Smad7和IL-6在原发性肝细胞癌中的表达及临床意义
2017-12-07张健李云陈淑华张冬琴唐公恩
张健 李云 陈淑华 张冬琴 唐公恩
(临沂市中心医院 感染科 山东 临沂 276400)
Smad7和IL-6在原发性肝细胞癌中的表达及临床意义
张健 李云 陈淑华 张冬琴 唐公恩
(临沂市中心医院 感染科 山东 临沂 276400)
目的探讨Smad7和IL-6在原发性肝细胞癌中的表达及临床意义。方法收集56例肝细胞癌患者术后肝癌组织及癌旁肝硬化组织,采用荧光定量 PCR检测Smad7转录情况,免疫组化方法检测 Smad7蛋白的表达水平,对比Smad7表达与患者一般临床病理特征如年龄、性别、肿瘤大小、肿瘤计数、组织病理分化、TNM 分期、是否存在包膜、门静脉系统侵犯、血清甲胎蛋白(AFP)浓度以及血清HBsAg阳性率的关系。术前采用ELISA法检测肝癌患者血清中IL-6表达水平,与36位健康体检者血清IL-6水平对比。结果肝癌组织中Smad7转录水平低于对应癌旁肝硬化组织,肝癌组织中Smad7蛋白阳性表达率均低于癌旁肝硬化组织(P<0.05)。肝癌组织Smad7阳性表达组与阴性表达组在肿瘤大小、组织病理分化、TNM 分期、门静脉系统侵犯方面比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);肝癌组血清中IL-6水平高于健康组(P<0.05)。结论原发性肝细胞癌中存在Smad7和IL-6的异常表达,Smad7和IL-6可能是评估患者病情新的生物标志物。
原发性肝细胞癌;Smad7;IL-6
肝细胞癌是临床最常见的肿瘤之一,我国肝癌发病率高,且术后复发率高,患者生存状况不佳[1-2]。因此,需要新的生物标记物来提高肝癌患者的早期诊断率,实现个体化治疗,改善肝癌患者的生存状况。研究表明,肝癌的发生发展与TGF-β信号通路密切相关,而Smad7是该通路的重要调控因子,可进一步引起IL-6水平的变化,与上皮细胞间质变等过程有关[3]。多项研究表明,TGF-β信号通路与食管癌、胃癌、肺癌等肿瘤密切相关,提示Smad7在肿瘤发生发展中具有重要作用[4]。本研究旨在探讨Smad7和IL-6在原发性肝细胞癌中的表达及临床意义,具体如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料选取2010年1月至2013年12月在临沂市中心医院行肝癌根治术的56例患者作为肝癌组,均合并乙型病毒性肝炎肝硬化,术后病理切片证实为肝细胞癌。其中男42例,女14例;年龄30~68岁,平均(49.0±3.8)岁;低分化11例,中分化39例,高分化6例;伴门静脉癌栓24例,无门静脉癌栓32例;依据国际TNM分期,Ⅰ期10例,Ⅱ期13例,Ⅲ期24例,Ⅳ期9例。患者手术前均接受“恩替卡韦,1次/d,口服”抗病毒治疗,术前均未接受任何放、化疗等其他抗癌治疗。分别取癌组织,癌旁肝硬化组织(距离癌组织边缘2 cm),所有标本均为肝癌根治术后获得的新鲜标本,获得标本后立即放入液氮罐中,多聚甲醛固定,经HE染色证实为肝细胞癌。收集同期健康体检者36例作为健康组。
1.2实验主要试剂PCR引物由上海生物工程技术服务公司完成。Trizol试剂购于invitrogen公司。逆转录试剂盒为日本TaKaRa公司。β-actin内参、抗Smad7抗体、人IL-6 ELISA试剂盒均购于Sigma公司。
1.3实验方法
1.3.1实时荧光定量PCR 提取癌组织及癌旁组织总RNA,逆转录RNA为cDNA。β-actin作为实验内参,查询Smad7基因序列,设计PCR引物序列。Smad7 上游引物序列:5’-AGC ACT GTG GTT TGG TAT CTG TCA G-3’;下游引物序列:5’-CAC CAG CTG TTT GGT ATC TGT CAG-3’。β-actin 上游引物序列:5’-GGT GTG ATG GTGGGT ATG GGT-3’;下游引物序列:5’-CTG GGT CAT CTT TTC ACG GT-3’,反应条件:首先94 ℃预变性15 s,然后扩增30个循环,每个循环包括95 ℃ 5 s和60 ℃ 30 s。用SDS(2.4版)进行荧光数据分析,数据分析采用比较Ct(ΔΔCt)值的方法。
1.3.2免疫组化 采用二步法免疫组化步骤,癌组织和癌旁正常组织脱水、常规处理后,滴加经PBS液稀释的一抗,加入二抗,经辣根过氧化物酶链霉卵白素液标记进行显色,脱水,封片,于镜下观察。在HCC中Smad7的着色主要定位于胞质,阳性颗粒为棕黄色。
