the increase of detection distance, and thereforethe type of malfunctions is determined by further understanding on the seed-reserve in the seed tube. The circuit simulation test results of the lower computer’s seeds’ tube show that the detection distance of the photoelectric sensor of the seeds’ tube is changed by 4-7 mm under the amplifier circuit; monitoring system prototype test results show that the accuracy of fault alarm at least reaches 92.5%, and the response time of lacking seeds and fertilization, blockage and leakage is less than or equal to 0.2, 0.3 and 0.3 s, respectively. The monitoring system realizes high-precision real-time monitoring of wheat seeding and it can improve the quality of wheat seeding.
monitoring; design; sensor; precision seeding-fertilizing machine; variable distance; MCGS touch screen
赵立新,张增辉,王成义,荐世春,刘 童,崔东云,丁筱玲. 基于变距光电传感器的小麦精播施肥一体机监测系统设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(13):27-34.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.13.004 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhao Lixin, Zhang Zenghui, Wang Chengyi, Jian Shichun, Liu Tong, Cui Dongyun, Ding Xiaoling. Design of monitoring system for wheat precision seeding-fertilizing machine based on variable distance photoelectric sensor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(13): 27-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.13.004 http://www.tcsae.org
2017-12-12
2018-04-04
山东省农机装备研发创新计划项目(2015YZ103);山东省农业重大应用技术创新项目(SNZY31955);山东农业大学现代农业智能化装备研发项目(SDAU24131)
赵立新,副教授,主要从事传感器技术、机电装备智能化设计、机电一体化技术等教学研究工作。Email:xlding103@163.com
丁筱玲,教授,研究生导师,主要从事模式识别与智能控制、自动化仪器仪表与装置、自动控制等方面的教学科研工作。 Email:xld@sdau.edu.cn
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.13.004
S223.2+4
A
1002-6819(2018)-13-0027-08