随机挑选每张切片中的5个100倍视野,于每个视野中计数100个细胞,得到阳性细胞所占百分比。所有切片结果的判读均经过两位高年资有经验的病理学老师确认。
1.3.3ELISA 血清稀释后加入反应孔中,常温孵育1 h,缓冲液冲洗后加入二抗(包含在ELISA试剂盒中)孵育1 h,缓冲液冲洗干净。加入底物显色15 min,最后加入终止物。酶标仪450 nm处显色,根据标准曲线计算血清中IL-6水平。
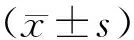
2 结果
2.1HCC与肝硬化组织中Smad7mRNA的表达HCC组织中Smad7 mRNA相对表达水平低于癌旁肝硬化组织,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图1。

图1HCC和癌旁肝硬化组织中Smad7 mRNA相对表达水平
2.2HCC及癌旁肝硬化组织中Smad7蛋白的表达HCC组织中Smad7蛋白表达水平低于癌旁肝硬化组织,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图2、表1。

A:Smad7在HCC组织中表达阴性;B:Smad7在肝硬化组织中表达阳性。
图2HCC及癌旁肝硬化组织中Smad7蛋白的表达(400×)
2.3Smad7蛋白表达与HCC分化及临床病理特征的关系HCC中Smad7蛋白阳性表达组与阴性表达组在肿瘤大小、组织病理分化、TNM 分期、门静脉系统侵犯比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表2。

表2 Smad7蛋白表达与HCC临床病理特征关系
2.4HCC患者及健康者血清中IL-6的表达HCC组血清中IL-6水平高于健康组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表3。
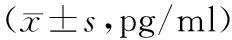
表3 HCC组和健康组患者血清 中IL-6的表达水平
3 讨论
目前临床已经广泛研究TGF-β信号通路在肝癌发生发展中的作用。在急性肝损伤发生时,TGF-β可抑制肝脏内皮细胞的生长,在HCC晚期,TGF-β失去抑制细胞生长的作用转而促进肿瘤细胞的增长[4]。Smad7是TGF-β的一个靶基因,为TGF-β家族细胞因子的一个生理性反馈抑制因子,在肿瘤发展的不同时期可能既有抑癌作用,也有促癌作用,在一些肿瘤中被阐释为肿瘤促进因子,该作用主要通过负性调控TGF-β信号通路实现[5]。
除了对TGF-β信号通路的负性调控机制外,Smad7抑制肿瘤的作用可能是通过其他信号通路实现,如氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)、NF-κB和信号传导与转录激活因子(signal transducer and activator of transcription,STAT)信号通路,该通路均被证实在HCC的进展中发挥重要作用[6]。研究显示,如果特异性敲除小鼠肝脏细胞特异性的STAT3基因,肝癌的发生发展过程与野生型小鼠有明显差异,提示STAT3对HCC的发展有至关重要的作用[7-8]。这些资料进一步提示IKKβ在肝细胞中的抑癌作用,Smad7可以通过抑制NF-κB信号通路发挥抑癌作用[9]。研究发现,基因敲除了Smad7的小鼠STAT3激活程度升高,HCC组低表达Smad7[10]。肝细胞具有在受到脂质体或者肝细胞生长因子刺激时产生IL-6的能力,但在肝脏组织中,自分泌的白介素-6(IL-6)主要由巨噬细胞和库夫细胞在肿瘤发展的初始阶段产生[11-14]。研究表明,Smad7可抑制巨噬细胞产生IL-6。血清中IL-6的水平主要受慢性乙型病毒性肝炎、肝硬化的影响,乙型肝炎病毒的X蛋白可以通过蛋白磷酸化调控IL-6的表达[15]。由于对中路细胞增殖及存活、肿瘤血管形成、肿瘤转移和炎症的多重作用,IL-6具有较强的促癌活性[16-17]。IL-6可与其他细胞因子相互作用,通过产生和介导免疫反应对HCC的发展产生深远影响。在肝脏细胞系中,一定浓度的IL-6可抑制肿瘤生长,当其浓度达到一定阈值后,抑癌和促癌间的平衡会丧失,进而促进肿瘤的发展[18-19]。研究表明,IL-6/STAT3可作为抑癌作用的Smad7的一个靶点,Smad7可能影响STAT3/pSTAT3蛋白的降解过程,比如通过影响泛素化的过程,该过程同其影响TGF-β的作用相似[20]。
本研究主要采用免疫组化及qRT-PCR检测HCC组织及癌旁肝硬化组织中Smad7的表达水平,结果显示HCC组织中Smad7蛋白的表达水平较癌旁肝硬化组织低(P<0.05);HCC组血清中IL-6水平高于健康组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Smad7的低表达与肿瘤大小、组织病理分化、TNM 分期、门静脉系统侵犯存在统计学差异。该结果提示肝癌中存在Smad7和IL-6的异常表达,Smad7和IL-6可能是评估患者病情的新的生物标志物。但两者异常表达水平的具体机制尚不清楚,有待进一步深入研究。
[1] Singal A G,El-Serag H B.Hepatocellular carcinoma from epidemiology to prevention: translating knowledge into practice[J].Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol,2015,13(12):2140-2151.
[2] El-Serag H B.Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Gastroenterology,2012,142(6):1264-1273.
[3] Feng T,Dzieran J,Gu X,et al.Smad7 regulates compensatory hepatocyte proliferation in damaged mouse liver and positively relates to better clinical outcome in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Clin Sci(Lond),2015,128(11):761-774.
[4] Xia H,Ooi L L,Hui K M.MicroRNA-216a/217-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition targets PTEN and SMAD7 to promote drug resistance and recurrence of liver cancer[J].Hepatology,2013,58(2):629-641.
[5] He G,Yu G Y,Temkin V,et al.Hepatocyte IKKbeta/ NF-kappaB inhibits tumor promotion and progression by preventing oxidative stress-driven STAT3 activation[J].Cancer Cell,2010,17(3):286-297.
[6] Jiang L L,Zhao Y J,Li Y.Expressions and clinical significance of TGF-βRⅡ and NF-κB in oral squamous cell?carcinoma[J].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue,2016,25(6):729-733.
[7] Stolfi C,Marafini I,De Simone V,et al.The dual role of Smad7 in the control of cancer growth and metastasis[J].Int J Mol Sci,2013,14(12):23774-23790.
[8] 司方莹,李朵璐,阚全程.STAT3与肿瘤关系研究进展[J].河南医学研究,2014,23(6):159-160.
[9] Bruix J,Gores G J,Mazzaferro V.Hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical frontiers and perspectives[J].Gut,2014,63(5):844-855.
[10] Liu Y,Liu A,Li H,et al.Celecoxib inhibits interleukin-6/interleukin-6 receptor- induced JAK2/STAT3 phosphorylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J].Cancer Prev Res (Phila),2011,4(8):1296-1305.
[11] Norris C A,He M,Kang L I,et al.Synthesis of IL-6 by hepatocytes is a normal response to common hepatic stimuli[J].PLoS One,2014,9(4):e96053.
[12] Naugler W E,Sakurai T,Kim S,et al.Gender disparity in liver cancer due to sex differences in MyD88-dependent IL-6 production[J].Science,2007,317(5834):121-124.
[13] Sakurai T,He G,Matsuzawa A,et al.Hepatocyte necrosis induced by oxidative stress and IL-1 alpha release mediate carcinogen- induced compensatory proliferation and liver tumorigenesis[J].Cancer Cell,2008,14(2):156-165.
[14] Meniconi R L,Komatsu S,Perdigao F,et al.Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma:A Western strategy that emphasizes the impact of pathologic profile of the first resection[J].Surgery,2015,157(3):454-462.
[15] Taniguchi K,Karin M.IL-6 and related cytokines as the critical lynchpins between inflammation and cancer[J].Semin Immunol,2014,26(1):54-74.
[16] Ara T,Declerck Y A.Interleukin-6 in bone metastasis and cancer progression[J].Eur J Cancer,2010,46(7):1223-1231.
[17] Jang J W,Oh B S,Kwon J H,et al.Serum interleukin-6 and C- reactive protein as a prognostic indicator in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Cytokine,2012,60(3):686-693.
[18] Klausen P,Pedersen L,Jurlander J,et al.Oncostatin M and Interleukin 6 inhibit cell cycle progression by prevention of p27kip1 degradation in HepG2 cells[J].Oncogene,2000,19(32):3675-3683.
[19] Feng T,Dzieran J,Gu X,et al.Smad7 regulates compensatory hepatocyte proliferation in damaged mouse liver and positively relates to better clinical outcome in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Clin Sci,2015,128(11):761-774.
[20] Pang X H,Zhang J P,Zhang Y J,et al.Preoperative levels of serum interleukin-6 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Hepatogastroenterology,2011,58(110-111):1687-1693.
ExpressionofSmad7andIL-6inprimaryhepatocellularcarcinomaandclinicalsignificance
Zhang Jian, Li Yun, Chen Shuhua, Zhang Dongqin, Tang Gongen
(DepartmentofInfectiousDiseases,theCentralHospitalofLinyi,Linyi276400,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the expression of Smad7 and IL-6 in primary hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical significance.MethodsThe hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and adjacent liver cirrhosis tissues of 56 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma were collected. The transcription level of Smad7 was detected by real-time PCR, and the expression of Smad7 protein was detected by immunohistochemical method. The relationship between expression of Smad7 and the general clinicopathological features such as age, sex, tumor size, tumor count, histopathological differentiation, TNM staging, presence of envelope, portal vein system invasion, serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) concentration and serum HBsAg were analyzed. Preoperative ELISA method was used to detect the expression of IL-6 in serum of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, and compared with the level of serum IL-6 in 36 healthy subjects.ResultsThe expression of Smad7 protein in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues was lower than that in adjacent liver cirrhosis tissues, and the positive expression rate of Smad7 protein in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues was lower than that in adjacent liver cirrhosis tissues (P<0.05). The level of IL-6 in hepatocellular carcinoma group was higher than that in healthy group (P<0.05). The level of IL-6 in hepatocellular carcinoma group was significantly higher than that in healthy group(P<0.05), and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).ConclusionThe expression of Smad7 and IL-6 was abnormal in hepatocellular carcinoma. Smad7 and IL-6 may be the new biomarkers to evaluate the condition of patients.
primary hepatocellular carcinoma; Smad7; IL-6
R 735.7
10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2017.21.010
2017-04-05)
